上篇我们讲述了消息容器ChannelPipeline的相关知识,这篇我们来看下由它管理的,负责对I/O事件或者I/O操作进行拦截和处理,可以选择性的拦截和处理自己感兴趣的事件,也可以透传和终止事件的传递,也是由我们亲自实现的ChannelHandler业务处理。而Netty也帮我们实现一些通用的Handler,我们直接用就可以,前边写的例子中应该都有体会。我们还是来先看知识思维导图吧:
一,类关系继承图:由于Netty提供了很多Handler,例如:对I/O操作和事件进行预处理的,编解码的,流量整形、读写超时、日志等等,这里给出几个典型的编解码Handler的讲解,也是前边写的示例中我们用的。先看下类的关系图吧:
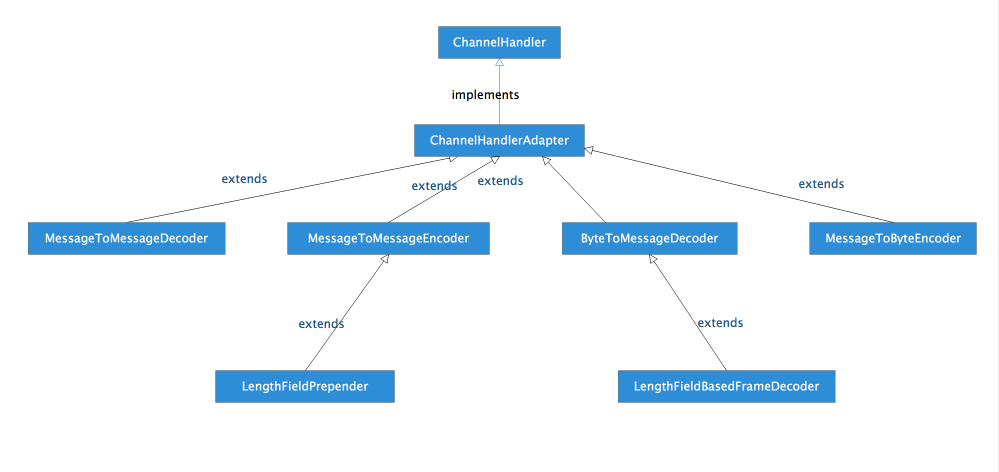
二,ChannelHandlerAdapter功能说明:看上边关系图,接口ChannelHandler提供了I/O操作和事件触发的一些方法,而ChannelHandlerAdapter类,则对所有接口实现都是事件透传,如果我们某个Handler相对某个或者某些事进行处理,只需要覆盖ChannelHandlerAdapter对应的方法即可,其它的直接继承父类ChannelHandlerAdapter即可。看下ChannelHandlerAdapter的实现事件怎么透传:
//说明:被@Skip注解的方法不会被调用,直接忽略;
//@Sharable:注解后多个ChannelPipeline公用一个ChannelHandler.
/**
* Return {@code true} if the implementation is {@link Sharable} and so can be added
* to different {@link ChannelPipeline}s.
*/
public boolean isSharable() {
/**
* Cache the result of {@link Sharable} annotation detection to workaround a condition. We use a
* {@link ThreadLocal} and {@link WeakHashMap} to eliminate the volatile write/reads. Using different
* {@link WeakHashMap} instances per {@link Thread} is good enough for us and the number of
* {@link Thread}s are quite limited anyway.
*
* See <a href="See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2289">#2289</a>.
*/
Class<?> clazz = getClass();
Map<Class<?>, Boolean> cache = InternalThreadLocalMap.get().handlerSharableCache();
Boolean sharable = cache.get(clazz);
if (sharable == null) {
sharable = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Sharable.class);
cache.put(clazz, sharable);
}
return sharable;
}
/**
* Calls {@link ChannelHandlerContext#read()} to forward
* to the next {@link ChannelHandler} in the {@link ChannelPipeline}.
*
* Sub-classes may override this method to change behavior.
*/
@Skip
@Override
public void read(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.read();
}
/**
* Calls {@link ChannelHandlerContext#write(Object)} to forward
* to the next {@link ChannelHandler} in the {@link ChannelPipeline}.
