我是靠谱客的博主 壮观金鱼,这篇文章主要介绍JavaScript ——十大经典排序算法汇总(整理中)冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)插入排序(Insertion Sort)选择排序(Selection Sort)归并排序(Merge Sort)快速排序 (Quick Sort),现在分享给大家,希望可以做个参考。
冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)
冒泡排序是一次比较两个元素,如果顺序是错误的就把它们交换过来。走访数列的工作会重复地进行,直到不需要再交换,也就是说该数列已经排序完成。
// 冒泡排序(已优化)
const bubbleSorted2 = arr=>{
const length = arr.length
if(length <=1){
return
}
for (let i = 0;i<length-1;i++){
let hasChange = false
for (let j = 0 ;j<length - i-1;j++){
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
const temp = arr[j]
arr[j] = arr[j+1]
arr[j+1] = temp
hasChange = true
}
}
if(!hasChange){
break
}
}
console.log(arr)
}
console.log("排序前:2,5,44,22,58,40,34,54,89")
bubbleSorted2([2,5,44,22,58,40,34,54,89])
插入排序(Insertion Sort)
插入排序算法描述的是一种简单直观的排序算法。它的工作原理是通过构建有序序列,对于未排序数据,在已排序序列中从后向前扫描,找到相应位置并插入,从而达到排序的效果。
const insertionSort = arr=>{
const len = arr.length
if (len <=1) return
let preIndex ,current;
for (let i =1;i<len;i++){
console.log(i)
preIndex = i-1;
current = arr[i]
while(preIndex >= 0 && arr[preIndex] > current){
arr[preIndex +1] = arr[preIndex]
console.log(" arr[preIndex +1]"+ arr[preIndex +1])
preIndex --;
console.log("preIndex"+preIndex)
}
if(preIndex +1 !== i){
arr[preIndex+1] = current
console.log("arr------"+arr)
}
}
return arr
}
console.log([23,54,76,34,55,33,1,545,64])
insertionSort([23,54,76,34,55,33,1,545,64])
选择排序(Selection Sort)
选择排序是一种简单直观的排序算法。它的工作原理是,首先将最小的元素存放在序列的起始位置,再从剩余未排序元素中继续寻找最小元素,然后放到已排序的序列后面……以此类推,直到所有元素均排序完毕。
const selectionSort = array => {
const len = array.length;
let minIndex, temp;
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
minIndex = i;
for (let j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {
if (array[j] < array[minIndex]) {
// 寻找最小的数
minIndex = j; // 将最小数的索引保存
}
}
temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[minIndex];
array[minIndex] = temp;
console.log('array: ', array);
}
console.log("res----"+array)
return array;
};
console.log("选择排序------"+[23,54,66,23,62,77,43])
selectionSort([23,54,66,23,62,77,43])
归并排序(Merge Sort)
将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。
const mergeSort = arr => {
//采用自上而下的递归方法
