这篇文章我是这样安排的---》首先对ArrayList类做一个介绍-》其次对ArrayList进行模拟实现-》最后我们将ArrayList的源码几个重要的点讲一下。
给大家分享个宝藏这里可以阅读ArrayList的详细源码讲解:ArrayList源码&扩容机制分析 | JavaGuide
本篇文章最后讲解ArrayList源码时候会参考这篇文章进行讲解。好,我们一起来学习ArrayList吧~~~~~
目录
ArrayList类介绍
ArrayList的模拟实现
ArrayList的类成员
toString方法或者display方法(数组元素的打印)
增加元素方法add(int data)
在某一个位置增加元素add方法add(int index,int data)
判断数组中是否包含某一个元素-->contains方法
找到元素的位置indexOf方法
获取index位置的元素get方法
给index位置更新元素set方法
删除数组中的元素remove方法
size()方法
clear()方法清空顺序表
ArrayList的构造方法
ArrayList的扩容机制
ArrayList类介绍
ArrayList是List接口实现的类,也就是这个类实现了List接口,同时还有一个重要的类那就是LinkedList,这两个类都是实现了List接口并且非常重要。
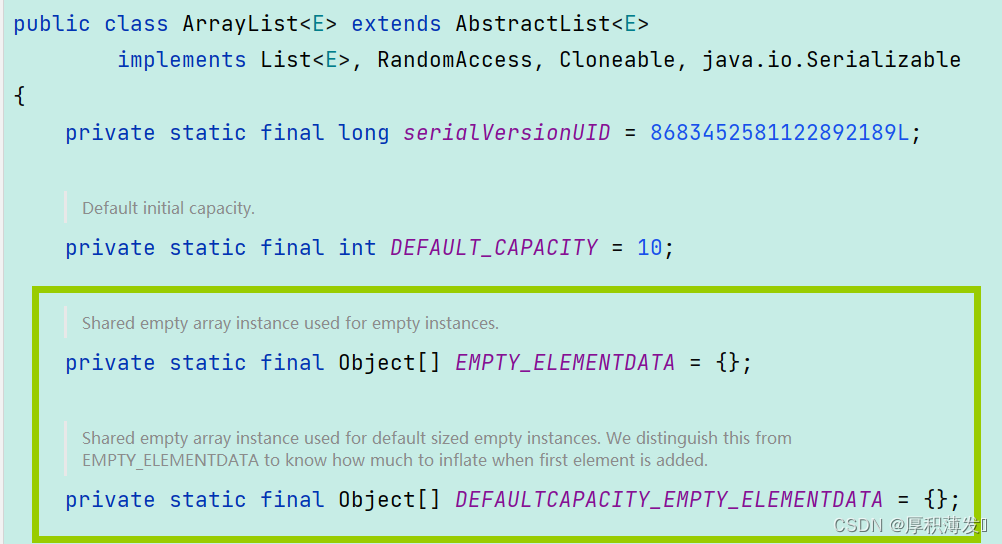
ArrayList通过看源码我们就知道ArrayList底层是一个动态数组,可以动态增容,如果数组元素满了,那就创建一个1.5倍的这样的数组,然后把旧数组利用copyOf方法将其进行拷贝到新的数组中然后返回新的数组。
ArrayList的模拟实现
ArrayList的类成员
首先ArrayList是一个动态数组,我们要有一个数组。
还有一个问题,既然是动态的那怎么才能实现呢?我们先来举个例子,比如个数组开辟了10个空间,我放入了元素0,0,0,0,0,9,那它是怎么计算的呢?没错我们就是需要一个计数器来计算数组中到底有多少个元素,也就是数组中元素的有效个数。当我们添加或者删除元素,这个有效个数就要执行相应的操作。
所以,在实现一个ArrayList类中我们要有两个最核心的东西,那就是一个数组,一个数组的有效个数。还有其他的就是ArrayList所需要实现的核心方法。
private int usedSize =0;
public static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY =10;
private int[] elem;
public MyArrayList() {
this.elem = new int[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
this.usedSize =0;
}
我们创建一个数组elem和有效个数usedSize,实现了一个构造方法对数组容量和有效个数进行相应的初始化,我们将这个数组容量初始化为10,有效个数初始化为0;
toString方法或者display方法(数组元素的打印)
我们先来实现一个简单地方法也就是将这个数组的元素打印出来,当然我们可以自己实现一个display方法也可以重写toString方法进行打印数组元素。
重写toString方法:
