1、背景介绍
模块中使用国产纳芯微的温感,型号为NST175,该温感通过I2C连接模块上的国产ZYNQ,实现温度采集功能。
通过查阅datasheet,能够发现该温感通过I2C读写时序为标准的I2C读写时序

Nst175的I2C地址为7位
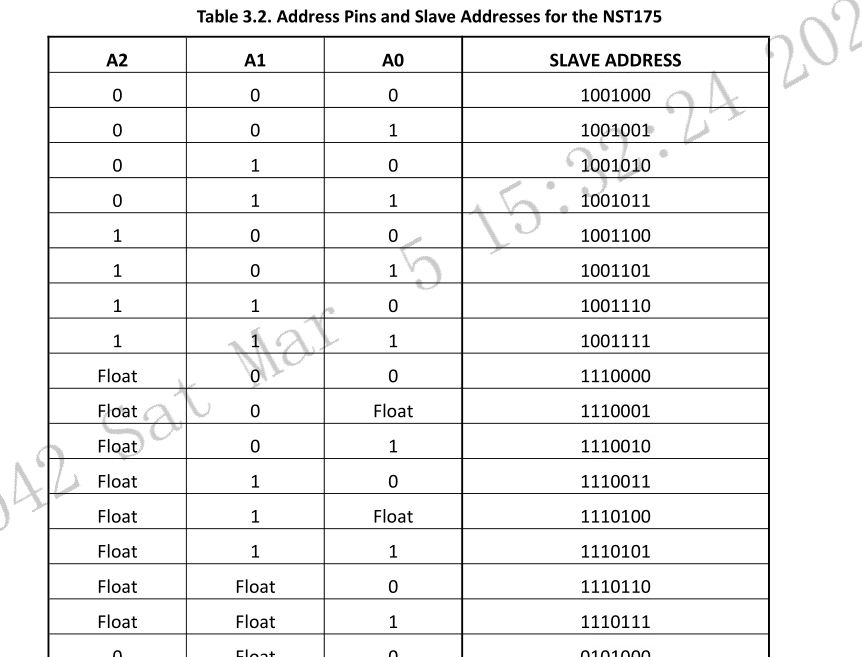
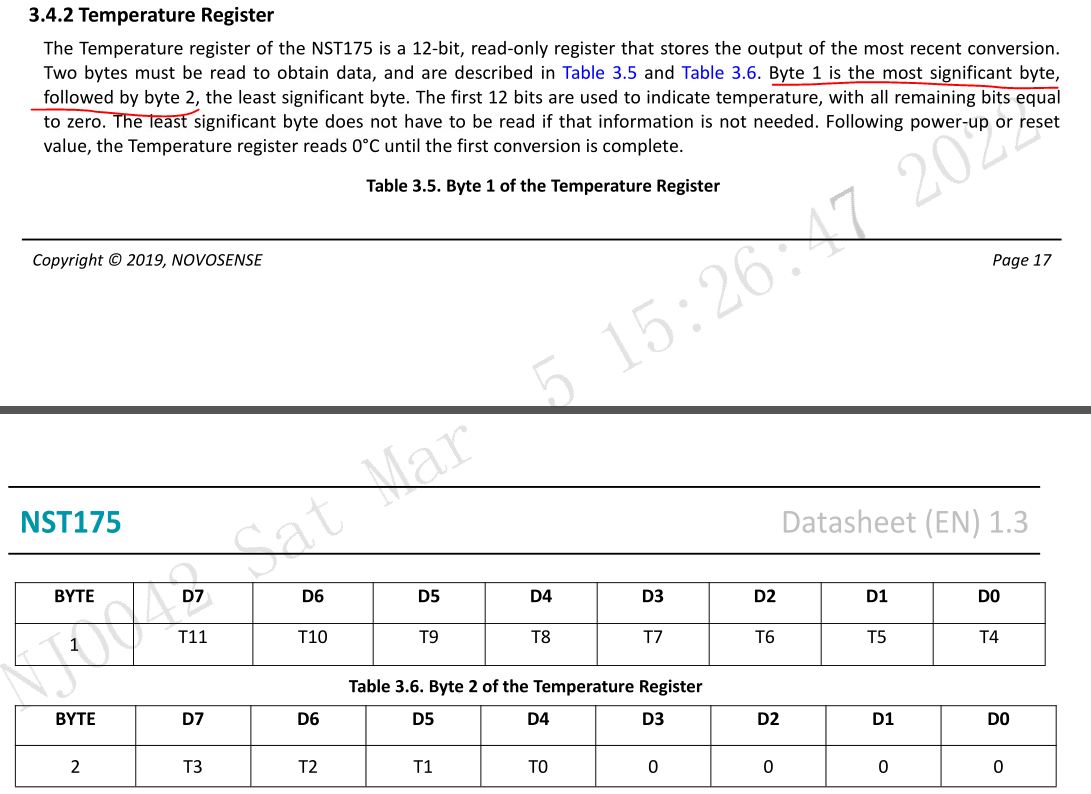
温度寄存器地址为0

温度寄存器是一个16位的数,一般取前8位即可
