目录
- 难度:简单
- 1. 组合两个表
- 2. 第二高的薪水
- 3. 第N高的薪水
- 4. 分数排名
- 5. 连续出现的数字
- 6. 超过经理收入的员工
- 7. 重新
- 8. 寻找用户推荐人
- 9. 销售员
- 10. 排名靠前的旅行者
- 11. 患某种疾病的患者
- 12. 修复表中的名字
- 13. 求关注者的数量
- 14. 可回收且低脂的产品
- 15. 计算特殊奖金
- 16. 丢失信息的雇员
- 17. 每个产品在不同商店的价格
- 18. 文章浏览
- 19. 上升的温度
- 20. 按日期分组销售产品
- 难度:中等
- 1.股票的资本损益
- 2. 当选者
- 2. 页面推荐
- 难度:困难
- 1. 部门工资前三高的所有员工
- 2. 行程和用户
- 3. 体育馆的人流量
- 4. 员工薪水的中位数
- 5. 同一天的第一个电话和最后一个电话
- 5. 查询员工的累计薪水
- 6. 给定数字的频率查询中位数
难度:简单
1. 组合两个表
表1:Person

PersonId 是上表主键
表2: Address

AddressId 是上表主键
编写一个 SQL 查询,满足条件:无论 person 是否有地址信息,都需要基于上述两表提供 person 的以下信息:
FirstName, LastName, City, State
select a.FirstName, a.LastName, b.City, b.State
from Person a
left join Address b
on a.PersonID = b.PersonID
2. 第二高的薪水
编写一个 SQL 查询,获取 Employee 表中第二高的薪水(Salary) 。
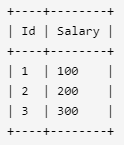
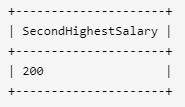
例如上述 Employee 表,SQL查询应该返回 200 作为第二高的薪水。如果不存在第二高的薪水,那么查询应返回 null。
方法一:
因为排序可能会出现薪资相同的情况,
select max(Salary) as SecondHighestSalary
from (
select Salary, row_number() over (order by Salary desc) as rnk
from employee b
group by Salary
) a
where a.rnk = 2
方法二:
通过取最大值再去排除最大值去找到第二高的薪水。
select max(Salary) as SecondHighestSalary
from Employee
where Salary < (select max(Salary) from Employee)
3. 第N高的薪水
有如下两张表T
编写一个 SQL 查询,获取 Employee 表中第 n 高的薪水(Salary)。
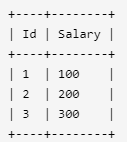
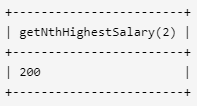
例如上述 Employee 表,n = 2 时,应返回第二高的薪水 200。如果不存在第 n 高的薪水,那么查询应返回 null。
方法一:
CREATE FUNCTION getNthHighestSalary(@N INT) RETURNS INT AS
BEGIN
RETURN (
select Salary as getNthHighestSalary
from (select Salary ,dense_rank() over(order by Salary desc) as rnk
from Employee
group by Salary) a
where rnk = @N );
END
方法二:
CREATE FUNCTION getNthHighestSalary(@N INT) RETURNS INT AS
BEGIN
RETURN ( select distinct Salary
from Employee
order by Salary desc
Offset @N-1 rows
Fetch next 1 rows only);
END
4. 分数排名
编写一个 SQL 查询来实现分数排名。
如果两个分数相同,则两个分数排名(Rank)相同。请注意,平分后的下一个名次应该是下一个连续的整数值。换句话说,名次之间不应该有“间隔”。
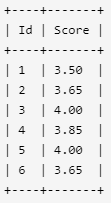
例如,根据上述给定的 Scores 表,你的查询应该返回(按分数从高到低排列):
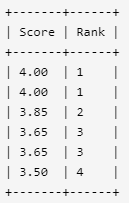
select Score,DENSE_RANK() OVER(ORDER BY Score desc) as Rank
from Scores
5. 连续出现的数字
表:Logs
编写一个 SQL 查询,查找所有至少连续出现三次的数字。
返回的结果表中的数据可以按 任意顺序 排列。
查询结果格式如下面的例子所示:
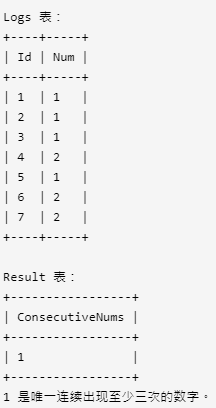
方法一:
如果是连续100次,1000次数值相同,那么这种方法就不适用了
select distinct a.Num as ConsecutiveNums
from Logs a
inner join Logs b
on a.ID = B.ID +1 and a.NUm = b.Num
inner join Logs c
on a.ID = C.ID +2 and b.Num = c.Num
方法二:
SELECT DISTINCT Num as ConsecutiveNums
FROM (SELECT Num,COUNT(1) as SerialCount
FROM (SELECT Id,Num,row_number() over(order by id) -ROW_NUMBER() over(partition by Num order by Id) as SerialNumberSubGroup
FROM Logs) as Sub
GROUP BY Num,SerialNumberSubGroup HAVING COUNT(1) >= 3) as Result
6. 超过经理收入的员工
Employee 表包含所有员工,他们的经理也属于员工。每个员工都有一个 Id,此外还有一列对应员工的经理的 Id。
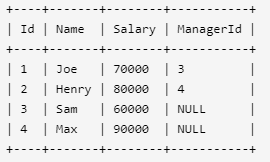
给定 Employee 表,编写一个 SQL 查询,该查询可以获取收入超过他们经理的员工的姓名。在上面的表格中,Joe 是唯一一个收入超过他的经理的员工。

