文章目录
- 运动学模型
- 小车坐标系下运动模型分析
- 小车坐标系与世界坐标系转换
- 小车坐标系转换到世界坐标系
- 世界坐标系转换到小车坐标系
- 小车运动与电机转动对应关系
- 完整代码
运动学模型
三轮全向轮小车结构示意图如图所示:
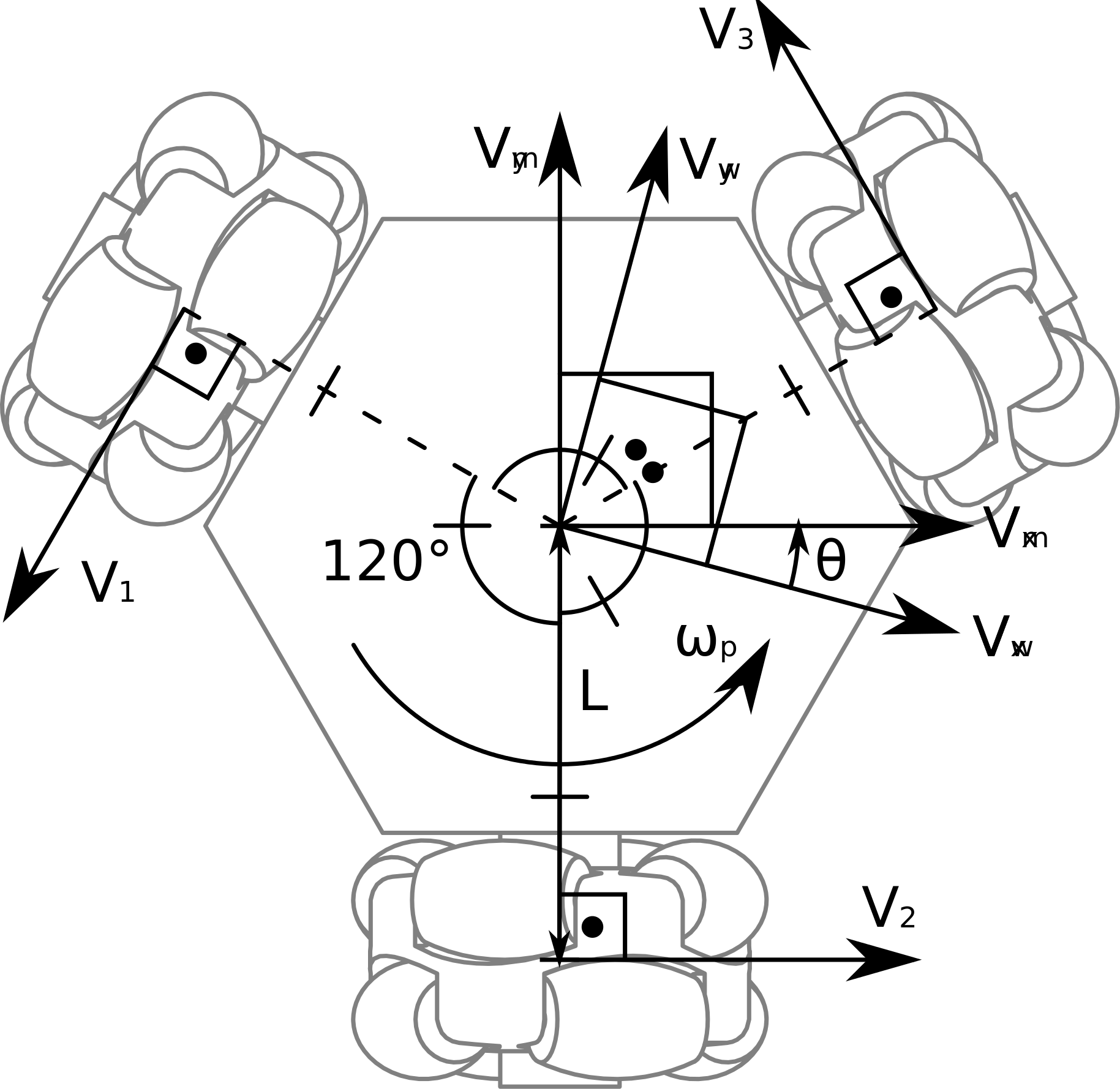
图中V1,V2和V3也分别称为V_left,V_back和V_right,对应三个轮子的转速,转动的正方向如图所示。
小车坐标系下运动模型分析
-
V x m = 2 V 2 − V 1 − V 3 3 {V}_x^m=frac{2V_2-V_1-V3}{3} Vxm=32V2−V1−V3
-
V y m = 3 V 3 − 3 V 1 3 {V}_y^m=frac{sqrt{3}V_3-sqrt{3}V_1}{3} Vym=33V3−3V1
-
ω p = V 1 + V 2 + V 3 3 L {omega}_p=frac{V_1+V_2+V_3}{3L} ωp=3LV1+V2+V3
对应C语言代码如下:
bool forwardMobile(smart_car::KinematicsForward::Request &request, smart_car::KinematicsForward::Response &response) {
response.output.x = ((2.0L * request.input.v_back) - request.input.v_left - request.input.v_right) / 3.0L;
response.output.y = ((sqrt3 * request.input.v_right) - (sqrt3 * request.input.v_left)) / 3.0L;
response.output.theta = (request.input.v_left + request.input.v_back + request.input.v_right) / L3;
return true;
}
小车坐标系与世界坐标系转换
小车坐标系转换到世界坐标系
小车坐标系转换到世界坐标系的公式如下:
-
V x w = cos ( θ ) V x m − sin ( θ ) V y m {V}_x^w=cos(theta)V_x^m-sin(theta)V_y^m Vxw=cos(θ)Vxm−sin(θ)Vym
-
V y w = sin ( θ ) V x m + cos ( θ ) V y m {V}_y^w=sin(theta)V_x^m+cos(theta)V_y^m Vyw=sin(θ)Vxm+cos(θ)Vym
其中
V
x
w
{V}_x^w
Vxw与
V
y
w
{V}_y^w
Vyw分别代表世界坐标系下
x
x
x与
y
y
y轴的方向,
V
x
m
{V}_x^m
Vxm与
V
y
m
{V}_y^m
Vym分别代表小车坐标系下
x
x
x与
y
y
y轴的方向。
对应c语言代码如下:
void mobileToWorldCore(double Vxm, double Vym, double& Vxw, double& Vyw) {
Vxw = (std::cos(theta) * Vxm) - (std::sin(theta) * Vym);
Vyw = (std::sin(theta) * Vxm) + (std::cos(theta) * Vym);
}
世界坐标系转换到小车坐标系
同理,小车坐标系转换到小车坐标系的公式如下:
-
V x m = cos ( θ ) V x w + sin ( θ ) V y w {V}_x^m=cos(theta)V_x^w+sin(theta)V_y^w Vxm=cos(θ)Vxw+sin(θ)Vyw
-
V y m = − sin ( θ ) V x w + cos ( θ ) V y w {V}_y^m=-sin(theta)V_x^w+cos(theta)V_y^w Vym=−sin(θ)Vxw+cos(θ)Vyw
对应c语言代码如下:
void worldToMobileCore(double Vxw, double Vyw, double& Vxm, double& Vym) {
Vxm = (std::cos(theta) * Vxw) + (std::sin(theta) * Vyw);
Vym = - (std::sin(theta) * Vxw) + (std::cos(theta) * Vyw);
}
小车运动与电机转动对应关系
-
V 1 = − V x m 2 − 3 V y m 2 + L ω p {V}_1=-frac{V_x^m}{2}-frac{sqrt{3}V_y^m}{2}+Lomega_p V1=−2Vxm−23Vym+Lωp
-
V 2 = V x m + L ω p {V}_2=V_x^m+Lomega_p V2=Vxm+Lωp
-
V 3 = − V x m 2 + 3 V y m 2 + L ω p {V}_3=-frac{V_x^m}{2}+frac{sqrt{3}V_y^m}{2}+Lomega_p V3=−2Vxm+23Vym+Lωp
对应C语言代码为:
bool inverseMobile(smart_car::KinematicsInverse::Request &request, smart_car::KinematicsInverse::Response &response) {
long double V__m_x2 = - request.input.x / 2.0L;