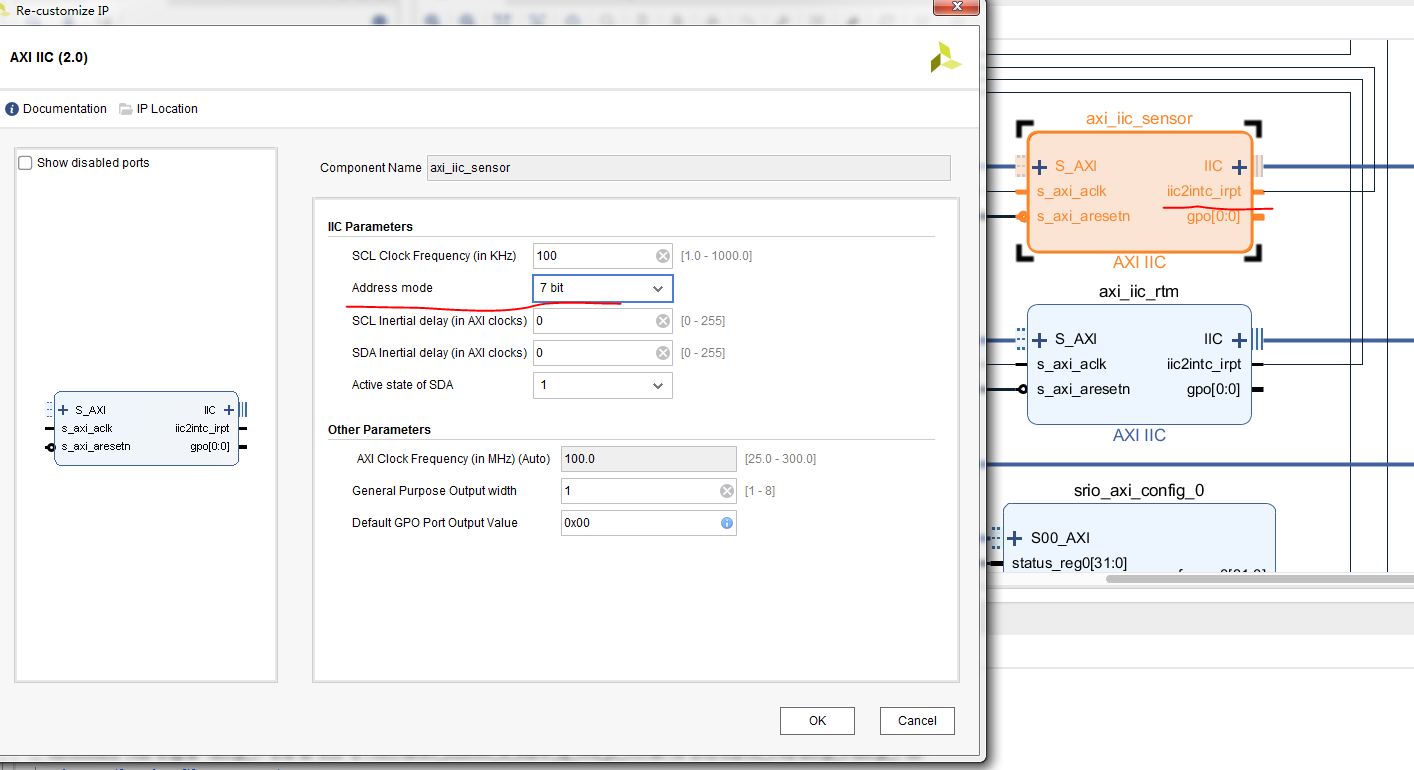
2、vivado工程配置
vivado中通过PL中的I2C IP核来连接NST175,注意模式选择7bit,同时把中断接上
3、内核配置
内核中需要添加i2c-nst175的驱动,将驱动编译进内核
驱动源码可参考之前的cps1848,代码见下
/*
* nst175 bus driver
*
* Copyright (C) 2014 CGT Corp.