const len = arr.length;
if (len < 2) {
return arr;
}
// length >> 1 和 Math.floor(len / 2) 等价
let middle = Math.floor(len / 2),
left = arr.slice(0, middle),
right = arr.slice(middle); // 拆分为两个子数组
return merge(mergeSort(left), mergeSort(right));
};
const merge = (left, right) => {
const result = [];
while (left.length && right.length) {
// 注意: 判断的条件是小于或等于,如果只是小于,那么排序将不稳定.
if (left[0] <= right[0]) {
result.push(left.shift());
} else {
result.push(right.shift());
}
}
while (left.length) result.push(left.shift());
while (right.length) result.push(right.shift());
return result;
};
console.log("[1,45,66,2,7,8,4,77]")
console.log(mergeSort([1,45,66,2,7,8,4,77]))
快速排序 (Quick Sort)
快速排序的基本思想是通过一趟排序,将待排记录分隔成独立的两部分,其中一部分记录的关键字均比另一部分的关键字小,则可以分别对这两部分记录继续进行排序,以达到整个序列有序。
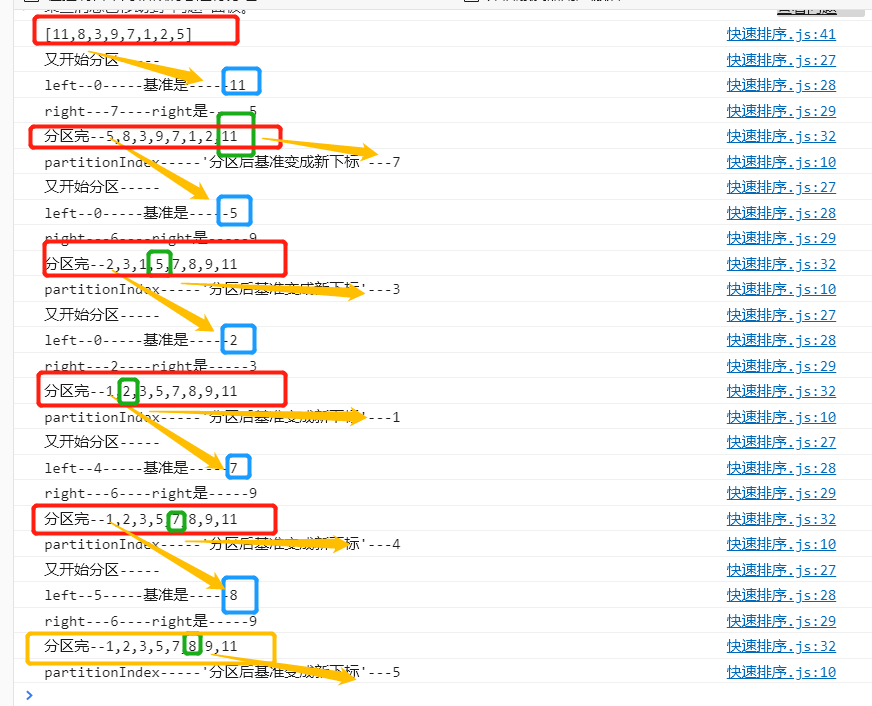
// 快速排序
const quickSort = (arr, left, right) => {
let len = arr.length,
partitionIndex;
left = typeof left != 'number' ? 0 : left;
right = typeof right != 'number' ? len - 1 : right;
if (left < right) {
partitionIndex = partition(arr, left, right);
console.log("partitionIndex-----'基准下标'---"+partitionIndex)
quickSort(arr, left, partitionIndex - 1);
quickSort(arr, partitionIndex + 1, right);
}
return arr;
};
const partition = (arr, left, right) => {
//分区操作
let pivot = left, //设定基准值(pivot)
index = pivot + 1;
for (let i = index; i <= right; i++) {
if (arr[i] < arr[pivot]) {
swap(arr, i, index);
index++;
}
}
console.log("又开始分区-----")
console.log("left--"+left+"-----基准是-----"+arr[pivot])
console.log('right---'+right+"----right是-----"+arr[right])
swap(arr, pivot, index - 1);
console.log("分区完--"+arr)
return index - 1;
};
const swap = (arr, i, j) => {
let temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
};
console.log("[11,8,3,9,7,1,2,5]")
quickSort([11,8,3,9,7,1,2,5])
归并排序(Merge Sort)与快速排序的区别
- 归并排序的处理过程是由下而上的,先处理子问题,然后再合并。
- 快排正好相反,它的处理过程是由上而下的,先分区,然后再处理子问题。
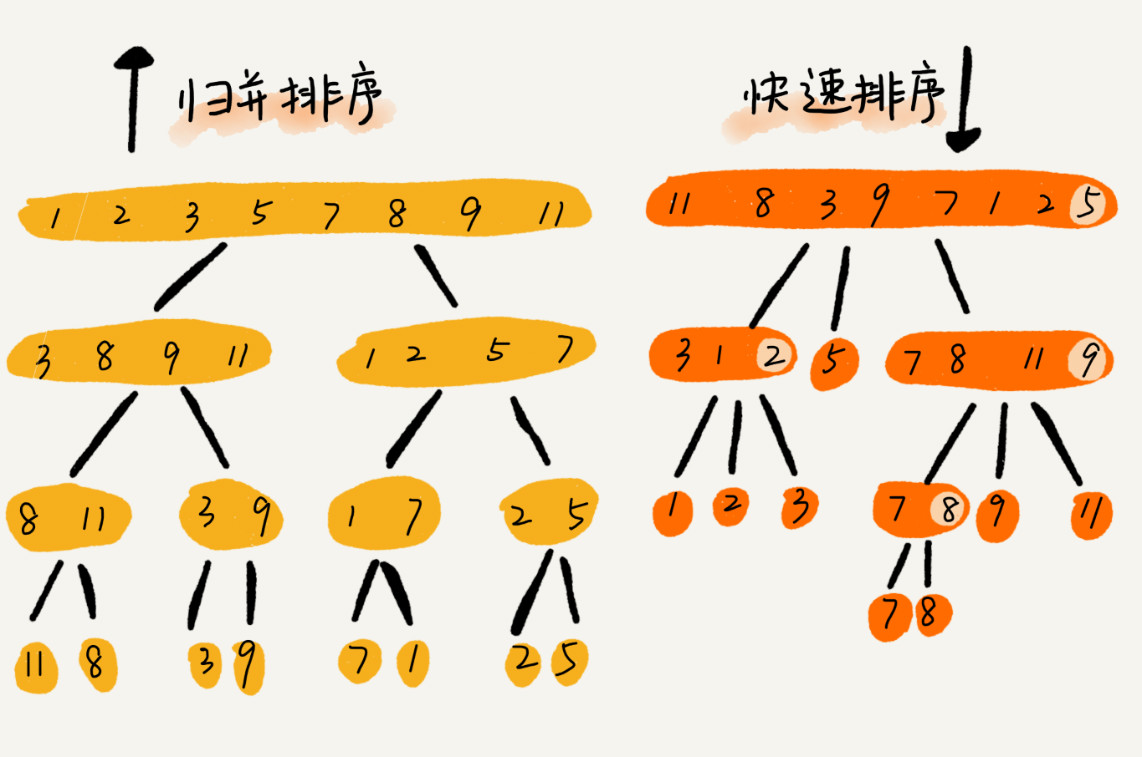
参考大佬
最后
以上就是壮观金鱼最近收集整理的关于JavaScript ——十大经典排序算法汇总(整理中)冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)插入排序(Insertion Sort)选择排序(Selection Sort)归并排序(Merge Sort)快速排序 (Quick Sort)的全部内容,更多相关JavaScript内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复