*
* Sub-classes may override this method to change behavior.
*/
@Skip
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
ctx.write(msg, promise);
}三,具体的实现类:
1,ByteToMessageDecoder:通过名字也很容易理解,就是为了方便我们将ByteBuf解码成业务POJO对象,为一个抽象的工具类,我们只需要继承它并实现decode方法即可。但是ByteToMessageDecoder并没有考虑TCP的粘包和拆包等问题,读半包需要我们自己处理。所以一般会继承它的子类来处理。看下源码吧:
//1,读信息
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//如果msg为ByteBuf,则进行解码,否则直接透传
if (msg instanceof ByteBuf) {
RecyclableArrayList out = RecyclableArrayList.newInstance();
try {
ByteBuf data = (ByteBuf) msg;
//判断cumulation是否为空,来判断是否缓存了半包消息。
first = cumulation == null;
if (first) {
//为空则是没有半包消息,直接复制
cumulation = data;
} else {
//有半包消息,则需要将data复制进行,进行组合。
cumulation = cumulator.cumulate(ctx.alloc(), cumulation, data);
}
//进行解码
callDecode(ctx, cumulation, out);
} catch (DecoderException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new DecoderException(t);
} finally {
if (cumulation != null && !cumulation.isReadable()) {
cumulation.release();
cumulation = null;
}
int size = out.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
ctx.fireChannelRead(out.get(i));
}
out.recycle();
}
} else {
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}
/**
* Called once data should be decoded from the given {@link ByteBuf}. This method will call
* {@link #decode(ChannelHandlerContext, ByteBuf, List)} as long as decoding should take place.
*
* @param ctx the {@link ChannelHandlerContext} which this {@link ByteToMessageDecoder} belongs to
* @param in the {@link ByteBuf} from which to read data
* @param out the {@link List} to which decoded messages should be added
*/
protected void callDecode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) {
try {
while (in.isReadable()) {
int outSize = out.size();
int oldInputLength = in.readableBytes();
//调用用户实现的decode方法
decode(ctx, in, out);
// Check if this handler was removed before continuing the loop.
// If it was removed, it is not safe to continue to operate on the buffer.
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/1664
if (ctx.isRemoved()) {
break;
}
//1,如果用户解码器没有消费ByteBuf,则说明是半包消息,需要继续读取后续的数据,直接退出循环;2,如果用户解码器消费了ByteBuf,说明可以继续进行;
if (outSize == out.size()) {
if (oldInputLength == in.readableBytes()) {
break;
} else {
continue;
}
}
//3,如果用户解码器没有消费ByteBuf,但是却多解码出一个或多个对象,则为异常
if (oldInputLength == in.readableBytes()) {
throw new DecoderException(
StringUtil.simpleClassName(getClass()) +
".decode() did not read anything but decoded a message.");
}
//4,如果是单条消息解码器,第一次解码完成之后直接退出循环。
if (isSingleDecode()) {
break;
}
}
} catch (DecoderException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable cause) {
throw new DecoderException(cause);
}
}2,MessageToMessageDecoder:通过名字可以知道它是将一个对象解码为其他对象,称作为二次解码器。ByteBuffer——>Java对象(httpRquest对象)——>其他Java(POJO)对象。相当于第二个环节。用户还是只需要实现decode方法即可。由于是对象到另个对象处理,没有半包问题,相对来说简单些。看下源码:
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
RecyclableArrayList out = RecyclableArrayList.newInstance();
try {
//进行类型判断
if (acceptInboundMessage(msg)) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
I cast = (I) msg;
try {
//调用我们写的decode方法
decode(ctx, cast, out);
} finally {
//释放msg对象
ReferenceCountUtil.release(cast);
}
} else {
out.add(msg);
}
} catch (DecoderException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new DecoderException(e);
} finally {
int size = out.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
ctx.fireChannelRead(out.get(i));
}
out.recycle();
}
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if the given message should be handled. If {@code false} it will be passed to the next
* {@link ChannelHandler} in the {@link ChannelPipeline}.
