=====================================================
H.264源代码分析文章列表:
【编码 - x264】
x264源代码简单分析:概述
x264源代码简单分析:x264命令行工具(x264.exe)
x264源代码简单分析:编码器主干部分-1
x264源代码简单分析:编码器主干部分-2
x264源代码简单分析:x264_slice_write()
x264源代码简单分析:滤波(Filter)部分
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
x264源代码简单分析:宏块编码(Encode)部分
x264源代码简单分析:熵编码(Entropy Encoding)部分
FFmpeg与libx264接口源代码简单分析
【解码 - libavcodec H.264 解码器】
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:概述
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解析器(Parser)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解码器主干部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:熵解码(EntropyDecoding)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:环路滤波(Loop Filter)部分
=====================================================
本文继续记录x264编码器主干部分的源代码。上一篇文章记录x264_encoder_open(),x264_encoder_headers(),和x264_encoder_close()这三个函数,本文记录x264_encoder_encode()函数。
函数调用关系图
X264编码器主干部分的源代码在整个x264中的位置如下图所示。
单击查看更清晰的图片
X264编码器主干部分的函数调用关系如下图所示。
从图中可以看出,x264主干部分最复杂的函数就是x264_encoder_encode(),该函数完成了编码一帧YUV为H.264码流的工作。与之配合的还有打开编码器的函数x264_encoder_open(),关闭编码器的函数x264_encoder_close(),以及输出SPS/PPS/SEI这样的头信息的x264_encoder_headers()。
x264_validate_parameters():检查输入参数(例如输入图像的宽高是否为正数)。
x264_predict_16x16_init():初始化Intra16x16帧内预测汇编函数。
x264_predict_4x4_init():初始化Intra4x4帧内预测汇编函数。
x264_pixel_init():初始化像素值计算相关的汇编函数(包括SAD、SATD、SSD等)。
x264_dct_init():初始化DCT变换和DCT反变换相关的汇编函数。
x264_mc_init():初始化运动补偿相关的汇编函数。
x264_quant_init():初始化量化和反量化相关的汇编函数。
x264_deblock_init():初始化去块效应滤波器相关的汇编函数。
x264_lookahead_init():初始化Lookahead相关的变量。x264_ratecontrol_new():初始化码率控制相关的变量。
x264_sps_write():输出SPS
x264_pps_write():输出PPS
x264_sei_version_write():输出SEI
x264_encoder_encode()编码一帧YUV为H.264码流。它调用了下面的函数:
x264_frame_pop_unused():获取1个x264_frame_t类型结构体fenc。如果frames.unused[]队列不为空,就调用x264_frame_pop()从unused[]队列取1个现成的;否则就调用x264_frame_new()创建一个新的。
x264_frame_copy_picture():将输入的图像数据拷贝至fenc。
x264_lookahead_put_frame():将fenc放入lookahead.next.list[]队列,等待确定帧类型。
x264_lookahead_get_frames():通过lookahead分析帧类型。该函数调用了x264_slicetype_decide(),x264_slicetype_analyse()和x264_slicetype_frame_cost()等函数。经过一些列分析之后,最终确定了帧类型信息,并且将帧放入frames.current[]队列。
x264_frame_shift():从frames.current[]队列取出1帧用于编码。
x264_reference_update():更新参考帧队列。
x264_reference_reset():如果为IDR帧,调用该函数清空参考帧列表。
x264_reference_hierarchy_reset():如果是非IDR的I帧、P帧、B帧(可做为参考帧),调用该函数。
x264_reference_build_list():创建参考帧列表list0和list1。
x264_ratecontrol_start():开启码率控制。
x264_slice_init():创建 Slice Header。
x264_slices_write():编码数据(最关键的步骤)。其中调用了x264_slice_write()完成了编码的工作(注意“x264_slices_write()”和“x264_slice_write()”名字差了一个“s”)。
x264_encoder_frame_end():编码结束后做一些后续处理,例如记录一些统计信息。其中调用了x264_encoder_encapsulate_nals()封装NALU(添加起始码),调用x264_frame_push_unused()将fenc重新放回frames.unused[]队列,并且调用x264_ratecontrol_end()结束码率控制。
x264_encoder_close()用于关闭解码器,其中释放了libx264初始化的时候使用的各种变量。它调用了下面的函数:
x264_lookahead_delete():释放Lookahead相关的变量。
x264_ratecontrol_summary():汇总码率控制信息。
x264_ratecontrol_delete():关闭码率控制。
上一篇文章已经记录了x264_encoder_open(),x264_encoder_headers(),和x264_encoder_close()这三个函数的源代码。本文继续上一篇文章的内容,记录x264_encoder_encode()函数的源代码。
x264_encoder_encode()
x264_encoder_encode()是libx264的API函数,用于编码一帧YUV为H.264码流。该函数的声明如下所示。/* x264_encoder_encode:
*
encode one picture.
*
*pi_nal is the number of NAL units outputted in pp_nal.
*
returns the number of bytes in the returned NALs.
*
returns negative on error and zero if no NAL units returned.
*
the payloads of all output NALs are guaranteed to be sequential in memory. */
int
x264_encoder_encode( x264_t *, x264_nal_t **pp_nal, int *pi_nal, x264_picture_t *pic_in, x264_picture_t *pic_out );/****************************************************************************
* x264_encoder_encode:
*
XXX: i_poc
: is the poc of the current given picture
*
i_frame : is the number of the frame being coded
*
ex:
type frame poc
*
I
0
2*0
*
P
1
2*3
*
B
2
2*1
*
B
3
2*2
*
P
4
2*6
*
B
5
2*4
*
B
6
2*5
*
* 注释和处理:雷霄骅
* http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
* leixiaohua1020@126.com
****************************************************************************/
//编码一帧数据
int
x264_encoder_encode( x264_t *h,
x264_nal_t **pp_nal, int *pi_nal,
x264_picture_t *pic_in,
x264_picture_t *pic_out )
{
x264_t *thread_current, *thread_prev, *thread_oldest;
int i_nal_type, i_nal_ref_idc, i_global_qp;
int overhead = NALU_OVERHEAD;
#if HAVE_OPENCL
if( h->opencl.b_fatal_error )
return -1;
#endif
if( h->i_thread_frames > 1 )
{
thread_prev
= h->thread[ h->i_thread_phase ];
h->i_thread_phase = (h->i_thread_phase + 1) % h->i_thread_frames;
thread_current = h->thread[ h->i_thread_phase ];
thread_oldest
= h->thread[ (h->i_thread_phase + 1) % h->i_thread_frames ];
x264_thread_sync_context( thread_current, thread_prev );
x264_thread_sync_ratecontrol( thread_current, thread_prev, thread_oldest );
h = thread_current;
}
else
{
thread_current =
thread_oldest
= h;
}
h->i_cpb_delay_pir_offset = h->i_cpb_delay_pir_offset_next;
/* no data out */
*pi_nal = 0;
*pp_nal = NULL;
/* ------------------- Setup new frame from picture -------------------- */
if( pic_in != NULL )
{
/* 1: Copy the picture to a frame and move it to a buffer */
//步骤1
//fenc存储了编码帧
//获取一帧的空间fenc,用来存放待编码的帧
x264_frame_t *fenc = x264_frame_pop_unused( h, 0 );
if( !fenc )
return -1;
//外部像素数据传递到内部系统
//pic_in(外部结构体x264_picture_t)到fenc(内部结构体x264_frame_t)
if( x264_frame_copy_picture( h, fenc, pic_in ) < 0 )
return -1;
//宽和高都确保是16的整数倍(宏块宽度的整数倍)
if( h->param.i_width != 16 * h->mb.i_mb_width ||
h->param.i_height != 16 * h->mb.i_mb_height )
x264_frame_expand_border_mod16( h, fenc );//扩展至16整数倍
fenc->i_frame = h->frames.i_input++;
if( fenc->i_frame == 0 )
h->frames.i_first_pts = fenc->i_pts;
if( h->frames.i_bframe_delay && fenc->i_frame == h->frames.i_bframe_delay )
h->frames.i_bframe_delay_time = fenc->i_pts - h->frames.i_first_pts;
if( h->param.b_vfr_input && fenc->i_pts <= h->frames.i_largest_pts )
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "non-strictly-monotonic PTSn" );
h->frames.i_second_largest_pts = h->frames.i_largest_pts;
h->frames.i_largest_pts = fenc->i_pts;
if( (fenc->i_pic_struct < PIC_STRUCT_AUTO) || (fenc->i_pic_struct > PIC_STRUCT_TRIPLE) )
fenc->i_pic_struct = PIC_STRUCT_AUTO;
if( fenc->i_pic_struct == PIC_STRUCT_AUTO )
{
#if HAVE_INTERLACED
int b_interlaced = fenc->param ? fenc->param->b_interlaced : h->param.b_interlaced;
#else
int b_interlaced = 0;
#endif
if( b_interlaced )
{
int b_tff = fenc->param ? fenc->param->b_tff : h->param.b_tff;
fenc->i_pic_struct = b_tff ? PIC_STRUCT_TOP_BOTTOM : PIC_STRUCT_BOTTOM_TOP;
}
else
fenc->i_pic_struct = PIC_STRUCT_PROGRESSIVE;
}
if( h->param.rc.b_mb_tree && h->param.rc.b_stat_read )
{
if( x264_macroblock_tree_read( h, fenc, pic_in->prop.quant_offsets ) )
return -1;
}
else
x264_stack_align( x264_adaptive_quant_frame, h, fenc, pic_in->prop.quant_offsets );
if( pic_in->prop.quant_offsets_free )
pic_in->prop.quant_offsets_free( pic_in->prop.quant_offsets );
//降低分辨率处理(原来的一半),线性内插
//注意这里并不是6抽头滤波器的半像素内插
if( h->frames.b_have_lowres )
x264_frame_init_lowres( h, fenc );
/* 2: Place the frame into the queue for its slice type decision */
//步骤2
//fenc放入lookahead.next.list[]队列,等待确定帧类型
x264_lookahead_put_frame( h, fenc );
if( h->frames.i_input <= h->frames.i_delay + 1 - h->i_thread_frames )
{
/* Nothing yet to encode, waiting for filling of buffers */
pic_out->i_type = X264_TYPE_AUTO;
return 0;
}
}
else
{
//输入数据为空的时候(Flush Encoder?),不需要lookahead
/* signal kills for lookahead thread */
x264_pthread_mutex_lock( &h->lookahead->ifbuf.mutex );
h->lookahead->b_exit_thread = 1;
x264_pthread_cond_broadcast( &h->lookahead->ifbuf.cv_fill );
x264_pthread_mutex_unlock( &h->lookahead->ifbuf.mutex );
}
h->i_frame++;
/* 3: The picture is analyzed in the lookahead */
// 步骤3
//通过lookahead分析帧类型
if( !h->frames.current[0] )
x264_lookahead_get_frames( h );
if( !h->frames.current[0] && x264_lookahead_is_empty( h ) )
return x264_encoder_frame_end( thread_oldest, thread_current, pp_nal, pi_nal, pic_out );
/* ------------------- Get frame to be encoded ------------------------- */
/* 4: get picture to encode */
//从frames.current[]队列取出1帧[0]用于编码
h->fenc = x264_frame_shift( h->frames.current );
/* If applicable, wait for previous frame reconstruction to finish */
if( h->param.b_sliced_threads )
if( x264_threadpool_wait_all( h ) < 0 )
return -1;
if( h->i_frame == h->i_thread_frames - 1 )
h->i_reordered_pts_delay = h->fenc->i_reordered_pts;
if( h->reconfig )
{
x264_encoder_reconfig_apply( h, &h->reconfig_h->param );
h->reconfig = 0;
}
if( h->fenc->param )
{
x264_encoder_reconfig_apply( h, h->fenc->param );
if( h->fenc->param->param_free )
{
h->fenc->param->param_free( h->fenc->param );
h->fenc->param = NULL;
}
}
// ok to call this before encoding any frames, since the initial values of fdec have b_kept_as_ref=0
//更新参考帧队列frames.reference[].若为B帧则不更新
//重建帧fdec移植参考帧列表,新建一个fdec
if( x264_reference_update( h ) )
return -1;
h->fdec->i_lines_completed = -1;
if( !IS_X264_TYPE_I( h->fenc->i_type ) )
{
int valid_refs_left = 0;
for( int i = 0; h->frames.reference[i]; i++ )
if( !h->frames.reference[i]->b_corrupt )
valid_refs_left++;
/* No valid reference frames left: force an IDR. */
if( !valid_refs_left )
{
h->fenc->b_keyframe = 1;
h->fenc->i_type = X264_TYPE_IDR;
}
}
if( h->fenc->b_keyframe )
{
h->frames.i_last_keyframe = h->fenc->i_frame;
if( h->fenc->i_type == X264_TYPE_IDR )
{
h->i_frame_num = 0;
h->frames.i_last_idr = h->fenc->i_frame;
}
}
h->sh.i_mmco_command_count =
h->sh.i_mmco_remove_from_end = 0;
h->b_ref_reorder[0] =
h->b_ref_reorder[1] = 0;
h->fdec->i_poc =
h->fenc->i_poc = 2 * ( h->fenc->i_frame - X264_MAX( h->frames.i_last_idr, 0 ) );
/* ------------------- Setup frame context ----------------------------- */
/* 5: Init data dependent of frame type */
if( h->fenc->i_type == X264_TYPE_IDR )
{
//I与IDR区别
//注意IDR会导致参考帧列清空,而I不会
//I图像之后的图像可以引用I图像之间的图像做运动参考
/* reset ref pictures */
i_nal_type
= NAL_SLICE_IDR;
i_nal_ref_idc = NAL_PRIORITY_HIGHEST;
h->sh.i_type = SLICE_TYPE_I;
//若是IDR帧,则清空所有参考帧
x264_reference_reset( h );
h->frames.i_poc_last_open_gop = -1;
}
else if( h->fenc->i_type == X264_TYPE_I )
{
//I与IDR区别
//注意IDR会导致参考帧列清空,而I不会
//I图像之后的图像可以引用I图像之间的图像做运动参考
i_nal_type
= NAL_SLICE;
i_nal_ref_idc = NAL_PRIORITY_HIGH; /* Not completely true but for now it is (as all I/P are kept as ref)*/
h->sh.i_type = SLICE_TYPE_I;
x264_reference_hierarchy_reset( h );
if( h->param.b_open_gop )
h->frames.i_poc_last_open_gop = h->fenc->b_keyframe ? h->fenc->i_poc : -1;
}
else if( h->fenc->i_type == X264_TYPE_P )
{
i_nal_type
= NAL_SLICE;
i_nal_ref_idc = NAL_PRIORITY_HIGH; /* Not completely true but for now it is (as all I/P are kept as ref)*/
h->sh.i_type = SLICE_TYPE_P;
x264_reference_hierarchy_reset( h );
h->frames.i_poc_last_open_gop = -1;
}
else if( h->fenc->i_type == X264_TYPE_BREF )
{
//可以作为参考帧的B帧,这是个特色
i_nal_type
= NAL_SLICE;
i_nal_ref_idc = h->param.i_bframe_pyramid == X264_B_PYRAMID_STRICT ? NAL_PRIORITY_LOW : NAL_PRIORITY_HIGH;
h->sh.i_type = SLICE_TYPE_B;
x264_reference_hierarchy_reset( h );
}
else
/* B frame */
{
//最普通
i_nal_type
= NAL_SLICE;
i_nal_ref_idc = NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE;
h->sh.i_type = SLICE_TYPE_B;
}
//重建帧与编码帧的赋值...