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
for(int i =0;i<this.size();++i) {
sb.append(elem[i]);
if(i!=this.size()-1) {
sb.append(",");
}
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}实现display()方法:
// 打印顺序表
public void display() {
for(int i =0;i<this.usedSize;++i) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}思路很简单:就是遍历这个数组打印对应的元素即可。
增加元素方法add(int data)
首先add方法我们要考虑的
- 数组是否满?如果满我们就需要增容
// 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增
public void add(int data) {
//增加元素前要先判断顺序表是否需要增容
if(isFull()) {
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
//开始增加元素
this.elem[this.usedSize] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}- isfull()
只需要检查数组是否满?如果满了就需要进行增容,如果不满就可以增加元素了。
//检查顺序表是否满?如果满了就需要增容
private Boolean isFull() {
return this.usedSize==this.elem.length;
}- 增加元素:
增加元素就是将元素放在对应usedSize下标,此时usedSize既充当数组中的有效个数又充当了待放入元素的下标,可谓是两全其美啊。
在某一个位置增加元素add方法add(int index,int data)
需要考虑如下几点:
- 数组是否满??
- index位置合不合法?
- 数组是否为空数组(其实这个可以不需要)
- 增加元素
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) throws PosIndexOfBoundsException, SqListEmptyException {
//在pos位置添加元素要判断pos位置的合法性
if(!checkInAdd(pos)) {
throw new PosIndexOfBoundsException("pos位置不合法");
}
//检查顺序表是否为空
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new SqListEmptyException("顺序表为空,无法新增pos位置元素");
}
//检查顺序表是否满了?
if(isFull()) {
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
//在pos位置新增元素
for(int i =this.usedSize-1;i>=pos;--i) {
