你已经不是小宝宝了,要学会自己找资料了,本文就不过多介绍一些基础细节了,我来说下这个应用的结构
首先这个应用包含了Client和Service,也就是客户端和服务端,因为我懒,不想写两个App,所以做了一些标识的区分,我准备了两台手机进行测试,一台是三星,一台是小米,小米开启Ap热点,好的,那么开始吧。
Service
首先,我们在小米手机上打开Service
private void initTopService() {
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(PORT);
Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
String remoteIP = clientSocket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
int remotePort = clientSocket.getLocalPort();
Log.e(MainActivity.TAG, "A client connected. IP:" + remoteIP + ", Port: " + remotePort);
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(clientSocket.getInputStream()));
out = new PrintStream(clientSocket.getOutputStream(), true, "utf-8");
while (true) {
String tmp = in.readLine();
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(tmp)) {
Message message = mHandler.obtainMessage();
message.obj = tmp;
message.what = H_DATA;
mHandler.sendMessage(message);
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(MainActivity.TAG, "serverSocket" + e.toString());
}
}
我们来分析一下这段代码,这段代码通过ServerSocket连接一个端口,这个端口是我写固定的:5000,实际上你只要对的上,写多少都行,然后就是一些常规操作了,我获取了输出流和输入流in和out,通过他们我就可以进行读写操作了,读的话这个里进行了死循环,只要读取到内容,我就通过Hander发送出去更新UI即可,那么输入流,实际上只需要
out.println(text);
只需要通过println就可以写入,也就是发送给Client了,服务端比较简单,到这里就没有东西了,我们再来看下客户端
Client
首先我要确保WIFI是否连接,如果连接了我就直接连接Service即可,但是如果没有连接的话,我应该做什么处理呢?所以我就有了如下的这段代码
if (WifiManager.getInstance().isWifiConnect(this)) {
Intent intent = new Intent(this, ChatActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("type","client");
startActivity(intent);
return;
}
if (!WifiManager.getInstance().isWifiEnabled()) {
WifiManager.getInstance().setWifiEnabled(true);
}
WifiManager.getInstance().startScan();
我先判断了WIFI是否连接,如果连接了我就跳转到聊天的界面,如果没有连接,我就判断WIFI有没有打开并且没有打开的话我就去打开,接着我就开始搜索设备了,如下界面:
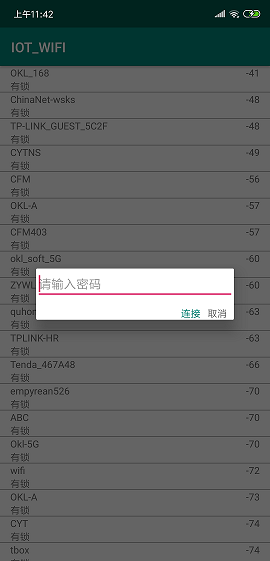
接着我会通过WIFIConfig去连接WIFI
/**
* 创建WIFI信息
*
* @param SSID
* @param Password
* @param Type
* @return
*/
public WifiConfiguration createWifiInfo(String SSID, String Password, String Type) {
WifiConfiguration config = new WifiConfiguration();
config.allowedAuthAlgorithms.clear();
config.allowedGroupCiphers.clear();
config.allowedKeyManagement.clear();
config.allowedPairwiseCiphers.clear();
config.allowedProtocols.clear();
config.SSID = """ + SSID + """;
if (Type.contains("WEP") || Type.contains("wep")) {
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(Password)) {
if (isHexWepKey(Password)) {
config.wepKeys[0] = Password;
} else {
config.wepKeys[0] = """ + Password + """;
}
}
config.allowedAuthAlgorithms.set(WifiConfiguration.AuthAlgorithm.OPEN);
config.allowedAuthAlgorithms.set(WifiConfiguration.AuthAlgorithm.SHARED);
config.allowedKeyManagement.set(WifiConfiguration.KeyMgmt.NONE);
config.wepTxKeyIndex = 0;
} else if (Type.contains("WPA") || Type.contains("wpa")) {
config.preSharedKey = """ + Password + """;
config.allowedAuthAlgorithms.set(WifiConfiguration.AuthAlgorithm.OPEN);
config.allowedGroupCiphers.set(WifiConfiguration.GroupCipher.TKIP);
config.allowedGroupCiphers.set(WifiConfiguration.GroupCipher.CCMP);
config.allowedKeyManagement.set(WifiConfiguration.KeyMgmt.WPA_PSK);
config.allowedPairwiseCiphers.set(WifiConfiguration.PairwiseCipher.TKIP);
config.allowedPairwiseCiphers.set(WifiConfiguration.PairwiseCipher.CCMP);
config.allowedProtocols.set(WifiConfiguration.Protocol.RSN);
config.allowedProtocols.set(WifiConfiguration.Protocol.WPA);
config.status = WifiConfiguration.Status.ENABLED;
} else {
config.allowedKeyManagement.set(WifiConfiguration.KeyMgmt.NONE);
}
return config;
}
/**
* 是否十六进制的密码
*
* @param wepKey
* @return
*/
private boolean isHexWepKey(String wepKey) {
final int len = wepKey.length();
// WEP-40, WEP-104, and some vendors using 256-bit WEP (WEP-232?)