h->fdec->i_type = h->fenc->i_type;
h->fdec->i_frame = h->fenc->i_frame;
h->fenc->b_kept_as_ref =
h->fdec->b_kept_as_ref = i_nal_ref_idc != NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE && h->param.i_keyint_max > 1;
h->fdec->mb_info = h->fenc->mb_info;
h->fdec->mb_info_free = h->fenc->mb_info_free;
h->fenc->mb_info = NULL;
h->fenc->mb_info_free = NULL;
h->fdec->i_pts = h->fenc->i_pts;
if( h->frames.i_bframe_delay )
{
int64_t *prev_reordered_pts = thread_current->frames.i_prev_reordered_pts;
h->fdec->i_dts = h->i_frame > h->frames.i_bframe_delay
? prev_reordered_pts[ (h->i_frame - h->frames.i_bframe_delay) % h->frames.i_bframe_delay ]
: h->fenc->i_reordered_pts - h->frames.i_bframe_delay_time;
prev_reordered_pts[ h->i_frame % h->frames.i_bframe_delay ] = h->fenc->i_reordered_pts;
}
else
h->fdec->i_dts = h->fenc->i_reordered_pts;
if( h->fenc->i_type == X264_TYPE_IDR )
h->i_last_idr_pts = h->fdec->i_pts;
/* ------------------- Init
----------------------------- */
/* build ref list 0/1 */
//创建参考帧列表list0和list1
x264_reference_build_list( h, h->fdec->i_poc );
/* ---------------------- Write the bitstream -------------------------- */
/* Init bitstream context */
//用于输出
if( h->param.b_sliced_threads )
{
for( int i = 0; i < h->param.i_threads; i++ )
{
bs_init( &h->thread[i]->out.bs, h->thread[i]->out.p_bitstream, h->thread[i]->out.i_bitstream );
h->thread[i]->out.i_nal = 0;
}
}
else
{
bs_init( &h->out.bs, h->out.p_bitstream, h->out.i_bitstream );
h->out.i_nal = 0;
}
if( h->param.b_aud )
{
int pic_type;
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_I )
pic_type = 0;
else if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_P )
pic_type = 1;
else if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
pic_type = 2;
else
pic_type = 7;
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_AUD, NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE );
bs_write( &h->out.bs, 3, pic_type );
bs_rbsp_trailing( &h->out.bs );
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
overhead += h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload + NALU_OVERHEAD;
}
h->i_nal_type = i_nal_type;
h->i_nal_ref_idc = i_nal_ref_idc;
if( h->param.b_intra_refresh )
{
if( IS_X264_TYPE_I( h->fenc->i_type ) )
{
h->fdec->i_frames_since_pir = 0;
h->b_queued_intra_refresh = 0;
/* PIR is currently only supported with ref == 1, so any intra frame effectively refreshes
* the whole frame and counts as an intra refresh. */
h->fdec->f_pir_position = h->mb.i_mb_width;
}
else if( h->fenc->i_type == X264_TYPE_P )
{
int pocdiff = (h->fdec->i_poc - h->fref[0][0]->i_poc)/2;
float increment = X264_MAX( ((float)h->mb.i_mb_width-1) / h->param.i_keyint_max, 1 );
h->fdec->f_pir_position = h->fref[0][0]->f_pir_position;
h->fdec->i_frames_since_pir = h->fref[0][0]->i_frames_since_pir + pocdiff;
if( h->fdec->i_frames_since_pir >= h->param.i_keyint_max ||
(h->b_queued_intra_refresh && h->fdec->f_pir_position + 0.5 >= h->mb.i_mb_width) )
{
h->fdec->f_pir_position = 0;
h->fdec->i_frames_since_pir = 0;
h->b_queued_intra_refresh = 0;
h->fenc->b_keyframe = 1;
}
h->fdec->i_pir_start_col = h->fdec->f_pir_position+0.5;
h->fdec->f_pir_position += increment * pocdiff;
h->fdec->i_pir_end_col = h->fdec->f_pir_position+0.5;
/* If our intra refresh has reached the right side of the frame, we're done. */
if( h->fdec->i_pir_end_col >= h->mb.i_mb_width - 1 )
{
h->fdec->f_pir_position = h->mb.i_mb_width;
h->fdec->i_pir_end_col = h->mb.i_mb_width - 1;
}
}
}
if( h->fenc->b_keyframe )
{
//每个关键帧前面重复加上SPS和PPS
/* Write SPS and PPS */
if( h->param.b_repeat_headers )
{
/* generate sequence parameters */
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_SPS, NAL_PRIORITY_HIGHEST );
x264_sps_write( &h->out.bs, h->sps );
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
/* Pad AUD/SPS to 256 bytes like Panasonic */
if( h->param.i_avcintra_class )
h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_padding = 256 - bs_pos( &h->out.bs ) / 8 - 2*NALU_OVERHEAD;
overhead += h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload + h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_padding + NALU_OVERHEAD;
/* generate picture parameters */
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_PPS, NAL_PRIORITY_HIGHEST );
x264_pps_write( &h->out.bs, h->sps, h->pps );
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
if( h->param.i_avcintra_class )
h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_padding = 256 - h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload - NALU_OVERHEAD;
overhead += h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload + h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_padding + NALU_OVERHEAD;
}
/* when frame threading is used, buffering period sei is written in x264_encoder_frame_end */
if( h->i_thread_frames == 1 && h->sps->vui.b_nal_hrd_parameters_present )
{
x264_hrd_fullness( h );
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_SEI, NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE );
x264_sei_buffering_period_write( h, &h->out.bs );
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
overhead += h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload + SEI_OVERHEAD;
}
}
/* write extra sei */
//下面很大一段代码用于写入SEI(一部分是为了适配其他的解码器)==========================================
for( int i = 0; i < h->fenc->extra_sei.num_payloads; i++ )
{
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_SEI, NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE );
x264_sei_write( &h->out.bs, h->fenc->extra_sei.payloads[i].payload, h->fenc->extra_sei.payloads[i].payload_size,
h->fenc->extra_sei.payloads[i].payload_type );
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
overhead += h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload + SEI_OVERHEAD;
if( h->fenc->extra_sei.sei_free )
{
h->fenc->extra_sei.sei_free( h->fenc->extra_sei.payloads[i].payload );
h->fenc->extra_sei.payloads[i].payload = NULL;
}
}
if( h->fenc->extra_sei.sei_free )
{
h->fenc->extra_sei.sei_free( h->fenc->extra_sei.payloads );
h->fenc->extra_sei.payloads = NULL;
h->fenc->extra_sei.sei_free = NULL;
}
//特殊的SEI信息(Avid等解码器需要)
if( h->fenc->b_keyframe )
{
/* Avid's decoder strictly wants two SEIs for AVC-Intra so we can't insert the x264 SEI */
if( h->param.b_repeat_headers && h->fenc->i_frame == 0 && !h->param.i_avcintra_class )
{
/* identify ourself */
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_SEI, NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE );
if( x264_sei_version_write( h, &h->out.bs ) )
return -1;
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
overhead += h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload + SEI_OVERHEAD;
}
if( h->fenc->i_type != X264_TYPE_IDR )
{
int time_to_recovery = h->param.b_open_gop ? 0 : X264_MIN( h->mb.i_mb_width - 1, h->param.i_keyint_max ) + h->param.i_bframe - 1;
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_SEI, NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE );
x264_sei_recovery_point_write( h, &h->out.bs, time_to_recovery );
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
overhead += h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload + SEI_OVERHEAD;
}
}
if( h->param.i_frame_packing >= 0 && (h->fenc->b_keyframe || h->param.i_frame_packing == 5) )
{
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_SEI, NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE );
x264_sei_frame_packing_write( h, &h->out.bs );
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
overhead += h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload + SEI_OVERHEAD;
}
/* generate sei pic timing */
if( h->sps->vui.b_pic_struct_present || h->sps->vui.b_nal_hrd_parameters_present )
{
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_SEI, NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE );
x264_sei_pic_timing_write( h, &h->out.bs );
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
overhead += h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload + SEI_OVERHEAD;
}
/* As required by Blu-ray. */
if( !IS_X264_TYPE_B( h->fenc->i_type ) && h->b_sh_backup )
{
h->b_sh_backup = 0;
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_SEI, NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE );
x264_sei_dec_ref_pic_marking_write( h, &h->out.bs );
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
overhead += h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload + SEI_OVERHEAD;
}
if( h->fenc->b_keyframe && h->param.b_intra_refresh )
h->i_cpb_delay_pir_offset_next = h->fenc->i_cpb_delay;
/* Filler space: 10 or 18 SEIs' worth of space, depending on resolution */
if( h->param.i_avcintra_class )
{
/* Write an empty filler NAL to mimic the AUD in the P2 format*/
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_FILLER, NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE );
x264_filler_write( h, &h->out.bs, 0 );
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
overhead += h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload + NALU_OVERHEAD;
/* All lengths are magic lengths that decoders expect to see */
/* "UMID" SEI */
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_SEI, NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE );
if( x264_sei_avcintra_umid_write( h, &h->out.bs ) < 0 )
return -1;
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
overhead += h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload + SEI_OVERHEAD;
int unpadded_len;
int total_len;
if( h->param.i_height == 1080 )
{
unpadded_len = 5780;
total_len = 17*512;
}
else
{
unpadded_len = 2900;
total_len = 9*512;
}
/* "VANC" SEI */
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_SEI, NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE );
if( x264_sei_avcintra_vanc_write( h, &h->out.bs, unpadded_len ) < 0 )
return -1;
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_padding = total_len - h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload - SEI_OVERHEAD;
overhead += h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload + h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_padding + SEI_OVERHEAD;
}
//写入SEI代码结束========================================================
/* Init the rate control */
/* FIXME: Include slice header bit cost. */
//码率控制单元初始化
x264_ratecontrol_start( h, h->fenc->i_qpplus1, overhead*8 );
i_global_qp = x264_ratecontrol_qp( h );
pic_out->i_qpplus1 =
h->fdec->i_qpplus1 = i_global_qp + 1;
if( h->param.rc.b_stat_read && h->sh.i_type != SLICE_TYPE_I )
{
x264_reference_build_list_optimal( h );
x264_reference_check_reorder( h );
}
if( h->i_ref[0] )
h->fdec->i_poc_l0ref0 = h->fref[0][0]->i_poc;
/* ------------------------ Create slice header
----------------------- */
//创建Slice Header
x264_slice_init( h, i_nal_type, i_global_qp );
/*------------------------- Weights -------------------------------------*/
//加权预测
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
x264_macroblock_bipred_init( h );
x264_weighted_pred_init( h );
if( i_nal_ref_idc != NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE )
h->i_frame_num++;
/* Write frame */
h->i_threadslice_start = 0;
h->i_threadslice_end = h->mb.i_mb_height;
if( h->i_thread_frames > 1 )
{
x264_threadpool_run( h->threadpool, (void*)x264_slices_write, h );
h->b_thread_active = 1;
}
else if( h->param.b_sliced_threads )
{
if( x264_threaded_slices_write( h ) )
return -1;
}
else{
//真正的编码——编码1个图像帧(注意这里“slices”后面有“s”)
if( (intptr_t)x264_slices_write( h ) )
return -1;
}
//结束的时候做一些处理,记录一些统计信息
//输出NALU
//输出重建帧
return x264_encoder_frame_end( thread_oldest, thread_current, pp_nal, pi_nal, pic_out );
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_encoder_encode()的流程大致如下:
(1)调用x264_frame_pop_unused获取一个空的fenc(x264_frame_t类型)用于存储一帧编码像素数据。下文将会按照步骤对上述函数进行简单的分析。
(2)调用x264_frame_copy_picture()将外部结构体的pic_in(x264_picture_t类型)的数据拷贝给内部结构体的fenc(x264_frame_t类型)。
(3)调用x264_lookahead_put_frame()将fenc放入Lookahead模块的队列中,等待确定帧类型。
(4)调用x264_lookahead_get_frames()分析Lookahead模块中一个帧的帧类型。分析后的帧保存在frames.current[]中。
(5)调用x264_frame_shift()从frames.current[]中取出分析帧类型之后的fenc。
(6)调用x264_reference_update()更新参考帧队列frames.reference[]。
(7)如果编码帧fenc是IDR帧,调用x264_reference_reset()清空参考帧队列frames.reference[]。
(8)调用x264_reference_build_list()创建参考帧列表List0和List1。
(9)根据选项做一些配置:a)如果b_aud不为0,输出AUD类型NALUb)在当前帧是关键帧的情况下,如果b_repeat_headers不为0,调用x264_sps_write()和x264_pps_write()输出SPS和PPS。c)输出一些特殊的SEI信息,用于适配各种解码器。(10)调用x264_slice_init()初始化Slice Header信息。
(11)调用x264_slices_write()进行编码。该部分是libx264的核心,在后续文章中会详细分析。(12)调用x264_encoder_frame_end()做一些编码后的后续处理。
x264_frame_pop_unused()
x264_frame_pop_unused()用于获取1个x264_frame_t类型结构体fenc。该函数的定义位于commonframe.c,如下所示。//获取一帧的编码帧fenc或者重建帧fdec
x264_frame_t *x264_frame_pop_unused( x264_t *h, int b_fdec )
{
x264_frame_t *frame;
if( h->frames.unused[b_fdec][0] )//unused队列不为空
frame = x264_frame_pop( h->frames.unused[b_fdec] );//从unused队列取
else
frame = x264_frame_new( h, b_fdec );//分配一帧空间
if( !frame )
return NULL;
frame->b_last_minigop_bframe = 0;
frame->i_reference_count = 1;
frame->b_intra_calculated = 0;
frame->b_scenecut = 1;
frame->b_keyframe = 0;
frame->b_corrupt = 0;
frame->i_slice_count = h->param.b_sliced_threads ? h->param.i_threads : 1;
memset( frame->weight, 0, sizeof(frame->weight) );
memset( frame->f_weighted_cost_delta, 0, sizeof(frame->f_weighted_cost_delta) );
return frame;
}
从源代码可以看出,如果frames.unused[]队列不为空,x264_frame_pop_unused()就调用x264_frame_pop()从unused[]队列取1个现成的;否则就调用x264_frame_new()创建一个新的。下面看一下这两个函数。
x264_frame_pop()
x264_frame_pop()用于从一个队列的尾部取出一个帧。该函数的定义位于commonframe.c,如下所示。//从队列的尾部取出一帧
x264_frame_t *x264_frame_pop( x264_frame_t **list )
{
x264_frame_t *frame;
int i = 0;
assert( list[0] );
while( list[i+1] ) i++;
frame = list[i];
list[i] = NULL;
return frame;
}从源代码中可以看出,x264_frame_pop()首先通过一个while()循环找到队列尾部的元素,然后将该元素作为返回值返回。
x264_frame_new()
x264_frame_new()用于新建一个x264_frame_t。该函数的定义位于commonframe.c,如下所示。//新建一个帧
//b_fdec:取1的时候为重建帧fdec,取0的时候为编码帧fenc
static x264_frame_t *x264_frame_new( x264_t *h, int b_fdec )
{
x264_frame_t *frame;
//注意转换后只有3种colorspace:X264_CSP_NV12(对应YUV420),X264_CSP_NV16(对应YUV422),X264_CSP_I444(对应YUV444)
int i_csp = x264_frame_internal_csp( h->param.i_csp );
int i_mb_count = h->mb.i_mb_count;
int i_stride, i_width, i_lines, luma_plane_count;
int i_padv = PADV << PARAM_INTERLACED;
int align = 16;
#if ARCH_X86 || ARCH_X86_64
if( h->param.cpu&X264_CPU_CACHELINE_64 )
align = 64;
else if( h->param.cpu&X264_CPU_CACHELINE_32 || h->param.cpu&X264_CPU_AVX2 )
align = 32;
#endif
#if ARCH_PPC
int disalign = 1<<9;
#else
int disalign = 1<<10;
#endif
//给frame分配内存,并置零
CHECKED_MALLOCZERO( frame, sizeof(x264_frame_t) );
PREALLOC_INIT
/* allocate frame data (+64 for extra data for me) */
//以像素为单位的宽高
i_width
= h->mb.i_mb_width*16;
i_lines
= h->mb.i_mb_height*16;
i_stride = align_stride( i_width + 2*PADH, align, disalign );
if( i_csp == X264_CSP_NV12 || i_csp == X264_CSP_NV16 )
{
//YUV422,YUV420情况
luma_plane_count = 1;
frame->i_plane = 2;
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
{
frame->i_width[i] = i_width >> i;
frame->i_lines[i] = i_lines >> (i && i_csp == X264_CSP_NV12);
frame->i_stride[i] = i_stride;
}
}
else if( i_csp == X264_CSP_I444 )
{
//YUV444情况
luma_plane_count = 3;
frame->i_plane = 3;
for( int i = 0; i < 3; i++ )
{
frame->i_width[i] = i_width;
frame->i_lines[i] = i_lines;
frame->i_stride[i] = i_stride;
}
}
else
goto fail;
//赋值赋值赋值...
