准备工作:
配置多数据之前,先准备好数据库。之前已经有一个数据库ds1了,还需要再添加一个数据库ds2。
创建数据库ds2并添加一张表:
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` varchar(16) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(64) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL,
`class` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC
添加两条测试数据:
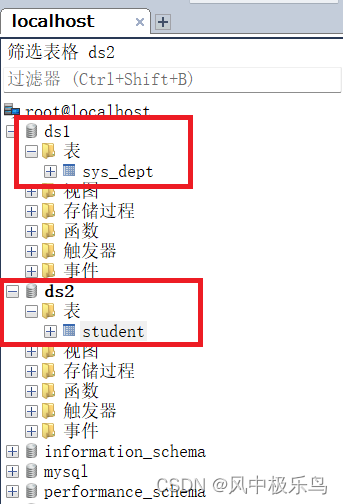
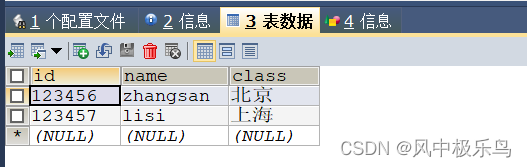 测试mysql库结构:
测试mysql库结构:
配置多数据源
01、修改项目数据库连接配置
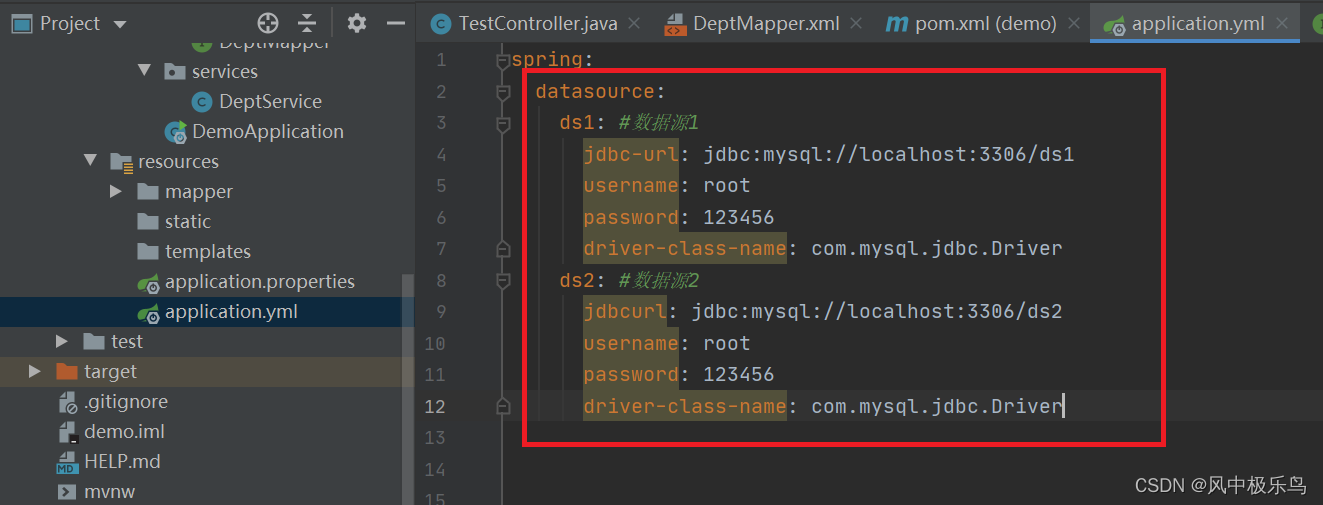 application.yml
application.yml
spring:
datasource:
ds1: #数据源1
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds1
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
ds2: #数据源2
jdbcurl: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds2
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# 配置mybatis规则
mybatis:
# config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: false
02、在mapper文件夹下创建两个文件夹,分别为ds1和ds2,同时将DeptMapper文件移动到ds1中。
ds1中的mapper文件使用的是数据源1;ds2中的则是数据源2。
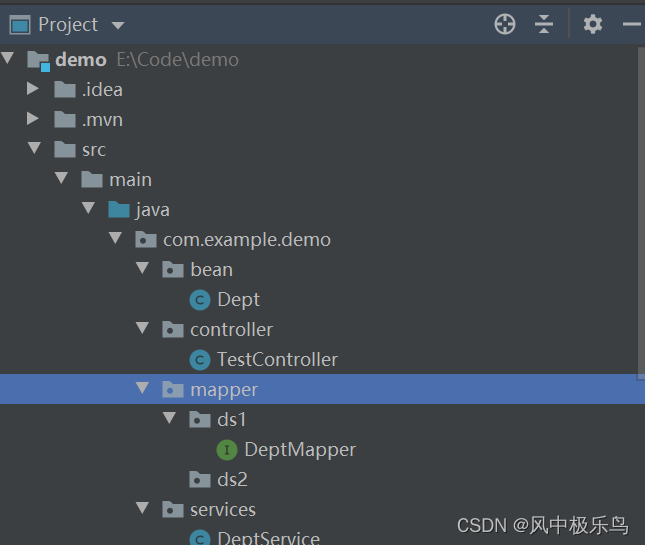 03、创建相关数据源配置文件。
03、创建相关数据源配置文件。
新建config文件夹,以后所有的配置文件都统一放在这里。
在此文件夹下创建两个配置文件:
Datasource1Configuration.java
package com.example.demo.config;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = {"com.example.demo.mapper.ds1"}, sqlSessionFactoryRef = "sqlSessionFactory1")
public class Datasource1Configuration {
@Value("${mybatis.mapper-locations}")
private String mapperLocation;
@Bean(name = "dataSource1")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.ds1") //读取application.yml中的配置参数映射成为一个对象
public DataSource dataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean("sqlSessionFactory1")
