写在前面
spring容器启动全过程,将组合、继承、反射、代理用到了极致。抽象工厂模式,简单工厂模式,策略模式,单例模式等都有涉及。
功能拆分,代码解耦,每一个功能都会有单独的方法来完成,代码流程条理清晰,逻辑鲜明。
这是一个漫长的过程,中间涉及到各种工作,很复杂,源码看起来很累。
我的源码入手顺序:
最初是为了弄清楚三级缓存的左右和循环依赖,所以看了关于DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton()的源码。
然后是为了弄清楚spring关于观察者模式的源码,也就是关于event-publisher-listener的源码,此部分源码涉及到了容器启动过程中监听器的注册,事件注册等源码。
最后想着已经看了这些了,还不如把整个容器初始化流程源码看完。
几个容易混淆的概念:
Bean与BeanDefinition
FactoryBean与BeanFactory
BeanPostProcessor与BeanFactoryPostProcessor
BeanFactory、BeanPostProcessor、以及数量最多的singleton beans都属于Bean范畴,但初始化过程是分开的。如图:
容器加载的相关类图:
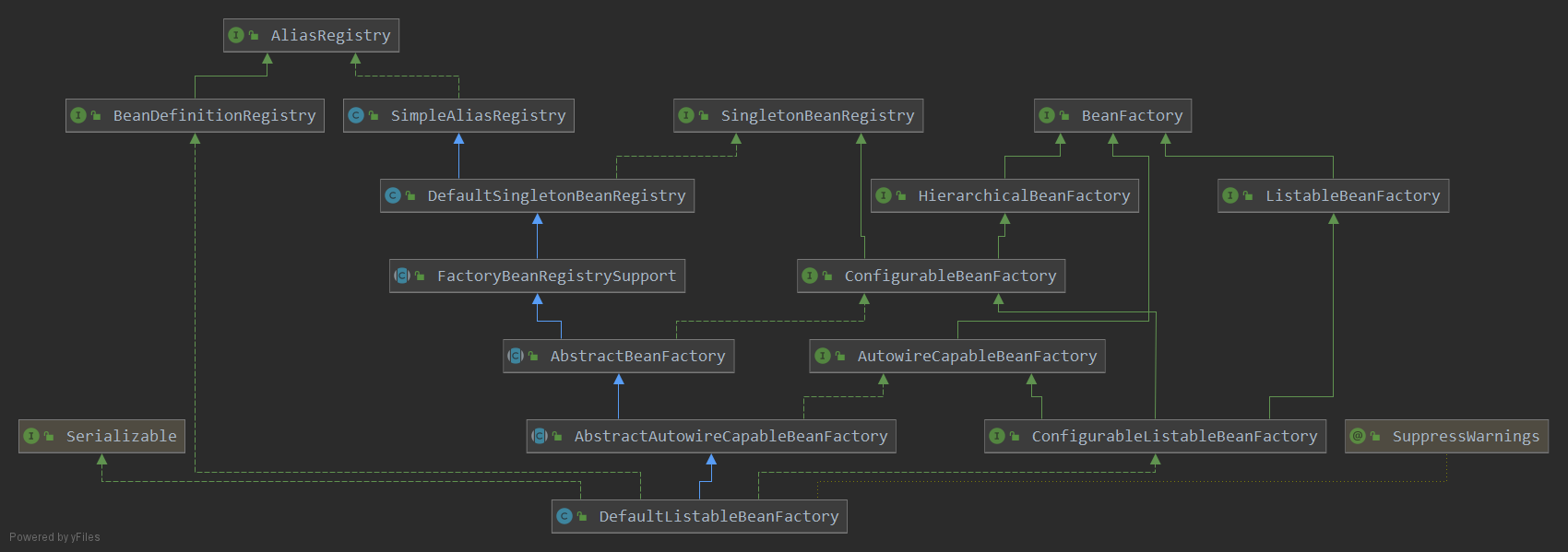
类图中各类的作用(从《Spring源码深度解析》中迁移的):
-
AliasRegistry:定义了对别名 alias 的简单增删改等操作。
-
BeanDefinitionRegistry:定义对 BeanDefinition 的各种增删改操作。
-
SimpleAliasRegistry:主要使用 map 作为 alias 的缓存,存储别名 alias 对应 bean name 的映射,并对接口 AliasRegistry 进行实现。
-
SingletonBeanRegistry:定义对单例的注册及获取。
-
BeanFactory:定义获取单个 bean 及 bean 的各种属性。
-
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry:对接口 SingletonBeanRegistry 各函数的实现,涉及到三级缓存和循环依赖。
-
HierarchicalBeanFactory:继承 BeanFactory,也就是在 BeanFactory 定义的功能的基础上增加了对 parentFactory 的支持,也就是提供纵向支持。
-
ListableBeanFactory:根据各种条件获取 bean 的配置清单,可以一次性获取多个bean,也就是提供横向支持。
-