frame->i_csp = i_csp;
frame->i_width_lowres = frame->i_width[0]/2;
frame->i_lines_lowres = frame->i_lines[0]/2;
frame->i_stride_lowres = align_stride( frame->i_width_lowres + 2*PADH, align, disalign<<1 );
for( int i = 0; i < h->param.i_bframe + 2; i++ )
for( int j = 0; j < h->param.i_bframe + 2; j++ )
PREALLOC( frame->i_row_satds[i][j], i_lines/16 * sizeof(int) );
frame->i_poc = -1;
frame->i_type = X264_TYPE_AUTO;
frame->i_qpplus1 = X264_QP_AUTO;
frame->i_pts = -1;
frame->i_frame = -1;
frame->i_frame_num = -1;
frame->i_lines_completed = -1;
frame->b_fdec = b_fdec;
frame->i_pic_struct = PIC_STRUCT_AUTO;
frame->i_field_cnt = -1;
frame->i_duration =
frame->i_cpb_duration =
frame->i_dpb_output_delay =
frame->i_cpb_delay = 0;
frame->i_coded_fields_lookahead =
frame->i_cpb_delay_lookahead = -1;
frame->orig = frame;
if( i_csp == X264_CSP_NV12 || i_csp == X264_CSP_NV16 )
{
int chroma_padv = i_padv >> (i_csp == X264_CSP_NV12);
int chroma_plane_size = (frame->i_stride[1] * (frame->i_lines[1] + 2*chroma_padv));
PREALLOC( frame->buffer[1], chroma_plane_size * sizeof(pixel) );
if( PARAM_INTERLACED )
PREALLOC( frame->buffer_fld[1], chroma_plane_size * sizeof(pixel) );
}
/* all 4 luma planes allocated together, since the cacheline split code
* requires them to be in-phase wrt cacheline alignment. */
for( int p = 0; p < luma_plane_count; p++ )
{
int luma_plane_size = align_plane_size( frame->i_stride[p] * (frame->i_lines[p] + 2*i_padv), disalign );
if( h->param.analyse.i_subpel_refine && b_fdec )
{
/* FIXME: Don't allocate both buffers in non-adaptive MBAFF. */
PREALLOC( frame->buffer[p], 4*luma_plane_size * sizeof(pixel) );
if( PARAM_INTERLACED )
PREALLOC( frame->buffer_fld[p], 4*luma_plane_size * sizeof(pixel) );
}
else
{
PREALLOC( frame->buffer[p], luma_plane_size * sizeof(pixel) );
if( PARAM_INTERLACED )
PREALLOC( frame->buffer_fld[p], luma_plane_size * sizeof(pixel) );
}
}
frame->b_duplicate = 0;
if( b_fdec ) /* fdec frame */
{
//重建帧fdec
PREALLOC( frame->mb_type, i_mb_count * sizeof(int8_t) );
PREALLOC( frame->mb_partition, i_mb_count * sizeof(uint8_t) );
PREALLOC( frame->mv[0], 2*16 * i_mb_count * sizeof(int16_t) );
PREALLOC( frame->mv16x16, 2*(i_mb_count+1) * sizeof(int16_t) );
PREALLOC( frame->ref[0], 4 * i_mb_count * sizeof(int8_t) );
if( h->param.i_bframe )
{
PREALLOC( frame->mv[1], 2*16 * i_mb_count * sizeof(int16_t) );
PREALLOC( frame->ref[1], 4 * i_mb_count * sizeof(int8_t) );
}
else
{
frame->mv[1]
= NULL;
frame->ref[1] = NULL;
}
PREALLOC( frame->i_row_bits, i_lines/16 * sizeof(int) );
PREALLOC( frame->f_row_qp, i_lines/16 * sizeof(float) );
PREALLOC( frame->f_row_qscale, i_lines/16 * sizeof(float) );
if( h->param.analyse.i_me_method >= X264_ME_ESA )
PREALLOC( frame->buffer[3], frame->i_stride[0] * (frame->i_lines[0] + 2*i_padv) * sizeof(uint16_t) << h->frames.b_have_sub8x8_esa );
if( PARAM_INTERLACED )
PREALLOC( frame->field, i_mb_count * sizeof(uint8_t) );
if( h->param.analyse.b_mb_info )
PREALLOC( frame->effective_qp, i_mb_count * sizeof(uint8_t) );
}
else /* fenc frame */
{
//编码帧fenc
if( h->frames.b_have_lowres )
{
int luma_plane_size = align_plane_size( frame->i_stride_lowres * (frame->i_lines[0]/2 + 2*PADV), disalign );
PREALLOC( frame->buffer_lowres[0], 4 * luma_plane_size * sizeof(pixel) );
for( int j = 0; j <= !!h->param.i_bframe; j++ )
for( int i = 0; i <= h->param.i_bframe; i++ )
{
PREALLOC( frame->lowres_mvs[j][i], 2*h->mb.i_mb_count*sizeof(int16_t) );
PREALLOC( frame->lowres_mv_costs[j][i], h->mb.i_mb_count*sizeof(int) );
}
PREALLOC( frame->i_propagate_cost, (i_mb_count+7) * sizeof(uint16_t) );
for( int j = 0; j <= h->param.i_bframe+1; j++ )
for( int i = 0; i <= h->param.i_bframe+1; i++ )
PREALLOC( frame->lowres_costs[j][i], (i_mb_count+3) * sizeof(uint16_t) );
}
if( h->param.rc.i_aq_mode )
{
PREALLOC( frame->f_qp_offset, h->mb.i_mb_count * sizeof(float) );
PREALLOC( frame->f_qp_offset_aq, h->mb.i_mb_count * sizeof(float) );
if( h->frames.b_have_lowres )
PREALLOC( frame->i_inv_qscale_factor, (h->mb.i_mb_count+3) * sizeof(uint16_t) );
}
}
PREALLOC_END( frame->base );
if( i_csp == X264_CSP_NV12 || i_csp == X264_CSP_NV16 )
{
int chroma_padv = i_padv >> (i_csp == X264_CSP_NV12);
frame->plane[1] = frame->buffer[1] + frame->i_stride[1] * chroma_padv + PADH;
if( PARAM_INTERLACED )
frame->plane_fld[1] = frame->buffer_fld[1] + frame->i_stride[1] * chroma_padv + PADH;
}
for( int p = 0; p < luma_plane_count; p++ )
{
int luma_plane_size = align_plane_size( frame->i_stride[p] * (frame->i_lines[p] + 2*i_padv), disalign );
if( h->param.analyse.i_subpel_refine && b_fdec )
{
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
frame->filtered[p][i] = frame->buffer[p] + i*luma_plane_size + frame->i_stride[p] * i_padv + PADH;
frame->filtered_fld[p][i] = frame->buffer_fld[p] + i*luma_plane_size + frame->i_stride[p] * i_padv + PADH;
}
frame->plane[p] = frame->filtered[p][0];
frame->plane_fld[p] = frame->filtered_fld[p][0];
}
else
{
frame->filtered[p][0] = frame->plane[p] = frame->buffer[p] + frame->i_stride[p] * i_padv + PADH;
frame->filtered_fld[p][0] = frame->plane_fld[p] = frame->buffer_fld[p] + frame->i_stride[p] * i_padv + PADH;
}
}
if( b_fdec )
{
M32( frame->mv16x16[0] ) = 0;
frame->mv16x16++;
if( h->param.analyse.i_me_method >= X264_ME_ESA )
frame->integral = (uint16_t*)frame->buffer[3] + frame->i_stride[0] * i_padv + PADH;
}
else
{
if( h->frames.b_have_lowres )
{
int luma_plane_size = align_plane_size( frame->i_stride_lowres * (frame->i_lines[0]/2 + 2*PADV), disalign );
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
frame->lowres[i] = frame->buffer_lowres[0] + (frame->i_stride_lowres * PADV + PADH) + i * luma_plane_size;
for( int j = 0; j <= !!h->param.i_bframe; j++ )
for( int i = 0; i <= h->param.i_bframe; i++ )
memset( frame->lowres_mvs[j][i], 0, 2*h->mb.i_mb_count*sizeof(int16_t) );
frame->i_intra_cost = frame->lowres_costs[0][0];
memset( frame->i_intra_cost, -1, (i_mb_count+3) * sizeof(uint16_t) );
if( h->param.rc.i_aq_mode )
/* shouldn't really be initialized, just silences a valgrind false-positive in x264_mbtree_propagate_cost_sse2 */
memset( frame->i_inv_qscale_factor, 0, (h->mb.i_mb_count+3) * sizeof(uint16_t) );
}
}
if( x264_pthread_mutex_init( &frame->mutex, NULL ) )
goto fail;
if( x264_pthread_cond_init( &frame->cv, NULL ) )
goto fail;
#if HAVE_OPENCL
frame->opencl.ocl = h->opencl.ocl;
#endif
return frame;
fail:
x264_free( frame );
return NULL;
}
从源代码中可以看出,x264_frame_new()声明了一个frame指针,并在后续过程中对该frame的成员变量进行内存分配和注释。需要注意的是编码帧fenc和重建帧fdec初始化的变量是不一样的——函数的输入参数b_fdec不为0的时候初始化重建帧,否则初始化编码帧。在这个函数中涉及到一个简单的函数x264_frame_internal_csp(),用于把种类繁多的外部Colorspace转换为简单的内部Colorspace。
x264_frame_internal_csp()
x264_frame_internal_csp()用于把外部Colorspace转换为内部Colorspace。该函数的定义如下所示。
//注意转换后只有3种内部colorspace:X264_CSP_NV12(对应YUV420),X264_CSP_NV16(对应YUV422),X264_CSP_I444(对应YUV444)
static int x264_frame_internal_csp( int external_csp )
{
switch( external_csp & X264_CSP_MASK )
{
case X264_CSP_NV12:
case X264_CSP_I420:
case X264_CSP_YV12:
return X264_CSP_NV12;
case X264_CSP_NV16:
case X264_CSP_I422:
case X264_CSP_YV16:
case X264_CSP_V210:
return X264_CSP_NV16;
case X264_CSP_I444:
case X264_CSP_YV24:
case X264_CSP_BGR:
case X264_CSP_BGRA:
case X264_CSP_RGB:
return X264_CSP_I444;
default:
return X264_CSP_NONE;
}
}x264_frame_copy_picture()
x264_frame_copy_picture()用于将外部结构体x264_picture_t的数据拷贝给内部结构体x264_frame_t。该函数的定义位于commonframe.c,如下所示。//拷贝帧数据
//src(外部结构体x264_picture_t)到dst(内部结构体x264_frame_t)
int x264_frame_copy_picture( x264_t *h, x264_frame_t *dst, x264_picture_t *src )
{
int i_csp = src->img.i_csp & X264_CSP_MASK;
//注意转换后只有3种内部colorspace:X264_CSP_NV12(对应YUV420),X264_CSP_NV16(对应YUV422),X264_CSP_I444(对应YUV444)
if( dst->i_csp != x264_frame_internal_csp( i_csp ) )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "Invalid input colorspacen" );
return -1;
}
#if HIGH_BIT_DEPTH
if( !(src->img.i_csp & X264_CSP_HIGH_DEPTH) )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "This build of x264 requires high depth input. Rebuild to support 8-bit input.n" );
return -1;
}
#else
if( src->img.i_csp & X264_CSP_HIGH_DEPTH )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "This build of x264 requires 8-bit input. Rebuild to support high depth input.n" );
return -1;
}
#endif
if( BIT_DEPTH != 10 && i_csp == X264_CSP_V210 )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "v210 input is only compatible with bit-depth of 10 bitsn" );
return -1;
}
//赋值赋值赋值
dst->i_type
= src->i_type;
dst->i_qpplus1
= src->i_qpplus1;
dst->i_pts
= dst->i_reordered_pts = src->i_pts;
dst->param
= src->param;
dst->i_pic_struct = src->i_pic_struct;
dst->extra_sei
= src->extra_sei;
dst->opaque
= src->opaque;
dst->mb_info
= h->param.analyse.b_mb_info ? src->prop.mb_info : NULL;
dst->mb_info_free = h->param.analyse.b_mb_info ? src->prop.mb_info_free : NULL;
uint8_t *pix[3];
int stride[3];
if( i_csp == X264_CSP_V210 )
{
stride[0] = src->img.i_stride[0];
pix[0] = src->img.plane[0];
h->mc.plane_copy_deinterleave_v210( dst->plane[0], dst->i_stride[0],
dst->plane[1], dst->i_stride[1],
(uint32_t *)pix[0], stride[0]/sizeof(uint32_t), h->param.i_width, h->param.i_height );
}
else if( i_csp >= X264_CSP_BGR )
{
stride[0] = src->img.i_stride[0];
pix[0] = src->img.plane[0];
if( src->img.i_csp & X264_CSP_VFLIP )
{
pix[0] += (h->param.i_height-1) * stride[0];
stride[0] = -stride[0];
}
int b = i_csp==X264_CSP_RGB;
h->mc.plane_copy_deinterleave_rgb( dst->plane[1+b], dst->i_stride[1+b],
dst->plane[0], dst->i_stride[0],
dst->plane[2-b], dst->i_stride[2-b],
(pixel*)pix[0], stride[0]/sizeof(pixel), i_csp==X264_CSP_BGRA ? 4 : 3, h->param.i_width, h->param.i_height );
}
else
{
int v_shift = CHROMA_V_SHIFT;
get_plane_ptr( h, src, &pix[0], &stride[0], 0, 0, 0 );
//拷贝像素
h->mc.plane_copy( dst->plane[0], dst->i_stride[0], (pixel*)pix[0],
stride[0]/sizeof(pixel), h->param.i_width, h->param.i_height );
if( i_csp == X264_CSP_NV12 || i_csp == X264_CSP_NV16 )
{
get_plane_ptr( h, src, &pix[1], &stride[1], 1, 0, v_shift );
h->mc.plane_copy( dst->plane[1], dst->i_stride[1], (pixel*)pix[1],
stride[1]/sizeof(pixel), h->param.i_width, h->param.i_height>>v_shift );
}
else if( i_csp == X264_CSP_I420 || i_csp == X264_CSP_I422 || i_csp == X264_CSP_YV12 || i_csp == X264_CSP_YV16 )
{
int uv_swap = i_csp == X264_CSP_YV12 || i_csp == X264_CSP_YV16;
get_plane_ptr( h, src, &pix[1], &stride[1], uv_swap ? 2 : 1, 1, v_shift );
get_plane_ptr( h, src, &pix[2], &stride[2], uv_swap ? 1 : 2, 1, v_shift );
h->mc.plane_copy_interleave( dst->plane[1], dst->i_stride[1],
(pixel*)pix[1], stride[1]/sizeof(pixel),
(pixel*)pix[2], stride[2]/sizeof(pixel),
h->param.i_width>>1, h->param.i_height>>v_shift );
}
else //if( i_csp == X264_CSP_I444 || i_csp == X264_CSP_YV24 )
{
get_plane_ptr( h, src, &pix[1], &stride[1], i_csp==X264_CSP_I444 ? 1 : 2, 0, 0 );
get_plane_ptr( h, src, &pix[2], &stride[2], i_csp==X264_CSP_I444 ? 2 : 1, 0, 0 );
h->mc.plane_copy( dst->plane[1], dst->i_stride[1], (pixel*)pix[1],
stride[1]/sizeof(pixel), h->param.i_width, h->param.i_height );
h->mc.plane_copy( dst->plane[2], dst->i_stride[2], (pixel*)pix[2],
stride[2]/sizeof(pixel), h->param.i_width, h->param.i_height );
}
}
return 0;
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_frame_t和x264_picture_t结构体中很多字段是一模一样的,x264_frame_copy_picture()只是简单地将x264_picture_t中字段的值赋值给了x264_frame_t。
x264_lookahead_put_frame()
x264_lookahead_put_frame()将编码帧放入Lookahead模块的队列中,等待确定帧类型。该函数的定义位于encoderlookahead.c,如下所示。//x264_frame_t放入x264_sync_frame_list_t队列
void x264_lookahead_put_frame( x264_t *h, x264_frame_t *frame )
{
if( h->param.i_sync_lookahead )
x264_sync_frame_list_push( &h->lookahead->ifbuf, frame );
else
x264_sync_frame_list_push( &h->lookahead->next, frame );//放入next队列
}
从源代码可以看出,i_sync_lookahead不为0的时候,会将编码帧放入lookahead.ifbuf[]中,否则会将编码帧放入lookahead.next[]中。放入帧的时候会调用x264_sync_frame_list_push()。
x264_sync_frame_list_push()
x264_sync_frame_list_push()用于向x264_sync_frame_list_t类型的队列中放入一个帧。该函数的定义位于commonframe.c,如下所示。void x264_sync_frame_list_push( x264_sync_frame_list_t *slist, x264_frame_t *frame )
{
x264_pthread_mutex_lock( &slist->mutex );
while( slist->i_size == slist->i_max_size )
x264_pthread_cond_wait( &slist->cv_empty, &slist->mutex );
//放入
slist->list[ slist->i_size++ ] = frame;
x264_pthread_mutex_unlock( &slist->mutex );
x264_pthread_cond_broadcast( &slist->cv_fill );
}
从源代码中可以看出,x264_sync_frame_list_push()将frame放在了x264_sync_frame_list_t.list的尾部。
x264_lookahead_get_frames()
x264_lookahead_get_frames()通过lookahead模块分析帧类型。该函数的定义位于encoderlookahead.c,如下所示。//通过lookahead分析帧类型
void x264_lookahead_get_frames( x264_t *h )
{
if( h->param.i_sync_lookahead )
{
/* We have a lookahead thread, so get frames from there */
x264_pthread_mutex_lock( &h->lookahead->ofbuf.mutex );
while( !h->lookahead->ofbuf.i_size && h->lookahead->b_thread_active )
x264_pthread_cond_wait( &h->lookahead->ofbuf.cv_fill, &h->lookahead->ofbuf.mutex );
x264_lookahead_encoder_shift( h );
x264_pthread_mutex_unlock( &h->lookahead->ofbuf.mutex );
}
else
{
/* We are not running a lookahead thread, so perform all the slicetype decide on the fly */
//currect[]必须为空,next不能为空?
