本文源代码下载请走连接:
struts2_servlet Struts2框架基础使用:Servlet的API访问、结果页面配置和数据的封装
在使用Struts2的框架的过程中,发现Struts2和Servlet的API是解耦合的。
在实际开发中,经常使用到Servlet的API,比如进行登录,将用户的信息保存到Session中,有的时候需要向页面输出一些内容,用到response对象。涉及到Servlet的API的访问。
1.0 truts2的Servlet的API的访问
1.1 完全解耦合的方式
- 注意:这种方式只能获得代表request、session、application的数据的Map集合,不能操作这些对象的本身的方法。
RequestDemo1.java
package com.edp.struts2.demo1;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Map;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
/**
*
* @Title: RequestDemo1.java
* @Package com.edp.struts2.demo1
* @author EdPeng
* @version 创建时间 2020年2月15日
* @Description 访问Servlet的API方式一:完全解耦合的方式
* @version V1.0
*/
public class RequestDemo1 extends ActionSupport {
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
// 接收参数
// 利用struts2中的对象ActionContext对象
ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();
// 调用ActionContext中的方法
// 类似于request.getParameterMap();
Map<String, Object> map = context.getParameters();
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
String[] valuse = (String[]) map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+" "+Arrays.toString(valuse));
}
//向域对象中存入数据
context.put("reqName", "reqValue");//相当于request.setAttribute();
context.getSession().put("sessName", "sessValue");//相当于session.setAttribute();
context.getApplication().put("appName", "appValue");//相当于application.setAttribute();
return SUCCESS;
}
}
demo1.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Struts2访问Servlet的API</h1>
<h3>方式一:完全解耦合的方式</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/requestDemo1.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name" /><br />
密码:<input type="text" name="password" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
demo2.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>显示数据</h1>
${reqName }<br/>
${ sessName}<br/>
${ appName}<br/>
</body>
</html>
1.2 使用Servlet的API的原生方式(*****)
- 注意:这种方式可以操作域对象的数据,同时也可以获得对象的方法。
RequestDemo2.java
package com.edp.struts2.demo1;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
/**
*
* @Title: RequestDemo2.java
* @Package com.edp.struts2.demo1
* @author EdPeng
* @version 创建时间 2020年2月15日
* @Description 访问Servlet的API方式二:原生的方式
* @version V1.0
*/
public class RequestDemo2 extends ActionSupport {
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
// 接收参数
//直接获得request对象,通过ServletActionContext
HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest();
Map<String, String[]> map = request.getParameterMap();
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
String[] values =map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+" "+Arrays.toString(values));
}
//向域对象中存入数据
//向request中保存数据
request.setAttribute("reqName", "reqValue");
//向session中保存数据
request.getSession().setAttribute("sessName", "sessValue");
//向application中保存数据
ServletActionContext.getServletContext().setAttribute("appName", "appValue");
return SUCCESS;
}
}
struts_demo1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<!-- START SNIPPET: -->
<struts>
<!-- Struts2为了管理action的配置,通过包进行管理。 -->
<!-- 配置Struts2的包========== -->
<!-- name唯一,随便写 -->
<!-- extends继承struts2-core-2.5.22.jar包下struts-default.xml的struts-default包 -->
<package name="demo1" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="requestDemo1" class="com.edp.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo1">
<result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="requestDemo2" class="com.edp.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo2">
<result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
<!-- END SNIPPET: -->
demo1.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Struts2访问Servlet的API</h1>