this.elem[i+1] = this.elem[i];
}
//此时pos位置已经是空着的,放入元素
this.elem[pos] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}- isEmpty()
//检查顺序表是否为空
private Boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize==0;
}
-
checkInAdd()检查下标是否合法
//检查pos位置的合法性
private Boolean checkInAdd(int pos) {
if(pos<0||pos>this.usedSize) {
return false;
}
return true;
}-
数组是否满?
//检查顺序表是否满?如果满了就需要增容
private Boolean isFull() {
return this.usedSize==this.elem.length;
}
- 增加元素
我们要先将这个index位置给空出来才能放入元素,所以我们从数组最后一个元素(注意可不是数组最后一个位置),开始挪动数据,将本位置的数据移动到本位置的下一个位置。最后将index位置空出来,我们就将这个位置放入data元素就可以了。
判断数组中是否包含某一个元素-->contains方法
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for(int i =0;i<this.usedSize;++i) {
if(elem[i]==toFind) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}思路:遍历数组看是否有这个元素,如果有返回true,没有返回false。
找到元素的位置indexOf方法
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int indexOf(int toFind) {
for(int i =0;i<this.usedSize;++i) {
if(elem[i]==toFind) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}思路:找到对应的元素返回对应的下标即可。
获取index位置的元素get方法
- 需要判断index位置是否合法
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int get(int pos) throws PosIndexOfBoundsException {
if(pos<0&&pos>=this.usedSize) {
throw new PosIndexOfBoundsException("获取pos位置的元素时pos位置不合法");
}
return this.elem[pos];
}思路:找到对应下标,返回对应元素。
给index位置更新元素set方法
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
public void set(int pos, int value) throws PosIndexOfBoundsException, SqListEmptyException {
