一、基本框架分析
输入子系统主要由三部分构成: 核心层(input.c)、事件处理层(evdev.c, joydev.c, mousedev.c 等等)、设备驱动层(具体硬件设备相关的驱动,比如按键驱动,触摸屏驱动等等 )
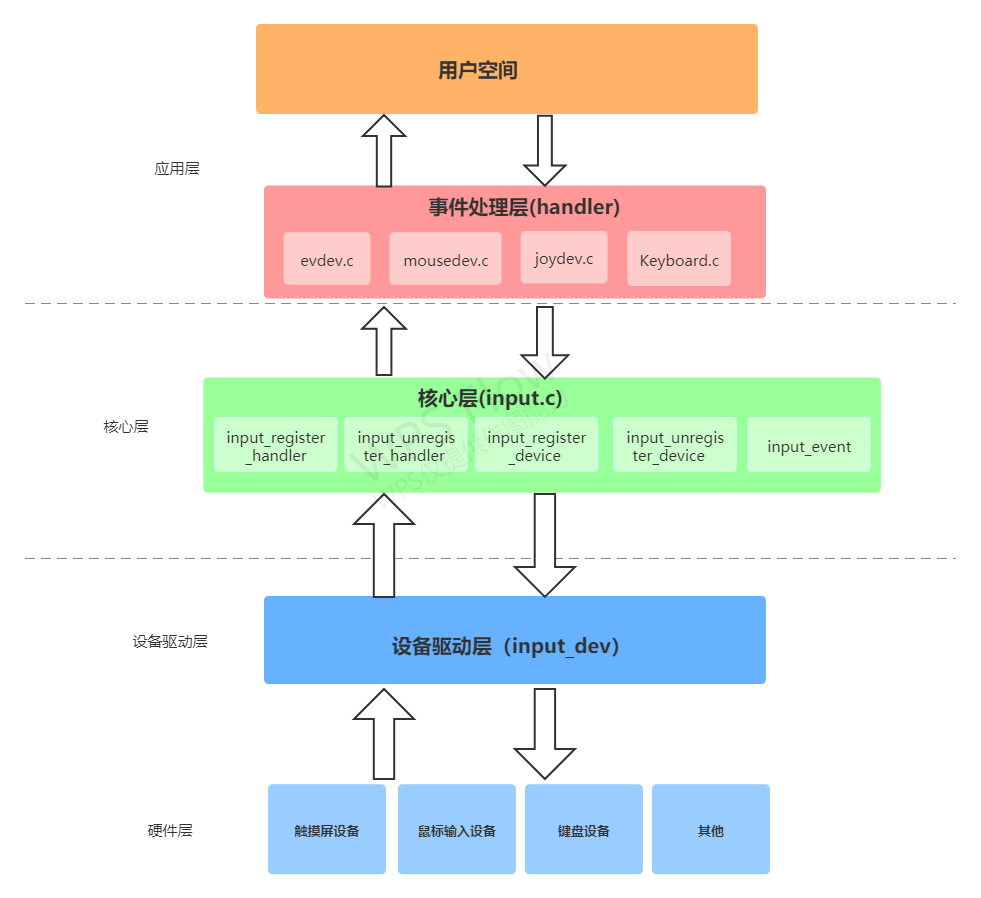
一个输入事件从产生到应用捕获的流程是: 产生事件(鼠标移动,触摸点击,按键等) -> 设备驱动捕获事件(通过硬件中断响应) , 上报事件(input_evnet) -> 事件处理层获取到事件, 上报用户 -> 用户获取事件进行逻辑处理。
事件处理层和设备层通过中间核心层接口进行注册和匹配,一个设备驱动可以匹配到多个事件处理层,产生的事件会上报到匹配到的事件处理层。
1、核心层 - input.c
这一层是linux内核实现的的一些通用的接口,可以向事件处理层和设备驱动层提供一些公用函数
- input_register_handler /input_unregister_handler -> 向事件处理层提供注册/释放一个hander的接口
- input_register_device /input_unregister_device -> 向设备驱动层提供注册/释放设备的接口(设备驱动程序会用到这两个接口来注册input设备)
- input_register_handle/input_unregister_handle -> 设备和事件匹配成功后会注册一个handle,通过这个handle来绑定上面的handler和device
- input_event -> 上报一个输入事件,由device驱动层调用上报到应用端去处理(设备驱动程序会调用该接口来上报事件,比如按键,鼠标等等)
以上就是input 子系统常用的接口,更多接口可阅读源码(driverinputinput.c)
2、事件处理层 - input_handler
这一层一般也是内核自己写好几个典型的事件处理驱动,比如 evdev.c, joydev.c,mousedev.c,keyboard.c. 调用 input_register_handler 来注册一个handler,注册handler的时候会去查找有没有匹配的device, 如果匹配成功, handler.connect 函数就会被调用。系统实现的这些事件处理驱动就够用了,不需要自己再去添加。input_handler的结构如下:
struct input_handler {
void *private;
void (*event)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
void (*events)(struct input_handle *handle,
const struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count);
bool (*filter)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
bool (*match)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev);
int (*connect)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, const struct input_device_id *id);
void (*disconnect)(struct input_handle *handle);
void (*start)(struct input_handle *handle);
bool legacy_minors;
int minor;
const char *name;
const struct input_device_id *id_table;
struct list_head h_list;
struct list_head node;
};3、设备驱动层 - input_device
