目录
- 1.用栈实现队列
- 2.用队列实现栈
- 3.有效的括号
- 4.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
- 5.逆波兰表达式求值
- 6.滑动窗口最大值
- 7.前 K 个高频元素
- 8.简化路径
- 9.基本计算器
1.用栈实现队列
232. 用栈实现队列-简单
b站-代码随想录
思路:两个栈,一个输入栈,一个输出栈
重点:在push数据的时候,只要数据放进输入栈就好,但在pop的时候,操作就复杂一些,输出栈如果为空,就把进栈数据全部导入进来(注意是全部导入)
使用两个数组的栈方法(push, pop) 实现队列
push():向数组末尾添加新元素,并返回新长度。
pop():移除数组的最后一个元素,并返回该元素。
var MyQueue = function() {
this.stackIn = [];
this.stackOut = [];
};
/**
* @param {number} x
* @return {void}
*/
MyQueue.prototype.push = function(x) {
this.stackIn.push(x);
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyQueue.prototype.pop = function() {
const size = this.stackOut.length;
if(size){
return this.stackOut.pop();
}
while(this.stackIn.length){
this.stackOut.push(this.stackIn.pop());
}
return this.stackOut.pop();
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
// peek()的实现,直接复用了pop()
MyQueue.prototype.peek = function() {
// let x = this.stackOut.pop();
let x = this.pop();
this.stackOut.push(x);
// return this.stackOut[this.stackOut.length - 1];
return x;
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyQueue.prototype.empty = function() {
return !this.stackIn.length && !this.stackOut.length;
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new MyQueue()
* obj.push(x)
* var param_2 = obj.pop()
* var param_3 = obj.peek()
* var param_4 = obj.empty()
*/
2.用队列实现栈
225. 用队列实现栈-简单
b站-代码随想录
使用数组(push, shift)模拟队列????
push():向数组末尾添加新元素,并返回新长度。
shift():移除数组的第一项元素,返回值是被移除的元素。
两个队列实现
思路:用两个队列que1和que2实现栈的功能,que2其实完全就是一个备份的作用,把que1除最后面的元素以外的元素都备份到que2,然后弹出最后面的元素,再把其他元素从que2导回que1。
var MyStack = function() {
this.queue1 = [];
this.queue2 = [];
};
/**
* @param {number} x
* @return {void}
*/
MyStack.prototype.push = function(x) {
this.queue1.push(x);
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyStack.prototype.pop = function() {
// 当queue1为空时 交换两个队列
if(!this.queue1.length){
[this.queue1,this.queue2] = [this.queue2,this.queue1];
}
while(this.queue1.length > 1){
this.queue2.push(this.queue1.shift());
}
return this.queue1.shift();
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyStack.prototype.top = function() {