if(!checkInAdd(pos)) {
throw new PosIndexOfBoundsException("pos位置不合法");
}
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new SqListEmptyException("顺序表为空,无法新增pos位置元素");
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
}
只要有位置就需要判断其合法性,还要判断一下数组是否为空数组,然后将index位置的元素覆盖成新的元素value。
删除数组中的元素remove方法
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) throws SqListEmptyException {
//第一步要先检查这个顺序表是否为空
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new SqListEmptyException("顺序表为空,无法删除元素");
}
//检查这个要删除的元素是否存在
int ret = indexOf(toRemove);
if(ret==-1) {
System.out.println("你要删除的元素不存在顺序表中,无法删除!!!");
return;
}
for(int i =ret;i<this.usedSize-1;++i) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i+1];
}
this.usedSize--;
}- 还是要判断数组是否为空数组,如果是空数组就不能删除元素。
- 找到要删除元素对应下标,是否存在这个元素。
- 从要删除元素的下标开始,对删除的元素的位置进行覆盖即可。
- 同时有效个数--
size()方法
// 获取顺序表长度
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}将有效长度返回即可。
clear()方法清空顺序表
只要将其有效个数设置为0即可。
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() {
this.usedSize = 0;
}
ArrayList的构造方法
ArrayList的构造方法有三种:
- 第一种就是不带参数的构造方法:
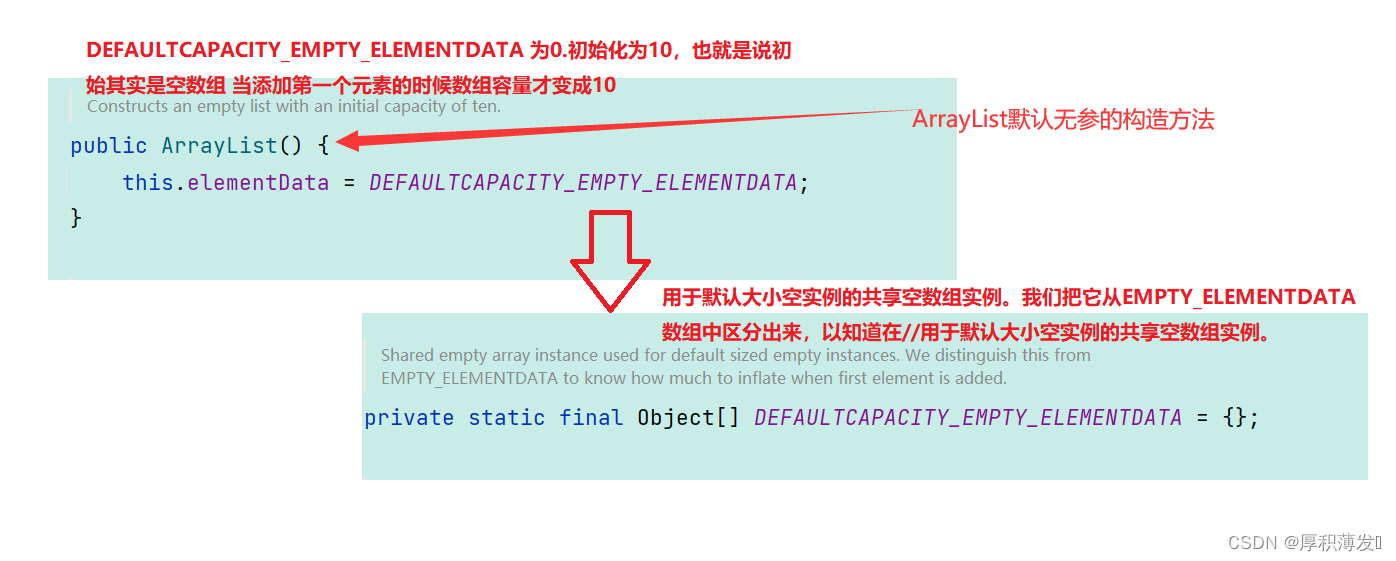
通过读源码和源码注释可以知道:数组默认容量是0(也就是没有添加元素的时候数组容量为0),而当我们添加了元素之后数组容量就变为了10;
- 第二种是带参数为初始容量的构造方法
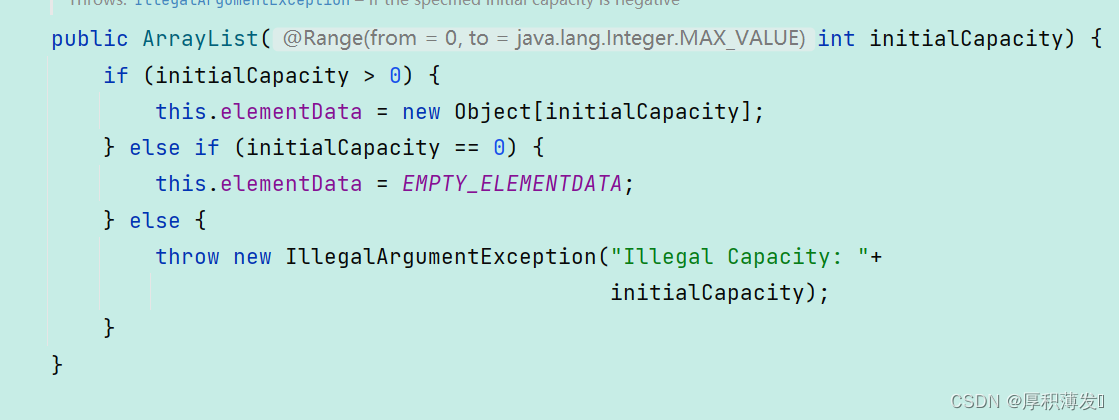
参数为initialCapacity,意思是用户可以自定义这个数组的容量大小,如果参数为0,这个数组就为空,其他情况非法报异常。
- 第三种构造方法
参数为E这个类型参数的子类或者本身。举个例子:
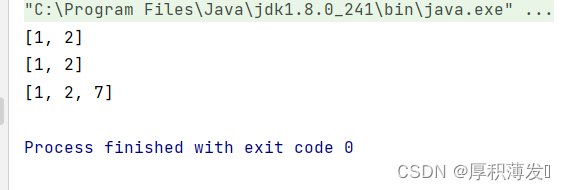
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add(1);
