参考网站:https://www.studytonight.com/operating-system/shortest-job-first
文章目录
- 1 概念
- 2 非抢占式SJF
- 2.1 非抢占式SJF的原理
- 2.2 非抢占式SJF的缺点
- 3 抢占式SJF
- 4 实现SJF
1 概念
最短工作优先调度首先处理突发时间或持续时间最短的过程。
-
这是最大限度地减少等待时间的最佳方法。
-
这在批处理系统中使用。
-
它有两种类型:
非抢占式Non Pre-emptive
抢占式Pre-emptive -
要成功实现它,处理器应事先知道流程的突发时间/持续时间,这实际上并非一直可行。
-
如果所有作业/进程同时可用,此调度算法是最佳的。
2 非抢占式SJF
2.1 非抢占式SJF的原理
考虑以下进程可用的队列中可供执行,到达时间作为所有和给定的突发时间。
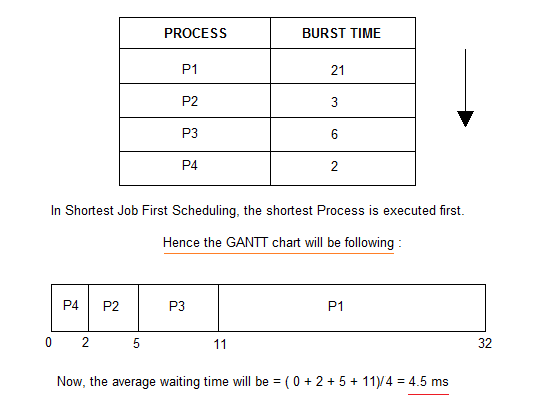
如上图中的GANTT图表所示,首先将执行P4,因为它具有最短的突发时间,然后依次是P2、P3、P1。
我们在上一个笔记中使用了先到先得算法,安排了相同的一组进程,并得到了平均等待时间,而使用SJF时,平均等待时间也是一样的道理。
2.2 非抢占式SJF的缺点
如果进程到达时间不同,这意味着所有进程在准备队列中都不可用,并且某一些作业在一段时间后到达。
在这种情况下,有时具有短突发时间的进程必须等待当前进程的执行完成,因为在非抢占式的SJF中,在持续时间较短的进程到达时,现有作业、进程的执行不会停止以首先执行短期作业。
这导致了Starvation饥饿的问题,在这个问题中,较短的进程必须等待很长时间才能执行当前的较长进程。如果较短的工作持续出现,则会发生这种情况,但是可以使用aging老化的概念来解决。
3 抢占式SJF
在抢先式最短作业优先调度中,作业在到达时会进入就绪队列,但随着突发时间较短的进程到达,现有进程将被抢占或从执行中删除,较短的作业将首先执行。
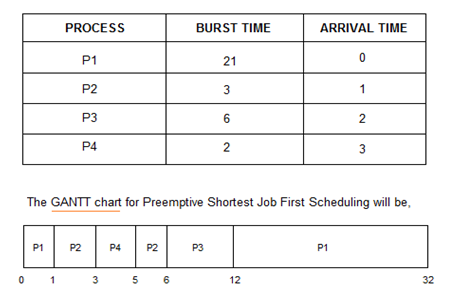
平均等待时间为:((5-3)+(6-2)+(12-1))/4=8.75
抢占式最短作业优先调度的平均等待时间小于非抢占式SJF调度和FCFS调度。
如您在上面的GANTT图表中所见,由于P1首先到达,因此它的执行立即开始,但是在1 ms之后,进程P2到达的突发时间为3 ms,小于P1的突发时间,
因此,将抢占过程P1(完成1 ms,还剩20 ms)并执行过程P2。
随着P2的执行,在1 ms之后,P3到达,但是它的突发时间大于P2的突发时间,因此P2的执行继续。但是再过一毫秒,P4以2 ms的突发时间到达,结果P2(完成2 ms,剩下的1 ms)被抢占并执行P4。
P4完成后,将启动过程P2并完成,然后将执行P2,最后执行P1。
抢占式SJF也称为最短剩余时间优先,因为在任何给定时间点,最先执行剩余时间最短的作业。
4 实现SJF
在下面的程序中,我们将所有作业的到达时间视为0。另外,在程序中,我们将根据所有作业的突发时间对所有作业进行排序,然后像在FCFS调度程序中一样,一一执行它们。
// c++ program to implement Shortest Job first
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Process
{
int pid; // process ID
int bt; // burst Time
};
/*
this function is used for sorting all
processes in increasing order of burst time
*/
bool comparison(Process a, Process b)
{
return (a.bt < b.bt);
}
// function to find the waiting time for all processes
void findWaitingTime(Process proc[], int n, int wt[])
{
// waiting time for first process is 0
wt[0] = 0;
// calculating waiting time
for (int i = 1; i < n ; i++)
{
wt[i] = proc[i-1].bt + wt[i-1] ;
}
}
// function to calculate turn around time
void findTurnAroundTime(Process proc[], int n, int wt[], int tat[])
{
// calculating turnaround time by adding bt[i] + wt[i]
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++)
{
tat[i] = proc[i].bt + wt[i];
}
}
// function to calculate average time
void findAverageTime(Process proc[], int n)
{
int wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0;
// function to find waiting time of all processes
findWaitingTime(proc, n, wt);
// function to find turn around time for all processes
findTurnAroundTime(proc, n, wt, tat);
// display processes along with all details
cout << "nProcesses "<< " Burst time "
<< " Waiting time " << " Turn around timen";
// calculate total waiting time and total turn around time
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
total_wt = total_wt + wt[i];
total_tat = total_tat + tat[i];
cout << " " << proc[i].pid << "tt"
<< proc[i].bt << "t " << wt[i]
<< "tt " << tat[i] <<endl;
}
cout << "Average waiting time = "
<< (float)total_wt / (float)n;
cout << "nAverage turn around time = "
<< (float)total_tat / (float)n;
}
// main function
int main()
{
Process proc[] = {{1, 21}, {2, 3}, {3, 6}, {4, 2}};
int n = sizeof proc / sizeof proc[0];
// sorting processes by burst time.
sort(proc, proc + n, comparison);
cout << "Order in which process gets executedn";
for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++)
{
cout << proc[i].pid <<" ";
}
findAverageTime(proc, n);
return 0;
}
output:
Order in which process gets executed
4 2 3 1
Processes Burst time Waiting time Turn around time
4 2 0 2
2 3 2 5
3 6 5 11
1 21 11 32
Average waiting time = 4.5
Average turn around time = 12.5
最后
以上就是健忘铅笔最近收集整理的关于[学习笔记]操作系统(四)最短工作优先1 概念2 非抢占式SJF3 抢占式SJF4 实现SJF的全部内容,更多相关[学习笔记]操作系统(四)最短工作优先1内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。




![[学习笔记]操作系统(四)最短工作优先1 概念2 非抢占式SJF3 抢占式SJF4 实现SJF](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg1.png)



发表评论 取消回复