long double sqrt3V__m_y2 = (sqrt3 * request.input.y) / 2.0L;
long double Lomega_p = L * request.input.theta;
response.output.v_left = V__m_x2 - sqrt3V__m_y2 + Lomega_p;
response.output.v_back = request.input.x + Lomega_p;
response.output.v_right = V__m_x2 + sqrt3V__m_y2 + Lomega_p;
return true;
完整代码
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/Pose2D.h>
#include <sensor_msgs/JointState.h>
#include <smart_car/FrameToFrame.h>
#include <smart_car/KinematicsForward.h>
#include <smart_car/KinematicsInverse.h>
#include <kdl/frames.hpp>
#include <kdl_parser/kdl_parser.hpp>
long double L;
long double L3;
long double sqrt3;
long double theta = 0;
void mobileToWorldCore(double Vxm, double Vym, double& Vxw, double& Vyw) {
Vxw = (std::cos(theta) * Vxm) - (std::sin(theta) * Vym);
Vyw = (std::sin(theta) * Vxm) + (std::cos(theta) * Vym);
}
bool mobileToWorld(smart_car::FrameToFrame::Request &request, smart_car::FrameToFrame::Response &response) {
mobileToWorldCore(request.input.x, request.input.y, response.output.x, response.output.y);
}
void worldToMobileCore(double Vxw, double Vyw, double& Vxm, double& Vym) {
Vxm = (std::cos(theta) * Vxw) + (std::sin(theta) * Vyw);
Vym = - (std::sin(theta) * Vxw) + (std::cos(theta) * Vyw);
}
bool worldToMobile(smart_car::FrameToFrame::Request &request, smart_car::FrameToFrame::Response &response) {
worldToMobileCore(request.input.x, request.input.y, response.output.x, response.output.y);
}
bool forwardMobile(smart_car::KinematicsForward::Request &request, smart_car::KinematicsForward::Response &response) {
response.output.x = ((2.0L * request.input.v_back) - request.input.v_left - request.input.v_right) / 3.0L;
response.output.y = ((sqrt3 * request.input.v_right) - (sqrt3 * request.input.v_left)) / 3.0L;
response.output.theta = (request.input.v_left + request.input.v_back + request.input.v_right) / L3;
return true;
}
bool forwardWorld(smart_car::KinematicsForward::Request &request, smart_car::KinematicsForward::Response &response) {
forwardMobile(request, response);
mobileToWorldCore(response.output.x, response.output.y, response.output.x, response.output.y);
return true;
}
bool inverseMobile(smart_car::KinematicsInverse::Request &request, smart_car::KinematicsInverse::Response &response) {
long double V__m_x2 = - request.input.x / 2.0L;
long double sqrt3V__m_y2 = (sqrt3 * request.input.y) / 2.0L;
long double Lomega_p = L * request.input.theta;