list1.add(2);
System.out.println(list1);
ArrayList<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(list1);
System.out.println(list2);
list2.add(7);
System.out.println(list2);
}我们可以将这个list1作为类型参数传递,这个list2就拥有了list1的元素。
ArrayList的扩容机制
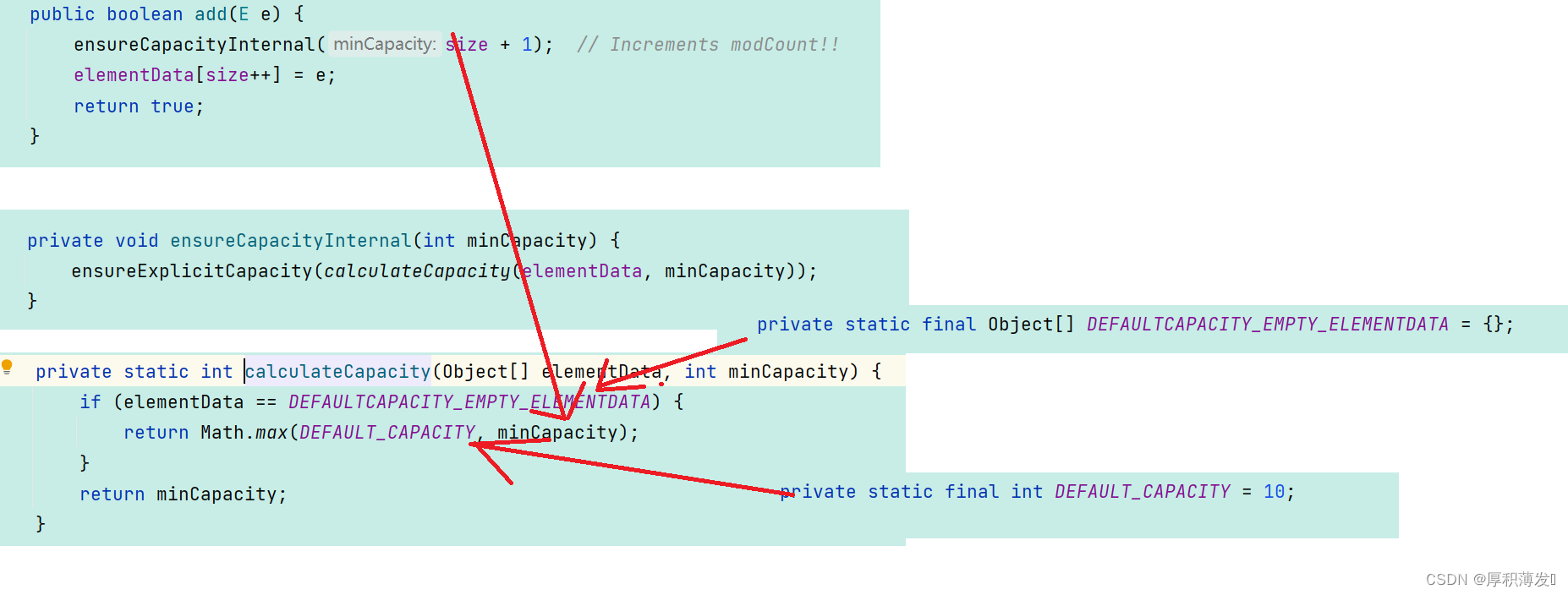
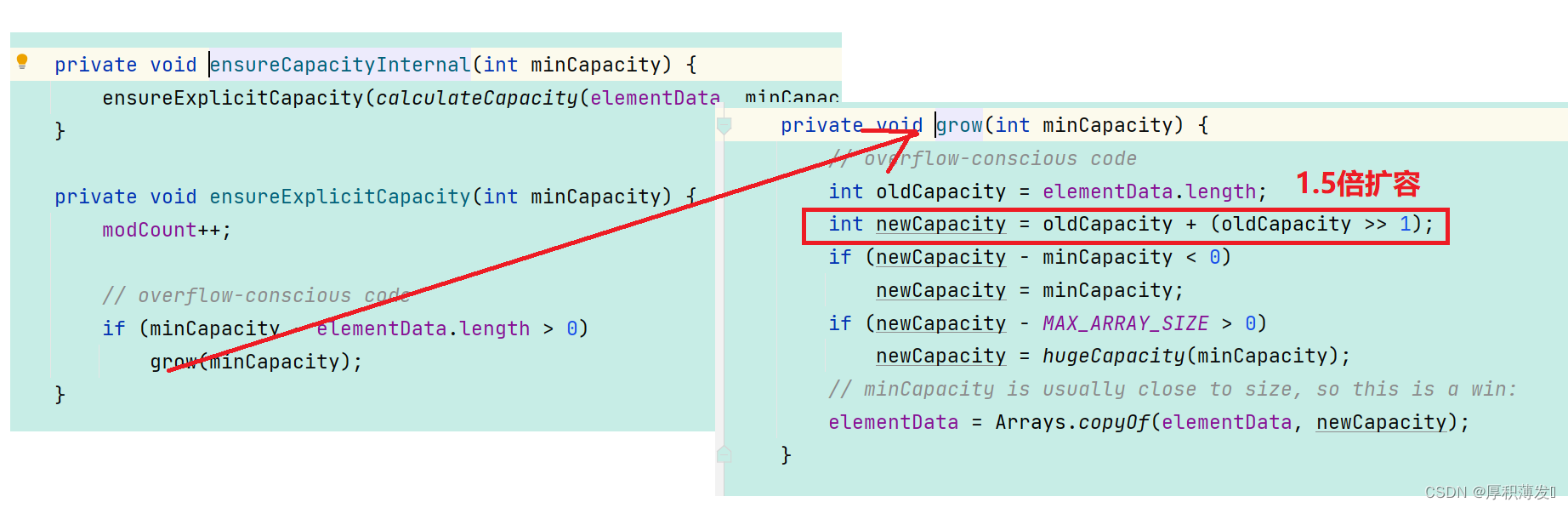
add方法-》ensureCapacityInternal()当 要 add 进第 1 个元素时,minCapacity 为 1,在 Math.max()方法比较后,minCapacity 为 10。)-》直到添加第 11 个元素,minCapacity(为 11)比 elementData.length(为 10)要大。进入 grow 方法进行扩容。-》int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1),所以 ArrayList 每次扩容之后容量都会变为原来的 1.5 倍左右(oldCapacity 为偶数就是 1.5 倍,否则是 1.5 倍左右)!-》
结论: ArrayList 每次扩容之后容量都会变为原来的 1.5 倍左右(oldCapacity 为偶数就是 1.5 倍,否则是 1.5 倍左右。
ArrayList接口练习扑克牌:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
class Poker {
private int rank;//扑克牌的排行
private String suit;//扑克牌的花色
public Poker(int rank, String suit) {
this.rank = rank;
this.suit = suit;
}
public int getRank() {
return rank;
}
public void setRank(int rank) {
this.rank = rank;
}
public String getSuit() {
return suit;
}
public void setSuit(String suit) {
this.suit = suit;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Poker{" +
"rank=" + rank +
", suit='" + suit + ''' +
'}';
}
}
public class TestDemo {
//买牌
public static final String Suit[]={"♠", "♥", "♣", "♦"};
public static void buyPoker(List<Poker> pokerList) {
//首先产生1-13个数字,然后每一个数字对应着四种花色
for(int i =1;i<=13;++i) {
for(int j=0;j<4;++j) {