if (len != 10 && len != 26 && len != 58) {
return false;
}
return isHex(wepKey);
}
/**
* 是否十六进制
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
private boolean isHex(String key) {
for (int i = key.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final char c = key.charAt(i);
if (!(c >= '0' && c <= '9' || c >= 'A' && c <= 'F' || c >= 'a' && c <= 'f')) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 连接WIFI
*
* @param mWifiConfiguration
* @return
*/
public boolean connetWifi(WifiConfiguration mWifiConfiguration) {
int netID = mWifiManager.addNetwork(mWifiConfiguration);
boolean enabled = mWifiManager.enableNetwork(netID, true);
return enabled;
}
这段代码也比较好理解,就是创建一个WIFI的信息类,然后通过connetWifi这个方法进行连接,连接成功后,因为我监听了WIFI状态
mWifiListReceiver = new WifiListReceiver();
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter();
//搜索结果
filter.addAction(android.net.wifi.WifiManager.SCAN_RESULTS_AVAILABLE_ACTION);
//WIFI改变
filter.addAction(android.net.wifi.WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_CHANGED_ACTION);
//网络改变
filter.addAction(android.net.wifi.WifiManager.NETWORK_STATE_CHANGED_ACTION);
//WIFI状态
filter.addAction(android.net.wifi.WifiManager.SUPPLICANT_STATE_CHANGED_ACTION);
registerReceiver(mWifiListReceiver, filter);
所以我可以通过广播来得到他已经连接上了,这个时候我就可以去获取Server的IP了
/**
* 获取热点IP
*
* @return
*/
public String getHotIp() {
DhcpInfo ipinfo = mWifiManager.getDhcpInfo();
String ip = fixIp(ipinfo.serverAddress);
return ip;
}
实测证明,正常的情况下都是192.168.43.1
这样我们就可以去搭建Client的通信了
private void initClient() {
Log.e(MainActivity.TAG, "initClient" + MainActivity.hot_ip);
try {
socket = new Socket(MainActivity.hot_ip, PORT);
output = new PrintStream(socket.getOutputStream(), true, "utf-8");
initService();
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(MainActivity.TAG, "initClient" + e.toString());
mHandler.postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//无限重连
initClient();
}
}).start();
}
},1000);
}
}
这里我创建了Socket,如果出现异常,比如Time Out ,我就会去延时重连,只到创建成果,这里用了一个ip就是刚才获取的服务端的IP以及端口,就是两端协定好的,在这里我就已经拿到了output,同样可以通过他去println就可以向服务端发送消息了,接着我们来看下他的接收
private void initService() {
Log.e(MainActivity.TAG, "initService");
readThread = new ReadThread();
readThread.start();
}
这里我创建了一个线程
private class ReadThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
//不断读取
while (true) {
byte[] data = receiveData();
if (data != null) {
if (data.length > 1) {
String text = new String(data);
Log.e(MainActivity.TAG, text);
Message message = new Message();
message.what = H_DATA;
message.obj = text;
mHandler.sendMessage(message);
}
}
}
}
}
线程里做的事情很简单也是死循环的去读取数据,有数据的话就通过Handler发送出去更新UI,所以我们重点看下receiveData
/**
* 接收数据
*
* @return
*/
public byte[] receiveData() {
byte[] data = null;
if (socket == null || socket.isClosed()) {
try {
Log.e(MainActivity.TAG,"receiveData:" + MainActivity.hot_ip);
socket = new Socket(MainActivity.hot_ip, PORT);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(MainActivity.TAG, "receiveData 1 " + e.toString());
}
}
if (socket.isConnected()) {
try {
bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
data = new byte[bufferedInputStream.available()];
bufferedInputStream.read(data);
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(MainActivity.TAG, "receiveData 2" + e.toString());
}
} else {
data = new byte[1];
}
return data;
}
这里我们就是不断的从缓冲区获取消息,也就是data返回出去,到这里他们就已经建立通信了
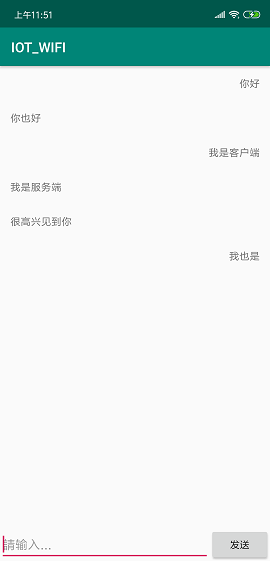
好的,这个到这里就结束了,有兴趣的可以继续深入了解下,我们一起学习物联网
点击下载源码
最后
以上就是包容小虾米最近收集整理的关于Android物联网(二)—— WIFI通讯的全部内容,更多相关Android物联网(二)——内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复