7. 重新
if object_id('department','u') is not null drop table department
create table department (
id int
,revenue INT
,MONTH VARCHAR(10)
)
INSERT INTO DEPARTMENT(id,REVENUE,MONTH)
VALUES
(1,8000 , 'Jan' )
,(2,9000 , 'Jan' )
,(3,10000 , 'Feb' )
,(1,7000 , 'Feb' )
,(1,6000 , 'Mar' )
select id
,sum(case when month = 'Jan' then revenue else null end) as jan_revenue
,sum(case when month = 'Feb' then revenue else null end) as Feb_revenue
,sum(case when month = 'Mar' then revenue else null end) as Mar_revenue
,sum(case when month = 'Apr' then revenue else null end) as Apr_revenue
,sum(case when month = 'May' then revenue else null end) as May_revenue
,sum(case when month = 'Jun' then revenue else null end) as Jun_revenue
,sum(case when month = 'Jul' then revenue else null end) as Jul_revenue
,sum(case when month = 'Aug' then revenue else null end) as Aug_revenue
,sum(case when month = 'Sep' then revenue else null end) as Sep_revenue
,sum(case when month = 'Oct' then revenue else null end) as Oct_revenue
,sum(case when month = 'Nov' then revenue else null end) as Nov_revenue
,sum(case when month = 'Dec' then revenue else null end) as Dec_revenue
from DEPARTMENT
group by id
8. 寻找用户推荐人
给定表 customer ,里面保存了所有客户信息和他们的推荐人。
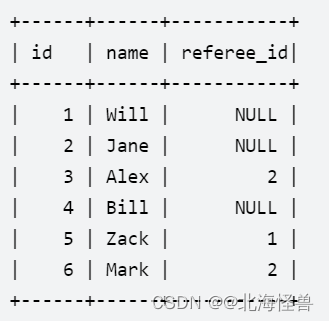
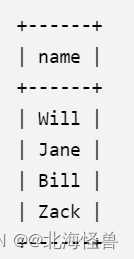
写一个查询语句,返回一个客户列表,列表中客户的推荐人的编号都 不是 2。
对于上面的示例数据,结果为:
--方法一:执行耗时852ms
select name
from customer
where isnull(referee_id,0) <> 2
--方法二:执行耗时1038ms
select name
from customer
where id not in (
select id from customer where referee_id = 2
)
9. 销售员
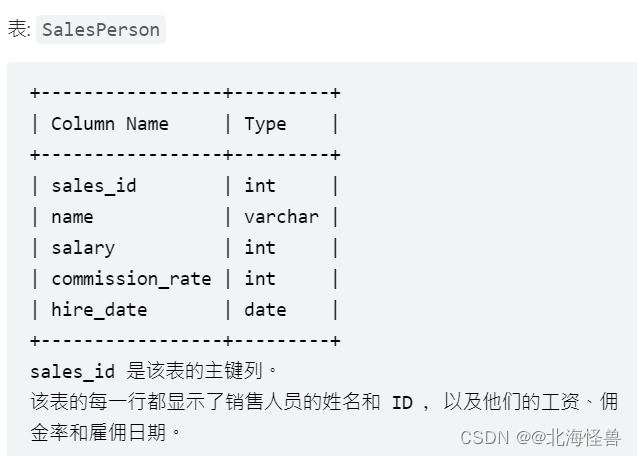