Poker poker = new Poker(i,Suit[j]);
pokerList.add(poker);
}
}
}
public static void SwapPoker(List<Poker>pokerList,int i,int index) {
//得到i下标的牌,
Poker tmp = pokerList.get(i);
//将i下标的位置设置为index下表的牌
pokerList.set(i,pokerList.get(index));
//再把i下标这个牌放到index的位置上去
pokerList.set(index,tmp);
}
private static List<Poker> shuffle(List<Poker> pokerList) {
//主要是将买好的牌进行打乱
for(int i = pokerList.size()-1;i>0;--i) {
//产生随机数
Random random = new Random();
int index = random.nextInt(i);
//得到这个随机位置的牌
SwapPoker(pokerList,i,index);
}
return pokerList;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实现一副扑克牌
List<Poker> pokerList = new ArrayList<>();
buyPoker(pokerList);//已经买好的牌
System.out.println(pokerList);
List<Poker> pokers =shuffle(pokerList);//洗过的牌
System.out.println(pokers);
//接下来三人开始斗地主
List<Poker> hand1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Poker> hand2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Poker> hand3 = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Poker>> hands = new ArrayList<>();
hands.add(hand1);
hands.add(hand2);
hands.add(hand3);
//接下来开始轮流发牌,每个人只有5张牌,一共法给3个人
for(int i=0;i<5;++i) {
for(int j =0;j<3;++j) {
//先从桌子上摸一张牌,然后给一个人
Poker card = pokers.remove(0);
hands.get(j).add(i,card);
}
}
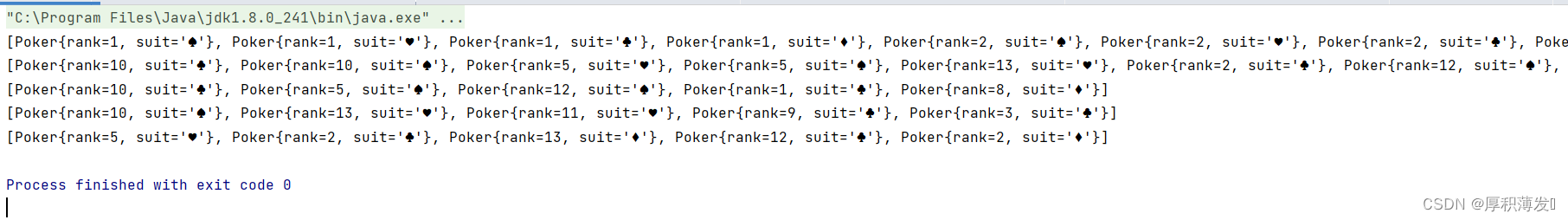
System.out.println(hand1);
System.out.println(hand2);
System.out.println(hand3);
}
}
最后
以上就是伶俐牛排最近收集整理的关于【JAVA 数据结构】 JAVA实现动态数组的全部内容,更多相关【JAVA内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复