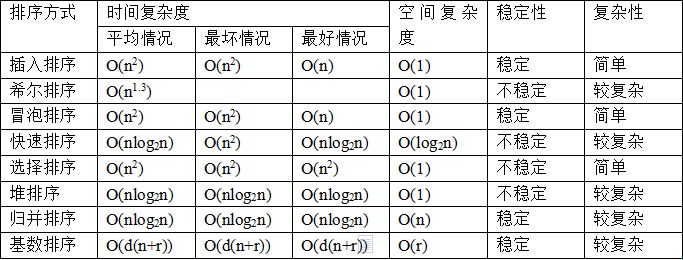
排序算法
一、插入排序
1)直接插入排序
2)折半插入排序(二分插入排序)
3)希尔排序
二、交换排序
1)冒泡排序
2)快速排序
三、 选择排序
1)简单选择排序
2)堆排序
四、归并排序
五、基数排序
package com;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class sort1 {
/*直接插入排序
*
* 将第一个元素假设为排序好的数组,将后面元素假设为未排序数组,从
* 未排序的数组取出一个元素插入到已经排序好的数组,以此类推。
*
* 平均时间复杂度:O(n^2)
*/
public static void InsertSort(int a[]) {
//show(a);//展示原数组
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
int temp = a[i];//设置哨兵,暂时存放移动的元素
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && a[j] > temp) {
a[j + 1] = a[j];
j--;
}
a[j + 1] = temp;
//show(a);//展示每轮排序的结果
}
show(a);//最终结果
}
/*折半插入排序
*
* 第一个元素为已排好位置,后面元素采用二分查找位置插入。
*
* 平均时间复杂度:O(n^2)
*/
public static void InsertSort1(int a[]) {
int i, j, low, high, mid;
for(i=1;i<a.length;i++) { //将a[1]-a[n]插入到已排序序列
int temp=a[i];//待插入元素
low=0;//设置查找范围
high=i-1;
while(low<=high) {
mid=(low+high)/2;
if(a[mid]>temp) {
high=mid-1;//查询左半子表
}else {
low=mid+1;//查询右半子表
}
}
for(j=i-1;j>=high+1;--j) {
a[j+1]=a[j]; //统一后移,空出插入位置
}
a[high+1]=temp;//插入
}
show(a);
}
/*希尔排序
*
* 设置一个增量,通过增量,每层循环将排序表划分成多个子表,然后将子表内的元素进行排序。
*
*/
public static void ShellSort(int a[]) {
int dk;//增量
int i,j,temp;
for(dk=a.length/2; dk>=1; dk=dk/2) {
for(i=dk; i<a.length; i++) {
if(a[i]<a[i-dk]) {
temp=a[i];
for(j=i-dk;j>=0 && temp<=a[j]; j-=dk) {
a[j+dk]=a[j]; //统一后移,空出插入位置
}
a[j+dk]=temp;//插入
}
}
}
show(a);
}
/*冒泡排序
*
* 每轮排序,确定一个元素的最终位置。
*
* 平均时间复杂度:O(n^2)
*/
public static void BubbleSort(int a[]) {
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { // i代表后i个数已经排好序了
for (int j = 0; j < a.length - i; j++) {
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
show(a);
}
/*快速排序
*
* 快排是一个通过枢轴进行交替搜索和交换的过程。
*
*/
public static void QuickSort(int[] a, int begin, int end) {
if (begin < end) {
sort st = new sort();
int i = begin + 1, j = end, flag = begin;//flag枢轴
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && a[i] >= a[flag])
i++;
while (i < j && a[j] <= a[flag])
j--;
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
if (a[i] <= a[flag])
i = i - 1;// 将放在第一位的标志位与中间元素互换位置
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[flag];
a[flag] = temp;
st.QuickSort(a, begin, i - 1);
st.QuickSort(a, i + 1, end);
}
}
/*选择排序
*
* 每轮排序找到最小元素,与之前最小元素进行比较排序。
*
* 平均时间复杂度:O(n^2)
*/
public static void SelectSort(int a[]) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {
int min = i;//记录最小元素位置
for (int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) {
if (a[j] < a[min])
min = j;
}
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[min];
a[min] = temp;
//show(a);//展示每轮排序的结果
}
show(a);
}
/*堆排序
*
* 构造大根堆,或者小根堆(大根堆:最大元素存放在根节点,非根结点的值小于其双亲结点)
*
* 平均时间复杂度:O(nlog2^n)
*/