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("dataSource1") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
// mapper的xml形式文件位置必须要配置,不然将报错:no statement (这种错误也可能是mapper的xml中,namespace与项目的路径不一致导致)
bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(mapperLocation));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean("sqlSessionTemplate1")
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("sqlSessionFactory1") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
@Bean("transactionManager1")
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(@Qualifier("dataSource1")DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}
Datasource2Configuration.java
package com.example.demo.config;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = {"com.example.demo.mapper.ds2"}, sqlSessionFactoryRef = "sqlSessionFactory2")
public class Datasource2Configuration {
@Value("${mybatis.mapper-locations}")
private String mapperLocation;
@Bean(name = "dataSource2")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.ds2") //读取application.yml中的配置参数映射成为一个对象
public DataSource dataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean("sqlSessionFactory2")
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("dataSource2") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
// mapper的xml形式文件位置必须要配置,不然将报错:no statement (这种错误也可能是mapper的xml中,namespace与项目的路径不一致导致)
bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(mapperLocation));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean("sqlSessionTemplate2")
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("sqlSessionFactory2") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
@Bean("transactionManager2")
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(@Qualifier("dataSource2") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}
 到此,多数据源已经配置好了。下面就测试一下效果。
到此,多数据源已经配置好了。下面就测试一下效果。
测试多数据源
数据源1已经有调用了,再补充一个调用数据源2的mapper。
首先在bean目录下创建实体类:
Student.java
package com.example.demo.bean;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Student {
public String id;
public String name;
public String _class;
}
然后在ds2 文件夹下创建StudentMapper文件。
StudentMapper.java
package com.example.demo.mapper.ds2;
import com.example.demo.bean.Student;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
@Select("SELECT id,name,class as _class FROM `student` WHERE id=#{id}")
public Student getStudentById(String id);
}
最后在services文件夹下创建StudentService.java
package com.example.demo.services;
import com.example.demo.bean.Student;
import com.example.demo.mapper.ds2.StudentMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
StudentMapper studentMapper;
public Student getStudentById(String id)
{
return studentMapper.getStudentById(id);
}
}
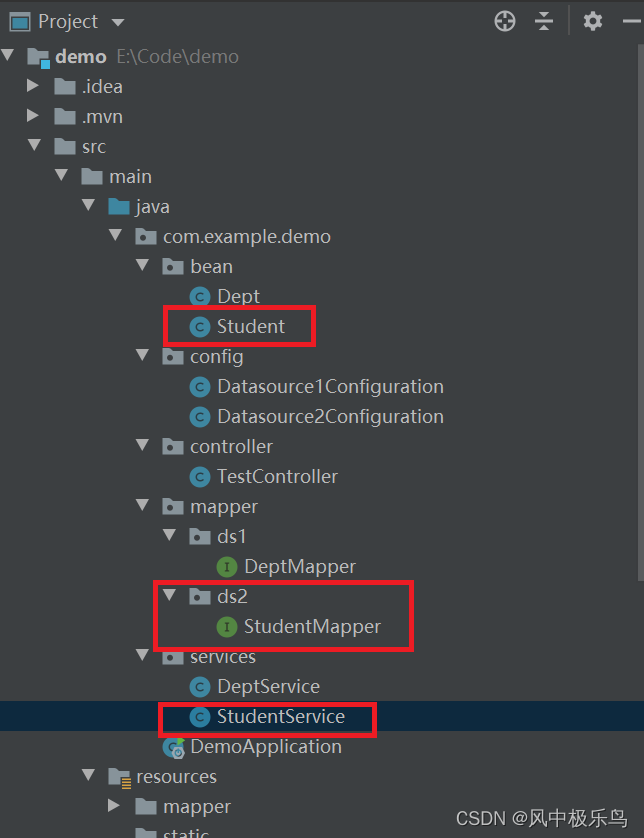
现在的项目目录结构如下:
 为了测试双数据源,在TestController中写一个新的测试接口:
为了测试双数据源,在TestController中写一个新的测试接口:
@Autowired
StudentService studentService;
@GetMapping("/get2Db")
public String get2DB(String id)
{
Student ss= studentService.getStudentById(id);
Dept dept=deptService.getDeptById("101");
return "数据源1中数据:"+dept.toString()+";数据源2中数据:"+ss.toString();
}