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation; version 2 of the License.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
*
*/
//#define DEBUG
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/serial_core.h>
/* Each client has this additional data */
#define USER_EEPROM_SIZE 128
#define USER_XFER_MAX_COUNT 0x8
/* Addresses to scan */
static const unsigned short nst175_i2c[] = { 0x3, I2C_CLIENT_END };
static unsigned read_timeout = 25;
module_param(read_timeout, uint, 0);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(read_timeout, "Time (in ms) to try reads (default 25)");
static unsigned write_timeout = 25;
module_param(write_timeout, uint, 0);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(write_timeout, "Time (in ms) to try writes (default 25)");
struct nst175_data {
struct mutex lock;
u8 *data;
};
static ssize_t nst175_read_data( struct i2c_client *client,
char *buf, unsigned offset, size_t count)
{
//printk("in tem.c, %sn", __func__);
struct i2c_msg msg[2];
u8 msgbuf[4];
unsigned long timeout, transfer_time;
int status;
struct nst175_data *data = i2c_get_clientdata(client);
memset(msg, 0, sizeof(msg));
msgbuf[0] =(u8)(offset& 0xff);
msg[0].addr = client->addr;
msg[0].buf = msgbuf;
msg[0].len = 1;
msg[1].addr = client->addr;
msg[1].flags = I2C_M_RD;
msg[1].buf = buf;
msg[1].len = count;
/*
* Reads fail if the previous write didn't complete yet. We may
* loop a few times until this one succeeds, waiting at least
* long enough for one entire page write to work.
*/
timeout = jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(read_timeout);
do {
transfer_time = jiffies;
mutex_lock(&data->lock);
status = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, msg, 1);
msleep(100);
status = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, &msg[1], 1);
mutex_unlock(&data->lock);
if (status == 2)
status = count;
// printk( "read %ld@0x%lx --> %d (%ld)n",
// count, (unsigned long)offset, status, jiffies);
if (status == count)
return count;
/* REVISIT: at HZ=100, this is sloooow */
msleep(1);
} while (time_before(transfer_time, timeout));
return -ETIMEDOUT;
}
static ssize_t nst175_read(struct file *filp, struct kobject *kobj,
struct bin_attribute *bin_attr,
char *buf, loff_t offset, size_t count)
{
//printk("in tem.c, %sn", __func__);
struct i2c_client *client = kobj_to_i2c_client(kobj);
struct nst175_data *data = i2c_get_clientdata(client);
ssize_t retval = 0;
if (offset > USER_EEPROM_SIZE)
return 0;
if (offset + count > USER_EEPROM_SIZE)
count = USER_EEPROM_SIZE - offset;
// printk("nst175 start1 read %ld@0x%lx ..n", count, (unsigned long)offset);
//printk("%s, count:%dn",__func__, count);
while (count > 0) {
ssize_t status = count>USER_XFER_MAX_COUNT?USER_XFER_MAX_COUNT:count;
#if 0
printk("nst175 start2 read %ld@0x%lx ..n", count, (unsigned long)offset);
#endif
status = nst175_read_data(client, buf, offset, status);
if (status <= 0) {
if (retval == 0)
retval = status;
break;
}
buf += status;
offset += status;
count -= status;
retval += status;
}
// printk( "nst175 end read %ld@0x%lx !n", retval, (unsigned long)offset);
return retval;
}
static ssize_t nst175_write_config(
struct i2c_client *client,
struct nst175_data *data,
char *buf, unsigned offset, size_t count)
{
struct i2c_msg msg[1];
u8 *msgbuf;
unsigned long timeout, transfer_time;
int status;
memset(msg, 0, sizeof(msg));
msgbuf = data->data;
#if 0
msgbuf[0] = 0x04;
msgbuf[1] =(u8)(offset& 0xff);
memcpy(msgbuf+2, buf, count);
msg[0].addr = client->addr;
msg[0].buf = msgbuf;
msg[0].len = 2 + count;
#else
msg[0].addr = client->addr;
msgbuf[0] = (u8)(offset& 0xff);
memcpy(msgbuf+1, buf, count);
msg[0].buf = msgbuf;
msg[0].len = 1 + count;
#endif
/*
* Reads fail if the previous write didn't complete yet. We may
* loop a few times until this one succeeds, waiting at least
* long enough for one entire page write to work.