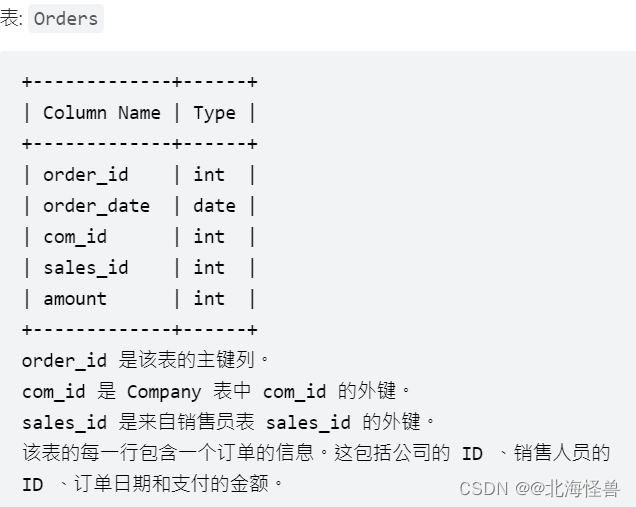
编写一个SQL查询,报告没有任何与名为 “RED” 的公司相关的订单的所有销售人员的姓名。
以 任意顺序 返回结果表。
--方法一:运行耗时903ms
SELECT s.name
FROM salesperson s
WHERE s.sales_id NOT IN (SELECT
o.sales_id
FROM orders o
LEFT JOIN company c
ON o.com_id = c.com_id
WHERE c.name = 'RED')
;
10. 排名靠前的旅行者
表:Users

表:Rides

写一段 SQL , 报告每个用户的旅行距离。
返回的结果表单,以 travelled_distance 降序排列 ,如果有两个或者更多的用户旅行了相同的距离, 那么再以 name 升序排列 。
查询结果格式如下例所示。
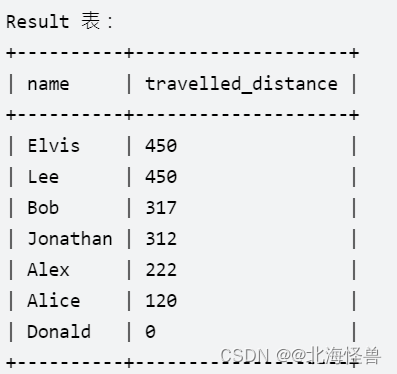
select name,travelled_distance from (
select b.id,b.name,isnull(sum(distance),0) as travelled_distance
from users b
left join rides a
on a.user_id = b.id
group by b.id,b.name ) a
order by travelled_distance desc,name asc
11. 患某种疾病的患者
患者信息表: Patients

写一条 SQL 语句,查询患有 I 类糖尿病的患者 ID (patient_id)、患者姓名(patient_name)以及其患有的所有疾病代码(conditions)。I 类糖尿病的代码总是包含前缀 DIAB1 。
按 任意顺序 返回结果表。
select *
from patients
where conditions like 'DIAB1%'
or conditions like '% DIAB1%'
12. 修复表中的名字
表: Users