response.output.v_left = V__m_x2 - sqrt3V__m_y2 + Lomega_p;
response.output.v_back = request.input.x + Lomega_p;
response.output.v_right = V__m_x2 + sqrt3V__m_y2 + Lomega_p;
return true;
}
bool inverseWorld(smart_car::KinematicsInverse::Request &request, smart_car::KinematicsInverse::Response &response) {
worldToMobileCore(request.input.x, request.input.y, request.input.x, request.input.y);
inverseMobile(request, response);
return true;
}
void onPoseWorldMessage(const geometry_msgs::Pose2D::ConstPtr& input){
theta = input->theta;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "kinematics");
ros::NodeHandle node;
{
std::string description;
if(!node.getParam("robot_description",description)) {
ROS_ERROR("Could not find '/robot_description'.");
return -1;
}
KDL::Tree tree;
if (!kdl_parser::treeFromString(description, tree)) {
ROS_ERROR("Failed to construct KDL tree.");
return -1;
}
KDL::Chain chain;
if (!tree.getChain("base_link", "rim_back_link", chain)) {
ROS_ERROR("Failed to get chain from KDL tree.");
return -1;
}
KDL::Frame frame = chain.getSegment(0).pose(0);
L = std::sqrt(std::pow(frame.p.x() - 0.0L, 2.0L) + std::pow(frame.p.y() - 0.0L, 2.0L));
node.setParam("parameter/wheel/distance", (double) L);
L3 = 3.0L * L;
sqrt3 = std::sqrt(3.0L);
double parameter;
if (!node.getParam("parameter/initial/theta", parameter)) {
parameter = 0;
}
theta = parameter;
}
ros::ServiceServer forwardMobileService = node.advertiseService("kinematics_forward_mobile", forwardMobile);
ros::ServiceServer forwardWorldService = node.advertiseService("kinematics_forward_world" , forwardWorld );
ros::ServiceServer inverseMobileService = node.advertiseService("kinematics_inverse_mobile", inverseMobile);
ros::ServiceServer inverseWorldService = node.advertiseService("kinematics_inverse_world" , inverseWorld );
ros::ServiceServer mobileToWorldService = node.advertiseService("kinematics_mobile_to_world" , mobileToWorld);
ros::ServiceServer worldToMobileService = node.advertiseService("kinematics_world_to_mobile" , worldToMobile);
ros::Subscriber subscriber = node.subscribe("pose/world", 1, onPoseWorldMessage);
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
最后
以上就是舒心发卡最近收集整理的关于ROS——Gazebo仿真——全向轮小车——运动学模型分析运动学模型小车坐标系下运动模型分析小车坐标系与世界坐标系转换小车运动与电机转动对应关系完整代码的全部内容,更多相关ROS——Gazebo仿真——全向轮小车——运动学模型分析运动学模型小车坐标系下运动模型分析小车坐标系与世界坐标系转换小车运动与电机转动对应关系完整代码内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复