完整TestController.java
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.bean.Dept;
import com.example.demo.bean.Student;
import com.example.demo.services.DeptService;
import com.example.demo.services.StudentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping(value="/Hello",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String Hello(String pra){
return "Hello world !"+pra;
}
@Autowired
DeptService deptService;
//测试注解方式操作数据库
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/getDept")
public List<Dept> getDept(){
return deptService.getDept();
}
//XML方式
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/getDeptById")
public Dept getTheDept(@RequestParam("id") String id){
return deptService.getDeptById(id);
}
@Autowired
StudentService studentService;
@GetMapping("/get2Db")
public String get2DB(String id)
{
Student ss= studentService.getStudentById(id);
Dept dept=deptService.getDeptById("101");
return "数据源1中数据:"+dept.toString()+";数据源2中数据:"+ss.toString();
}
}
启动运行项目:
在浏览器地址栏中输入:http://localhost:8080/get2Db?id=123456
响应如图:
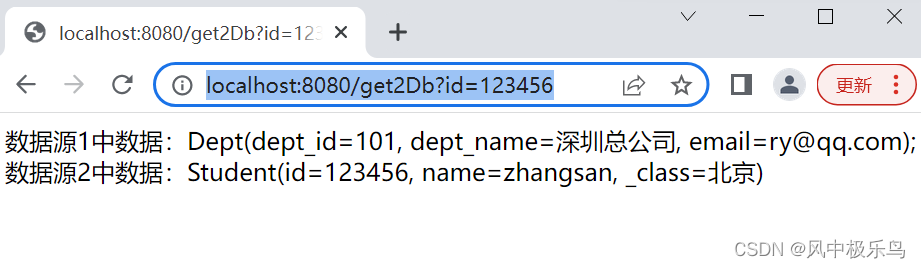 可知,双数据源中的数据已经全部可以正常取出来了。
可知,双数据源中的数据已经全部可以正常取出来了。
最后,集成druid
安装依赖:
在pom文件中增加:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.17</version>
</dependency>
更新安装依赖。
配置druid:
druid:
aop-patterns: com.example.demo.* #监控SpringBean
filters: stat,wall # 底层开启功能,stat(sql监控),wall(防火墙)
stat-view-servlet: # 配置监控页功能
enabled: true
login-username: admin
login-password: admin
resetEnable: false
web-stat-filter: # 监控web
enabled: true
urlPattern: /*
exclusions: '*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*'