<h3>方式一:完全解耦合的方式</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/requestDemo1.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name" /><br />
密码:<input type="text" name="password" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<h3>方式二:使用原生的方式访问</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/requestDemo2.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name" /><br />
密码:<input type="text" name="password" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
1.3 接口注入的方式(很少用)
RequestDemo3.java
package com.edp.struts2.demo1;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ServletRequestAware;
import org.apache.struts2.util.ServletContextAware;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
/**
*
* @Title: RequestDemo3.java
* @Package com.edp.struts2.demo1
* @author EdPeng
* @version 创建时间 2020年2月15日
* @Description 接口注入的方式
* @version V1.0
*/
// 接口注入需要实现 org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ServletRequestAware接口
public class RequestDemo3 extends ActionSupport implements ServletRequestAware,ServletContextAware {
private HttpServletRequest request;
private ServletContext context;
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
// 1.接收参数
// 通过接口注入的方式获得request对象
Map<String, String[]> map = request.getParameterMap();
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
String[] values = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " " + Arrays.toString(values));
}
// 向域对象中存入数据
// 向request中保存数据
request.setAttribute("reqName", "reqValue");
// 向session中保存数据
request.getSession().setAttribute("sessName", "sessValue");
// 向application中保存数据
// 可以:ServletActionContext.getServletContext().setAttribute("appName", "appValue");
context.setAttribute("appName", "appValue");
return SUCCESS;
}
@Override
public void setServletRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
this.request = request;
}
@Override
public void setServletContext(ServletContext context) {
this.context=context;
}
}
struts_demo1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<!-- START SNIPPET: -->
<struts>
<!-- Struts2为了管理action的配置,通过包进行管理。 -->
<!-- 配置Struts2的包========== -->
<!-- name唯一,随便写 -->
<!-- extends继承struts2-core-2.5.22.jar包下struts-default.xml的struts-default包 -->
<package name="demo1" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="requestDemo1" class="com.edp.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo1">
<result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="requestDemo2" class="com.edp.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo2">
<result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="requestDemo3" class="com.edp.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo3">
<result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
<!-- END SNIPPET: -->
demo1.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Struts2访问Servlet的API</h1>
<h3>方式一:完全解耦合的方式</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/requestDemo1.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name" /><br />
密码:<input type="text" name="password" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<h3>方式二:使用原生的方式访问</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/requestDemo2.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name" /><br />
密码:<input type="text" name="password" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<h3>方式三:接口注入的方式</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/requestDemo3.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name" /><br />
密码:<input type="text" name="password" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
- Servlet是单例的,多个程序访问同一个Servlet只会创建一个Servlet的实例。Action是多例的,一次请求,创建一个Action的实例(不会出现线程安全的问题)。
2.0 结果页面的配置
2.1 全局结果页面
- 全局结果页面:全局结果页面指的是,在包中配置一次,其他的在这个包中的所有的action只要返回了这个值,都可以跳转到这个页面。
