一般用户态传递参数是通过main函数,第一个参数表示args个数,即argc,第二个参数表示具体的参数
在kernel态,无法通过这样的方式传递参数,一般使用宏module_param的方式,步骤如下:
1.使用module_param指定模块的参数
2.加载driver时给模块传递参数
该宏的定义见/linux/moduleparam.h中
/**
* module_param - typesafe helper for a module/cmdline parameter
* @value: the variable to alter, and exposed parameter name.
* @type: the type of the parameter
* @perm: visibility in sysfs.
*
* @value becomes the module parameter, or (prefixed by KBUILD_MODNAME and a
* ".") the kernel commandline parameter. Note that - is changed to _, so
* the user can use "foo-bar=1" even for variable "foo_bar".
*
* @perm is 0 if the the variable is not to appear in sysfs, or 0444
* for world-readable, 0644 for root-writable, etc. Note that if it
* is writable, you may need to use kparam_block_sysfs_write() around
* accesses (esp. charp, which can be kfreed when it changes).
*
* The @type is simply pasted to refer to a param_ops_##type and a
* param_check_##type: for convenience many standard types are provided but
* you can create your own by defining those variables.
*
* Standard types are:
* byte, short, ushort, int, uint, long, ulong
* charp: a character pointer
* bool: a bool, values 0/1, y/n, Y/N.
* invbool: the above, only sense-reversed (N = true).
*/
#define module_param(name, type, perm)
module_param_named(name, name, type, perm)具体使用为:
适用于2.4与2.6内核的模块输入参数模板
#include <linux/module.h>
#ifdef LINUX26
#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
#endif
int debug = 0;
char *mode = "800x600";
int tuner[4] = {1, 1, 1, 1};
#ifdef LINUX26
int tuner_c = 1;
#endif
#ifdef LINUX26
MODULE_PARM(debug, "i");
MODULE_PARM(mode, "s");
MODULE_PARM(tuner,"1-4i");
#else
module_param(debug, int, 0644);
module_param(mode, charp, 0644);
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE >= KERNEL_VERSION(2, 6, 10)
module_param_array(tuner, int, &tuner_c, 0644);
#else
module_param_array(tuner, int, tuner_c, 0644);
#endif
#endif模块编译生成后,加载模块时可以输入:`modprobe my_module mode=1024x768 debug=1 tuner=22,33`。
还有一类,是函数回调 module_param_cb,类似于module_param_call
/**
* module_param_cb - general callback for a module/cmdline parameter
* @name: a valid C identifier which is the parameter name.
* @ops: the set & get operations for this parameter.
* @perm: visibility in sysfs.
*
* The ops can have NULL set or get functions.
*/
#define module_param_cb(name, ops, arg, perm)
__module_param_call(MODULE_PARAM_PREFIX, name, ops, arg, perm, -1, 0)具体实例如下:
在codec驱动代码中添加对寄存器访问的控制方式。调试codec的时候,可以直接查看或修改寄存器,免去了编译内核或模块的工作,节省宝贵时间。
static int nau8810_debug_reg_set(const char *buffer, struct kernel_param *kp)
{
u16 reg, val;
if(!buffer)
return -EINVAL;
if(sscanf(buffer, "%x,%x", (uint *)®, (uint *)&val) != 2) {
printk(KERN_ERR "invalid val = %sn", buffer);
return -EINVAL;
}
if(debug)
printk(KERN_INFO"%s:R0x%x=0x%xn", __func__, reg, val);
snd_soc_write(nau8810_codec, reg, val);
return 0;
}
static int nau8810_debug_reg_get(char *buffer, struct kernel_param *kp)
{
u16 reg, val;
int len = 0;
len = sprintf(buffer, "nau8810 DUMP registers:");
for(reg = 0; reg < NAU8810_CACHEREGNUM; reg++) {
val = snd_soc_read(nau8810_codec, reg);
if(!(reg%8))
len += sprintf(buffer+len,"n");
len += sprintf(buffer+len, "R%02x:%03x ", reg, val);
}
return len;
}
static unsigned int dummy = 0;
module_param_call(regs, nau8810_debug_reg_set, nau8810_debug_reg_get, &dummy, 0644);系统启动后,会在目录/sys/module/snd_soc_nau8810/parameters创建regs节点,此时即可对此节点进行相应的操作:
1. 读操作:cat regs
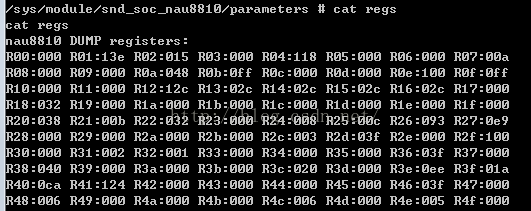
2. 写操作:如写0x5寄存器的值为1 echo 0x5,0x1 > regs
最后
以上就是贤惠裙子最近收集整理的关于module_param的全部内容,更多相关module_param内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复