let x = this.pop();
this.queue1.push(x);
return x;
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyStack.prototype.empty = function() {
return !this.queue1.length && !this.queue2.length;
};
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new MyStack()
* obj.push(x)
* var param_2 = obj.pop()
* var param_3 = obj.top()
* var param_4 = obj.empty()
*/
一个队列实现
思路:一个队列在模拟栈弹出元素的时候只要将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部,此时再去弹出元素就是栈的顺序了。
var MyStack = function() {
this.queue = [];
};
/**
* @param {number} x
* @return {void}
*/
MyStack.prototype.push = function(x) {
this.queue.push(x);
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyStack.prototype.pop = function() {
let size = this.queue.length;
while(size > 1){
this.queue.push(this.queue.shift());
size--;
}
return this.queue.shift();
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyStack.prototype.top = function() {
let x = this.pop();
this.queue.push(x);
return x;
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyStack.prototype.empty = function() {
return !this.queue.length;
};
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new MyStack()
* obj.push(x)
* var param_2 = obj.pop()
* var param_3 = obj.top()
* var param_4 = obj.empty()
*/
注意该用while的时候不要写成if
3.有效的括号
20. 有效的括号-简单
b站-代码随想录
三种不匹配情况:①左括号多余②左右括号不匹配③右括号多余
细节:在匹配左括号的时候,让其对应的右括号入栈,再遇到右括号时,就只需要比较当前元素和栈顶相不相等就可以了,比左括号先入栈代码实现要简单的多。
按照代码随想录思路信心满满地写出如下题解,提交时发现:一对括号匹配时运行正确,多对就不行了
原因:最后一个else if(stack.length === 0 || stack.pop() !== c)中多执行了一遍pop操作,而在java等版本中,此处用的是peek()。所以js解时,推荐使用map或对象
var isValid = function(s) {
// 剪枝
if(Math.floor(s.length%2)) return false;
let stack = [];
let sArr = Array.from(s);
// 遍历字符串
for(const c of sArr){
if(c === '('){
stack.push(')');
}else if(c === '['){
stack.push(']');
}else if(c === '{'){
stack.push('}');
// stack[stack.length - 1] 其实就是取栈顶元素
}else if(stack.length === 0 || stack[stack.length - 1] !== c){
return false;
}else{
stack.pop();
}
}
return !stack.length;
};
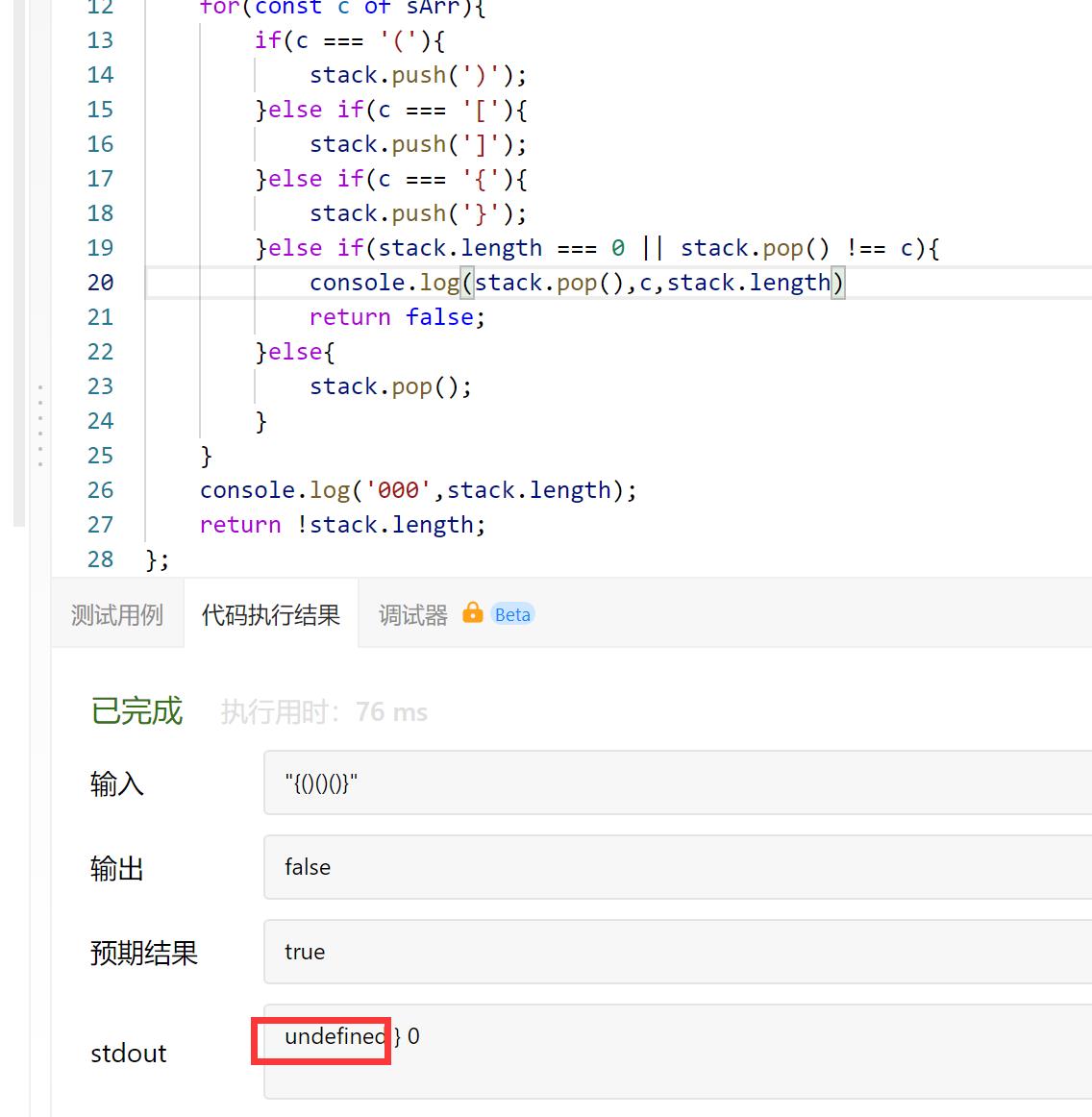
想到js中没有peek()操作,然后我问怎么取栈顶元素...那不就是查看数组的最后一个元素嘛....不活了....