这一层就是具体的驱动程序,这一层就是需要我们自己来实现的。我们先分配一个input_dev结构指针,然后可以调用input_register_device 函数来注册一个input_device,同时在注册的时候也会去扫描有没有匹配的handler, 如果有匹配的,handler.connect 就会被调用。注册一个input device的具体步骤如下:
- 分配一个input_dev -- input_allocate_device
- 初始化input_dev成员变量
- 做一些硬件相关的操作,比如中断申请等
- 注册一个input_dev -- input_register_device
4、input_dev、input_handler 以及 input_handle之间的关系
依赖关系图如下:
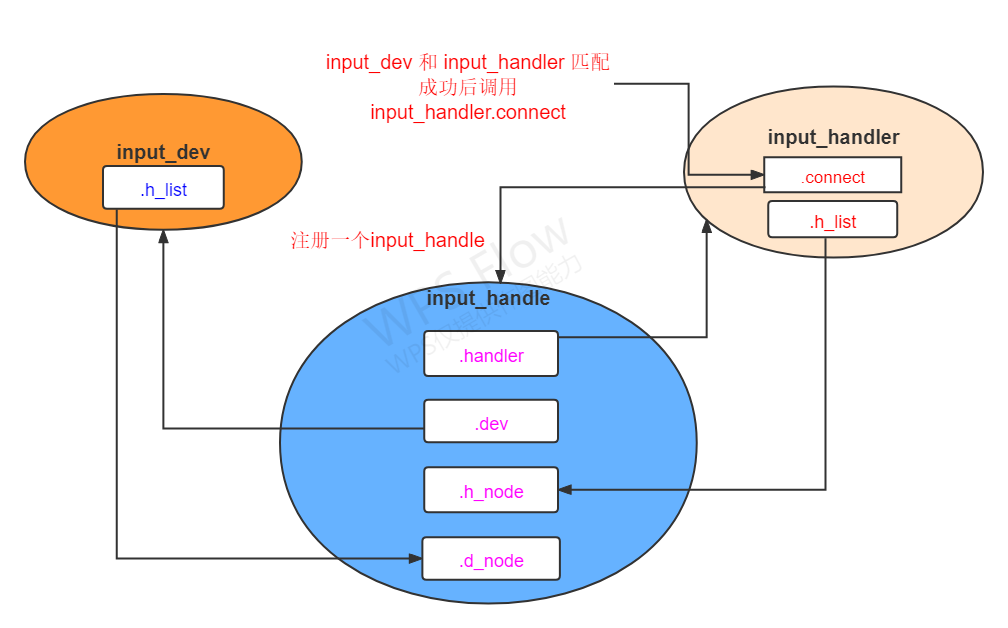
注册input_handler的时候会去扫描input_dev_list 链表中有没有匹配的input_dev。同时在注册input_dev的时候也会去扫描input_handler_list 链表查找是否有与之匹配的input_handler 。如果input_device 和 input_handler有匹配成功的,input_handler ->connect函数就会调用。
connect 函数里面会为input_device 分配一个minor(次设备号),并且注册一个handle,将input_dev 和 input_handler 地址分别赋值给 handle.dev 和 handle.handler,通过一个handle将input_dev和input_handler 绑定起来。
input_register_handle 调用时,将handle->d_node 添加到 input_dev->h_list, 将handle->h_node 添加到input_handler->h_list中,这样在input_dev中就能通过input_dev->h_list 找到input_handle, 然后根据input_handle->handler成员找到对应的事件处理层。同理也可以通过input_handler ->h_list 找到input_handle, 然后再通过input_handle->dev 成员找到对应的input_dev。至此input_dev和input_handler就能通过一个input_handle 一一对应起来。设备和事件处理层就连同通了,事件处理层上面的就是用户层。input_register_handle源码如下:
/**
* input_register_handle - register a new input handle
* @handle: handle to register
*
* This function puts a new input handle onto device's
* and handler's lists so that events can flow through
* it once it is opened using input_open_device().
*
* This function is supposed to be called from handler's
* connect() method.
*/
int input_register_handle(struct input_handle *handle)
{
struct input_handler *handler = handle->handler;
struct input_dev *dev = handle->dev;
int error;
/*
* We take dev->mutex here to prevent race with
* input_release_device().
*/
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&dev->mutex);
if (error)
return error;
/*
* Filters go to the head of the list, normal handlers
* to the tail.