- 针对这个包下的所有的action的配置都有效。
struts_demo1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<!-- START SNIPPET: -->
<struts>
<!-- Struts2为了管理action的配置,通过包进行管理。 -->
<!-- 配置Struts2的包========== -->
<!-- name唯一,随便写 -->
<!-- extends继承struts2-core-2.5.22.jar包下struts-default.xml的struts-default包 -->
<package name="demo1" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<!-- 全局结果页面 -->
<global-results>
<result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result>
</global-results>
<action name="requestDemo1" class="com.edp.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo1"/>
<action name="requestDemo2" class="com.edp.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo2"/>
<action name="requestDemo3" class="com.edp.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo3"/>
</package>
</struts>
<!-- END SNIPPET: -->
2.2 局部结果页面
- 局部结果页面:局部结果页面指的是,只能在当前的action中的配置有效。
- 针对当前的action有效。
struts_demo1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<!-- START SNIPPET: -->
<struts>
<!-- Struts2为了管理action的配置,通过包进行管理。 -->
<!-- 配置Struts2的包========== -->
<!-- name唯一,随便写 -->
<!-- extends继承struts2-core-2.5.22.jar包下struts-default.xml的struts-default包 -->
<package name="demo1" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<!-- 全局结果页面 -->
<global-results>
<result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result>
</global-results>
<action name="requestDemo1" class="com.edp.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo1">
<!-- 局部全局结果页面 -->
<result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="requestDemo2" class="com.edp.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo2"/>
<action name="requestDemo3" class="com.edp.struts2.demo1.RequestDemo3"/>
</package>
</struts>
<!-- END SNIPPET: -->
2.3 result标签的配置
- result标签用于配置页面的跳转。在result标签上有两个属性:
- name属性 :逻辑视图的名称。默认值:success
- type属性 :页面跳转的类型。很多值,常用的有以下几种:
- dispatcher :默认值,请求转发。(Action转发JSP)(常用)
- redirect :重定向。(Action重定向JSP)(常用)
- chain :转发。(Action转发Action)
- redirectAction :重定向。(Action重定向Action)
- stream :Struts2中提供文件下载的功能。
3.0 数据的封装
Struts2框架是一个web层框架,web层框架(框架:软件的办成品,完成一部分功能)。Struts2提供了数据封装的功能。
3.1 Struts2的数据封装
提供一个User.java
package com.edp.struts2.domain;
/**
*
* @Title: User.java
* @Package com.edp.struts2.domain
* @author EdPeng
* @version 创建时间 2020年2月15日
* @Description TODO
* @version V1.0
*/
import java.util.Date;
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
private Double salary;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public Double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(Double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [username=" + username + ", password=" + password + ", age=" + age + ", birthday=" + birthday
+ ", salary=" + salary + "]";
}
}
3.2 属性驱动
1. 提供属性set方法的方式(不常用)
demo2/demo1.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Struts2的数据封装</h1>
<h3>方式一:属性驱动——提供set方法的方式</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/userAction1.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br />
密码:<input type="password" name="password" /><br />
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" /><br />
生日:<input type="text" name="birthday" /><br />
工资:<input type="text" name="salary" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
com.edp.struts2.demo2.struts_demo2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<!-- START SNIPPET: -->
<struts>
<!-- Struts2为了管理action的配置,通过包进行管理。 -->
<!-- 配置Struts2的包========== -->
<!-- name唯一,随便写 -->
<!-- extends继承struts2-core-2.5.22.jar包下struts-default.xml的struts-default包 -->
<package name="demo2" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<!-- 全局结果页面 -->
<global-results>
<result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result>