代码随想录版①
var isValid = function (s) {
const stack = [];
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
let c = s[i];
switch (c) {
case '(':
stack.push(')');
break;
case '[':
stack.push(']');
break;
case '{':
stack.push('}');
break;
default:
if (c !== stack.pop()) {
return false;
}
}
}
return stack.length === 0;
};
代码随想录版②
var isValid = function(s) {
const stack = [],
map = {
"(":")",
"{":"}",
"[":"]"
};
for(const x of s) {
if(x in map) {
stack.push(x);
continue;
};
if(map[stack.pop()] !== x) return false;
}
return !stack.length;
};
4.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项-简单
b站-代码随想录
匹配问题都是栈的强项
自己写的
利用push()和pop()从尾部操作stack
var removeDuplicates = function(s) {
if(s.length == 1) return s;
let stack = [];
let sArr = Array.from(s);
while(sArr.length > 0 ){
if(stack.length === 0 || sArr[sArr.length - 1] !== stack[stack.length - 1]){
stack.push(sArr.pop());
}else{
sArr.pop();
stack.pop();
}
}
return stack.reverse().join('');
};
自己写的
利用unshift()和shift()从首部操作stack
var removeDuplicates = function(s) {
if(s.length == 1) return s;
let stack = [];
let sArr = Array.from(s);
while(sArr.length > 0 ){
if(stack.length === 0 || sArr[sArr.length - 1] !== stack[0]){
stack.unshift(sArr.pop());
}else{
sArr.pop();
stack.shift();
}
}
return stack.join('');
};
但不知道为什么时间差好多啊,从首部操作stack要将近4s
代码随想录版????
栈
var removeDuplicates = function(s) {
const stack = [];
for(const x of s) {
let c = null;
if(stack.length && x === (c = stack.pop())) continue;
c && stack.push(c);
stack.push(x);
}
return stack.join("");
};
双指针(模拟栈)
// 原地解法(双指针模拟栈)
var removeDuplicates = function(s) {
s = [...s];
let top = -1; // 指向栈顶元素的下标
for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
if(top === -1 || s[top] !== s[i]) { // top === -1 即空栈
s[++top] = s[i]; // 入栈
} else {
top--; // 推出栈
}
}
s.length = top + 1; // 栈顶元素下标 + 1 为栈的长度
return s.join('');
};
5.逆波兰表达式求值
150. 逆波兰表达式求值-中等
b站-代码随想录
逆波兰表达式:一种后缀表达式,后缀指运算符写在后面,(相当于二叉树的后序遍历),这样的话便于计算机按顺序执行操作,不用考虑括号、优先级。我们平常使用的是中缀表达式:(1+2)*(3+4)
优点:
- 去掉括号后表达式无歧义,上式即便写成 1 2 + 3 4 + * 也可以依据次序计算出正确结果。
- 适合用栈操作运算:遇到数字则入栈;遇到算符则取出栈顶两个数字进行计算,并将结果压入栈中。
思路:遇到数字就入栈,遇到操作符就从栈中取出两个数字进行操作。关键:找出规律什么时候进行消除操作
自己写的????