*/
if (handler->filter)
list_add_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list);
else
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list);
mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex);
/*
* Since we are supposed to be called from ->connect()
* which is mutually exclusive with ->disconnect()
* we can't be racing with input_unregister_handle()
* and so separate lock is not needed here.
*/
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->h_node, &handler->h_list);
if (handler->start)
handler->start(handle);
return 0;
}二、 基于input子系统实现的按键驱动实例
这个实例是基于 imx6ull 开发板, Linux4.9.80 内核实现的, 代码如下:
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/of_irq.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <asm/current.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
static struct input_dev *input_key_dev;
struct input_gpio_key{
int m_gpio; //引脚号
struct gpio_desc * m_gpiod;
int m_irq;
int m_flag;
int m_code;
struct timer_list m_timer;
} ;
static struct input_gpio_key * input_keys_gpio;
static irqreturn_t input_key_irq(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct input_gpio_key * key_desc = (struct input_gpio_key *)dev_id;
printk(KERN_INFO "irq:key_desc->m_code=%dn", key_desc->m_code);
mod_timer(&key_desc->m_timer, jiffies+HZ/100);
return IRQ_RETVAL(IRQ_HANDLED);
}
void input_key_timer_fn(unsigned long arg)
{
int val;
struct input_gpio_key * key_desc = (struct input_gpio_key *)arg;
val = gpiod_get_value(key_desc->m_gpiod);
/* 上报按键值 0: 按下 1: 抬起 */
input_report_key(input_key_dev, key_desc->m_code, val);
input_sync(input_key_dev);
}
static int input_key_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int retval = 0;
int err, i;
int count;
enum of_gpio_flags flags;
struct device_node * node = pdev->dev.of_node;
count = of_gpio_count(node); //获取设备节点下 gpios属性有几个gpio
if(!count){
retval = -1;
goto exit_entry;
}
input_keys_gpio = kmalloc(sizeof(struct input_gpio_key) * count, GFP_KERNEL);
if(!input_keys_gpio){
retval = -1;
goto exit_entry;
}
for(i = 0; i < count; i++){
input_keys_gpio[i].m_gpio = of_get_gpio_flags(node, i, &flags);
input_keys_gpio[i].m_gpiod = gpio_to_desc(input_keys_gpio[i].m_gpio); //根据gpio引脚转换成gpio desc
input_keys_gpio[i].m_irq = gpiod_to_irq(input_keys_gpio[i].m_gpiod); //获取gpio中断号
input_keys_gpio[i].m_flag = flags & OF_GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW; //只获取低电平触发中断的标志
input_keys_gpio[i].m_code = KEY_1+i; //user key1,2
setup_timer(&input_keys_gpio[i].m_timer, input_key_timer_fn, (unsigned long)&input_keys_gpio[i]);
add_timer(&input_keys_gpio[i].m_timer);
}
//申请中断
for(i = 0; i < count; i++){
err = request_irq(input_keys_gpio[i].m_irq, input_key_irq, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "input_gpio_key", &input_keys_gpio[i]);
}
input_key_dev = input_allocate_device(); //分配一个 input_dev 结构体
if(input_key_dev == NULL){
printk(KERN_ERR "input_allocate_device filed");
retval = -1;
goto exit_entry;
}
input_key_dev->name = "input_key_dev";
//设置支持的输入事件类型
set_bit(EV_KEY, input_key_dev->evbit);
//set_bit(EV_LED, input_key_dev->evbit);
//设置key支持的事件码(支持哪些按键)
set_bit(KEY_1, input_key_dev->keybit);
set_bit(KEY_2, input_key_dev->keybit);
//注册一个输入设备
retval = input_register_device(input_key_dev);
exit_entry:
return retval;
}
static int input_key_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int retval = 0;
int count, i;
count = of_gpio_count(pdev->dev.of_node);
for(i = 0 ; i < count; i++){
free_irq(input_keys_gpio[i].m_irq, &input_keys_gpio[i]);
del_timer(&input_keys_gpio[i].m_timer);
}
kfree(input_keys_gpio);
if(input_key_dev != NULL){
input_unregister_device(input_key_dev);
input_free_device(input_key_dev);
input_key_dev = NULL;
}
return retval;
}
static const struct of_device_id input_key_table[] = {
{.compatible = "100ask,gpio_key"},
{ },
};
static struct platform_driver input_key_driver = {
.probe = input_key_probe,
.remove = input_key_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "InputKey", //会根据这个名字去匹配device
.of_match_table = input_key_table,
},
};
static int __init input_key_init(void)
{
platform_driver_register(&input_key_driver); //注册platfrom 驱动
return 0;
}
static void __exit input_key_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&input_key_driver);
}
module_init(input_key_init);
module_exit(input_key_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
最后
以上就是鲤鱼嚓茶最近收集整理的关于Linux Input 子系统一、基本框架分析二、 基于input子系统实现的按键驱动实例的全部内容,更多相关Linux内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复