public static void buildHeap(int[] a, int i, int len) {
int left = 2 * i + 1, right = 2 * i + 2, min = i;
if (left < len && a[left] < a[min])
min = left; // 这两步是为了找到i节点的最小子节点
if (right < len && a[right] < a[min])
min = right;
if (min != i) { // 如果min 不是 i,则代表此时不是小顶堆,所以要与最小子节点交换位置,
int temp = a[i];// 交换完位置,可能改变子节点的小顶堆结构,所以还需对子节点进行小顶堆构造。
a[i] = a[min];
a[min] = temp;
buildHeap(a, min, len);// 因为改变了结构 所以还需进行子树的堆建造
}
}
// 堆排序
public static void HeapSort(int a[]) {
int len = a.length;
for (int i = len / 2; i >= 0; i--) {// 初始化构造一个小顶堆,除了叶子结点外,
buildHeap(a, i, len); // 需要从最末尾节点开始,依次构造以该节点为根节点的小顶堆
//show(a);//输出小根堆的每轮排序
}
// 根节点为最小值
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int temp = a[i]; // 把最小值放到数组最后面,此时a[0]为最小值
a[i] = a[0];
a[0] = temp;
len = len - 1;// 完成一次交换后,就找到了一个最小值,所以长度减一
buildHeap(a, 0, len);// 交换后,需要再形成一个小顶堆
}
show(a);
}
/*归并排序
*
* 假设二路归并:每趟排序构建若干的小组,然后两两小组进行排序比较。
*
*/
public static int[] merge(int[] left, int[] right) {
int[] result = new int[left.length + right.length];
int i = 0;
while (left.length > 0 && right.length > 0) {
if (left[0] <= right[0]) {
result[i++] = left[0];
left = Arrays.copyOfRange(left, 1, left.length);// 对数组进行切割减小
} else {
result[i++] = right[0];
right = Arrays.copyOfRange(right, 1, right.length);
}
}
while (left.length > 0) {
result[i++] = left[0];
left = Arrays.copyOfRange(left, 1, left.length);
}
while (right.length > 0) {
result[i++] = right[0];
right = Arrays.copyOfRange(right, 1, right.length);
}
return result;
}
public static int[] MergeSort(int[] a) {
sort st = new sort();
if (a.length < 2)
return a;
int mid = (int) Math.floor(a.length / 2);
int[] left = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, 0, mid);
int[] right = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, mid, a.length);
return merge(st.MergeSort(left), st.MergeSort(right));
}
//输出函数
static void show(int[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[] {8, 4, 3, 6, 9, 1, 2, 5, 10, 7 };
System.out.println("待排序数组:");
show(a);
System.out.println("n直接插入排序:");
InsertSort(a);
System.out.println("n折半插入排序:");
InsertSort1(a);
System.out.println("n希尔排序排序:");
ShellSort(a);
System.out.println("n冒泡排序:");
BubbleSort(a);
System.out.println("n快速排序:");
QuickSort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
show(a);
System.out.println("n选择排序:");
SelectSort(a);
System.out.println("n堆排序:");
HeapSort(a);
System.out.println("n归并排序:");
show(MergeSort(a));
}
}

最后
以上就是坚定睫毛最近收集整理的关于常见的基本排序算法排序算法的全部内容,更多相关常见内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。


![JavaScript 快速排序要求将数组参数中的数字从小到大进行排序并返回该数组。示例:输入:quickSort([0,-1,1,-2,2]).输出:[-2,-1,0,1,2]](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg4.png)





发表评论 取消回复