var evalRPN = function(tokens) {
let stack = [];
let num1 = 0, num2 = 0, num = 0;
for(let i = 0; i < tokens.length; i++){
if(tokens[i] === '+'){
// 因为tokens是字符串数组,所以要parseInt()
num1 = parseInt(stack.shift());
num2 = parseInt(stack.shift());
num = parseInt(num2 + num1);
stack.unshift(num);
}else if(tokens[i] === '-'){
num1 = parseInt(stack.shift());
num2 = parseInt(stack.shift());
num = parseInt(num2 - num1);
stack.unshift(num);
}else if(tokens[i] === '*'){
num1 = parseInt(stack.shift());
num2 = parseInt(stack.shift());
num = parseInt(num2 * num1);
console.log(num);
stack.unshift(num);
}else if(tokens[i] === '/'){
num1 = parseInt(stack.shift());
num2 = parseInt(stack.shift());
num = parseInt(num2 / num1);
stack.unshift(num);
}else{
stack.unshift(tokens[i]);
}
}
return stack.shift();
};
代码随想录版
关于栈的这种“消除”题目,还是用对象来做,比较简便
var evalRPN = function(tokens) {
const s = new Map([
["+", (a, b) => a * 1 + b * 1],
["-", (a, b) => b - a],
["*", (a, b) => b * a],
["/", (a, b) => (b / a) | 0]
]);
const stack = [];
for (const i of tokens) {
if(!s.has(i)) {
stack.push(i);
continue;
}
stack.push(s.get(i)(stack.pop(),stack.pop()))
}
return stack.pop();
};
还不太理解 stack.push(s.get(i)(stack.pop(),stack.pop())) 这种写法
6.滑动窗口最大值
239. 滑动窗口最大值-困难
b站-代码随想录
暴力解法: 遍历整个数组,还要遍历每个k窗口,时间复杂度O(n*k)
优先级队列(大顶堆/小顶堆):不能确定pop()的元素是不是我们要pop()的,即:窗口是移动的,而大顶堆每次只能弹出最大值,我们无法移除其他数值,这样就造成大顶堆维护的不是滑动窗口里面的数值了。所以不能用大顶堆。
单调队列: 维持队列内的元素单调递增/递减,保持队列中的最大值在队列的出口处。
关键:其实队列没有必要维护窗口里的所有元素,只需要维护有可能成为窗口里最大值的元素就可以了,同时保证队里里的元素数值是由大到小的。

var maxSlidingWindow = function(nums, k) {
if(k === 1) return nums;
if(k === nums.length) return [Math.max(...nums)];
class MonoQueue{
// 实现单调队列 (从大到小)
queue;
constructor() {
this.queue = [];
}
// 如果入队的元素大于队尾的元素 就将其弹出
// 保证队列是递减的
enqueue(val) {
let back = this.queue[this.queue.length - 1];
while(back !== undefined && back < val){
this.queue.pop();
back = this.queue[this.queue.length - 1];
}
this.queue.push(val);
}
// 当val与队首元素相等时 将其pop
// 不相等就说明它已经在enqueue中被弹出了
dequeue(val) {
let front = this.front();
if(front === val) {
this.queue.shift();
}
}
// 查询当前队列里的最大值 即直接返回队首元素
front() {
return this.queue[0];
}
}
let myQueue = new MonoQueue();
let i = 0, j = 0;
let ans = [];
// 先将前k的元素放进队列
// 此时滑动窗口的长度已经固定了
while(j < k){
myQueue.enqueue(nums[j++]);
}
ans.push(myQueue.front());
while (j < nums.length) {
// 滑动窗口 加入最后面的元素
myQueue.enqueue(nums[j]);
// 滑动窗口 移除最前面的元素
// 当nums[i]与queue队头元素相等时才弹出,否则说明已经被弹出了
myQueue.dequeue(nums[i]);
// 记录对应的最大值
ans.push(myQueue.front());
i++,j++;
}
return ans;
};
时:O(n)
空:O(k)
7.前 K 个高频元素
347. 前 K 个高频元素-中等
b站-代码随想录
map
思路:统计各个元素出现的频率,放进map,key是元素,value是元素对应的频率,将map按照value排序,取出前k个key。排序:O(nlogn)。若按堆的思路取出前k个元素,则O(nlogk)。注:此处应该用小顶堆实现,因为大顶堆每次都把最大值,即根节点弹出了,留下的其实是最小的k个值
优先级队列
优先级队列底层实现是大顶堆/小顶堆。
思路:使用优先级队列对部分频率排序
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} k
* @return {number[]}
*/
var topKFrequent = function(nums, k) {
// 统计各个元素出现的频率
const map = new Map();
for(const num of nums){
map.set(num, (map.get(num) || 0) + 1);
}
// 创建小顶堆 按照value进行排序
const priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue((a,b) => a[1] - b[1]);
// entry是一个长度为2的数组,0位置存储key 1位置存储value
for (const entry of map.entries()) {
priorityQueue.push(entry);
if (priorityQueue.size() > k) {
priorityQueue.pop();
}
}
const ans = [];
for(let i = priorityQueue.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ans[i] = priorityQueue.pop()[0];
}
return ans;
};
// 优先级队列 compareFn?