if( h->frames.current[0] || !h->lookahead->next.i_size )
return;
//分析lookahead->next->list帧的类型
x264_stack_align( x264_slicetype_decide, h );
//更新lookahead->last_nonb
x264_lookahead_update_last_nonb( h, h->lookahead->next.list[0] );
int shift_frames = h->lookahead->next.list[0]->i_bframes + 1;
//lookahead->next.list移动到lookahead->ofbuf.list
x264_lookahead_shift( &h->lookahead->ofbuf, &h->lookahead->next, shift_frames );
/* For MB-tree and VBV lookahead, we have to perform propagation analysis on I-frames too. */
if( h->lookahead->b_analyse_keyframe && IS_X264_TYPE_I( h->lookahead->last_nonb->i_type ) )
x264_stack_align( x264_slicetype_analyse, h, shift_frames );
//lookahead->ofbuf.list帧移动到frames->current
x264_lookahead_encoder_shift( h );
}
}
从源代码中可以看出,x264_lookahead_get_frames()调用了x264_slicetype_decide()用于确定帧类型。在这里需要注意,Lookahead模块的代码量比较大,暂时不做详细的分析,仅简单理一下脉络。
x264_slicetype_decide()
x264_slicetype_decide()用于确定帧类型,该函数的定义位于encoderslicetype.c,如下所示。//确定帧的类型(I、B、P)
void x264_slicetype_decide( x264_t *h )
{
x264_frame_t *frames[X264_BFRAME_MAX+2];
x264_frame_t *frm;
int bframes;
int brefs;
if( !h->lookahead->next.i_size )
return;
int lookahead_size = h->lookahead->next.i_size;
//遍历next队列
for( int i = 0; i < h->lookahead->next.i_size; i++ )
{
if( h->param.b_vfr_input )
{
if( lookahead_size-- > 1 )
h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_duration = 2 * (h->lookahead->next.list[i+1]->i_pts - h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_pts);
else
h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_duration = h->i_prev_duration;
}
else
h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_duration = delta_tfi_divisor[h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_pic_struct];
h->i_prev_duration = h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_duration;
h->lookahead->next.list[i]->f_duration = (double)h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_duration
* h->sps->vui.i_num_units_in_tick
/ h->sps->vui.i_time_scale;
if( h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_frame > h->i_disp_fields_last_frame && lookahead_size > 0 )
{
h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_field_cnt = h->i_disp_fields;
h->i_disp_fields += h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_duration;
h->i_disp_fields_last_frame = h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_frame;
}
else if( lookahead_size == 0 )
{
h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_field_cnt = h->i_disp_fields;
h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_duration = h->i_prev_duration;
}
}
if( h->param.rc.b_stat_read )
{
//b_stat_read在2pass模式的第2遍才不为0
/* Use the frame types from the first pass */
for( int i = 0; i < h->lookahead->next.i_size; i++ )
h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_type =
x264_ratecontrol_slice_type( h, h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_frame );
}
else if( (h->param.i_bframe && h->param.i_bframe_adaptive)
|| h->param.i_scenecut_threshold
|| h->param.rc.b_mb_tree
|| (h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size && h->param.rc.i_lookahead) )
x264_slicetype_analyse( h, 0 );//分析帧的类型(I、B、P)
//===========================================================================
for( bframes = 0, brefs = 0;; bframes++ )
{
//从next队列取出1个
frm = h->lookahead->next.list[bframes];
//BREF的处理
if( frm->i_type == X264_TYPE_BREF && h->param.i_bframe_pyramid < X264_B_PYRAMID_NORMAL &&
brefs == h->param.i_bframe_pyramid )
{
//BREF改成B
frm->i_type = X264_TYPE_B;
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "B-ref at frame %d incompatible with B-pyramid %s n",
frm->i_frame, x264_b_pyramid_names[h->param.i_bframe_pyramid] );
}
/* pyramid with multiple B-refs needs a big enough dpb that the preceding P-frame stays available.
smaller dpb could be supported by smart enough use of mmco, but it's easier just to forbid it. */
else if( frm->i_type == X264_TYPE_BREF && h->param.i_bframe_pyramid == X264_B_PYRAMID_NORMAL &&
brefs && h->param.i_frame_reference <= (brefs+3) )
{
frm->i_type = X264_TYPE_B;
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "B-ref at frame %d incompatible with B-pyramid %s and %d reference framesn",
frm->i_frame, x264_b_pyramid_names[h->param.i_bframe_pyramid], h->param.i_frame_reference );
}
//Keyframe处理
if( frm->i_type == X264_TYPE_KEYFRAME )
frm->i_type = h->param.b_open_gop ? X264_TYPE_I : X264_TYPE_IDR;
/* Limit GOP size */
if( (!h->param.b_intra_refresh || frm->i_frame == 0) && frm->i_frame - h->lookahead->i_last_keyframe >= h->param.i_keyint_max )
{
if( frm->i_type == X264_TYPE_AUTO || frm->i_type == X264_TYPE_I )
frm->i_type = h->param.b_open_gop && h->lookahead->i_last_keyframe >= 0 ? X264_TYPE_I : X264_TYPE_IDR;
int warn = frm->i_type != X264_TYPE_IDR;
if( warn && h->param.b_open_gop )
warn &= frm->i_type != X264_TYPE_I;
if( warn )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "specified frame type (%d) at %d is not compatible with keyframe intervaln", frm->i_type, frm->i_frame );
frm->i_type = h->param.b_open_gop && h->lookahead->i_last_keyframe >= 0 ? X264_TYPE_I : X264_TYPE_IDR;
}
}
if( frm->i_type == X264_TYPE_I && frm->i_frame - h->lookahead->i_last_keyframe >= h->param.i_keyint_min )
{
if( h->param.b_open_gop )
{
h->lookahead->i_last_keyframe = frm->i_frame; // Use display order
if( h->param.b_bluray_compat )
h->lookahead->i_last_keyframe -= bframes; // Use bluray order
frm->b_keyframe = 1;
}
else
frm->i_type = X264_TYPE_IDR;
}
if( frm->i_type == X264_TYPE_IDR )
{
/* Close GOP */
//设置当前帧为“上一个关键帧”
h->lookahead->i_last_keyframe = frm->i_frame;
frm->b_keyframe = 1;
if( bframes > 0 )
{
bframes--;
h->lookahead->next.list[bframes]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
}
}
if( bframes == h->param.i_bframe ||
!h->lookahead->next.list[bframes+1] )
{
if( IS_X264_TYPE_B( frm->i_type ) )
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "specified frame type is not compatible with max B-framesn" );
if( frm->i_type == X264_TYPE_AUTO
|| IS_X264_TYPE_B( frm->i_type ) )
frm->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
}
if( frm->i_type == X264_TYPE_BREF )
brefs++;
if( frm->i_type == X264_TYPE_AUTO )
frm->i_type = X264_TYPE_B;
else if( !IS_X264_TYPE_B( frm->i_type ) ) break;
}
if( bframes )
h->lookahead->next.list[bframes-1]->b_last_minigop_bframe = 1;
h->lookahead->next.list[bframes]->i_bframes = bframes;
/* insert a bref into the sequence */
if( h->param.i_bframe_pyramid && bframes > 1 && !brefs )
{
h->lookahead->next.list[bframes/2]->i_type = X264_TYPE_BREF;
brefs++;
}
/* calculate the frame costs ahead of time for x264_rc_analyse_slice while we still have lowres */
if( h->param.rc.i_rc_method != X264_RC_CQP )
{
x264_mb_analysis_t a;
int p0, p1, b;
p1 = b = bframes + 1;
x264_lowres_context_init( h, &a );
frames[0] = h->lookahead->last_nonb;
memcpy( &frames[1], h->lookahead->next.list, (bframes+1) * sizeof(x264_frame_t*) );
if( IS_X264_TYPE_I( h->lookahead->next.list[bframes]->i_type ) )
p0 = bframes + 1;
else // P
p0 = 0;
x264_slicetype_frame_cost( h, &a, frames, p0, p1, b, 0 );
if( (p0 != p1 || bframes) && h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size )
{
/* We need the intra costs for row SATDs. */
x264_slicetype_frame_cost( h, &a, frames, b, b, b, 0 );
/* We need B-frame costs for row SATDs. */
p0 = 0;
for( b = 1; b <= bframes; b++ )
{
if( frames[b]->i_type == X264_TYPE_B )
for( p1 = b; frames[p1]->i_type == X264_TYPE_B; )
p1++;
else
p1 = bframes + 1;
x264_slicetype_frame_cost( h, &a, frames, p0, p1, b, 0 );
if( frames[b]->i_type == X264_TYPE_BREF )
p0 = b;
}
}
}
/* Analyse for weighted P frames */
if( !h->param.rc.b_stat_read && h->lookahead->next.list[bframes]->i_type == X264_TYPE_P
&& h->param.analyse.i_weighted_pred >= X264_WEIGHTP_SIMPLE )
{
x264_emms();
x264_weights_analyse( h, h->lookahead->next.list[bframes], h->lookahead->last_nonb, 0 );
}
/* shift sequence to coded order.
use a small temporary list to avoid shifting the entire next buffer around */
int i_coded = h->lookahead->next.list[0]->i_frame;
if( bframes )
{
int idx_list[] = { brefs+1, 1 };
for( int i = 0; i < bframes; i++ )
{
int idx = idx_list[h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_type == X264_TYPE_BREF]++;
frames[idx] = h->lookahead->next.list[i];
frames[idx]->i_reordered_pts = h->lookahead->next.list[idx]->i_pts;
}
frames[0] = h->lookahead->next.list[bframes];
frames[0]->i_reordered_pts = h->lookahead->next.list[0]->i_pts;
memcpy( h->lookahead->next.list, frames, (bframes+1) * sizeof(x264_frame_t*) );
}
for( int i = 0; i <= bframes; i++ )
{
h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_coded = i_coded++;
if( i )
{
x264_calculate_durations( h, h->lookahead->next.list[i], h->lookahead->next.list[i-1], &h->i_cpb_delay, &h->i_coded_fields );
h->lookahead->next.list[0]->f_planned_cpb_duration[i-1] = (double)h->lookahead->next.list[i]->i_cpb_duration *
h->sps->vui.i_num_units_in_tick / h->sps->vui.i_time_scale;
}
else
x264_calculate_durations( h, h->lookahead->next.list[i], NULL, &h->i_cpb_delay, &h->i_coded_fields );
}
}
x264_slicetype_decide()源代码比较长,还没有细看。该函数中调用了一个比较重要的函数x264_slicetype_analyse()。
x264_slicetype_analyse()
x264_slicetype_analyse()用于分析帧类型。该函数的定义位于encoderslicetype.c,如下所示。//分析帧的类型(I、B、P)
void x264_slicetype_analyse( x264_t *h, int intra_minigop )
{
x264_mb_analysis_t a;
x264_frame_t *frames[X264_LOOKAHEAD_MAX+3] = { NULL, };
int num_frames, orig_num_frames, keyint_limit, framecnt;
int i_mb_count = NUM_MBS;
int cost1p0, cost2p0, cost1b1, cost2p1;
// 确定最大的搜索长度
// 在我的调试当中, h->lookahead->next.i_size = 4
int i_max_search = X264_MIN( h->lookahead->next.i_size, X264_LOOKAHEAD_MAX );
int vbv_lookahead = h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size && h->param.rc.i_lookahead;
/* For determinism we should limit the search to the number of frames lookahead has for sure
* in h->lookahead->next.list buffer, except at the end of stream.
* For normal calls with (intra_minigop == 0) that is h->lookahead->i_slicetype_length + 1 frames.