filter:
stat: # 对上面filters里面的stat的详细配置
slow-sql-millis: 1000
logSlowSql: true
enabled: true
wall:
enabled: true
config:
drop-table-allow: false
此时完整的配置文件
applaction.yml
spring:
datasource:
ds1: #数据源1
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds1
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
ds2: #数据源2
jdbcurl: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds2
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
druid:
aop-patterns: com.example.demo.* #监控SpringBean
filters: stat,wall # 底层开启功能,stat(sql监控),wall(防火墙)
stat-view-servlet: # 配置监控页功能
enabled: true
login-username: admin
login-password: admin
resetEnable: false
web-stat-filter: # 监控web
enabled: true
urlPattern: /*
exclusions: '*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*'
filter:
stat: # 对上面filters里面的stat的详细配置
slow-sql-millis: 1000
logSlowSql: true
enabled: true
wall:
enabled: true
config:
drop-table-allow: false
# 配置mybatis规则
mybatis:
# config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: false
现在重启运行项目,之后在浏览器地址栏中输入:http://localhost:8080/druid/login.html
打开页面如图:
 输入admin/admin登录:
输入admin/admin登录:
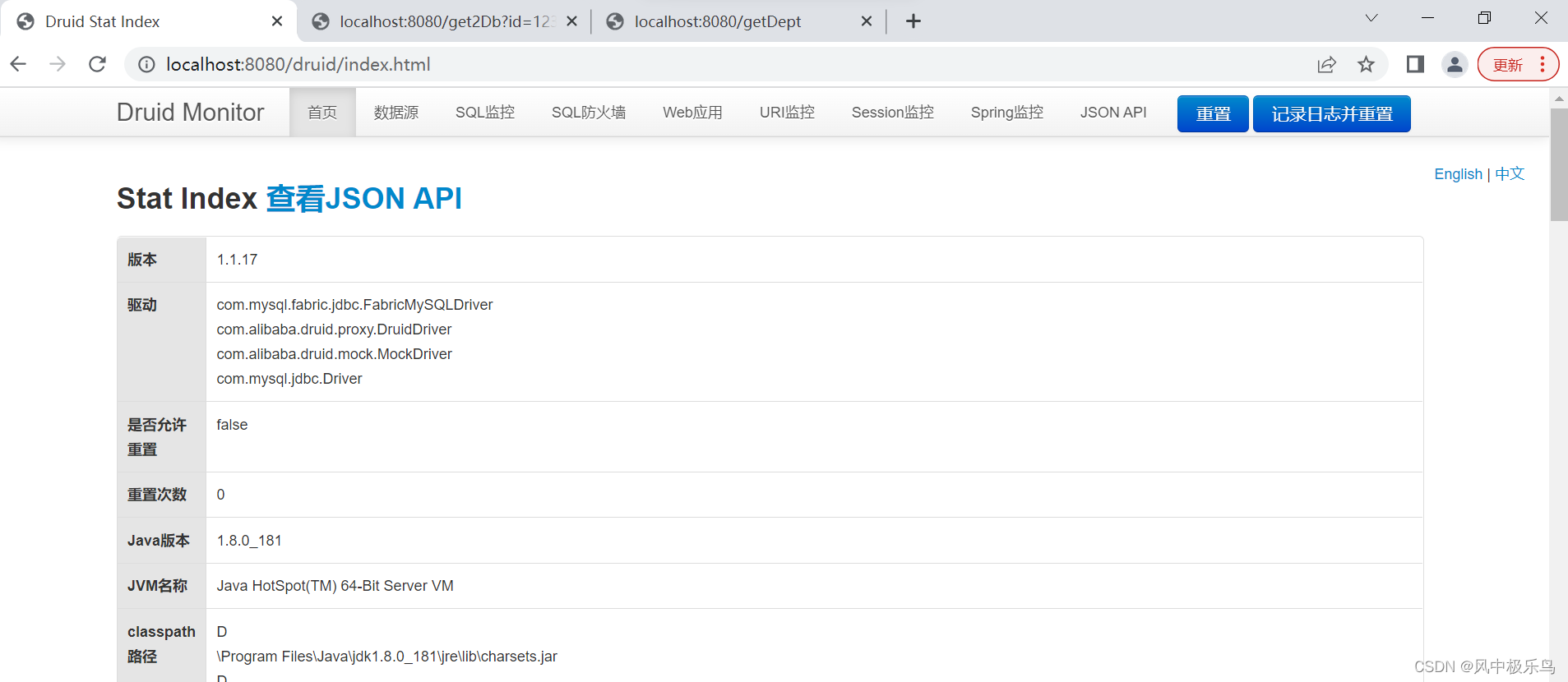
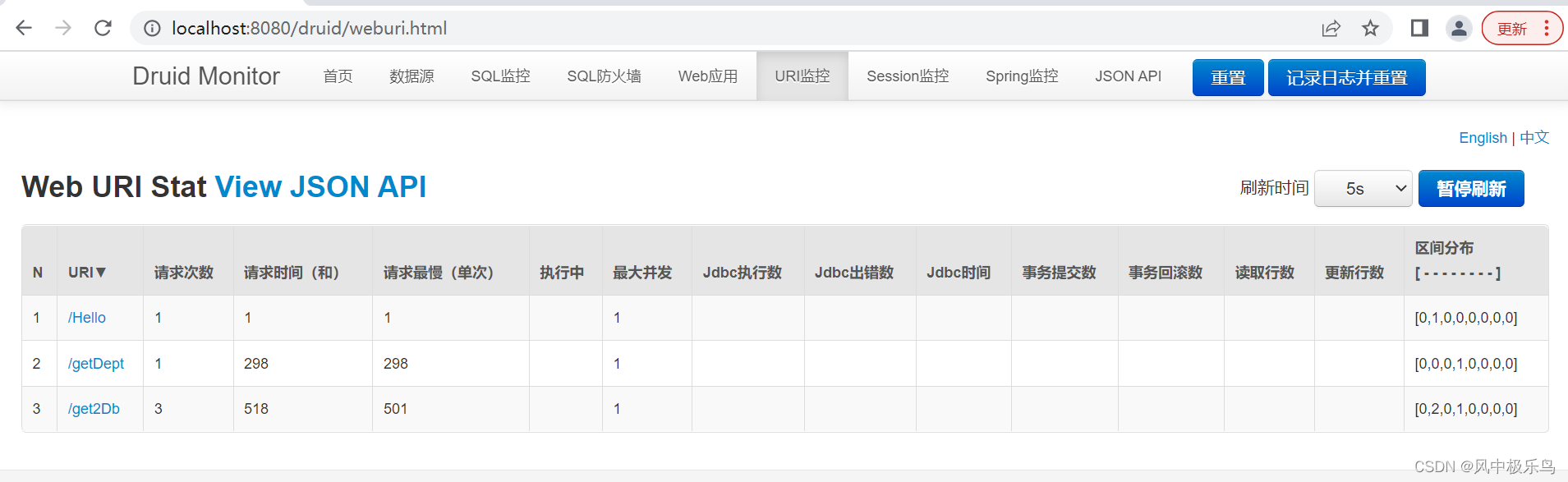 可以看到,普通的监控都是可以的,但是,数据源监控有问题,sql监控也不管用 。如果是单数据源的话,就没有这些问题。因此,还需要改进。具体怎么整,下一篇接着说。循序渐渐,不要嫌啰嗦。
可以看到,普通的监控都是可以的,但是,数据源监控有问题,sql监控也不管用 。如果是单数据源的话,就没有这些问题。因此,还需要改进。具体怎么整,下一篇接着说。循序渐渐,不要嫌啰嗦。

最后
以上就是漂亮小土豆最近收集整理的关于【03】idea搭建SpringBoot服务demo:集成mybaits+knief4j+netty-socketio的全部内容,更多相关【03】idea搭建SpringBoot服务demo内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复