#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int uart_init(int fd)
{
struct termios newtio, oldtio;
fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,0);/*恢复串口为阻塞状态*/
if ( tcgetattr(fd, &oldtio ) != 0) {
perror("tcgetattr error");
return -1;
}
bzero( &newtio, sizeof(newtio) );
newtio.c_cflag |= B115200 | CLOCAL | CREAD; // 设置波特率,本地连接,接收使能
newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
newtio.c_cflag |= CS8; // 数据位为 8 ,CS7 for 7
newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB; // 一位停止位, 两位停止为 |= CSTOPB
newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARENB; // 无校验
//newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB; //有校验
//newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARODD // 偶校验
//newtio.c_cflag |= PARODD // 奇校验
//newtio.c_cc[VTIME] = 0; // 等待时间,单位百毫秒 (读)。后有详细说明
//newtio.c_cc[VMIN] = 0; // 最小字节数 (读)。后有详细说明
tcflush(fd, TCIOFLUSH); // TCIFLUSH刷清输入队列。
//TCOFLUSH刷清输出队列。
//TCIOFLUSH刷清输入、输出队列。
tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &newtio); // TCSANOW立即生效;
//TCSADRAIN:Wait until everything has been transmitted;
//TCSAFLUSH:Flush input and output buffers and make the change
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char buff[100] = {0};
//char w_buff[] = {0xaa, 0x55, 0x00, 0x30, 0x00, 0x08, 0x00, 0x00, 0xff, 0x07, 0x56, 0x78, 0x9a, 0xbc, 0xde, 0xf0, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0d, 0x0a };
char w_buff[100] = {"AT+ATKCLDCLSrn"};
char a_buff[100]={"AT+ATKCLDSTA="35236902567762109213","12345678"rn"};
int read_size = 0, i = 0, write_size = 0;
//int fd = open("/dev/ttyAMA0", O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY|O_NDELAY);
int fd = open("/dev/ttymxc2", O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY);
if(-1 == fd){
perror("can't open serialport");
return -1;
}
uart_init(fd);
write_size = write(fd, w_buff, sizeof(w_buff));
usleep(3000000);
write_size = write(fd, a_buff, sizeof(a_buff));
while(1)
{
usleep(3000000);
read_size = read(fd, buff, sizeof(buff));
// memset(buff,0,sizeof(buff));
// printf("write_size = %d .receive length:%d data:", write_size, read_size);
printf("%srnnn",buff);
usleep(3000000);
// memset(buff,0,sizeof(buff));
// printf("n");
}
}
uart_init(int fd)是对串口进行配置,在imx6ull中,串口3的设备文件就是/dev/ttymxc2,所以用串口之前需要对其进行配置。
write()函数是通过串口传输命令给esp8266;
read()函数是通过串口接收esp8266传回来的数据。
write_size = write(fd, w_buff, sizeof(w_buff));是首先断开与原子云的连接;
(用完必须先断开,才能再次使用,否则无法再与其连接,无法再与原子云通信,亲测,不懂为啥)
write_size = write(fd, a_buff, sizeof(a_buff)); 是用来连接原子云的设备
连接上之后,再发送数据原子云就可以直接接收,收到的数据也会有原子云发给设备的。
read_size = read(fd, buff, sizeof(buff));是接收esp8266传回来的数据。
疑点:
经测试, read_size = read(fd, buff, sizeof(buff));串口3接收的数据获取之后不会消失,会一直保留,一直不明白这个地方;
如图:“
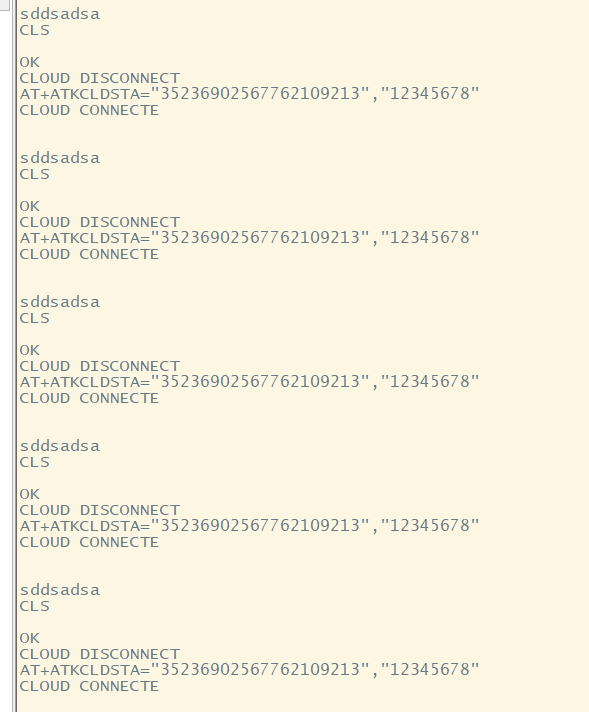
其中sddsadsa是用原子云发送的数据。
以后数据处理的时候要注意就行。
还有printf执行慢,所以如果清空的一个字符串的话不能直接在printf之后,这样会在打印出来之前已经把字符串清空了。这个程序是在printf后面延时了一下才可。
最后
以上就是清新菠萝最近收集整理的关于imx6ull串口使用的全部内容,更多相关imx6ull串口使用内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复