FactoryBeanRegistrySupport:在 DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry 基础上增加了对 FactoryBean 的特殊处理功能。
-
ConfigurableBeanFactory:大多数bean工厂要实现的配置接口。除了提供BeanFactory 接口中的 bean 工厂客户端方法之外,还提供配置 beanFactory的各种方法。
-
AbstractBeanFactory:综合 FactoryBeanRegistrySupport 和 ConfigurableBeanFactory 的功能。
-
AutowireCapableBeanFactory:提供创建 bean、自动注入、初始化以及应用 bean 的后处理器。
-
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory:综合 AbstarctBeanFactory 并对接口 AutowireCapableBeanFactory 进行实现。
-
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory:BeanFactory 配置清单,指定忽略类型及接口等。
-
DeafultListableBeanFactory:综合上面所有功能,主要是对 Bean 注册后的处理。
了解这些类的大致作用对理解源码有很大帮助,换句话说想要弄懂源码也就需要去知道这些类的作用。
开始源码分析
最简单的spring容器加载应该是从xml配置文件开始,也就是通过代码:
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring-context.xml");
这个代码通过读取 spring-context.xml 文件来加载各种 bean ,配置上下文环境,构建 spring 容器。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的继承关系图:
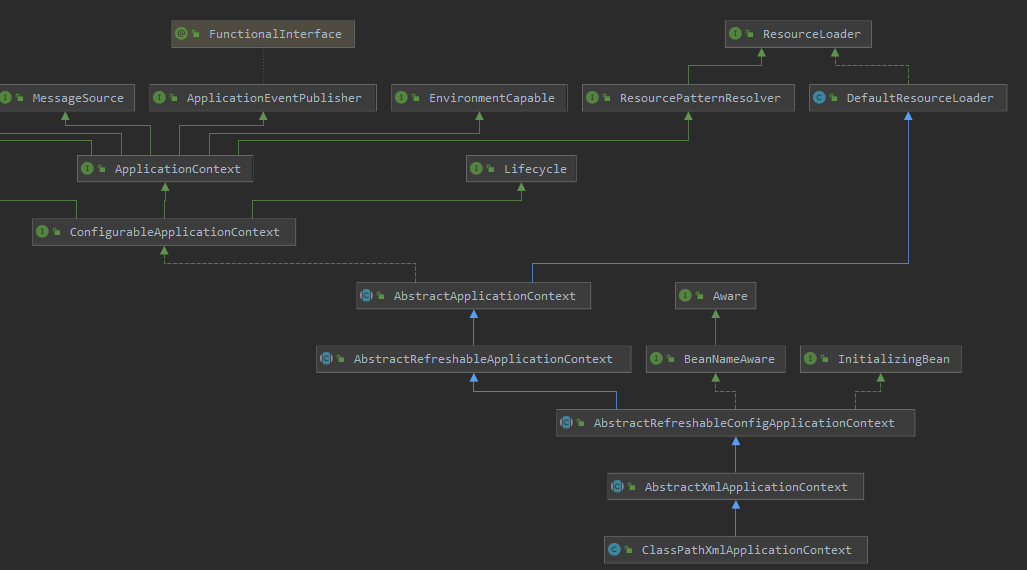
其中最主要的类,也是功能最多的类,应该会是 AbstractApplicationContext 了,启动容器并完成的代码就在其中。
源码分析的切入点也从此开始。
/**
* Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext, loading the definitions
* from the given XML files and automatically refreshing the context.