* And for I-frame calls (intra_minigop != 0) we already removed intra_minigop frames from there. */
if( h->param.b_deterministic )
i_max_search = X264_MIN( i_max_search, h->lookahead->i_slicetype_length + 1 - intra_minigop );
int keyframe = !!intra_minigop;
assert( h->frames.b_have_lowres );
if( !h->lookahead->last_nonb )
return;
//frames[0]指向上一次的非B帧
frames[0] = h->lookahead->last_nonb;
//frames[] 依次指向 lookahead->next链表中的帧
for( framecnt = 0; framecnt < i_max_search && h->lookahead->next.list[framecnt]->i_type == X264_TYPE_AUTO; framecnt++ )
frames[framecnt+1] = h->lookahead->next.list[framecnt];
x264_lowres_context_init( h, &a );
if( !framecnt )
{
if( h->param.rc.b_mb_tree )
x264_macroblock_tree( h, &a, frames, 0, keyframe );
return;
}
keyint_limit = h->param.i_keyint_max - frames[0]->i_frame + h->lookahead->i_last_keyframe - 1;
orig_num_frames = num_frames = h->param.b_intra_refresh ? framecnt : X264_MIN( framecnt, keyint_limit );
/* This is important psy-wise: if we have a non-scenecut keyframe,
* there will be significant visual artifacts if the frames just before
* go down in quality due to being referenced less, despite it being
* more RD-optimal. */
if( (h->param.analyse.b_psy && h->param.rc.b_mb_tree) || vbv_lookahead )
num_frames = framecnt;
else if( h->param.b_open_gop && num_frames < framecnt )
num_frames++;
else if( num_frames == 0 )
{
frames[1]->i_type = X264_TYPE_I;
return;
}
int num_bframes = 0;
int num_analysed_frames = num_frames;
int reset_start;
//通过scenecut()函数判断是否有场景切换,从而确定I帧
if( h->param.i_scenecut_threshold && scenecut( h, &a, frames, 0, 1, 1, orig_num_frames, i_max_search ) )
{
frames[1]->i_type = X264_TYPE_I;
return;
}
#if HAVE_OPENCL
x264_opencl_slicetype_prep( h, frames, num_frames, a.i_lambda );
#endif
//允许有B帧的时候
if( h->param.i_bframe )
{
if( h->param.i_bframe_adaptive == X264_B_ADAPT_TRELLIS )
{
if( num_frames > 1 )
{
char best_paths[X264_BFRAME_MAX+1][X264_LOOKAHEAD_MAX+1] = {"","P"};
int best_path_index = num_frames % (X264_BFRAME_MAX+1);
/* Perform the frametype analysis. */
for( int j = 2; j <= num_frames; j++ )
x264_slicetype_path( h, &a, frames, j, best_paths );
num_bframes = strspn( best_paths[best_path_index], "B" );
/* Load the results of the analysis into the frame types. */
for( int j = 1; j < num_frames; j++ )
frames[j]->i_type = best_paths[best_path_index][j-1] == 'B' ? X264_TYPE_B : X264_TYPE_P;
}
frames[num_frames]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
}
else if( h->param.i_bframe_adaptive == X264_B_ADAPT_FAST )
{
for( int i = 0; i <= num_frames-2; )
{
//i+2作为P帧编码的代价
//注:i+2始终为P帧
cost2p1 = x264_slicetype_frame_cost( h, &a, frames, i+0, i+2, i+2, 1 );
if( frames[i+2]->i_intra_mbs[2] > i_mb_count / 2 )
{
frames[i+1]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
frames[i+2]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
i += 2;
continue;
}
#if HAVE_OPENCL
if( h->param.b_opencl )
{
int b_work_done = 0;
b_work_done |= x264_opencl_precalculate_frame_cost(h, frames, a.i_lambda, i+0, i+2, i+1 );
b_work_done |= x264_opencl_precalculate_frame_cost(h, frames, a.i_lambda, i+0, i+1, i+1 );
b_work_done |= x264_opencl_precalculate_frame_cost(h, frames, a.i_lambda, i+1, i+2, i+2 );
if( b_work_done )
x264_opencl_flush( h );
}
#endif
//计算代价
//x264_slicetype_frame_cost(,,,p0,p1,b,)
//p0 b p1
//p1!=b为B帧,否则为P帧
// i + 1 作为B帧编码的代价
cost1b1 = x264_slicetype_frame_cost( h, &a, frames, i+0, i+2, i+1, 0 );
// i + 1 作为P帧编码的代价
cost1p0 = x264_slicetype_frame_cost( h, &a, frames, i+0, i+1, i+1, 0 );
// i + 2 作为P帧编码的代价
cost2p0 = x264_slicetype_frame_cost( h, &a, frames, i+1, i+2, i+2, 0 );
//如果i+1作为P帧编码的代价 + i+2作为P帧编码的代价
//小于 i+1作为B帧编码的代价
+ i+2作为P帧编码的代价
if( cost1p0 + cost2p0 < cost1b1 + cost2p1 )
{
//那么i+1将作为P帧编码
//然后直接continue
frames[i+1]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
i += 1;
continue;
}
// arbitrary and untuned
#define INTER_THRESH 300
#define P_SENS_BIAS (50 - h->param.i_bframe_bias)
// i+1 将作为B帧编码
frames[i+1]->i_type = X264_TYPE_B;
int j;
for( j = i+2; j <= X264_MIN( i+h->param.i_bframe, num_frames-1 ); j++ )
{
int pthresh = X264_MAX(INTER_THRESH - P_SENS_BIAS * (j-i-1), INTER_THRESH/10);
// 预测j+1作为P帧编码代价
int pcost = x264_slicetype_frame_cost( h, &a, frames, i+0, j+1, j+1, 1 );
// 如果pcost 满足下述条件, 则确定了一个P帧,跳出循环
if( pcost > pthresh*i_mb_count || frames[j+1]->i_intra_mbs[j-i+1] > i_mb_count/3 )
break;
// 否则就是B帧
frames[j]->i_type = X264_TYPE_B;
}
// 将j帧确定为P帧
frames[j]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
i = j;
}
// 最后一帧确定为P帧
frames[num_frames]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
num_bframes = 0;
// 确定有多少个B帧
while( num_bframes < num_frames && frames[num_bframes+1]->i_type == X264_TYPE_B )
num_bframes++;
}
else
{
// 确定多少B帧
num_bframes = X264_MIN(num_frames-1, h->param.i_bframe);
// 每num_bframes + 1一个P帧, 其余皆为B帧
for( int j = 1; j < num_frames; j++ )
frames[j]->i_type = (j%(num_bframes+1)) ? X264_TYPE_B : X264_TYPE_P;
// 最后一帧为P帧
frames[num_frames]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
}
/* Check scenecut on the first minigop. */
// 如果B帧中, 有帧有场景切换, 则改变其为P帧
for( int j = 1; j < num_bframes+1; j++ )
if( h->param.i_scenecut_threshold && scenecut( h, &a, frames, j, j+1, 0, orig_num_frames, i_max_search ) )
{
frames[j]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
num_analysed_frames = j;
break;
}
reset_start = keyframe ? 1 : X264_MIN( num_bframes+2, num_analysed_frames+1 );
}
else
{
//h->param.i_bframe为 0
//则所有的帧皆为P帧
for( int j = 1; j <= num_frames; j++ )
frames[j]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
reset_start = !keyframe + 1;
num_bframes = 0;
}
/* Perform the actual macroblock tree analysis.
* Don't go farther than the maximum keyframe interval; this helps in short GOPs. */
if( h->param.rc.b_mb_tree )
x264_macroblock_tree( h, &a, frames, X264_MIN(num_frames, h->param.i_keyint_max), keyframe );
/* Enforce keyframe limit. */
if( !h->param.b_intra_refresh )
for( int i = keyint_limit+1; i <= num_frames; i += h->param.i_keyint_max )
{
//迫使为I帧
frames[i]->i_type = X264_TYPE_I;
reset_start = X264_MIN( reset_start, i+1 );
if( h->param.b_open_gop && h->param.b_bluray_compat )
while( IS_X264_TYPE_B( frames[i-1]->i_type ) )
i--;
}
if( vbv_lookahead )
x264_vbv_lookahead( h, &a, frames, num_frames, keyframe );
/* Restore frametypes for all frames that haven't actually been decided yet. */
for( int j = reset_start; j <= num_frames; j++ )
frames[j]->i_type = X264_TYPE_AUTO;
#if HAVE_OPENCL
x264_opencl_slicetype_end( h );
#endif
}
通过源代码可以看出,x264_slicetype_analyse()分析了frames[]队列中的视频帧的帧类型。简单总结一下该函数的流程:
(1)如果frames[1]通过scenecut()判断为场景切换,设置为I帧,并且直接返回。有关帧类型判断在代码中已经做了注释,不再详细记录,下文继续看一下x264_slicetype_frame_cost()函数。
(2)如果i_bframe为0,即不使用B帧,则将所有帧都设置为P帧。
(3)如果i_bframe不为0,即使用B帧,则需要进行比较复杂的帧开销计算。这时候需要调用一帧图像开销的计算函数x264_slicetype_frame_cost()。
x264_slicetype_frame_cost()
x264_slicetype_frame_cost()用于计算一帧图像的开销。该函数的定义位于encoderslicetype.c,如下所示。//一帧图像的开销
//x264_slicetype_frame_cost(,,,p0,p1,b,)
// p0 b p1
static int x264_slicetype_frame_cost( x264_t *h, x264_mb_analysis_t *a,
x264_frame_t **frames, int p0, int p1, int b,
int b_intra_penalty )
{
int i_score = 0;
int do_search[2];
const x264_weight_t *w = x264_weight_none;
x264_frame_t *fenc = frames[b];
/* Check whether we already evaluated this frame
* If we have tried this frame as P, then we have also tried
* the preceding frames as B. (is this still true?) */
/* Also check that we already calculated the row SATDs for the current frame. */
//如果已经计算过就不用算了
if( fenc->i_cost_est[b-p0][p1-b] >= 0 && (!h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size || fenc->i_row_satds[b-p0][p1-b][0] != -1) )
i_score = fenc->i_cost_est[b-p0][p1-b];
else
{
int dist_scale_factor = 128;
/* For each list, check to see whether we have lowres motion-searched this reference frame before. */
do_search[0] = b != p0 && fenc->lowres_mvs[0][b-p0-1][0][0] == 0x7FFF;
do_search[1] = b != p1 && fenc->lowres_mvs[1][p1-b-1][0][0] == 0x7FFF;
if( do_search[0] )
{
if( h->param.analyse.i_weighted_pred && b == p1 )
{
x264_emms();
x264_weights_analyse( h, fenc, frames[p0], 1 );
w = fenc->weight[0];
}
fenc->lowres_mvs[0][b-p0-1][0][0] = 0;
}
if( do_search[1] ) fenc->lowres_mvs[1][p1-b-1][0][0] = 0;
if( p1 != p0 )
dist_scale_factor = ( ((b-p0) << 8) + ((p1-p0) >> 1) ) / (p1-p0);
int output_buf_size = h->mb.i_mb_height + (NUM_INTS + PAD_SIZE) * h->param.i_lookahead_threads;
int *output_inter[X264_LOOKAHEAD_THREAD_MAX+1];
int *output_intra[X264_LOOKAHEAD_THREAD_MAX+1];
output_inter[0] = h->scratch_buffer2;
output_intra[0] = output_inter[0] + output_buf_size;
#if HAVE_OPENCL
if( h->param.b_opencl )
{
x264_opencl_lowres_init(h, fenc, a->i_lambda );
if( do_search[0] )
{
x264_opencl_lowres_init( h, frames[p0], a->i_lambda );
x264_opencl_motionsearch( h, frames, b, p0, 0, a->i_lambda, w );
}
if( do_search[1] )
{
x264_opencl_lowres_init( h, frames[p1], a->i_lambda );
x264_opencl_motionsearch( h, frames, b, p1, 1, a->i_lambda, NULL );
}
if( b != p0 )
x264_opencl_finalize_cost( h, a->i_lambda, frames, p0, p1, b, dist_scale_factor );
x264_opencl_flush( h );
i_score = fenc->i_cost_est[b-p0][p1-b];
}
else
#endif
{
if( h->param.i_lookahead_threads > 1 )
{
x264_slicetype_slice_t s[X264_LOOKAHEAD_THREAD_MAX];
for( int i = 0; i < h->param.i_lookahead_threads; i++ )
{
x264_t *t = h->lookahead_thread[i];
/* FIXME move this somewhere else */
t->mb.i_me_method = h->mb.i_me_method;
t->mb.i_subpel_refine = h->mb.i_subpel_refine;
t->mb.b_chroma_me = h->mb.b_chroma_me;
s[i] = (x264_slicetype_slice_t){ t, a, frames, p0, p1, b, dist_scale_factor, do_search, w,
output_inter[i], output_intra[i] };
t->i_threadslice_start = ((h->mb.i_mb_height *
i
+ h->param.i_lookahead_threads/2) / h->param.i_lookahead_threads);
t->i_threadslice_end
= ((h->mb.i_mb_height * (i+1) + h->param.i_lookahead_threads/2) / h->param.i_lookahead_threads);
int thread_height = t->i_threadslice_end - t->i_threadslice_start;
int thread_output_size = thread_height + NUM_INTS;
memset( output_inter[i], 0, thread_output_size * sizeof(int) );
memset( output_intra[i], 0, thread_output_size * sizeof(int) );
output_inter[i][NUM_ROWS] = output_intra[i][NUM_ROWS] = thread_height;
output_inter[i+1] = output_inter[i] + thread_output_size + PAD_SIZE;
output_intra[i+1] = output_intra[i] + thread_output_size + PAD_SIZE;
x264_threadpool_run( h->lookaheadpool, (void*)x264_slicetype_slice_cost, &s[i] );
}
for( int i = 0; i < h->param.i_lookahead_threads; i++ )
x264_threadpool_wait( h->lookaheadpool, &s[i] );
}
else
{
h->i_threadslice_start = 0;
h->i_threadslice_end = h->mb.i_mb_height;
memset( output_inter[0], 0, (output_buf_size - PAD_SIZE) * sizeof(int) );
memset( output_intra[0], 0, (output_buf_size - PAD_SIZE) * sizeof(int) );
output_inter[0][NUM_ROWS] = output_intra[0][NUM_ROWS] = h->mb.i_mb_height;
//作为参数的结构体
x264_slicetype_slice_t s = (x264_slicetype_slice_t){ h, a, frames, p0, p1, b, dist_scale_factor, do_search, w,
output_inter[0], output_intra[0] };
//一个slice的开销
//输入输出参数都在s结构体中
x264_slicetype_slice_cost( &s );
}
/* Sum up accumulators */
if( b == p1 )
fenc->i_intra_mbs[b-p0] = 0;
if( !fenc->b_intra_calculated )
{
fenc->i_cost_est[0][0] = 0;
fenc->i_cost_est_aq[0][0] = 0;
}
fenc->i_cost_est[b-p0][p1-b] = 0;
fenc->i_cost_est_aq[b-p0][p1-b] = 0;
int *row_satd_inter = fenc->i_row_satds[b-p0][p1-b];
int *row_satd_intra = fenc->i_row_satds[0][0];
for( int i = 0; i < h->param.i_lookahead_threads; i++ )
{
//累加output_inter[]或output_intra[]
//这2个变量中存储了整帧的开销
if( b == p1 )
fenc->i_intra_mbs[b-p0] += output_inter[i][INTRA_MBS];
if( !fenc->b_intra_calculated )
{
//帧内编码的代价
fenc->i_cost_est[0][0] += output_intra[i][COST_EST];
fenc->i_cost_est_aq[0][0] += output_intra[i][COST_EST_AQ];
}
//帧间编码的代价
fenc->i_cost_est[b-p0][p1-b] += output_inter[i][COST_EST];
fenc->i_cost_est_aq[b-p0][p1-b] += output_inter[i][COST_EST_AQ];
if( h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size )
{
int row_count = output_inter[i][NUM_ROWS];
memcpy( row_satd_inter, output_inter[i] + NUM_INTS, row_count * sizeof(int) );
if( !fenc->b_intra_calculated )
memcpy( row_satd_intra, output_intra[i] + NUM_INTS, row_count * sizeof(int) );
row_satd_inter += row_count;
row_satd_intra += row_count;
}
}
//一帧的开销
i_score = fenc->i_cost_est[b-p0][p1-b];
if( b != p1 )//B帧
i_score = (uint64_t)i_score * 100 / (120 + h->param.i_bframe_bias);
else
fenc->b_intra_calculated = 1;
fenc->i_cost_est[b-p0][p1-b] = i_score;
x264_emms();
}
}
if( b_intra_penalty )
{
// arbitrary penalty for I-blocks after B-frames
int nmb = NUM_MBS;
i_score += (uint64_t)i_score * fenc->i_intra_mbs[b-p0] / (nmb * 8);
}
//返回一帧的开销值
return i_score;
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_slicetype_analyse()调用了x264_slicetype_slice_cost()来计算一个slice的开销。
x264_slicetype_slice_cost()
x264_slicetype_slice_cost()用来计算一个slice的开销。该函数的定义位于encoderslicetype.c,如下所示。//一个slice的开销
static void x264_slicetype_slice_cost( x264_slicetype_slice_t *s )
{
x264_t *h = s->h;
/* Lowres lookahead goes backwards because the MVs are used as predictors in the main encode.