</global-results>
<action name="userAction1" class="com.edp.struts2.demo2.UserAction1">
<!-- <result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result> -->
</action>
</package>
</struts>
<!-- END SNIPPET: -->
UserAction1.java
package com.edp.struts2.demo2;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.jws.soap.SOAPBinding.Use;
import com.edp.struts2.domain.User;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
/**
*
* @Title: UserAction1.java
* @Package com.edp.struts2.demo2
* @author EdPeng
* @version 创建时间 2020年2月15日
* @Description TODO
* @version V1.0
*/
public class UserAction1 extends ActionSupport {
// 提供了对应的属性
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
private Double salary;
// 提供属性对应的set方法
// 接收数据
// 封装数据
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(birthday);
System.out.println(salary);
//封装数据
User user = new User();
user.setUsername(username);
user.setPassword(password);
user.setAge(age);
user.setBirthday(birthday);
user.setSalary(salary);
return NONE;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public void setSalary(Double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
2. 页面中提供表达式方式
新建UserAction2.java
package com.edp.struts2.demo2;
import com.edp.struts2.domain.User;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
/**
*
* @Title: UserAction2.java
* @Package com.edp.struts2.demo2
* @author EdPeng
* @version 创建时间 2020年2月15日
* @Description 属性驱动——在页面中提供表达式方式
* @version V1.0
*/
public class UserAction2 extends ActionSupport{
//提供一个User对象
private User user;
//提供user的set和get方法,一定要提供get方法
//拦截器完成数据的封装,它需要把相应的对象创建
//通过get方法可以获得同一个对象,将数据封装到同一个对象中。
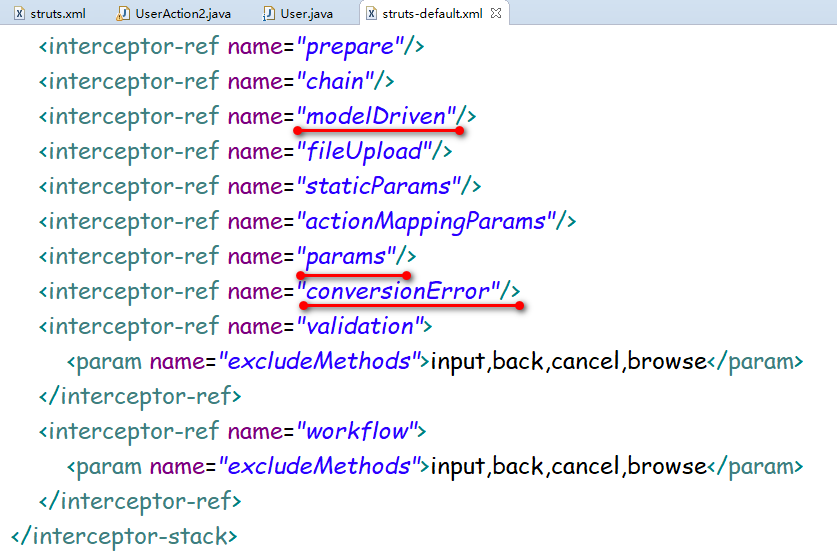
//源代码,核心core包中struts-default.xml中的各种拦截器完成属性封装
//<interceptor-ref name="params"/>属性封装
// <interceptor-ref name="modelDriven"/>模型封装
//<interceptor-ref name="conversionError"/>类型转换的拦截器
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
System.out.println(user.toString());
return NONE;
}
}
相对应的struts-default.xml部分源代码:
demo1.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Struts2的数据封装</h1>
<h3>方式一:属性驱动——提供set方法的方式</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/userAction1.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br />
密码:<input type="password" name="password" /><br />
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" /><br />
生日:<input type="text" name="birthday" /><br />
工资:<input type="text" name="salary" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<h3>方式二:属性驱动——在页面中提供表达式方式</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/userAction2.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="user.username" /><br />
密码:<input type="password" name="user.password" /><br />
年龄:<input type="text" name="user.age" /><br />
生日:<input type="text" name="user.birthday" /><br />
工资:<input type="text" name="user.salary" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
<input type="password" name="user.password" />中"user.password"是struts2中内部的一种表达式——OJNL(Object-Graph Navigation Language)表达式
struts_demo2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<!-- START SNIPPET: -->
<struts>
<!-- Struts2为了管理action的配置,通过包进行管理。 -->
<!-- 配置Struts2的包========== -->
<!-- name唯一,随便写 -->
<!-- extends继承struts2-core-2.5.22.jar包下struts-default.xml的struts-default包 -->
<package name="demo2" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="userAction1" class="com.edp.struts2.demo2.UserAction1"/>
<action name="userAction2" class="com.edp.struts2.demo2.UserAction2"/>
</package>
</struts>
<!-- END SNIPPET: -->
3.3 模型驱动:采用模型驱动方式(最常用)
demo1.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Struts2的数据封装</h1>