*/
public boolean acceptInboundMessage(Object msg) throws Exception {
return matcher.match(msg);
}3,LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder:为了解决粘包拆包导致的拆包问题,在以前的例子中 Netty(二)——粘包、拆包解决之道我们用过LineBasedFramDecoder和DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder来处理半包。这里说下LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder。回顾一下前边如何区分一个整包信息:a,固定长度,不足的前边补零,解码器只需要读取固定长度的字节处理即可;b,通过回车、换行符区分消息;c,通过分隔符区分整包消息;d,通过指定长度来标识整包消息等 。 而LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder就是通过长度进行区分的。适用通常由消息长度字段+消息体组成的协议。看下源码吧:
| lengthFieldOffset | 长度字段的偏移量 |
| lengthFieldLength | 字段的长度量 |
| lengthAdjustment | 要添加到长度字段值的补偿值 |
| initialBytesToStrip | 从解码帧中去除的第一段的字节数 |
/**
* 核心构造方法
* Creates a new instance.
*
* @param byteOrder
* the {@link ByteOrder} of the length field
* @param maxFrameLength
* the maximum length of the frame. If the length of the frame is
* greater than this value, {@link TooLongFrameException} will be
* thrown.
* @param lengthFieldOffset
* the offset of the length field
* @param lengthFieldLength
* the length of the length field
* @param lengthAdjustment
* the compensation value to add to the value of the length field
* @param initialBytesToStrip
* the number of first bytes to strip out from the decoded frame
* @param failFast
* If <tt>true</tt>, a {@link TooLongFrameException} is thrown as
* soon as the decoder notices the length of the frame will exceed
* <tt>maxFrameLength</tt> regardless of whether the entire frame
* has been read. If <tt>false</tt>, a {@link TooLongFrameException}
* is thrown after the entire frame that exceeds <tt>maxFrameLength</tt>
* has been read.
*/
public LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(
ByteOrder byteOrder, int maxFrameLength, int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength,
int lengthAdjustment, int initialBytesToStrip, boolean failFast) {
if (byteOrder == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("byteOrder");
}
if (maxFrameLength <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"maxFrameLength must be a positive integer: " +
maxFrameLength);
}
if (lengthFieldOffset < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"lengthFieldOffset must be a non-negative integer: " +
lengthFieldOffset);
}
if (initialBytesToStrip < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"initialBytesToStrip must be a non-negative integer: " +
initialBytesToStrip);
}
if (lengthFieldOffset > maxFrameLength - lengthFieldLength) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"maxFrameLength (" + maxFrameLength + ") " +
"must be equal to or greater than " +
"lengthFieldOffset (" + lengthFieldOffset + ") + " +
"lengthFieldLength (" + lengthFieldLength + ").");
}
this.byteOrder = byteOrder;
this.maxFrameLength = maxFrameLength;
this.lengthFieldOffset = lengthFieldOffset;
this.lengthFieldLength = lengthFieldLength;
this.lengthAdjustment = lengthAdjustment;
lengthFieldEndOffset = lengthFieldOffset + lengthFieldLength;
this.initialBytesToStrip = initialBytesToStrip;
this.failFast = failFast;
}
//进行解码,解码成功加入到list中
@Override
protected final void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
Object decoded = decode(ctx, in);
if (decoded != null) {
out.add(decoded);
}
}
/**
* 解码的具体实现,根据指定长度进行相应的切割,来保证整包
* Create a frame out of the {@link ByteBuf} and return it.
*
* @param ctx the {@link ChannelHandlerContext} which this {@link ByteToMessageDecoder} belongs to
* @param in the {@link ByteBuf} from which to read data
* @return frame the {@link ByteBuf} which represent the frame or {@code null} if no frame could
* be created.
