需求:
同一位置不同时间拍20张照片或多或少有些偏移,需要矫正。
解决思路:
原理就不介绍了,就是简单的图片配准(找关键点、关键点匹配、筛选关键点、计算变换矩阵、变换)
参考:
网上搜了下大致有两种思路,试过效果都不错:
-
一、利用ORB/SURF提取特征点、查找单应性矩阵、对图片变换
stackoverflow上一个回答(ORB)
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6418742/how-to-register-an-image-manually-image-registration
OpenCV的图像配准融合(SURF)
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27737701/article/details/82289607
Opencv官网对这一块的介绍
https://docs.opencv.org/3.4.2/db/d61/group__reg.html -
二、Image Alignment (ECC) in OpenCV
这个介绍的比较详细了
https://www.learnopencv.com/image-alignment-ecc-in-opencv-c-python/
使用:
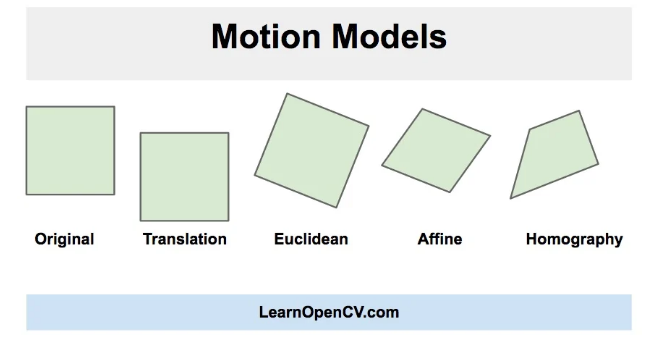
opencv配准对其时候有四种方式:平移、欧几里得、仿射、单应。变换矩阵详细介绍
具体使用哪一种看自己需求:比如我只希望进行图片的平移和旋转,不希望造成图片的畸变,所以我用Euclidean。
代码:
就是摘自上边的链接利用ORB/SURF提取特征点、查找单应性矩阵、对图片变换、Image Alignment (ECC) in OpenCV 细微的改动了下。
利用ORB/SURF提取特征点、查找单应性矩阵、对图片变换
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include "opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
const int MAX_FEATURES = 500;
const float GOOD_MATCH_PERCENT = 0.15f;
void alignImages(Mat &im1, Mat &im2, Mat &im1Reg, Mat &h)
{
Mat im1Gray, im2Gray;
cvtColor(im1, im1Gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(im2, im2Gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
// Variables to store keypoints and descriptors
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints1, keypoints2;
Mat descriptors1, descriptors2;
// Detect ORB features and compute descriptors.
Ptr<Feature2D> orb = ORB::create(MAX_FEATURES);
orb->detectAndCompute(im1Gray, Mat(), keypoints1, descriptors1);
orb->detectAndCompute(im2Gray, Mat(), keypoints2, descriptors2);
// Match features.
std::vector<DMatch> matches;
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");
matcher->match(descriptors1, descriptors2, matches, Mat());
// Sort matches by score
std::sort(matches.begin(), matches.end());
// Remove not so good matches
const int numGoodMatches = matches.size() * GOOD_MATCH_PERCENT;
matches.erase(matches.begin()+numGoodMatches, matches.end());
// Draw top matches
Mat imMatches;
drawMatches(im1, keypoints1, im2, keypoints2, matches, imMatches);
imwrite("matches.jpg", imMatches);
// Extract location of good matches
std::vector<Point2f> points1, points2;
for( size_t i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++ )
{
points1.push_back( keypoints1[ matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
points2.push_back( keypoints2[ matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
}
// Find homography
h = findHomography( points1, points2, RANSAC );
// Use homography to warp image
warpPerspective(im1, im1Reg, h, im2.size());
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// Read reference image
string refFilename("form.jpg");
cout << "Reading reference image : " << refFilename << endl;
Mat imReference = imread(refFilename);
// Read image to be aligned
string imFilename("scanned-form.jpg");
cout << "Reading image to align : " << imFilename << endl;
Mat im = imread(imFilename);
// Registered image will be resotred in imReg.
// The estimated homography will be stored in h.
Mat imReg, h;
// Align images
cout << "Aligning images ..." << endl;
alignImages(im, imReference, imReg, h);
// Write aligned image to disk.
string outFilename("aligned.jpg");
cout << "Saving aligned image : " << outFilename << endl;
imwrite(outFilename, imReg);
// Print estimated homography
cout << "Estimated homography : n" << h << endl;
}
Image Alignment (ECC) in OpenCV
int main(int, char **) {
// 【1】图像对齐(配准)
// 读取图像
Mat im1 = imread("/home/yx/Desktop/11/_0.png");
Mat im2 = imread("/home/yx/Desktop/11/_18.png");
// 将图像转换为灰度;
Mat im1_gray, im2_gray;
cvtColor(im1, im1_gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(im2, im2_gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
// 定义运动模型
const int warp_mode = MOTION_EUCLIDEAN;
// MOTION_TRANSLATION 平移
// MOTION_EUCLIDEAN 欧几里得
// MOTION_AFFINE 仿射
// MOTION_HOMOGRAPHY 单应性
// 根据运动模型设置2x3或3x3变形矩阵。
Mat warp_matrix;
// 初始化矩阵以进行标识
if ( warp_mode == MOTION_HOMOGRAPHY ) {
warp_matrix = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_32F);
} else {
warp_matrix = Mat::eye(2, 3, CV_32F);
}
// 指定迭代次数。
int number_of_iterations = 50;
// 指定两次迭代之间相关系数增量的阈值
double termination_eps = 1e-10;
// 定义终止条件
TermCriteria criteria (TermCriteria::COUNT +
TermCriteria::EPS,
number_of_iterations,
termination_eps);
//运行ECC算法。结果存储在warp_matrix中。
findTransformECC(
im1_gray,
im2_gray,
warp_matrix,
warp_mode,
criteria
);
// 存放变形的图像。
Mat im2_aligned;
warpAffine(im2, im2_aligned, warp_matrix, im1.size(), INTER_LINEAR + WARP_INVERSE_MAP);
// 显示最终结果
imshow("Image 2", im2);
imshow("Image 2 Aligned", im2_aligned);
//【2】图像平滑 (高斯滤波)
qint32 kernel_length = 3;
GaussianBlur(im2_aligned, im2_aligned, Size(kernel_length, kernel_length), 0, 0);
imshow("Image 2 Aligned GaussianBlur", im2_aligned);
//【3】图像去血管
waitKey(0);
}
最后
以上就是谦让镜子最近收集整理的关于利用opencv实现图片的配准/对齐的全部内容,更多相关利用opencv实现图片内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复