编写一个 SQL 查询来修复名字,使得只有第一个字符是大写的,其余都是小写的。
返回按 user_id 排序的结果表。
select user_id,
concat(upper(left(name, 1)), lower(right(name, len(name) - 1))) name
from Users
order by user_id
13. 求关注者的数量
表: Followers

写出 SQL 语句,对于每一个用户,返回该用户的关注者数量。
按 user_id 的顺序返回结果表。
select user_id ,isnull(count(*),0) as followers_count
from Followers
group by user_id
14. 可回收且低脂的产品
表:Products

写出 SQL 语句,查找既是低脂又是可回收的产品编号。
返回结果 无顺序要求 。
select product_id from Products
where low_fats ='Y' and recyclable ='Y'
15. 计算特殊奖金
表: Employees

写出一个SQL 查询语句,计算每个雇员的奖金。如果一个雇员的id是奇数并且他的名字不是以’M’开头,那么他的奖金是他工资的100%,否则奖金为0。
Return the result table ordered by employee_id.
返回的结果集请按照employee_id排序。
select employee_id
,case when employee_id % 2 = 1 and left(name ,1) <>'M'
then salary else 0 end as bonus
from Employees
order by employee_id
16. 丢失信息的雇员
表: Employees

表: Salaries
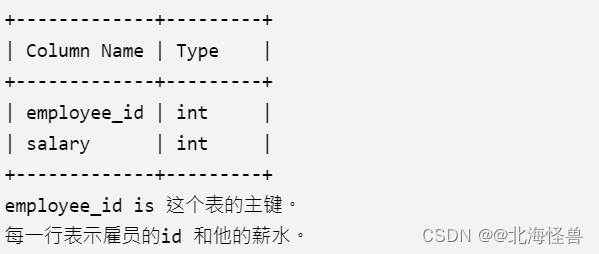
写出一个查询语句,找到所有 丢失信息 的雇员id。当满足下面一个条件时,就被认为是雇员的信息丢失:
雇员的 姓名 丢失了,或者
雇员的 薪水信息 丢失了,或者
返回这些雇员的id employee_id , 从小到大排序 。
select employee_id from
(
select employee_id from Employees
union all
select employee_id from Salaries
)as t
group by employee_id
having count(employee_id) = 1
order by employee_id
17. 每个产品在不同商店的价格
表:Products
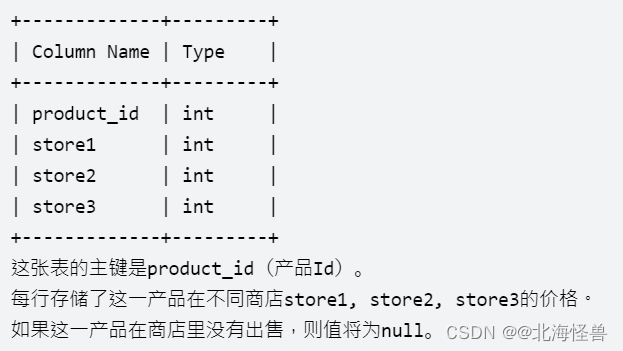
请你重构 Products 表,查询每个产品在不同商店的价格,使得输出的格式变为(product_id, store, price) 。如果这一产品在商店里没有出售,则不输出这一行。