* @param configLocations array of resource locations
* @throws BeansException if context creation failed
*/
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, true, null);
}
此构造方法随后会去调用如下构造方法:
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
// 一直往上调用所有父类构造方法,最终是将所有环境融合起来
super(parent);
// 设置要读取的配置文件的位置
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
// 重点代码,负责初始化并创造完成容器
refresh();
}
}
这里就要进入初始化以及创建完成容器的方法,也就是 refresh 方法。
首先总体介绍 refresh 方法。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
//先加锁,防止其他线程再次启动或者销毁容器
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
//准备工作,记录下容器的启动时间、标记已启动状态,初始化上下文环境中的任何占位符属性源,
//验证所有标记为必需的属性都是可解析的
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//初始化bean factory,将各种bean注册到BeanFactory中,这里的Bean还没有初始化,只是信息被提取了出来
//注册也只是将这些信息保存在了注册中心(也就是beanName -> beanDefinition 的 map)
//DefaultListableBeanFactory基本实现了所有定义的BeanFactory接口,是最强的BeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 设置 BeanFactory 的类加载器,添加几个 BeanPostProcessor,手动注册几个特殊的 bean
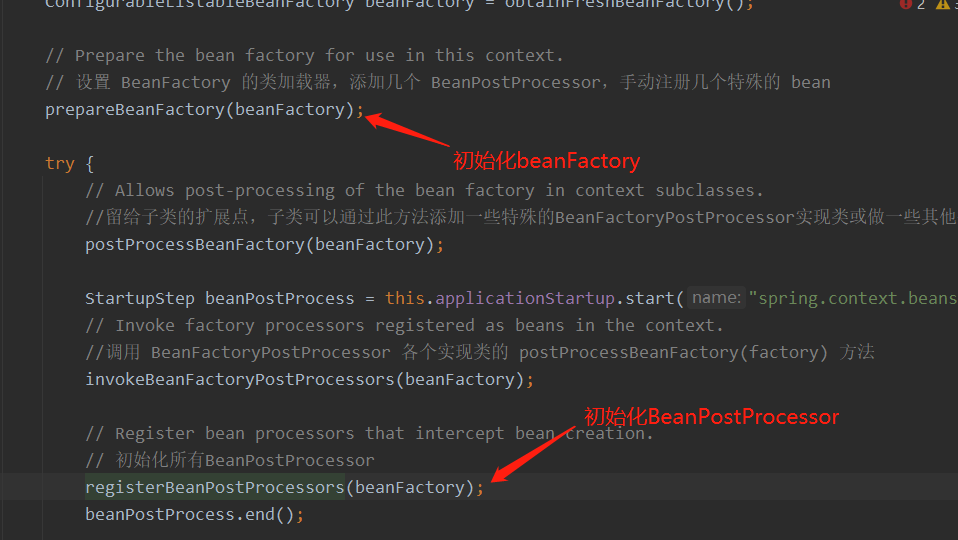
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
//留给子类的扩展点,子类可以通过此方法添加一些特殊的BeanPostProcessor实现类或做一些其他操作
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
//调用 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 各个实现类的 postProcessBeanFactory(factory) 方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 初始化所有BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化事件多播处理器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 负责初始化一些特殊Bean,比如 ThemeSource
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 注册所有 Listener
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
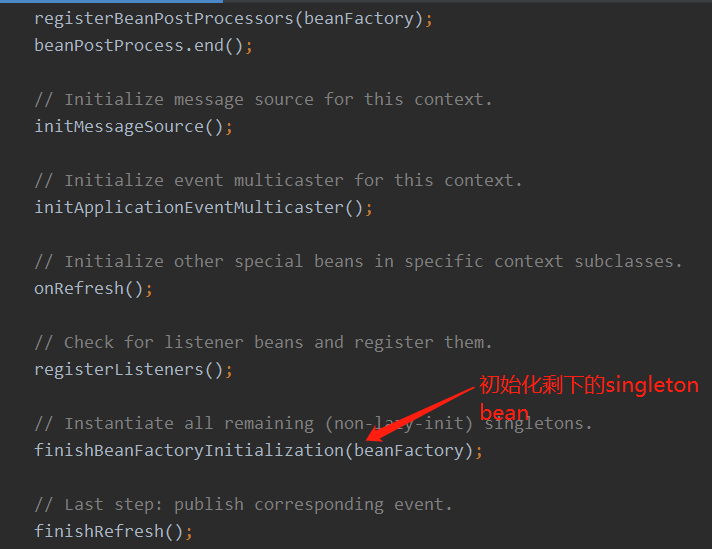
// 初始化所有非懒加载的 singleton bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
我们需要对每个方法都进行解析,此过程会非常复杂、冗长切乏味,但是是弄懂源码的必经之路。
准备工作
开始注册并加载 Bean 前需要对各种环境资源进行检查校验以及初始化。
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
}
else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
// 校验 xml 配置文件,实现类在AbstractEnvironment中
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...