* This considerably improves MV prediction overall. */
/* The edge mbs seem to reduce the predictive quality of the
* whole frame's score, but are needed for a spatial distribution. */
int do_edges = h->param.rc.b_mb_tree || h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size || h->mb.i_mb_width <= 2 || h->mb.i_mb_height <= 2;
int start_y = X264_MIN( h->i_threadslice_end - 1, h->mb.i_mb_height - 2 + do_edges );
int end_y = X264_MAX( h->i_threadslice_start, 1 - do_edges );
int start_x = h->mb.i_mb_width - 2 + do_edges;
int end_x = 1 - do_edges;
//逐个计算每个MB的开销
for( h->mb.i_mb_y = start_y; h->mb.i_mb_y >= end_y; h->mb.i_mb_y-- )
for( h->mb.i_mb_x = start_x; h->mb.i_mb_x >= end_x; h->mb.i_mb_x-- )
x264_slicetype_mb_cost( h, s->a, s->frames, s->p0, s->p1, s->b, s->dist_scale_factor,
s->do_search, s->w, s->output_inter, s->output_intra );
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_slicetype_slice_cost()循环遍历了每一个宏块,针对每一个宏块调用了x264_slicetype_mb_cost()。
x264_slicetype_mb_cost()
x264_slicetype_mb_cost()用于计算一个宏块的编码代价。该函数的定义位于encoderslicetype.c,如下所示。//一个MB的开销
static void x264_slicetype_mb_cost( x264_t *h, x264_mb_analysis_t *a,
x264_frame_t **frames, int p0, int p1, int b,
int dist_scale_factor, int do_search[2], const x264_weight_t *w,
int *output_inter, int *output_intra )
{
x264_frame_t *fref0 = frames[p0];
x264_frame_t *fref1 = frames[p1];
x264_frame_t *fenc
= frames[b];
const int b_bidir = (b < p1);
const int i_mb_x = h->mb.i_mb_x;
const int i_mb_y = h->mb.i_mb_y;
const int i_mb_stride = h->mb.i_mb_width;
const int i_mb_xy = i_mb_x + i_mb_y * i_mb_stride;
const int i_stride = fenc->i_stride_lowres;
const int i_pel_offset = 8 * (i_mb_x + i_mb_y * i_stride);
const int i_bipred_weight = h->param.analyse.b_weighted_bipred ? 64 - (dist_scale_factor>>2) : 32;
int16_t (*fenc_mvs[2])[2] = { &fenc->lowres_mvs[0][b-p0-1][i_mb_xy], &fenc->lowres_mvs[1][p1-b-1][i_mb_xy] };
int (*fenc_costs[2]) = { &fenc->lowres_mv_costs[0][b-p0-1][i_mb_xy], &fenc->lowres_mv_costs[1][p1-b-1][i_mb_xy] };
int b_frame_score_mb = (i_mb_x > 0 && i_mb_x < h->mb.i_mb_width - 1 &&
i_mb_y > 0 && i_mb_y < h->mb.i_mb_height - 1) ||
h->mb.i_mb_width <= 2 || h->mb.i_mb_height <= 2;
ALIGNED_ARRAY_16( pixel, pix1,[9*FDEC_STRIDE] );
pixel *pix2 = pix1+8;
x264_me_t m[2];
int i_bcost = COST_MAX;
int list_used = 0;
/* A small, arbitrary bias to avoid VBV problems caused by zero-residual lookahead blocks. */
int lowres_penalty = 4;
//计算只涉及一个分量
h->mb.pic.p_fenc[0] = h->mb.pic.fenc_buf;
//从低分辨率(1/2线性内插)图像中拷贝数据
h->mc.copy[PIXEL_8x8]( h->mb.pic.p_fenc[0], FENC_STRIDE, &fenc->lowres[0][i_pel_offset], i_stride, 8 );
if( p0 == p1 )
goto lowres_intra_mb;
// no need for h->mb.mv_min[]
h->mb.mv_limit_fpel[0][0] = -8*h->mb.i_mb_x - 4;
h->mb.mv_limit_fpel[1][0] = 8*( h->mb.i_mb_width - h->mb.i_mb_x - 1 ) + 4;
h->mb.mv_min_spel[0] = 4*( h->mb.mv_limit_fpel[0][0] - 8 );
h->mb.mv_max_spel[0] = 4*( h->mb.mv_limit_fpel[1][0] + 8 );
if( h->mb.i_mb_x >= h->mb.i_mb_width - 2 )
{
h->mb.mv_limit_fpel[0][1] = -8*h->mb.i_mb_y - 4;
h->mb.mv_limit_fpel[1][1] = 8*( h->mb.i_mb_height - h->mb.i_mb_y - 1 ) + 4;
h->mb.mv_min_spel[1] = 4*( h->mb.mv_limit_fpel[0][1] - 8 );
h->mb.mv_max_spel[1] = 4*( h->mb.mv_limit_fpel[1][1] + 8 );
}
#define LOAD_HPELS_LUMA(dst, src)
{
(dst)[0] = &(src)[0][i_pel_offset];
(dst)[1] = &(src)[1][i_pel_offset];
(dst)[2] = &(src)[2][i_pel_offset];
(dst)[3] = &(src)[3][i_pel_offset];
}
#define LOAD_WPELS_LUMA(dst,src)
(dst) = &(src)[i_pel_offset];
#define CLIP_MV( mv )
{
mv[0] = x264_clip3( mv[0], h->mb.mv_min_spel[0], h->mb.mv_max_spel[0] );
mv[1] = x264_clip3( mv[1], h->mb.mv_min_spel[1], h->mb.mv_max_spel[1] );
}
#define TRY_BIDIR( mv0, mv1, penalty )
{
int i_cost;
if( h->param.analyse.i_subpel_refine <= 1 )
{
int hpel_idx1 = (((mv0)[0]&2)>>1) + ((mv0)[1]&2);
int hpel_idx2 = (((mv1)[0]&2)>>1) + ((mv1)[1]&2);
pixel *src1 = m[0].p_fref[hpel_idx1] + ((mv0)[0]>>2) + ((mv0)[1]>>2) * m[0].i_stride[0];
pixel *src2 = m[1].p_fref[hpel_idx2] + ((mv1)[0]>>2) + ((mv1)[1]>>2) * m[1].i_stride[0];
h->mc.avg[PIXEL_8x8]( pix1, 16, src1, m[0].i_stride[0], src2, m[1].i_stride[0], i_bipred_weight );
}
else
{
intptr_t stride1 = 16, stride2 = 16;
pixel *src1, *src2;
src1 = h->mc.get_ref( pix1, &stride1, m[0].p_fref, m[0].i_stride[0],
(mv0)[0], (mv0)[1], 8, 8, w );
src2 = h->mc.get_ref( pix2, &stride2, m[1].p_fref, m[1].i_stride[0],
(mv1)[0], (mv1)[1], 8, 8, w );
h->mc.avg[PIXEL_8x8]( pix1, 16, src1, stride1, src2, stride2, i_bipred_weight );
}
i_cost = penalty * a->i_lambda + h->pixf.mbcmp[PIXEL_8x8](
m[0].p_fenc[0], FENC_STRIDE, pix1, 16 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_bcost, i_cost, list_used, 3 );
}
//帧间编码(后面还有帧内编码)
//处理m[0]
m[0].i_pixel = PIXEL_8x8;
m[0].p_cost_mv = a->p_cost_mv;
m[0].i_stride[0] = i_stride;
m[0].p_fenc[0] = h->mb.pic.p_fenc[0];
m[0].weight = w;
m[0].i_ref = 0;
//加载1/2插值像素点
LOAD_HPELS_LUMA( m[0].p_fref, fref0->lowres );
m[0].p_fref_w = m[0].p_fref[0];
if( w[0].weightfn )
LOAD_WPELS_LUMA( m[0].p_fref_w, fenc->weighted[0] );
//双线预测,处理m[1]
if( b_bidir )
{
int16_t *mvr = fref1->lowres_mvs[0][p1-p0-1][i_mb_xy];
ALIGNED_ARRAY_8( int16_t, dmv,[2],[2] );
m[1].i_pixel = PIXEL_8x8;
m[1].p_cost_mv = a->p_cost_mv;
m[1].i_stride[0] = i_stride;
m[1].p_fenc[0] = h->mb.pic.p_fenc[0];
m[1].i_ref = 0;
m[1].weight = x264_weight_none;
LOAD_HPELS_LUMA( m[1].p_fref, fref1->lowres );
m[1].p_fref_w = m[1].p_fref[0];
dmv[0][0] = ( mvr[0] * dist_scale_factor + 128 ) >> 8;
dmv[0][1] = ( mvr[1] * dist_scale_factor + 128 ) >> 8;
dmv[1][0] = dmv[0][0] - mvr[0];
dmv[1][1] = dmv[0][1] - mvr[1];
CLIP_MV( dmv[0] );
CLIP_MV( dmv[1] );
if( h->param.analyse.i_subpel_refine <= 1 )
M64( dmv ) &= ~0x0001000100010001ULL; /* mv & ~1 */
//双向预测,其中包含了mc.avg[PIXEL_8x8]()
TRY_BIDIR( dmv[0], dmv[1], 0 );
if( M64( dmv ) )
{
int i_cost;
h->mc.avg[PIXEL_8x8]( pix1, 16, m[0].p_fref[0], m[0].i_stride[0], m[1].p_fref[0], m[1].i_stride[0], i_bipred_weight );
i_cost = h->pixf.mbcmp[PIXEL_8x8]( m[0].p_fenc[0], FENC_STRIDE, pix1, 16 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_bcost, i_cost, list_used, 3 );
}
}
for( int l = 0; l < 1 + b_bidir; l++ )
{
if( do_search[l] )
{
int i_mvc = 0;
int16_t (*fenc_mv)[2] = fenc_mvs[l];
ALIGNED_4( int16_t mvc[4][2] );
/* Reverse-order MV prediction. */
M32( mvc[0] ) = 0;
M32( mvc[2] ) = 0;
#define MVC(mv) { CP32( mvc[i_mvc], mv ); i_mvc++; }
if( i_mb_x < h->mb.i_mb_width - 1 )
MVC( fenc_mv[1] );
if( i_mb_y < h->i_threadslice_end - 1 )
{
MVC( fenc_mv[i_mb_stride] );
if( i_mb_x > 0 )
MVC( fenc_mv[i_mb_stride-1] );
if( i_mb_x < h->mb.i_mb_width - 1 )
MVC( fenc_mv[i_mb_stride+1] );
}
#undef MVC
if( i_mvc <= 1 )
CP32( m[l].mvp, mvc[0] );
else
x264_median_mv( m[l].mvp, mvc[0], mvc[1], mvc[2] );
/* Fast skip for cases of near-zero residual.
Shortcut: don't bother except in the mv0 case,
* since anything else is likely to have enough residual to not trigger the skip. */
if( !M32( m[l].mvp ) )
{
m[l].cost = h->pixf.mbcmp[PIXEL_8x8]( m[l].p_fenc[0], FENC_STRIDE, m[l].p_fref[0], m[l].i_stride[0] );
if( m[l].cost < 64 )
{
M32( m[l].mv ) = 0;
goto skip_motionest;
}
}
//运动搜索,开销存在m[l].cost中
x264_me_search( h, &m[l], mvc, i_mvc );
m[l].cost -= a->p_cost_mv[0]; // remove mvcost from skip mbs
if( M32( m[l].mv ) )
m[l].cost += 5 * a->i_lambda;
skip_motionest:
CP32( fenc_mvs[l], m[l].mv );
*fenc_costs[l] = m[l].cost;
}
else
{
CP32( m[l].mv, fenc_mvs[l] );
m[l].cost = *fenc_costs[l];
}
//如果更小就拷贝
//帧间编码开销,存储于i_bcost
COPY2_IF_LT( i_bcost, m[l].cost, list_used, l+1 );
}
if( b_bidir && ( M32( m[0].mv ) || M32( m[1].mv ) ) )
TRY_BIDIR( m[0].mv, m[1].mv, 5 );
lowres_intra_mb:
//帧内编码
if( !fenc->b_intra_calculated )
{
ALIGNED_ARRAY_16( pixel, edge,[36] );
pixel *pix = &pix1[8+FDEC_STRIDE];
pixel *src = &fenc->lowres[0][i_pel_offset];
const int intra_penalty = 5 * a->i_lambda;
int satds[3];
int pixoff = 4 / sizeof(pixel);
/* Avoid store forwarding stalls by writing larger chunks */
memcpy( pix-FDEC_STRIDE, src-i_stride, 16 * sizeof(pixel) );
for( int i = -1; i < 8; i++ )
M32( &pix[i*FDEC_STRIDE-pixoff] ) = M32( &src[i*i_stride-pixoff] );
//8x8块的SAD/SATD计算
//x3打表计算了V,H,DC三种模式,开销存储在satds[3]数组的3个元素中
h->pixf.intra_mbcmp_x3_8x8c( h->mb.pic.p_fenc[0], pix, satds );
//帧内编码开销,存储于i_icost
int i_icost = X264_MIN3( satds[0], satds[1], satds[2] );
if( h->param.analyse.i_subpel_refine > 1 )
{
h->predict_8x8c[I_PRED_CHROMA_P]( pix );
int satd = h->pixf.mbcmp[PIXEL_8x8]( pix, FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fenc[0], FENC_STRIDE );
i_icost = X264_MIN( i_icost, satd );
h->predict_8x8_filter( pix, edge, ALL_NEIGHBORS, ALL_NEIGHBORS );
for( int i = 3; i < 9; i++ )
{
h->predict_8x8[i]( pix, edge );
satd = h->pixf.mbcmp[PIXEL_8x8]( pix, FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fenc[0], FENC_STRIDE );
i_icost = X264_MIN( i_icost, satd );
}
}
i_icost += intra_penalty + lowres_penalty;
//存一下
fenc->i_intra_cost[i_mb_xy] = i_icost;
int i_icost_aq = i_icost;
if( h->param.rc.i_aq_mode )
i_icost_aq = (i_icost_aq * fenc->i_inv_qscale_factor[i_mb_xy] + 128) >> 8;
output_intra[ROW_SATD] += i_icost_aq;
if( b_frame_score_mb )
{
//累加。[COST_EST]用于整帧的开销计算
output_intra[COST_EST] += i_icost;
output_intra[COST_EST_AQ] += i_icost_aq;
}
}
i_bcost += lowres_penalty;
/* forbid intra-mbs in B-frames, because it's rare and not worth checking */
/* FIXME: Should we still forbid them now that we cache intra scores? */
if( !b_bidir )
{
int i_icost = fenc->i_intra_cost[i_mb_xy];
//帧内开销比帧间更小,b_intra就会取1
int b_intra = i_icost < i_bcost;
if( b_intra )
{
//赋值给i_bcost
i_bcost = i_icost;
list_used = 0;
}
if( b_frame_score_mb )
output_inter[INTRA_MBS] += b_intra;//[INTRA_MBS]统计有多少个帧内模式的宏块
}
/* In an I-frame, we've already added the results above in the intra section. */
if( p0 != p1 )
{
int i_bcost_aq = i_bcost;
if( h->param.rc.i_aq_mode )
i_bcost_aq = (i_bcost_aq * fenc->i_inv_qscale_factor[i_mb_xy] + 128) >> 8;
output_inter[ROW_SATD] += i_bcost_aq;
if( b_frame_score_mb )
{
/* Don't use AQ-weighted costs for slicetype decision, only for ratecontrol. */
//累加。[COST_EST]用于整帧的开销计算
output_inter[COST_EST] += i_bcost;
output_inter[COST_EST_AQ] += i_bcost_aq;
}
}
//存储开销i_bcost
fenc->lowres_costs[b-p0][p1-b][i_mb_xy] = X264_MIN( i_bcost, LOWRES_COST_MASK ) + (list_used << LOWRES_COST_SHIFT);
}
#undef TRY_BIDIR
宏块开销这里在源代码上写了比较详细的注释,不再详细记录。在这里有一点需要注意:处理的图像是经过1/2线性差值的“低分辨率(lowres)”图片(这样速度更快?),而其中宏块的大小也是以8x8而不是16x16为单位的。
x264_frame_shift()
x264_frame_shift()用于从队列头部取出1帧。该函数的定义位于commonframe.c,如下所示。//从队列的头部取出一帧
x264_frame_t *x264_frame_shift( x264_frame_t **list )
{
x264_frame_t *frame = list[0];
int i;
for( i = 0; list[i]; i++ )
list[i] = list[i+1];
assert(frame);
return frame;