// function PriorityQueue(compareFn) {
// this.compareFn = compareFn;
// this.queue = [];
// }
// 优先级队列 compareFn?
var PriorityQueue = function(compareFn) {
this.compareFn = compareFn;
this.queue = [];
}
PriorityQueue.prototype.push = function(val){
this.queue.push(val);
let index = this.queue.length - 1;
let parent = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
// 上浮
while(parent >= 0 && this.compare(parent, index) > 0) {
// 交换
[this.queue[index], this.queue[parent]] = [this.queue[parent], this.queue[index]];
index = parent;
parent = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
}
}
// 获取堆顶元素并移除
PriorityQueue.prototype.pop = function(){
const ret = this.queue[0];
// 把最后一个节点移到堆顶
this.queue[0] = this.queue.pop();
let index = 0;
// 左子节点下标,left + 1 就是右子节点下标
let left = 1;
let selectedChild = this.compare(left, left + 1) > 0 ? left + 1 : left;
// 下沉
while(selectedChild !== undefined && this.compare(index, selectedChild) > 0){
// 交换
[this.queue[index], this.queue[selectedChild]] = [this.queue[selectedChild], this.queue[index]];
index = selectedChild;
left = 2 * index + 1;
selectedChild = this.compare(left, left + 1) > 0 ? left + 1 : left;
}
return ret;
}
PriorityQueue.prototype.size = function(){
return this.queue.length;
}
// 使用传入的 compareFn 比较两个位置的元素
PriorityQueue.prototype.compare = function(index1, index2) {
if (this.queue[index1] === undefined) {
return 1;
}
if (this.queue[index2] === undefined) {
return -1;
}
return this.compareFn(this.queue[index1], this.queue[index2]);
}
8.简化路径
71. 简化路径-中等
栈
var simplifyPath = function(path) {
const names = path.split('/');
const stack = [];
for(const name of names) {
if(name === '..'){
if(stack.length) stack.pop();
}else if(name !== '.' && name.length){
stack.push(name);
}
}
return '/'+stack.join('/');
};
时间复杂度:O(n),其中n是字符串path的长度。
空间复杂度:O(n)。我们需要O(n)的空间存储names中的所有字符串。
9.基本计算器
224. 基本计算器-困难
①括号展开+栈
var calculate = function(s) {
const ops = [1];
let sign = 1;
let ans = 0;
const len = s.length;
let i =0;
while(i < len){
if (s[i] === ' '){
} else if (s[i] === '+') {
sign = ops[ops.length - 1];
} else if (s[i] === '-') {
sign = -ops[ops.length - 1];
} else if (s[i] === '(') {
ops.push(sign);
} else if (s[i] === ')') {
ops.pop();
} else {
let num = 0;
while (i < len && !(isNaN(Number(s[i]))) && s[i] !== ' ') {
num = num * 10 + s[i].charCodeAt() - '0'.charCodeAt();
i++;
}
ans += sign * num;
i--;
}
i++;
}
return ans;
};
②双栈
最后
以上就是欣喜白羊最近收集整理的关于leetcode每天5题-Day341.用栈实现队列2.用队列实现栈3.有效的括号4.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项5.逆波兰表达式求值6.滑动窗口最大值7.前 K 个高频元素8.简化路径9.基本计算器的全部内容,更多相关leetcode每天5题-Day341.用栈实现队列2.用队列实现栈3.有效的括号4.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项5.逆波兰表达式求值6.滑动窗口最大值7.前内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复