// 初始化 listener 存储容器
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
}
else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
// 初始化早期事件存储器
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
obtainFreshBeanFactory:创建Bean容器,加载并注册 Bean
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
// 关闭旧的 BeanFactory (如果有),创建新的 BeanFactory,加载 Bean 定义、注册 Bean 等等
// AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext类有实现
refreshBeanFactory();
// 返回刚刚创建的 BeanFactory
return getBeanFactory();
}
进入 AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext 类的 refreshBeanFactory 方法
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
// 销毁旧容器和beans
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//ApplicationContext 通过创建这个 BeanFactory 来注册并管理 Bean
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
//设置 BeanFactory 的两个配置属性:是否允许 Bean 覆盖、是否允许循环引用
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//加载Bean到BeanFactory中,包括从xml提取(AbstractXmlApplicationContext),通过注解方式提取(AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext)
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
其中 customizeBeanFactory 方法涉及到两个知识点,bean 覆盖和循环依赖问题,这里不再展开,但是都是需要弄明白的。
然后看一下 AbstractXmlApplicationContext 关于 loadBeanDefinitions 方法的实现:
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
// 设置环境、资源加载器等
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
// 通过 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 解析 xml 配置文件,加载注册 Bean
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
然后在 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 的 loadBeanDefinitions 方法中会对 通过策略模式对 xml 中各种标签进行解析,然后转化成 BeanDefinition 注册至 BeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory)中。
这里需要了解一下 BeanDefinition,官方解释:
BeanDefinition描述一个bean实例,该实例具有属性值、构造函数参数值和具体实现提供的进一步信息。
通俗讲就是存储了关于该 Bean 的所有相关信息,包括需要加载的具体类、作用域、属性值等。
public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement {
// 我们可以看到,默认只提供 sington 和 prototype 两种,
// 很多读者都知道还有 request, session, globalSession, application, websocket 这几种,
// 不过,它们属于基于 web 的扩展。
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON;
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE;
// 比较不重要,直接跳过吧
int ROLE_APPLICATION = 0;
int ROLE_SUPPORT = 1;
int ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE = 2;
// 设置父 Bean,这里涉及到 bean 继承,不是 java 继承。请参见附录介绍
void setParentName(String parentName);
// 获取父 Bean
String getParentName();
// 设置 Bean 的类名称
void setBeanClassName(String beanClassName);
// 获取 Bean 的类名称
String getBeanClassName();
// 设置 bean 的 scope
void setScope(String scope);
String getScope();
// 设置是否懒加载
void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit);
boolean isLazyInit();
// 设置该 Bean 依赖的所有的 Bean,注意,这里的依赖不是指属性依赖(如 @Autowire 标记的),
// 是 depends-on="" 属性设置的值。
void setDependsOn(String... dependsOn);
// 返回该 Bean 的所有依赖
String[] getDependsOn();
// 设置该 Bean 是否可以注入到其他 Bean 中,只对根据类型注入有效,
// 如果根据名称注入,即使这边设置了 false,也是可以的
void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate);
// 该 Bean 是否可以注入到其他 Bean 中
boolean isAutowireCandidate();
// 主要的。同一接口的多个实现,如果不指定名字的话,Spring 会优先选择设置 primary 为 true 的 bean
void setPrimary(boolean primary);
// 是否是 primary 的
boolean isPrimary();
// 如果该 Bean 采用工厂方法生成,指定工厂名称。对工厂不熟悉的读者,请参加附录
void setFactoryBeanName(String factoryBeanName);
// 获取工厂名称
String getFactoryBeanName();
// 指定工厂类中的 工厂方法名称
void setFactoryMethodName(String factoryMethodName);
// 获取工厂类中的 工厂方法名称