*/
timeout = jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(write_timeout);
do {
transfer_time = jiffies;
status = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, msg, 1);
if (status == 1)
status = count;
dev_dbg(&client->dev, "write %ld@0x%lx --> %d (%ld)n",
count, (unsigned long)offset, status, jiffies);
if (status == count)
return count;
/* REVISIT: at HZ=100, this is sloooow */
msleep(1);
} while (time_before(transfer_time, timeout));
return -ETIMEDOUT;
}
static ssize_t nst175_write(struct file *filp, struct kobject *kobj,
struct bin_attribute *bin_attr,
char *buf, loff_t offset, size_t count)
{
struct i2c_client *client = kobj_to_i2c_client(kobj);
struct nst175_data *data = i2c_get_clientdata(client);
ssize_t retval = 0;
if (offset > USER_EEPROM_SIZE)
return 0;
if (offset + count > USER_EEPROM_SIZE)
count = USER_EEPROM_SIZE - offset;
mutex_lock(&data->lock);
dev_dbg(&client->dev, "nst175 start write %ld@0x%lx ..n", count, (unsigned long)offset);
while (count > 0) {
ssize_t status = count>USER_XFER_MAX_COUNT?USER_XFER_MAX_COUNT:count;
status = nst175_write_config(client, data, buf, offset, status);
if (status <= 0) {
if (retval == 0)
retval = status;
break;
}
buf += status;
offset += status;
count -= status;
retval += status;
}
dev_dbg(&client->dev, "nst175 end write %ld@0x%lx !n", retval, (unsigned long)offset);
mutex_unlock(&data->lock);
return retval;
}
static struct bin_attribute user_nst175_attr = {
.attr = {
.name = "nst175",
.mode = (S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR),
},
.size = USER_EEPROM_SIZE,
.read = nst175_read,
.write = nst175_write,
};
/* Return 0 if detection is successful, -ENODEV otherwise */
static int nst175_detect(struct i2c_client *client, struct i2c_board_info *info)
{
struct i2c_adapter *adapter = client->adapter;
if (!i2c_check_functionality(adapter, I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA)) {
dev_dbg(&client->dev, "nst175 detect error for BYTE access !n");
return -ENODEV;
}
strlcpy(info->type, "nst175", I2C_NAME_SIZE);
return 0;
}
static int nst175_probe(struct i2c_client *client,
const struct i2c_device_id *id)
{
struct i2c_adapter *adapter = client->adapter;
struct nst175_data *data;
int err ;
printk( "in %s ... n", __func__ );
if (!i2c_check_functionality(adapter, I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA)) {
dev_err(&client->dev, "nst175 data driver: BYTE DATA not supported! n" );
return -ENODEV;
}
if (!(data = kzalloc(sizeof(struct nst175_data), GFP_KERNEL))) {
dev_err(&client->dev, "nst175 data driver: Memory alloc error ! n" );
return -ENOMEM;
}
/* alloc buffer */
data->data = devm_kzalloc(&client->dev, USER_XFER_MAX_COUNT + 8, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!data->data) {
dev_err(&client->dev, "nst175 data driver: Memory alloc error ! n" );
err = -ENOMEM;
goto exit_kfree;
}
/* Init real i2c_client */