<h3>方式一:属性驱动——提供set方法的方式</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/userAction1.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br />
密码:<input type="password" name="password" /><br />
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" /><br />
生日:<input type="text" name="birthday" /><br />
工资:<input type="text" name="salary" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<h3>方式二:属性驱动——在页面中提供表达式方式</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/userAction2.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="user.username" /><br />
密码:<input type="password" name="user.password" /><br />
年龄:<input type="text" name="user.age" /><br />
生日:<input type="text" name="user.birthday" /><br />
工资:<input type="text" name="user.salary" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<h3>方式三:模型驱动——模型驱动方式</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/userAction3.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br />
密码:<input type="password" name="password" /><br />
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" /><br />
生日:<input type="text" name="birthday" /><br />
工资:<input type="text" name="salary" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
struts_demo2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<!-- START SNIPPET: -->
<struts>
<!-- Struts2为了管理action的配置,通过包进行管理。 -->
<!-- 配置Struts2的包========== -->
<!-- name唯一,随便写 -->
<!-- extends继承struts2-core-2.5.22.jar包下struts-default.xml的struts-default包 -->
<package name="demo2" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="userAction1" class="com.edp.struts2.demo2.UserAction1">
<!-- <result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result> -->
</action>
<action name="userAction2" class="com.edp.struts2.demo2.UserAction2" />
<action name="userAction3" class="com.edp.struts2.demo2.UserAction3" />
</package>
</struts>
<!-- END SNIPPET: -->
UserAction3.java
package com.edp.struts2.demo2;
import com.edp.struts2.domain.User;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ModelDriven;
/**
*
* @Title: UserAction3.java
* @Package com.edp.struts2.demo2
* @author EdPeng
* @version 创建时间 2020年2月15日
* @Description 方式三:模型驱动——模型驱动方式
* @version V1.0
*/
public class UserAction3 extends ActionSupport implements ModelDriven<User> {
// 首先得实现模型驱动的接口
// 必须手动提供对象的实例
private User user = new User();// 手动实例化User
@Override
// 模型驱动需要使用的方法
public User getModel() {
return user;
}
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
System.out.println(user);
return NONE;
}
}
模型驱动方式最常用的方式:
- 缺点:只能同时向一个对象中封装数据。
- 使用第2种可以向多个对象中同时封装数据
4.0 INPUT的逻辑视图的配置
Action接口中提供了五个逻辑视图的名称:
* 实现接口的方式:提供5个常量(5个逻辑视图的名称)
* * SUCCESS = "success"; 成功(可自定义)
* * NONE = "none"; 不跳转(可自定义)
* * ERROR = "error"; 失败(可自定义)
* * INPUT = "input"; 表单校验出错或者类型转换出错。(不能私自修改)
* * LOGIN = "login"; 登录出错的页面的跳转(可自定义)
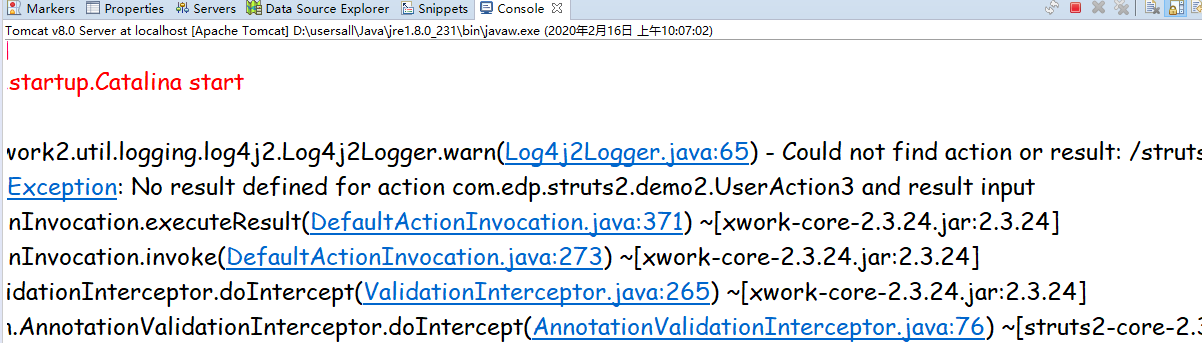
INPUT 在某些拦截器中使用。比如在输入数据时:

Struts2所有拦截器,默认栈下的拦截器都会依次执行(jar包里面的struts-default.xml):

没有按规定格式输入。会报如下错误:
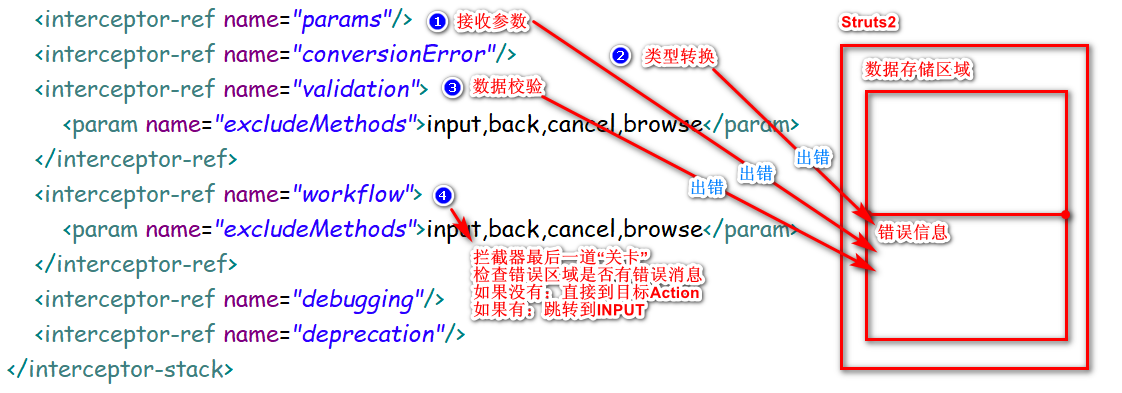
INPUT工作内部原理:
处理方式只需要写一个input的逻辑视图即可。修改struts_demo2.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<!-- START SNIPPET: -->
<struts>
<!-- Struts2为了管理action的配置,通过包进行管理。 -->
<!-- 配置Struts2的包========== -->
<!-- name唯一,随便写 -->
<!-- extends继承struts2-core-2.5.22.jar包下struts-default.xml的struts-default包 -->
<package name="demo2" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<global-results>
<result name="input">/demo2/demo1.jsp</result>
</global-results>
<action name="userAction1" class="com.edp.struts2.demo2.UserAction1">
<!-- <result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result> -->
</action>
<action name="userAction2" class="com.edp.struts2.demo2.UserAction2" />
<action name="userAction3" class="com.edp.struts2.demo2.UserAction3" />