String getFactoryMethodName();
// 构造器参数
ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues();
// Bean 中的属性值,后面给 bean 注入属性值的时候会说到
MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues();
// 是否 singleton
boolean isSingleton();
// 是否 prototype
boolean isPrototype();
// 如果这个 Bean 原生是抽象类,那么不能实例化
boolean isAbstract();
int getRole();
String getDescription();
String getResourceDescription();
BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
}
小结一下:到这通过 obtainFreshBeanFactory 方法已经在 ApplicationContext 中创建出了 BeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory),并通过 xml 配置或者注解配置 将所有 Bean 都加载并注册到了该BeanFactory 中(以 BeanName -> BeanDefinition 的 Map 的形式)。
Bean 容器实例化后,开始准备使用 Bean 容器
开始进入 prepareBeanFactory 方法。此方法的作用是设置 BeanFactory 的类加载器,添加几个 BeanPostProcessor,手动注册几个特殊的 bean。
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
// 设置当前ApplicationContext的类加载器
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
if (!shouldIgnoreSpel) {
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
// 添加一个 BeanPostProcessor,这个 processor 比较简单,
// 实现了 Aware 接口的几个特殊的 beans 在初始化的时候,这个 processor 负责回调
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
// 如果某个 bean 依赖于以下几个接口的实现类,在自动装配的时候忽略它们,
// Spring 会通过其他方式来处理这些依赖。
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationStartupAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
/**
* 下面几行就是为特殊的几个 bean 赋值,如果有 bean 依赖了以下几个,会注入这边相应的值,
* 之前我们说过,"当前 ApplicationContext 持有一个 BeanFactory",这里解释了第一行
* ApplicationContext 继承了 ResourceLoader、ApplicationEventPublisher、MessageSource
* 所以对于这几个,可以赋值为 this,注意 this 是一个 ApplicationContext
* 那这里怎么没看到为 MessageSource 赋值呢?那是因为 MessageSource 被注册成为了一个普通的 bean
*/
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
// 将检测内部bean的早期后置处理器注册为applicationlistener
// 这个 BeanPostProcessor 也很简单,在 bean 实例化后,如果是 ApplicationListener 的子类,
// 那么将其添加到 listener 列表中,可以理解成:注册事件监听器
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
/**
* 从下面几行代码我们可以知道,Spring 往往很 "智能" 就是因为它会帮我们默认注册一些有用的 bean,
* 我们也可以选择覆盖
*/
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_STARTUP_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_STARTUP_BEAN_NAME, getApplicationStartup());
}
}
AbstractApplicationContext 准备完 BeanFactory 后,让子类进行一些扩展准备,添加一些特殊的BeanPostProcessor实现类
也就是 postProcessBeanFactory 方法,实现类包括 AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext 、GenericWebApplicationContext、 ResourceAdapterApplicationContext、StaticWebApplicationContext等。
BeanFactory创建并初始化完成,执行所有后置处理方法
BeanFactory的后置处理器是BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,将在invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors调用所有实现类的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法。
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 执行所有后置处理方法
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
进入 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()) 方法
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// WARNING: Although it may appear that the body of this method can be easily
// refactored to avoid the use of multiple loops and multiple lists, the use
// of multiple lists and multiple passes over the names of processors is
// intentional. We must ensure that we honor the contracts for PriorityOrdered
// and Ordered processors. Specifically, we must NOT cause processors to be
// instantiated (via getBean() invocations) or registered in the ApplicationContext
// in the wrong order.