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_frame_shift()取出了list[0]并且作为返回值返回。
x264_reference_update()
x264_reference_update()用于更新参考帧队列(将重建帧fdec加入参考帧队列)。该函数的定义位于encoderencoder.c,如下所示。//更新参考帧队列,若为非参考B帧则不更新
//重建帧移植参考帧列表,新建一个重建帧
static inline int x264_reference_update( x264_t *h )
{
//如果不是被参考的帧
if( !h->fdec->b_kept_as_ref )
{
if( h->i_thread_frames > 1 )
{
x264_frame_push_unused( h, h->fdec );
h->fdec = x264_frame_pop_unused( h, 1 );
if( !h->fdec )
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
/* apply mmco from previous frame. */
for( int i = 0; i < h->sh.i_mmco_command_count; i++ )
for( int j = 0; h->frames.reference[j]; j++ )
if( h->frames.reference[j]->i_poc == h->sh.mmco[i].i_poc )
x264_frame_push_unused( h, x264_frame_shift( &h->frames.reference[j] ) );
/* move frame in the buffer */
//重建帧加入参考帧列表
x264_frame_push( h->frames.reference, h->fdec );
//列表满了,则要移除1帧
if( h->frames.reference[h->sps->i_num_ref_frames] )
x264_frame_push_unused( h, x264_frame_shift( h->frames.reference ) );
//重新初始化重建帧fdec
h->fdec = x264_frame_pop_unused( h, 1 );
if( !h->fdec )
return -1;
return 0;
}
从源代码可以看出,如果重建帧fdec是不被参考的B帧,则直接返回;如果fdec是被参考的帧,则会调用x264_frame_push()将该帧加入frames.reference[]队列的尾部。如果frames.reference[]已经满了,则会调用x264_frame_shift()和x264_frame_push_unused()将frames.reference[]队列头部的帧移动到frames.unused[]队列。最后函数还会调用x264_frame_pop_unused()获取一个新的重建帧fdec。
x264_reference_reset()
如果编码帧为IDR帧,就会调用x264_reference_reset()函数清空参考帧列表。该函数定义位于encoderencoder.c,如下所示。//清空所有参考帧
static inline void x264_reference_reset( x264_t *h )
{
//把frames.reference[]中所有帧移动到frames.unused[]
while( h->frames.reference[0] )
x264_frame_push_unused( h, x264_frame_pop( h->frames.reference ) );
h->fdec->i_poc =
h->fenc->i_poc = 0;
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_reference_reset()中调用x264_frame_pop()和x264_frame_push_unused()将frames.reference[]队列中的帧移动到frames.unused[]队列中。
x264_slice_init()
x264_slice_init()用于创建Slice Header,初始化其中的信息。该函数的定义位于encoderencoder.c,如下所示。//创建Slice Header
static inline void x264_slice_init( x264_t *h, int i_nal_type, int i_global_qp )
{
/* ------------------------ Create slice header
----------------------- */
if( i_nal_type == NAL_SLICE_IDR )
{
//I帧
//对x264_slice_header_t进行赋值
x264_slice_header_init( h, &h->sh, h->sps, h->pps, h->i_idr_pic_id, h->i_frame_num, i_global_qp );
/* alternate id */
if( h->param.i_avcintra_class )
{
switch( h->i_idr_pic_id )
{
case 5:
h->i_idr_pic_id = 3;
break;
case 3:
h->i_idr_pic_id = 4;
break;
case 4:
default:
h->i_idr_pic_id = 5;
break;
}
}
else
h->i_idr_pic_id ^= 1;
}
else
{
//非IDR帧
x264_slice_header_init( h, &h->sh, h->sps, h->pps, -1, h->i_frame_num, i_global_qp );
//参考帧列表
h->sh.i_num_ref_idx_l0_active = h->i_ref[0] <= 0 ? 1 : h->i_ref[0];
h->sh.i_num_ref_idx_l1_active = h->i_ref[1] <= 0 ? 1 : h->i_ref[1];
if( h->sh.i_num_ref_idx_l0_active != h->pps->i_num_ref_idx_l0_default_active ||
(h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B && h->sh.i_num_ref_idx_l1_active != h->pps->i_num_ref_idx_l1_default_active) )
{
h->sh.b_num_ref_idx_override = 1;
}
}
if( h->fenc->i_type == X264_TYPE_BREF && h->param.b_bluray_compat && h->sh.i_mmco_command_count )
{
h->b_sh_backup = 1;
h->sh_backup = h->sh;
}
h->fdec->i_frame_num = h->sh.i_frame_num;
if( h->sps->i_poc_type == 0 )
{
h->sh.i_poc = h->fdec->i_poc;
if( PARAM_INTERLACED )
{
h->sh.i_delta_poc_bottom = h->param.b_tff ? 1 : -1;
h->sh.i_poc += h->sh.i_delta_poc_bottom == -1;
}
else
h->sh.i_delta_poc_bottom = 0;
h->fdec->i_delta_poc[0] = h->sh.i_delta_poc_bottom == -1;
h->fdec->i_delta_poc[1] = h->sh.i_delta_poc_bottom ==
1;
}
else
{
/* Nothing to do ? */
}
//主要对mb结构体赋初值
x264_macroblock_slice_init( h );
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_slice_init()调用x264_slice_header_init()完成了Slice Header “通用”的初始化工作,然后根据帧类型的不同,做了一些特殊参数的设置。下面看一下x264_slice_header_init()。
x264_slice_header_init()
x264_slice_header_init()用于对Slice Header进行初始化工作。该函数的定义如下所示。/* Fill "default" values */
//对x264_slice_header_t进行赋值
static void x264_slice_header_init( x264_t *h, x264_slice_header_t *sh,
x264_sps_t *sps, x264_pps_t *pps,
int i_idr_pic_id, int i_frame, int i_qp )
{
x264_param_t *param = &h->param;
/* First we fill all fields */
sh->sps = sps;
sh->pps = pps;
sh->i_first_mb
= 0;
sh->i_last_mb
= h->mb.i_mb_count - 1;
sh->i_pps_id
= pps->i_id;
sh->i_frame_num = i_frame;
sh->b_mbaff = PARAM_INTERLACED;
sh->b_field_pic = 0;
/* no field support for now */
sh->b_bottom_field = 0; /* not yet used */
sh->i_idr_pic_id = i_idr_pic_id;
/* poc stuff, fixed later */
sh->i_poc = 0;
sh->i_delta_poc_bottom = 0;
sh->i_delta_poc[0] = 0;
sh->i_delta_poc[1] = 0;
sh->i_redundant_pic_cnt = 0;
h->mb.b_direct_auto_write = h->param.analyse.i_direct_mv_pred == X264_DIRECT_PRED_AUTO
&& h->param.i_bframe
&& ( h->param.rc.b_stat_write || !h->param.rc.b_stat_read );
if( !h->mb.b_direct_auto_read && sh->i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
{
if( h->fref[1][0]->i_poc_l0ref0 == h->fref[0][0]->i_poc )
{
if( h->mb.b_direct_auto_write )
sh->b_direct_spatial_mv_pred = ( h->stat.i_direct_score[1] > h->stat.i_direct_score[0] );
else
sh->b_direct_spatial_mv_pred = ( param->analyse.i_direct_mv_pred == X264_DIRECT_PRED_SPATIAL );
}
else
{
h->mb.b_direct_auto_write = 0;
sh->b_direct_spatial_mv_pred = 1;
}
}
/* else b_direct_spatial_mv_pred was read from the 2pass statsfile */
sh->b_num_ref_idx_override = 0;
sh->i_num_ref_idx_l0_active = 1;
sh->i_num_ref_idx_l1_active = 1;
sh->b_ref_pic_list_reordering[0] = h->b_ref_reorder[0];
sh->b_ref_pic_list_reordering[1] = h->b_ref_reorder[1];
/* If the ref list isn't in the default order, construct reordering header */
for( int list = 0; list < 2; list++ )
{
if( sh->b_ref_pic_list_reordering[list] )
{
int pred_frame_num = i_frame;
for( int i = 0; i < h->i_ref[list]; i++ )
{
int diff = h->fref[list][i]->i_frame_num - pred_frame_num;
sh->ref_pic_list_order[list][i].idc = ( diff > 0 );
sh->ref_pic_list_order[list][i].arg = (abs(diff) - 1) & ((1 << sps->i_log2_max_frame_num) - 1);
pred_frame_num = h->fref[list][i]->i_frame_num;
}
}
}
sh->i_cabac_init_idc = param->i_cabac_init_idc;
sh->i_qp = SPEC_QP(i_qp);
sh->i_qp_delta = sh->i_qp - pps->i_pic_init_qp;
sh->b_sp_for_swidth = 0;
sh->i_qs_delta = 0;
int deblock_thresh = i_qp + 2 * X264_MIN(param->i_deblocking_filter_alphac0, param->i_deblocking_filter_beta);
/* If effective qp <= 15, deblocking would have no effect anyway */
if( param->b_deblocking_filter && (h->mb.b_variable_qp || 15 < deblock_thresh ) )
sh->i_disable_deblocking_filter_idc = param->b_sliced_threads ? 2 : 0;
else
sh->i_disable_deblocking_filter_idc = 1;
sh->i_alpha_c0_offset = param->i_deblocking_filter_alphac0 << 1;
sh->i_beta_offset = param->i_deblocking_filter_beta << 1;
}
可以看出x264_slice_header_init()对x264_slice_header_t结构体的成员变量进行了赋值。
x264_slices_write()
编码数据(最关键的步骤)。其中调用了x264_slice_write()完成了编码的工作(注意“x264_slices_write()”和“x264_slice_write()”名字差了一个“s”)。//真正的编码——编码1个图像帧
//注意“slice”后面有一个“s”
//它其中又调用了一个x264_slice_write()
//这一点要区分开
static void *x264_slices_write( x264_t *h )
{
int i_slice_num = 0;
int last_thread_mb = h->sh.i_last_mb;
/* init stats */
memset( &h->stat.frame, 0, sizeof(h->stat.frame) );
h->mb.b_reencode_mb = 0;
//循环每一个slice(一幅图像可以由多个Slice构成)
while( h->sh.i_first_mb + SLICE_MBAFF*h->mb.i_mb_stride <= last_thread_mb )
{
h->sh.i_last_mb = last_thread_mb;
if( !i_slice_num || !x264_frame_new_slice( h, h->fdec ) )
{
if( h->param.i_slice_max_mbs )
{
if( SLICE_MBAFF )
{
// convert first to mbaff form, add slice-max-mbs, then convert back to normal form
int last_mbaff = 2*(h->sh.i_first_mb % h->mb.i_mb_width)
+ h->mb.i_mb_width*(h->sh.i_first_mb / h->mb.i_mb_width)
+ h->param.i_slice_max_mbs - 1;
int last_x = (last_mbaff % (2*h->mb.i_mb_width))/2;
int last_y = (last_mbaff / (2*h->mb.i_mb_width))*2 + 1;
h->sh.i_last_mb = last_x + h->mb.i_mb_stride*last_y;
}
else
{
h->sh.i_last_mb = h->sh.i_first_mb + h->param.i_slice_max_mbs - 1;
if( h->sh.i_last_mb < last_thread_mb && last_thread_mb - h->sh.i_last_mb < h->param.i_slice_min_mbs )
h->sh.i_last_mb = last_thread_mb - h->param.i_slice_min_mbs;
}
i_slice_num++;
}
else if( h->param.i_slice_count && !h->param.b_sliced_threads )
{
int height = h->mb.i_mb_height >> PARAM_INTERLACED;
int width = h->mb.i_mb_width << PARAM_INTERLACED;
i_slice_num++;
h->sh.i_last_mb = (height * i_slice_num + h->param.i_slice_count/2) / h->param.i_slice_count * width - 1;
}
}
h->sh.i_last_mb = X264_MIN( h->sh.i_last_mb, last_thread_mb );
//真正的编码——编码1个Slice
//x264_stack_align()应该是平台优化过程中内存对齐的工作
//实际上就是调用x264_slice_write()
if( x264_stack_align( x264_slice_write, h ) )
goto fail;
//注意这里对i_first_mb进行了赋值
h->sh.i_first_mb = h->sh.i_last_mb + 1;
// if i_first_mb is not the last mb in a row then go to the next mb in MBAFF order
if( SLICE_MBAFF && h->sh.i_first_mb % h->mb.i_mb_width )
h->sh.i_first_mb -= h->mb.i_mb_stride;
}
return (void *)0;
fail:
/* Tell other threads we're done, so they wouldn't wait for it */
if( h->param.b_sliced_threads )
x264_threadslice_cond_broadcast( h, 2 );
return (void *)-1;
}
在这里需要注意,x264_slices_write()调用了x264_slice_write()。其中x264_slices_write()的单位为帧,而x264_slice_write()的单位为Slice。最常见的情况下一个帧里面只有一个Slice,但是也有可能一个帧里面有多个Slice。
x264_slice_write()
x264_slice_write()是完成编码工作的函数。该函数中包含了去块效应滤波,运动估计,宏块编码,熵编码等模块,它的调用结构大致如下图所示。
x264_encoder_frame_end()
x264_encoder_frame_end()用于在编码结束后做一些后续处理,例如封装NALU(加上起始码),释放一些中间变量,记录一些统计信息等。该函数的定义位于encoderencoder.c,如下所示。//结束的时候做一些处理,记录一些统计信息
//pp_nal:输出的NALU
//pic_out:输出的重建帧
static int x264_encoder_frame_end( x264_t *h, x264_t *thread_current,
x264_nal_t **pp_nal, int *pi_nal,
x264_picture_t *pic_out )
{
char psz_message[80];
if( !h->param.b_sliced_threads && h->b_thread_active )
{
h->b_thread_active = 0;
if( (intptr_t)x264_threadpool_wait( h->threadpool, h ) )
return -1;
}
if( !h->out.i_nal )
{
pic_out->i_type = X264_TYPE_AUTO;
return 0;
}
x264_emms();
/* generate buffering period sei and insert it into place */
if( h->i_thread_frames > 1 && h->fenc->b_keyframe && h->sps->vui.b_nal_hrd_parameters_present )
{
x264_hrd_fullness( h );
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_SEI, NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE );
x264_sei_buffering_period_write( h, &h->out.bs );
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
/* buffering period sei must follow AUD, SPS and PPS and precede all other SEIs */
int idx = 0;
while( h->out.nal[idx].i_type == NAL_AUD ||
h->out.nal[idx].i_type == NAL_SPS ||
h->out.nal[idx].i_type == NAL_PPS )
idx++;
x264_nal_t nal_tmp = h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1];
memmove( &h->out.nal[idx+1], &h->out.nal[idx], (h->out.i_nal-idx-1)*sizeof(x264_nal_t) );
h->out.nal[idx] = nal_tmp;
}
//封装一帧数据对应的NALU.