</package>
</struts>
<!-- END SNIPPET: -->
为了方便显示错误,修改demo1,jsp文件:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Struts2的数据封装</h1>
<h3>方式一:属性驱动——提供set方法的方式</h3>
<!-- s:fielderror某一个字段的错误 -->
<s:fielderror/>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/userAction1.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br />
密码:<input type="password" name="password" /><br />
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" /><br />
生日:<input type="text" name="birthday" /><br />
工资:<input type="text" name="salary" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<h3>方式二:属性驱动——在页面中提供表达式方式</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/userAction2.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="user.username" /><br />
密码:<input type="password" name="user.password" /><br />
年龄:<input type="text" name="user.age" /><br />
生日:<input type="text" name="user.birthday" /><br />
工资:<input type="text" name="user.salary" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<h3>方式三:模型驱动——模型驱动方式</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/userAction3.action" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br />
密码:<input type="password" name="password" /><br />
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" /><br />
生日:<input type="text" name="birthday" /><br />
工资:<input type="text" name="salary" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
运行:

5.0 复杂类型的数据封装
在实际开发中,有可能遇到批量向数据库中插入记录,需要在页面中将数据封装到集合中。
5.1 封装数据到List集合中
demo3/demo1.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Struts2的复杂类型的数据封装</h1>
<h3>封装到list集合中:批量插入商品</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/productAction1.action" method="post">
商品名称:<input type="text" name="products[0].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="products[0].price" /><br />
商品名称:<input type="text" name="products[1].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="products[1].price" /><br />
商品名称:<input type="text" name="products[2].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="products[2].price" /><br />
商品名称:<input type="text" name="products[3].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="products[3].price" /><br />
商品名称:<input type="text" name="products[4].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="products[4].price" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Product.java
package com.edp.struts2.domain;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @Title: Product.java
* @Package com.edp.struts2.domain
* @author EdPeng
* @version 创建时间 2020年2月16日
* @Description 产品的实体类
* @version V1.0
*/
public class Product {
private String name;
private Double price;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Product [name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
struts_demo3.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<!-- START SNIPPET: -->
<struts>
<!-- Struts2为了管理action的配置,通过包进行管理。 -->
<!-- 配置Struts2的包========== -->
<!-- name唯一,随便写 -->
<!-- extends继承struts2-core-2.5.22.jar包下struts-default.xml的struts-default包 -->
<package name="demo3" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<global-results>
<result name="input">/demo3/demo1.jsp</result>
</global-results>
<action name="productAction1" class="com.edp.struts2.demo3.ProductAction1">
<!-- <result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result> -->
</action>
</package>
</struts>
<!-- END SNIPPET: -->
ProductAction1.java
package com.edp.struts2.demo3;
/**
*
* @Title: ProductAction1.java
* @Package com.edp.struts2.demo3
* @author EdPeng
* @version 创建时间 2020年2月16日
* @Description 复杂类型的数据封装:封装到list集合
* @version V1.0
*/
import java.util.List;