*/
protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
if (discardingTooLongFrame) {
long bytesToDiscard = this.bytesToDiscard;
int localBytesToDiscard = (int) Math.min(bytesToDiscard, in.readableBytes());
in.skipBytes(localBytesToDiscard);
bytesToDiscard -= localBytesToDiscard;
this.bytesToDiscard = bytesToDiscard;
failIfNecessary(false);
}
if (in.readableBytes() < lengthFieldEndOffset) {
return null;
}
int actualLengthFieldOffset = in.readerIndex() + lengthFieldOffset;
long frameLength = getUnadjustedFrameLength(in, actualLengthFieldOffset, lengthFieldLength, byteOrder);
if (frameLength < 0) {
in.skipBytes(lengthFieldEndOffset);
throw new CorruptedFrameException(
"negative pre-adjustment length field: " + frameLength);
}
frameLength += lengthAdjustment + lengthFieldEndOffset;
if (frameLength < lengthFieldEndOffset) {
in.skipBytes(lengthFieldEndOffset);
throw new CorruptedFrameException(
"Adjusted frame length (" + frameLength + ") is less " +
"than lengthFieldEndOffset: " + lengthFieldEndOffset);
}
if (frameLength > maxFrameLength) {
long discard = frameLength - in.readableBytes();
tooLongFrameLength = frameLength;
if (discard < 0) {
// buffer contains more bytes then the frameLength so we can discard all now
in.skipBytes((int) frameLength);
} else {
// Enter the discard mode and discard everything received so far.
discardingTooLongFrame = true;
bytesToDiscard = discard;
in.skipBytes(in.readableBytes());
}
failIfNecessary(true);
return null;
}
// never overflows because it's less than maxFrameLength
int frameLengthInt = (int) frameLength;
if (in.readableBytes() < frameLengthInt) {
return null;
}
if (initialBytesToStrip > frameLengthInt) {
in.skipBytes(frameLengthInt);
throw new CorruptedFrameException(
"Adjusted frame length (" + frameLength + ") is less " +
"than initialBytesToStrip: " + initialBytesToStrip);
}
in.skipBytes(initialBytesToStrip);
// extract frame
int readerIndex = in.readerIndex();
int actualFrameLength = frameLengthInt - initialBytesToStrip;
ByteBuf frame = extractFrame(ctx, in, readerIndex, actualFrameLength);
in.readerIndex(readerIndex + actualFrameLength);
return frame;
}4,MessageToByteEncoder:负责将POJO对象编码为ByteBuf,用户只需继承此类,实现encode方法即可。相对容易理解,看源码:
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = null;
try {
//判断当前编码器是否支持要发送的消息类型
if (acceptOutboundMessage(msg)) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
I cast = (I) msg;
buf = allocateBuffer(ctx, cast, preferDirect);
try {
//调用实现直接编码
encode(ctx, cast, buf);
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(cast);
}
if (buf.isReadable()) {
//发送
ctx.write(buf, promise);
} else {
buf.release();
ctx.write(Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER, promise);
}
buf = null;
} else {
ctx.write(msg, promise);
}
} catch (EncoderException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new EncoderException(e);
} finally {
if (buf != null) {
//释放缓冲区
buf.release();
}
}
}
/**对于直接内存分配ioBuffer(堆外内存),对于堆内存通过heapBuffer进行分配
* Allocate a {@link ByteBuf} which will be used as argument of {@link #encode(ChannelHandlerContext, I, ByteBuf)}.
* Sub-classes may override this method to returna {@link ByteBuf} with a perfect matching {@code initialCapacity}.