输出结果表中的 顺序不作要求 。
select *from (
select product_id,store,price
from Products
unpivot(price for store in(store1 ,store2,store3 )) c)a
where price is not null
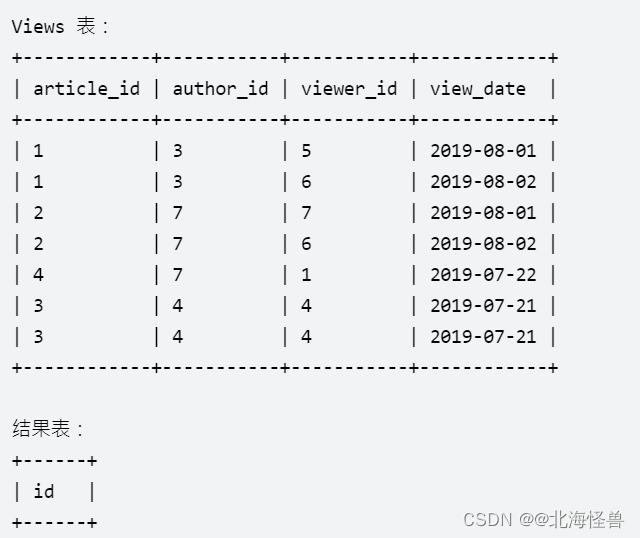
18. 文章浏览
请编写一条 SQL 查询以找出所有浏览过自己文章的作者,结果按照 id 升序排列。
查询结果的格式如下所示:
--distinct 去重
select distinct author_id as id
from Views
where author_id = viewer_id
order by author_id
--group by 去重
select author_id as id
from Views
where author_id = viewer_id
group by author_id
order by author_id
19. 上升的温度
编写一个 SQL 查询,来查找与之前(昨天的)日期相比温度更高的所有日期的 id 。
返回结果 不要求顺序 。
查询结果格式如下例。
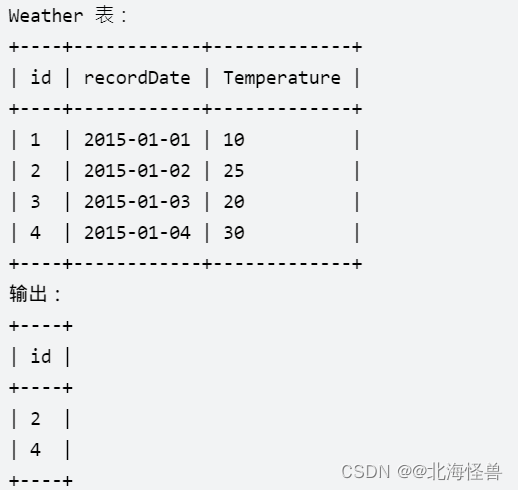
select a.id from weather a
left join weather b
on a.recordDate = dateadd(day,1,b.recordDate)
where a.temperature > b.temperature
20. 按日期分组销售产品
编写一个 SQL 查询来查找每个日期、销售的不同产品的数量及其名称。
每个日期的销售产品名称应按词典序排列。
返回按 sell_date 排序的结果表。
查询结果格式如下例所示。
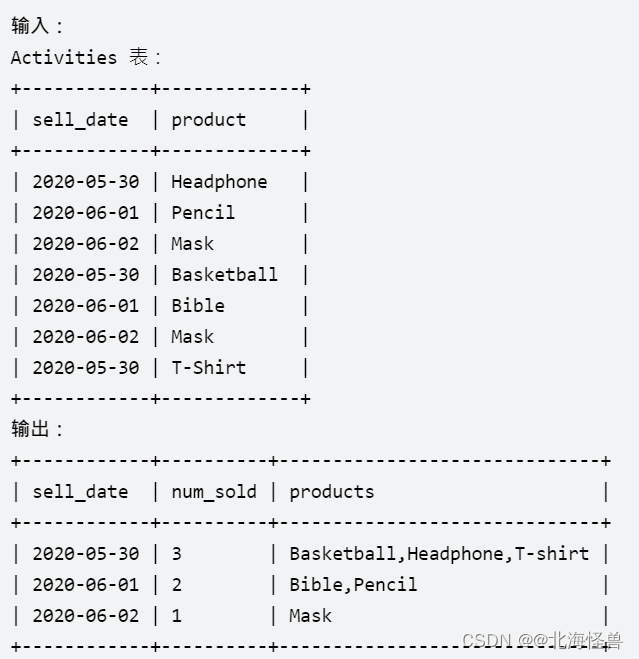
--MS SQL SERVER
select sell_date ,count(distinct product) as num_sold
,STUFF((select distinct ','+product
from activities B
where A.sell_date = B.sell_date
FOR XML PATH('')),1,1,'') as products
from activities a
group by sell_date
--MySQL
select
sell_date,
count(distinct product) as num_sold,
group_concat(distinct product order by product separator ',') as products
from Activities
group by sell_date
order by sell_date;
难度:中等
1.股票的资本损益
Stocks 表:

编写一个SQL查询来报告每支股票的资本损益。
股票的资本损益是一次或多次买卖股票后的全部收益或损失。
以任意顺序返回结果即可。
SELECT stock_name,
SUM(
CASE operation WHEN 'sell'
THEN price ELSE -price
END
) AS capital_gain_loss
FROM Stocks
GROUP BY stock_name
2. 当选者
编写一个SQL查询来报告获胜候选人的名字(即获得最多选票的候选人)。
生成测试用例以确保 只有一个候选人赢得选举。
查询结果格式如下所示。
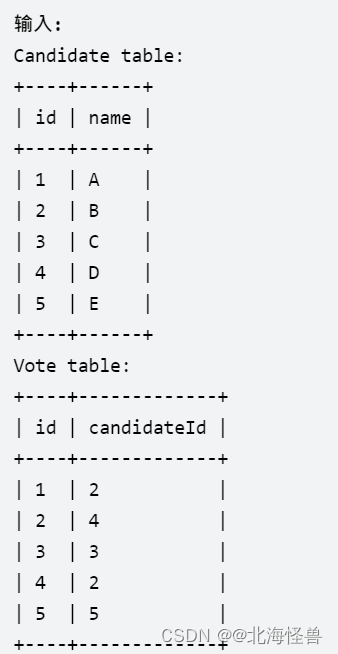