//例如给NALU添加起始码0x00000001
int frame_size = x264_encoder_encapsulate_nals( h, 0 );
if( frame_size < 0 )
return -1;
/* Set output picture properties */
//pic_out为x264_picture_t类型结构体。是libx264对外的结构体
//fenc,fdec是x264_frame_t类型结构体。是libx264的内部结构体
pic_out->i_type = h->fenc->i_type;
pic_out->b_keyframe = h->fenc->b_keyframe;
pic_out->i_pic_struct = h->fenc->i_pic_struct;
pic_out->i_pts = h->fdec->i_pts;
pic_out->i_dts = h->fdec->i_dts;
if( pic_out->i_pts < pic_out->i_dts )
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "invalid DTS: PTS is less than DTSn" );
pic_out->opaque = h->fenc->opaque;
pic_out->img.i_csp = h->fdec->i_csp;
#if HIGH_BIT_DEPTH
pic_out->img.i_csp |= X264_CSP_HIGH_DEPTH;
#endif
pic_out->img.i_plane = h->fdec->i_plane;
//图像数据
for( int i = 0; i < pic_out->img.i_plane; i++ )
{
pic_out->img.i_stride[i] = h->fdec->i_stride[i] * sizeof(pixel);
pic_out->img.plane[i] = (uint8_t*)h->fdec->plane[i];
}
//回收用过的编码帧fenc
x264_frame_push_unused( thread_current, h->fenc );
/* ---------------------- Update encoder state ------------------------- */
/* update rc */
int filler = 0;
if( x264_ratecontrol_end( h, frame_size * 8, &filler ) < 0 )
return -1;
pic_out->hrd_timing = h->fenc->hrd_timing;
pic_out->prop.f_crf_avg = h->fdec->f_crf_avg;
/* Filler in AVC-Intra mode is written as zero bytes to the last slice
* We don't know the size of the last slice until encapsulation so we add filler to the encapsulated NAL */
if( h->param.i_avcintra_class )
{
x264_t *h0 = h->thread[0];
int ret = x264_check_encapsulated_buffer( h, h0, h->out.i_nal, frame_size, frame_size + filler );
if( ret < 0 )
return -1;
memset( h->out.nal[0].p_payload + frame_size, 0, filler );
h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_payload += filler;
h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal-1].i_padding = filler;
frame_size += filler;
}
else
{
while( filler > 0 )
{
int f, overhead;
overhead = (FILLER_OVERHEAD - h->param.b_annexb);
if( h->param.i_slice_max_size && filler > h->param.i_slice_max_size )
{
int next_size = filler - h->param.i_slice_max_size;
int overflow = X264_MAX( overhead - next_size, 0 );
f = h->param.i_slice_max_size - overhead - overflow;
}
else
f = X264_MAX( 0, filler - overhead );
if( x264_bitstream_check_buffer_filler( h, f ) )
return -1;
x264_nal_start( h, NAL_FILLER, NAL_PRIORITY_DISPOSABLE );
x264_filler_write( h, &h->out.bs, f );
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
int total_size = x264_encoder_encapsulate_nals( h, h->out.i_nal-1 );
if( total_size < 0 )
return -1;
frame_size += total_size;
filler -= total_size;
}
}
/* End bitstream, set output
*/
*pi_nal = h->out.i_nal;
*pp_nal = h->out.nal;
h->out.i_nal = 0;
x264_noise_reduction_update( h );
/* ---------------------- Compute/Print statistics --------------------- */
x264_thread_sync_stat( h, h->thread[0] );
/* Slice stat */
//stat中存储了统计信息
//帧数+1 (根据类型)
h->stat.i_frame_count[h->sh.i_type]++;
//帧大小
h->stat.i_frame_size[h->sh.i_type] += frame_size;
h->stat.f_frame_qp[h->sh.i_type] += h->fdec->f_qp_avg_aq;
//统计MB个数,把不同类型的累加起来
for( int i = 0; i < X264_MBTYPE_MAX; i++ )
h->stat.i_mb_count[h->sh.i_type][i] += h->stat.frame.i_mb_count[i];
for( int i = 0; i < X264_PARTTYPE_MAX; i++ )
h->stat.i_mb_partition[h->sh.i_type][i] += h->stat.frame.i_mb_partition[i];
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
h->stat.i_mb_count_8x8dct[i] += h->stat.frame.i_mb_count_8x8dct[i];
for( int i = 0; i < 6; i++ )
h->stat.i_mb_cbp[i] += h->stat.frame.i_mb_cbp[i];
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
for( int j = 0; j < 13; j++ )
h->stat.i_mb_pred_mode[i][j] += h->stat.frame.i_mb_pred_mode[i][j];
if( h->sh.i_type != SLICE_TYPE_I )
for( int i_list = 0; i_list < 2; i_list++ )
for( int i = 0; i < X264_REF_MAX*2; i++ )
h->stat.i_mb_count_ref[h->sh.i_type][i_list][i] += h->stat.frame.i_mb_count_ref[i_list][i];
for( int i = 0; i < 3; i++ )
h->stat.i_mb_field[i] += h->stat.frame.i_mb_field[i];
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_P && h->param.analyse.i_weighted_pred >= X264_WEIGHTP_SIMPLE )
{
h->stat.i_wpred[0] += !!h->sh.weight[0][0].weightfn;
h->stat.i_wpred[1] += !!h->sh.weight[0][1].weightfn || !!h->sh.weight[0][2].weightfn;
}
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
{
h->stat.i_direct_frames[ h->sh.b_direct_spatial_mv_pred ] ++;
if( h->mb.b_direct_auto_write )
{
//FIXME somewhat arbitrary time constants
if( h->stat.i_direct_score[0] + h->stat.i_direct_score[1] > h->mb.i_mb_count )
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
h->stat.i_direct_score[i] = h->stat.i_direct_score[i] * 9/10;
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
h->stat.i_direct_score[i] += h->stat.frame.i_direct_score[i];
}
}
else
h->stat.i_consecutive_bframes[h->fenc->i_bframes]++;
psz_message[0] = '�';
double dur = h->fenc->f_duration;
h->stat.f_frame_duration[h->sh.i_type] += dur;
//需要计算PSNR
if( h->param.analyse.b_psnr )
{
//SSD(Sum of Squared Difference)即差值的平方和
int64_t ssd[3] =
{
h->stat.frame.i_ssd[0],
h->stat.frame.i_ssd[1],
h->stat.frame.i_ssd[2],
};
int luma_size = h->param.i_width * h->param.i_height;
int chroma_size = CHROMA_SIZE( luma_size );
//SSD是已经在“滤波”环节计算过的
//SSD简单换算成PSNR,调用x264_psnr()
pic_out->prop.f_psnr[0] = x264_psnr( ssd[0], luma_size );
pic_out->prop.f_psnr[1] = x264_psnr( ssd[1], chroma_size );
pic_out->prop.f_psnr[2] = x264_psnr( ssd[2], chroma_size );
//平均值
pic_out->prop.f_psnr_avg = x264_psnr( ssd[0] + ssd[1] + ssd[2], luma_size + chroma_size*2 );
//mean系列的需要累加
h->stat.f_ssd_global[h->sh.i_type]
+= dur * (ssd[0] + ssd[1] + ssd[2]);
h->stat.f_psnr_average[h->sh.i_type] += dur * pic_out->prop.f_psnr_avg;
h->stat.f_psnr_mean_y[h->sh.i_type]
+= dur * pic_out->prop.f_psnr[0];
h->stat.f_psnr_mean_u[h->sh.i_type]
+= dur * pic_out->prop.f_psnr[1];
h->stat.f_psnr_mean_v[h->sh.i_type]
+= dur * pic_out->prop.f_psnr[2];
snprintf( psz_message, 80, " PSNR Y:%5.2f U:%5.2f V:%5.2f", pic_out->prop.f_psnr[0],
pic_out->prop.f_psnr[1],
pic_out->prop.f_psnr[2] );
}
//需要计算SSIM
if( h->param.analyse.b_ssim )
{
//SSIM是已经在“滤波”环节计算过的
pic_out->prop.f_ssim = h->stat.frame.f_ssim / h->stat.frame.i_ssim_cnt;
//mean系列的需要累加
h->stat.f_ssim_mean_y[h->sh.i_type] += pic_out->prop.f_ssim * dur;
snprintf( psz_message + strlen(psz_message), 80 - strlen(psz_message),
" SSIM Y:%.5f", pic_out->prop.f_ssim );
}
psz_message[79] = '�';
//Debug时候输出
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_DEBUG,
"frame=%4d QP=%.2f NAL=%d Slice:%c Poc:%-3d I:%-4d P:%-4d SKIP:%-4d size=%d bytes%sn",
h->i_frame,
h->fdec->f_qp_avg_aq,
h->i_nal_ref_idc,
h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_I ? 'I' : (h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_P ? 'P' : 'B' ),
h->fdec->i_poc,
h->stat.frame.i_mb_count_i,
h->stat.frame.i_mb_count_p,
h->stat.frame.i_mb_count_skip,
frame_size,
psz_message );
// keep stats all in one place
x264_thread_sync_stat( h->thread[0], h );
// for the use of the next frame
x264_thread_sync_stat( thread_current, h );
#ifdef DEBUG_MB_TYPE
{
static const char mb_chars[] = { 'i', 'i', 'I', 'C', 'P', '8', 'S',
'D', '<', 'X', 'B', 'X', '>', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B', '8', 'S' };
for( int mb_xy = 0; mb_xy < h->mb.i_mb_width * h->mb.i_mb_height; mb_xy++ )
{
if( h->mb.type[mb_xy] < X264_MBTYPE_MAX && h->mb.type[mb_xy] >= 0 )
fprintf( stderr, "%c ", mb_chars[ h->mb.type[mb_xy] ] );
else
fprintf( stderr, "? " );
if( (mb_xy+1) % h->mb.i_mb_width == 0 )
fprintf( stderr, "n" );
}
}
#endif
/* Remove duplicates, must be done near the end as breaks h->fref0 array
* by freeing some of its pointers. */
for( int i = 0; i < h->i_ref[0]; i++ )
if( h->fref[0][i] && h->fref[0][i]->b_duplicate )
{
x264_frame_push_blank_unused( h, h->fref[0][i] );
h->fref[0][i] = 0;
}
if( h->param.psz_dump_yuv )
x264_frame_dump( h );
x264_emms();
return frame_size;
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_encoder_frame_end()中大部分代码用于把统计信息记录到x264_t的stat中。此外做了一些后续处理:调用了x264_encoder_encapsulate_nals()封装NALU(添加起始码),调用x264_frame_push_unused()将fenc重新放回frames.unused[]队列,并且调用x264_ratecontrol_end()结束码率控制。
x264_encoder_encapsulate_nals()
x264_encoder_encapsulate_nals()用于封装一帧数据对应的NALU,其代码如下所示。//封装一帧数据对应的NALU.
//例如给NALU添加起始码0x00000001
static int x264_encoder_encapsulate_nals( x264_t *h, int start )
{
x264_t *h0 = h->thread[0];
int nal_size = 0, previous_nal_size = 0;
if( h->param.nalu_process )
{
for( int i = start; i < h->out.i_nal; i++ )
nal_size += h->out.nal[i].i_payload;
return nal_size;
}
for( int i = 0; i < start; i++ )
previous_nal_size += h->out.nal[i].i_payload;
for( int i = start; i < h->out.i_nal; i++ )
nal_size += h->out.nal[i].i_payload;
/* Worst-case NAL unit escaping: reallocate the buffer if it's too small. */
int necessary_size = previous_nal_size + nal_size * 3/2 + h->out.i_nal * 4 + 4 + 64;
for( int i = start; i < h->out.i_nal; i++ )
necessary_size += h->out.nal[i].i_padding;
if( x264_check_encapsulated_buffer( h, h0, start, previous_nal_size, necessary_size ) )
return -1;
uint8_t *nal_buffer = h0->nal_buffer + previous_nal_size;
//一个一个NALU处理
for( int i = start; i < h->out.i_nal; i++ )
{
int old_payload_len = h->out.nal[i].i_payload;
h->out.nal[i].b_long_startcode = !i || h->out.nal[i].i_type == NAL_SPS || h->out.nal[i].i_type == NAL_PPS ||
h->param.i_avcintra_class;
//添加起始码
x264_nal_encode( h, nal_buffer, &h->out.nal[i] );
nal_buffer += h->out.nal[i].i_payload;
if( h->param.i_avcintra_class )
{
h->out.nal[i].i_padding -= h->out.nal[i].i_payload - (old_payload_len + NALU_OVERHEAD);
if( h->out.nal[i].i_padding > 0 )
{
memset( nal_buffer, 0, h->out.nal[i].i_padding );
nal_buffer += h->out.nal[i].i_padding;
h->out.nal[i].i_payload += h->out.nal[i].i_padding;
}
h->out.nal[i].i_padding = X264_MAX( h->out.nal[i].i_padding, 0 );
}
}
x264_emms();
return nal_buffer - (h0->nal_buffer + previous_nal_size);
}
从源代码中可以看出,x264_encoder_encapsulate_nals()调用了另外一个函数x264_nal_encode()逐个给一帧数据中的各个NALU添加起始码以及NALU Header等。
x264_nal_encode()
x264_nal_encode()用于给NALU添加起始码以及NALU Header等。该函数的定义位于commonbitstream.c,如下所示。
/****************************************************************************
* x264_nal_encode:
****************************************************************************/
//添加起始码
void x264_nal_encode( x264_t *h, uint8_t *dst, x264_nal_t *nal )
{
uint8_t *src = nal->p_payload;
uint8_t *end = nal->p_payload + nal->i_payload;
uint8_t *orig_dst = dst;
//起始码 ============================================
//annexb格式,起始码为0x00000001
if( h->param.b_annexb )
{
if( nal->b_long_startcode )
*dst++ = 0x00;
*dst++ = 0x00;
*dst++ = 0x00;
*dst++ = 0x01;
}
else /* save room for size later */
dst += 4;//mp4格式
//NALU Header =======================================
/* nal header */
*dst++ = ( 0x00 << 7 ) | ( nal->i_ref_idc << 5 ) | nal->i_type;
dst = h->bsf.nal_escape( dst, src, end );
int size = (dst - orig_dst) - 4;
/* Write the size header for mp4/etc */
//重新回到起始码的位置,写入mp4格式的起始码(size大小,不含起始码)
if( !h->param.b_annexb )
{
/* Size doesn't include the size of the header we're writing now. */
orig_dst[0] = size>>24;
orig_dst[1] = size>>16;
orig_dst[2] = size>> 8;
orig_dst[3] = size>> 0;
}
//NALU负载大小,包含起始码
nal->i_payload = size+4;
nal->p_payload = orig_dst;
x264_emms();
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_nal_encode()给NALU数据添加了起始码以及NALU Header。在这里简单总结一下起始码的添加过程。
H.264码流有两种格式:
(1)annexb模式(传统模式)。这种模式下每个NALU包含起始码0x00000001;而且SPS、PPS存储在ES码流中。常见的H.264裸流就是属于这种格式。从源代码中可以看出,x264_nal_encode()根据H.264码流格式的不同分成两种情况给NALU添加起始码:
(2)mp4模式。这种模式下每个NALU不包含起始码,原本存储起始码前4个字节存储的是这个NALU的长度(不包含前4字节);而且SPS、PPS被单独放在容器的其他位置上。这种H.264一般存储在某些容器中,例如MP4中。
(1)annexb模式下,在每个NALU前面添加0x00000001。
(2)mp4模式下,先计算NALU的长度(不包含前4字节),再将长度信息写入NALU前面的4个字节
至此有关编码器主干部分有关x264_encoder_encode()的源代码就分析完了。从下一篇文章开始将会开始分析编码Slice的函数——x264_slice_write()。
雷霄骅
leixiaohua1020@126.com
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
最后
以上就是明理时光最近收集整理的关于x264源代码简单分析:编码器主干部分-2的全部内容,更多相关x264源代码简单分析内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
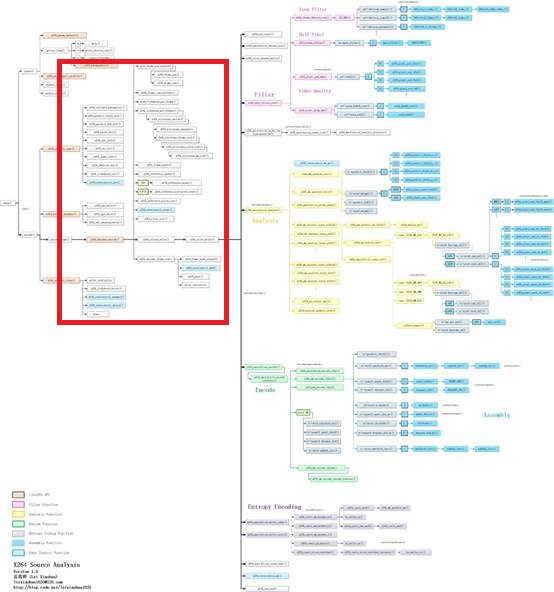
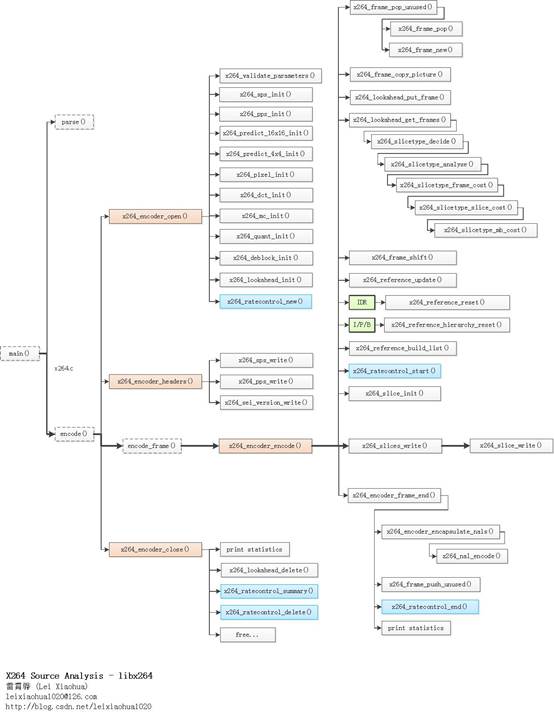
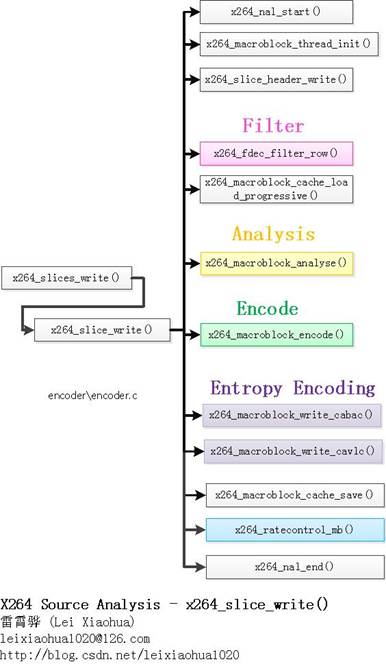






![x264 quantizer 量化相关 [学习笔记2]](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg14.png)

发表评论 取消回复