*/
protected ByteBuf allocateBuffer(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, @SuppressWarnings("unused") I msg,
boolean preferDirect) throws Exception {
if (preferDirect) {
return ctx.alloc().ioBuffer();
} else {
return ctx.alloc().heapBuffer();
}
}5,MessageToMessageEncoder:将一个POJO对象编码成另一个对象,例如:POJO Java对象——>HttpResponse对象——>ByteBuf。我们也是继承此类,实现encode接口方法即可。看源码:
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
RecyclableArrayList out = null;
try {
if (acceptOutboundMessage(msg)) {
out = RecyclableArrayList.newInstance();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
I cast = (I) msg;
try {
encode(ctx, cast, out);
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(cast);
}
if (out.isEmpty()) {
out.recycle();
out = null;
throw new EncoderException(
StringUtil.simpleClassName(this) + " must produce at least one message.");
}
} else {
ctx.write(msg, promise);
}
} catch (EncoderException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new EncoderException(t);
} finally {
if (out != null) {
final int sizeMinusOne = out.size() - 1;
if (sizeMinusOne == 0) {
ctx.write(out.get(0), promise);
} else if (sizeMinusOne > 0) {
// Check if we can use a voidPromise for our extra writes to reduce GC-Pressure
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2525
ChannelPromise voidPromise = ctx.voidPromise();
boolean isVoidPromise = promise == voidPromise;
for (int i = 0; i < sizeMinusOne; i ++) {
ChannelPromise p;
if (isVoidPromise) {
p = voidPromise;
} else {
p = ctx.newPromise();
}
ctx.write(out.get(i), p);
}
ctx.write(out.get(sizeMinusOne), promise);
}
out.recycle();
}
}
}6,LengthFieldPrePender:如果协议中第一个字段为长度字段,此编码器可以计算当前待发送消息的二进制字节长度,添加到ByteBuf的缓冲区头中,编码后的消息组成:长度字段+原消息。也是和上边相对应的,看下源码:
/**
* 构造方法
* Creates a new instance.
*
* @param lengthFieldLength the length of the prepended length field.
* Only 1, 2, 3, 4, and 8 are allowed.
* @param lengthAdjustment the compensation value to add to the value
* of the length field
* @param lengthIncludesLengthFieldLength
* if {@code true}, the length of the prepended
* length field is added to the value of the
* prepended length field.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if {@code lengthFieldLength} is not 1, 2, 3, 4, or 8
*/
public LengthFieldPrepender(int lengthFieldLength, int lengthAdjustment, boolean lengthIncludesLengthFieldLength) {
if (lengthFieldLength != 1 && lengthFieldLength != 2 &&
lengthFieldLength != 3 && lengthFieldLength != 4 &&
lengthFieldLength != 8) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"lengthFieldLength must be either 1, 2, 3, 4, or 8: " +
lengthFieldLength);
}
this.lengthFieldLength = lengthFieldLength;
this.lengthIncludesLengthFieldLength = lengthIncludesLengthFieldLength;
this.lengthAdjustment = lengthAdjustment;
}
//编码实现
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
int length = msg.readableBytes() + lengthAdjustment;
if (lengthIncludesLengthFieldLength) {
length += lengthFieldLength;
}
//调整后的长度<0,剖出异常
if (length < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Adjusted frame length (" + length + ") is less than zero");
}
//对消息长度所占字节进行判断:
switch (lengthFieldLength) {
case 1:
//1最大可以为255个字节2^8,writeByte
if (length >= 256) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"length does not fit into a byte: " + length);
}
out.add(ctx.alloc().buffer(1).writeByte((byte) length));
break;
case 2:
//2最大为2^16字节,writeShort
if (length >= 65536) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"length does not fit into a short integer: " + length);
}
out.add(ctx.alloc().buffer(2).writeShort((short) length));
break;
case 3:
//3最大为2^24字节,writeMedium
if (length >= 16777216) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"length does not fit into a medium integer: " + length);
}
out.add(ctx.alloc().buffer(3).writeMedium(length));
break;
case 4:
//4,writeInt
out.add(ctx.alloc().buffer(4).writeInt(length));
break;
case 8:
//8,writeLong
out.add(ctx.alloc().buffer(8).writeLong(length));
break;
default:
throw new Error("should not reach here");
}
//添加到List<Object> out中
out.add(msg.retain());
}好,这篇讲了ChannelHandler的相关知识,主要讲述了三个解码器和对应的编码器,对比着看这些源码其实会很容易的。我们不仅可以使用netty提供的一些默认的Handler,还可以根据这些Handler的源码学习,来写出适合自己业务更加合理的Handler。好,继续中……
最后
以上就是和谐奇异果最近收集整理的关于Netty(十三)——ChannelHandler之意的全部内容,更多相关Netty(十三)——ChannelHandler之意内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复