--MS SQL Server
select name
from Candidate
where id in (
select candidateId
from (select top 1 candidateId,count(*) as cnt
from vote
group by candidateId
order by count(*) desc)a
)
--MySQL
select Name from Candidate
where id =(
select CandidateId from Vote
group by CandidateId
order by count(CandidateId) desc limit 1)
2. 页面推荐
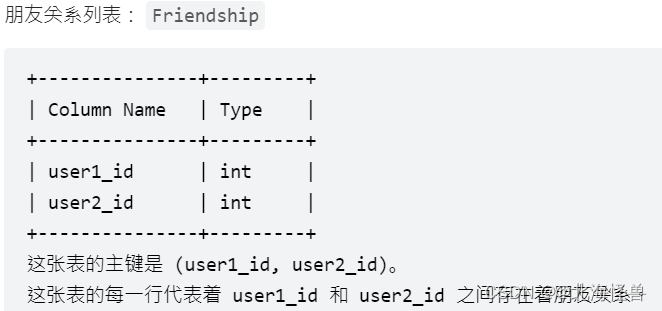
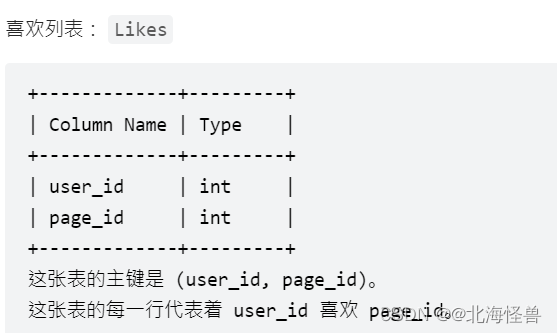
写一段 SQL 向user_id = 1 的用户,推荐其朋友们喜欢的页面。不要推荐该用户已经喜欢的页面。
你返回的结果中不应当包含重复项。
select distinct page_id as recommended_page
from Likes
where user_id in (select user2_id
from (select user1_id , user2_id from friendship
union
select user2_id ,user1_id from friendship) a
where user1_id = 1 )
and page_id not in (select page_id from Likes where user_id = 1 )
难度:困难
1. 部门工资前三高的所有员工
Employee 表包含所有员工信息,每个员工有其对应的工号 Id,姓名 Name,工资 Salary 和部门编号 DepartmentId 。
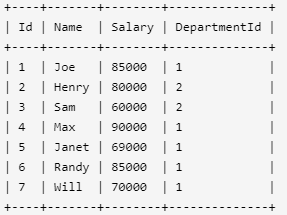
Department 表包含公司所有部门的信息。
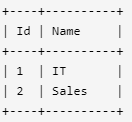
编写一个 SQL 查询,找出每个部门获得前三高工资的所有员工。例如,根据上述给定的表,查询结果应返回:
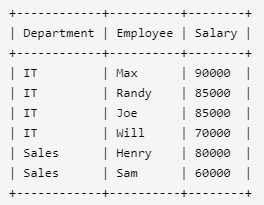
解释:
IT部门中,Max获得了最高的工资,Randy和Joe都拿到了第二高的工资,Will的工资排第三。销售部门(Sales)只有两名员工,Henry的工资最高,Sam的工资排第二。
select b.Name as Department,a.Name as Employee,a.Salary
from (select *,dense_rank() over(partition by departmentid order by Salary desc) as rnk from Employee) a
left join department b
on a.departmentid = b.Id
where a.rnk <= 3
2. 行程和用户
表:Trips
表:Users
3. 体育馆的人流量
编写一个 SQL 查询以找出每行的人数大于或等于 100 且 id 连续的三行或更多行记录。
返回按 visit_date 升序排列的结果表。
if object_id('stadium','u') is not null drop table stadium
create table stadium(
id int identity(1,1)
,visit_date date
,people int
)
insert into stadium(visit_date, people)
values
('2017-01-01' , 10 )
,('2017-01-02' , 109 )
,('2017-01-03' , 150 )
,('2017-01-04' , 99 )
,('2017-01-05' , 145 )
,('2017-01-06' , 1455 )
,('2017-01-07' , 199 )
,('2017-01-09' , 188 )
select id,visit_date,people
from (
select id, visit_date, people, count(*) over (partition by (fz)) as cnt
from (
select *, id - row_number() over (order by id ) as fz
from stadium
where people >= 100
) a
) a
where cnt > 3
4. 员工薪水的中位数
写一个SQL查询,找出每个公司的工资中位数。
以 任意顺序 返回结果表。
查询结果格式如下所示。
Employee表:
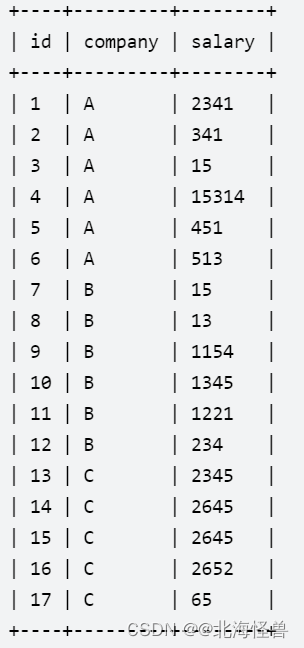
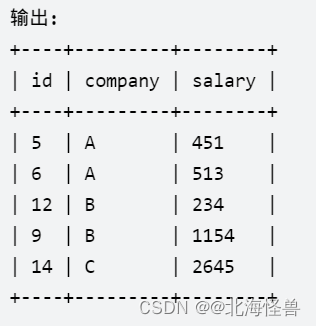
--方法一:
--注意事项:排序时用row_number,会有排名相同的情况
--中位数的逻辑了解:不论个数是奇数偶数,中位数在总数除以2和总数除以2加1之间
select id ,company,salary
from (
select *
,row_number() over(partition by company order by salary) as rnk
,count(*) over(partition by company ) as cnt
from Employee) a
where rnk BETWEEN cnt*1.0/2 AND cnt*1.0/2 + 1
5. 同一天的第一个电话和最后一个电话
编写一个 SQL 查询来找出那些ID们在任意一天的第一个电话和最后一个电话都是和同一个人的。这些电话不论是拨打者还是接收者都会被记录。
结果请放在一个任意次序约束的表中。
查询结果格式如下所示:

--MySQL
with temp as (select * from calls
union all
select recipient_id caller_id, caller_id recipient_id, call_time from calls
),
temp1 as (select
*,
dense_rank() over (partition by date_format(call_time,"%Y-%m-%d"),caller_id order by call_time asc) rk1,
dense_rank() over (partition by date_format(call_time,"%Y-%m-%d"),caller_id order by call_time desc) rk2
from temp
)
select
distinct caller_id as user_id
from temp1
where rk1 = 1 or rk2 = 1
group by caller_id, date_format(call_time,"%Y-%m-%d")
having count(distinct recipient_id) = 1
5. 查询员工的累计薪水
Employee 表保存了一年内的薪水信息。
请你编写 SQL 语句,对于每个员工,查询他除最近一个月(即最大月)之外,剩下每个月的近三个月的累计薪水(不足三个月也要计算)。
结果请按 Id 升序,然后按 Month 降序显示。
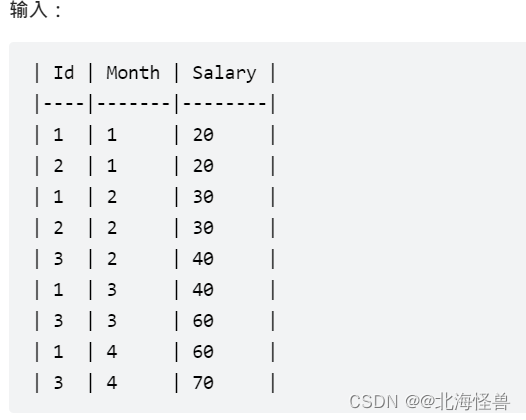
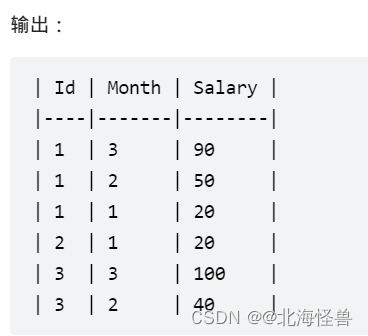
--MySQL
--注意点:剔除最大月要以员工为单位去看,还有就是其他月份算累计只要计算近三个月的
select a.id ,a.month ,sum(b.salary) as Salary
from Employee a
left join Employee b
on a.id = b.id and a.Month >= b.Month and a.Month < b.Month + 3
where (a.Id, a.Month) NOT IN (SELECT Id, MAX(Month) FROM Employee GROUP BY Id)
group by a.id ,a.month
order by id asc ,month desc
--MS SQL Server
WITH T AS (
select id,max(month) as month from Employee group by id
)
select a.id ,a.month ,sum(b.salary) as Salary
from Employee a
left join Employee b
on a.id = b.id and a.Month >= b.Month and a.Month < b.Month + 3
where NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM t b where a.id = b.id and a.month = b.month)
group by a.id ,a.month
order by id asc ,month desc
6. 给定数字的频率查询中位数
中位数 是将数据样本中半数较高值和半数较低值分隔开的值。
编写一个 SQL 查询,解压 Numbers 表,报告数据库中所有数字的 中位数 。结果四舍五入至 一位小数 。
查询结果如下例所示。

--中位数逻辑:按大小排序后,不论正序降序排序,中位数的排序都会大于总数的一半
select cast (sum(num)*1.0/count(num) as decimal(19,1)) as median
from
(select Num, frequency,
sum(frequency) over(order by Num asc) as total,
sum(frequency) over(order by Num desc) as total1
from Numbers
)as a
where total>=(select sum(frequency) from Numbers)/2
and total1>=(select sum(frequency) from Numbers)/2
最后
以上就是飘逸唇膏最近收集整理的关于Leetcode题库(数据库合集)难度:简单难度:中等难度:困难的全部内容,更多相关Leetcode题库(数据库合集)难度内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复