i2c_set_clientdata(client, data);
mutex_init(&data->lock);
err = sysfs_create_bin_file(&client->dev.kobj, &user_nst175_attr);
if (err) {
dev_err(&client->dev, "nst175 data driver: sysfs create error ! n" );
goto exit_kfree;
}
return 0;
exit_kfree:
if(data->data)
kfree(data->data);
kfree(data);
return err;
}
static int nst175_remove(struct i2c_client *client)
{
struct nst175_data *data = i2c_get_clientdata(client);
sysfs_remove_bin_file(&client->dev.kobj, &user_nst175_attr);
if(data->data)
kfree(data->data);
kfree(data);
return 0;
}
static const struct i2c_device_id nst175_id[] = {
{ "nst175", 0 },
{ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(i2c, nst175_id);
static struct i2c_driver nst175_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "nst175",
},
.probe = nst175_probe,
.remove = nst175_remove,
.id_table = nst175_id,
.class = I2C_CLASS_SPD,
.detect = nst175_detect,
.address_list = nst175_i2c,
};
module_i2c_driver(nst175_driver);
MODULE_AUTHOR("RobinLee");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("nst175 driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
4、devicetree设置
设备树中需要增加两个nst175的节点,i2c地址需要跟硬件确认,如下

5、应用测试
系统启动后能够看到找到了两个nst175设备

编写应用代码,代码如下
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <memory.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/poll.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include "xadc_core.h"
#define I2C_0 "/sys/class/i2c-dev/i2c-2/device/2-0049/nst175"
#define I2C_1 "/sys/class/i2c-dev/i2c-2/device/2-004a/nst175"
int fp_i2c_0, fp_i2c_1;
extern void printadc();
void init_i2c_file_opt()
{
fp_i2c_0 = open(I2C_0, O_RDWR);
printf("input fd:%d !n", fp_i2c_0);
if (fp_i2c_0 <0)
{
printf("open ic-0 failed..n");
}
fp_i2c_1 = open(I2C_1, O_RDWR);
printf("input fd:%d !n", fp_i2c_1);
if (fp_i2c_1 <0)
{
printf("open ic-1 failed..n");
}
}
int read_temperatue(unsigned int num, unsigned int offset)
{
int fd = -1;
char value = -1;
if (num == 0)
{
fd = fp_i2c_0;
}
else if (num == 1)
{
fd = fp_i2c_1;
}
else
{
printf("input error::Invalid param !n");
return 0;
}
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("Invalid device handle !n");
return value;
}
if (lseek(fd, offset, SEEK_SET) == (off_t) - 1)
{
printf("failed for seek to offset 0x%x !n", offset);
return value;
}
if (read(fd, &value, sizeof(value)) != sizeof(value))
{
printf("failed for read from offset 0x%x !n", offset);
return value;
}
return value;
}
int main()
{
int value = 0;
int i = 0;
init_i2c_file_opt();
xadc_initialization();
printadc();
while (i < 2)
{
value = read_temperatue(i, 0);
printf("No. %d----value:%d centn", i, value);
sleep(1);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
执行应用后能看到正确获取到温度寄存器的第一个字节,和实际温度一致。
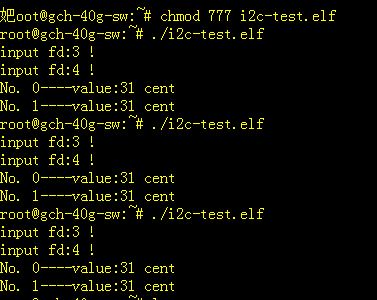
最后
以上就是无语棒球最近收集整理的关于Zynq-Linux移植学习笔记之55-国产ZYNQ Linux下适配NST175温感的全部内容,更多相关Zynq-Linux移植学习笔记之55-国产ZYNQ内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复