在明白了去噪自动编码机(dA)的理论之后,在本篇博文中,我们将讨论用Theano来实现一个去噪自动编码机。
通过上篇博文的讨论,我们知道去噪自动编码机(dA)工作主要有四步组成:第一步是向原始输入信号中加入随机噪音(使原始信号在某些维度上值为零);第二步是将加入噪音的信号输入网络,经过编码器部分,在中间层生成输入信号的压缩信号;第三步是经过解码器层,在输出层得到输出信号;第四步将输出信号与原始输入信号相比较,求出误差,然后根据随机梯度下降算法,更新网络的连接权值。我们通过定义去噪自动编码机(DenosingAutoencoder)类,来实现这些功能,代码如下所示:
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import sys
import timeit
import numpy
import theano
import theano.tensor as T
from theano.tensor.shared_randomstreams import RandomStreams
class DenosingAutoencoder(object):
def __init__(
self,
numpy_rng,
theano_rng=None,
input=None,
n_visible=784,
n_hidden=500,
W=None,
bhid=None,
bvis=None
):
self.n_visible = n_visible
self.n_hidden = n_hidden
if not theano_rng:
theano_rng = RandomStreams(numpy_rng.randint(2 ** 30))
if not W:
initial_W = numpy.asarray(
numpy_rng.uniform(
low=-4 * numpy.sqrt(6. / (n_hidden + n_visible)),
high=4 * numpy.sqrt(6. / (n_hidden + n_visible)),
size=(n_visible, n_hidden)
),
dtype=theano.config.floatX
)
W = theano.shared(value=initial_W, name='W', borrow=True)
if not bvis:
bvis = theano.shared(
value=numpy.zeros(
n_visible,
dtype=theano.config.floatX
),
borrow=True
)
if not bhid:
bhid = theano.shared(
value=numpy.zeros(
n_hidden,
dtype=theano.config.floatX
),
name='b',
borrow=True
)
self.W = W
self.b = bhid
self.b_prime = bvis
self.W_prime = self.W.T
self.theano_rng = theano_rng
if input is None:
self.x = T.dmatrix(name='input')
else:
self.x = input
self.params = [self.W, self.b, self.b_prime]
def get_corrupted_input(self, input, corruption_level):
return self.theano_rng.binomial(size=input.shape, n=1,
p=1 - corruption_level,
dtype=theano.config.floatX) * input
def get_hidden_values(self, input):
return T.nnet.sigmoid(T.dot(input, self.W) + self.b)
def get_reconstructed_input(self, hidden):
return T.nnet.sigmoid(T.dot(hidden, self.W_prime) + self.b_prime)
def get_cost_updates(self, corruption_level, learning_rate):
tilde_x = self.get_corrupted_input(self.x, corruption_level)
y = self.get_hidden_values(tilde_x)
z = self.get_reconstructed_input(y)
L = - T.sum(self.x * T.log(z) + (1 - self.x) * T.log(1 - z), axis=1)
cost = T.mean(L)
gparams = T.grad(cost, self.params)
updates = [
(param, param - learning_rate * gparam)
for param, gparam in zip(self.params, gparams)
]
return (cost, updates)
numpy_rng:随机数生成引擎,用于生成随机的连接权值
input:网络的输入信号,如果是独立的去噪自动编码机,该值为空,如果是堆叠去噪自动编码机的话,则其为前一层去噪自动编码机的输出层
n_visible:输出层神经元数目
n_hidden:中间层神经元数目
W:层间神经元的连接权值矩阵
bhid:中间层神经元Bias值向量
bvis:输出层神经元Bias值向量
需要注意的是,我们所定义的去噪自动编码机(dA)采用中间隐藏层到输出层的连接权值向量是输入层到中间隐藏层连接权值向量的转置,即: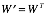 。另外,我们信号重建过程中的交叉熵来定义我们的误差:
。另外,我们信号重建过程中的交叉熵来定义我们的误差:
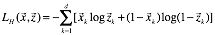 式1
式1
在定义好了去噪自动编码机(dA)之后,我们来定义DAMnistEngine,用来装入MNIST数据,并对其进行训练,代码如下所示:
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import sys
import timeit
import numpy
import theano
import theano.tensor as T
from theano.tensor.shared_randomstreams import RandomStreams
from mnist_loader import MnistLoader
from denosing_autoencoder import DenosingAutoencoder
from dlt_utils import tile_raster_images
try:
import PIL.Image as Image
except ImportError:
import Image
class DAMnistEngine(object):
def train(self, learning_rate=0.1, training_epochs=15,
dataset='mnist.pkl.gz',
batch_size=20, output_folder='dA_plots'):
loader = MnistLoader()
datasets = loader.load_data(dataset)
train_set_x, train_set_y = datasets[0]
n_train_batches = train_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] // batch_size
index = T.lscalar()
x = T.matrix('x')
if not os.path.isdir(output_folder):
os.makedirs(output_folder)
os.chdir(output_folder)
self.train_da(x, learning_rate, train_set_x, index, batch_size,
training_epochs, n_train_batches, 'filters_corruption_0.png', 0.0)
self.train_da(x, learning_rate, train_set_x, index, batch_size,
training_epochs, n_train_batches, 'filters_corruption_30.png', 0.3)
os.chdir('../')
def train_da(self, x, learning_rate, train_set_x, index, batch_size,
training_epochs, n_train_batches,
img_file,
corruption_level=0.0):
rng = numpy.random.RandomState(123)
theano_rng = RandomStreams(rng.randint(2 ** 30))
da = DenosingAutoencoder(
numpy_rng=rng,
theano_rng=theano_rng,
input=x,
n_visible=28 * 28,
n_hidden=500
)
cost, updates = da.get_cost_updates(
corruption_level=corruption_level,
learning_rate=learning_rate
)
train_da = theano.function(
[index],
cost,
updates=updates,
givens={
x: train_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
start_time = timeit.default_timer()
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
c = []
for batch_index in range(n_train_batches):
c.append(train_da(batch_index))
print('Training epoch %d, cost ' % epoch, numpy.mean(c))
end_time = timeit.default_timer()
training_time = (end_time - start_time)
print(('The no corruption code for file ' +
os.path.split(__file__)[1] +
' ran for %.2fm' % ((training_time) / 60.)), file=sys.stderr)
image = Image.fromarray(
tile_raster_images(X=da.W.get_value(borrow=True).T,
img_shape=(28, 28), tile_shape=(10, 10),
tile_spacing=(1, 1)))
image.save(img_file)
def run():
print('run Denosing Autoencoder...')
我们可以通过如下代码,运行并训练我们的去噪自动编码机(dA):
from d_a_mnist_engine import DAMnistEngine
if __name__ == '__main__':
engine = DAMnistEngine()
engine.train()有了单层的去噪自动编码机(dA)之后,我们将在下一篇博文中讨论堆叠自动编码机(dA)的原理、实现和应用。
最后
以上就是优美鸵鸟最近收集整理的关于深度学习算法实践14---去噪自动编码机(dA)的Theano实现的全部内容,更多相关深度学习算法实践14---去噪自动编码机(dA)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复