import com.edp.struts2.domain.Product;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
public class ProductAction1 extends ActionSupport {
private List<Product> products;
// 提供集合的set方法和get方法(get方法必不可少)
public void setProducts(List<Product> products) {
this.products = products;
}
public List<Product> getProducts() {
return products;
}
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
for (Product product : products) {
System.out.println(product);
}
return NONE;
}
}
5.2 封装数据到Map集合中
demo3/demo1.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Struts2的复杂类型的数据封装</h1>
<h3>封装到list集合中:批量插入商品</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/productAction1.action" method="post">
商品名称:<input type="text" name="products[0].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="products[0].price" /><br />
商品名称:<input type="text" name="products[1].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="products[1].price" /><br />
商品名称:<input type="text" name="products[2].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="products[2].price" /><br />
商品名称:<input type="text" name="products[3].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="products[3].price" /><br />
商品名称:<input type="text" name="products[4].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="products[4].price" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<h3>封装到Map集合中:批量插入商品</h3>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/productAction2.action" method="post">
商品名称:<input type="text" name="map['one'].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="map['one'].price" /><br />
商品名称:<input type="text" name="map['two'].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="map['two'].price" /><br />
商品名称:<input type="text" name="map['three'].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="map['three'].price" /><br />
商品名称:<input type="text" name="map['four'].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="map['four'].price" /><br />
商品名称:<input type="text" name="map['five'].name" /><br />
商品价格:<input type="text" name="map['five'].price" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
ProductAction2.java
package com.edp.struts2.demo3;
import java.util.Map;
import com.edp.struts2.domain.Product;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.sun.swing.internal.plaf.metal.resources.metal;
/**
*
* @Title: ProductAction2.java
* @Package com.edp.struts2.demo3
* @author EdPeng
* @version 创建时间 2020年2月16日
* @Description 复杂数据类型的封装:封装数据到Map集合中
* @version V1.0
*/
public class ProductAction2 extends ActionSupport {
private Map<String, Product> map;
public Map<String, Product> getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, Product> map) {
this.map = map;
}
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
Product product = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+" "+product);
}
return NONE;
}
}
struts_demo3.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<!-- START SNIPPET: -->
<struts>
<!-- Struts2为了管理action的配置,通过包进行管理。 -->
<!-- 配置Struts2的包========== -->
<!-- name唯一,随便写 -->
<!-- extends继承struts2-core-2.5.22.jar包下struts-default.xml的struts-default包 -->
<package name="demo3" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<global-results>
<result name="input">/demo3/demo1.jsp</result>
</global-results>
<action name="productAction1" class="com.edp.struts2.demo3.ProductAction1">
<!-- <result name="success">/demo1/demo2.jsp</result> -->
</action>
<action name="productAction2" class="com.edp.struts2.demo3.ProductAction2"/>
</package>
</struts>
<!-- END SNIPPET: -->
END
最后
以上就是安静小虾米最近收集整理的关于【Java中级】16.0 SSH之Struts2框架(三)——Servlet的API访问、结果页面配置和数据的封装...的全部内容,更多相关【Java中级】16.0内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复