//
// Before submitting a pull request (PR) to change this method, please review the
// list of all declined PRs involving changes to PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate
// to ensure that your proposal does not result in a breaking change:
// https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues?q=PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate+is%3Aclosed+label%3A%22status%3A+declined%22
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
/**
* 如果 beanFactory 还实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistry的功能,
* 需要先执行 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法
*/
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
/**
* 对传入参数 beanFactoryPostProcessors 中的元素进行过滤,
* 区分出实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口的元素和未实现该接口的元素
* 并执行容器中所有 实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口的类的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,
* 用于修改其内部bean定义注册表
*/
// 用户存储未实现 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 集合
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 用于存储实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 集合
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
/**
* 在应用程序上下文的标准初始化之后修改其内部bean定义注册表。所有常规bean定义都将被加载,
* 但是还没有bean被实例化。这允许在下一个后处理阶段开始之前添加进一步的bean定义。
*/
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
/**
* 用于存储将要被调用的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 实现类集合,总共会先后包含三类实现类
* 第一类是实现了 PriorityOrdered 接口排序的实现类
* 第二类是实现了 Ordered 接口排序的实现类
* 第三类是剩下的所有未排序的实现类
* 这三类实现类会按先后顺序被调用
*/
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
// 首先,调用实现 PriorityOrdered 接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors。
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
// 排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 执行所有存在优先级的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
// 接下来,调用实现 Ordered 接口的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors。
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
// 排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
// 执行传入参数 beanFactoryPostProcessors 中的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// 执行传入参数 beanFactoryPostProcessors 中的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
/**
* 到这才开始执行所有关于 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的实现类
* 跟上边调用 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 一样,分为三个集合存储
* 第一个是实现了 PriorityOrdered 接口的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类
* 第二个是实现了 Ordered 接口的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 实现类
* 第三个就是所有剩下的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 实现类,即未排序的实现类
*/
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// 获取到 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的所有实现类
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 过滤出那些实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口的实现类
// 因为这些实现类已经在上边的代码中被调用过了作为 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 实现类的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
关于BeanFactory的后置处理器执行完后,开始注册BeanPostProcessor
后置处理程序执行完,也就是说关于容器中注册的所有bean定义已经完备,可以开始注册关于Bean的前置和后置处理程序BeanPostProcessor。进入 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory) 方法:
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 跟 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法一样,
// 都是通过调用 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate 类的同名方法实现
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}
进入方法内:
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// 首先获取所有 BeanPostProcessor 接口的实现类
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// 添加 BeanPostProcessorChecker
// 用于当bean在BeanPostProcessor实例化期间被创建时,即当一个bean不符合被所有BeanPostProcessor处理的条件时,记录一个信息消息。
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
// 根据是否实现 PriorityOrdered、Ordered 或 rest 进行分离
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 用于存储实现 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 接口的类
// 在bean实例化完毕后调用 可以用来修改merged BeanDefinition的一些properties 或者用来给后续回调中缓存一些meta信息使用
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 最后注册 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 实现类
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
// 将 ApplicationListenerDetector 移动到最后
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
Bean后置处理器注册完毕,开始初始化上下文消息源和事件多播处理器以及一些特殊Bean
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化事件多播处理器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
这两个方法内容差不多,是对以下两个属性的初始化:
/** MessageSource we delegate our implementation of this interface to. */
@Nullable
private MessageSource messageSource;
/** Helper class used in event publishing. */
@Nullable
private ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster;
而对于特殊bean,则要通过扩展 onRefresh 方法来初始化
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 负责初始化一些特殊Bean,比如 ThemeSource
onRefresh();
比如 AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext :
/**
* Initialize the theme capability.
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
this.themeSource = UiApplicationContextUtils.initThemeSource(this);
}
开始注册 Listener
/**
* Add beans that implement ApplicationListener as listeners.
* Doesn't affect other listeners, which can be added without being beans.
*/
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
/**
* 系统内置的listener添加
*/
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
/**
* 自定义实现ApplicationListener的Bean名称添加
* 这里添加的虽然是Bean名称的集合,但是在发布事件前会通过
* {@link org.springframework.context.event.AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster#getApplicationListeners(ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType)}
* 获取到与事件相关的全部Listener Bean
*/
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(earlyEventsToProcess)) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
重头戏,开始初始化所有非懒加载的Bean
/**
* Finish the initialization of this context's bean factory,
* initializing all remaining singleton beans.
*/
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
//首先初始化conversionService
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// (such as a PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
// 停止使用临时ClassLoader进行类型匹配。
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
// 到这一步的时候,Spring 已经开始预初始化 singleton beans 了,
// 肯定不希望这个时候还出现 bean 定义解析、加载、注册。开始允许缓存所有的bean信息
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 开始初始化singleton bean
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
直接进入最后的beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons()方法,实现在功能最多的 DefaultListableBeanFactory 类中:
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
// 获取所有已经注册的 bean name
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 合并父 Bean 中的配置,如 <bean id="" class="" parent="" /> 中的 parent
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 只处理非抽象、单例、非懒加载的Bean
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 处理factoryBean(FactoryBean可以理解为复杂Bean加工厂,通过getObject方法直接获取到加工好的复杂Bean)
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
// FactoryBean 的话,在 beanName 前面加上 ‘&’ 符号。
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
// 判断当前 FactoryBean 是否是 SmartFactoryBean 的实现,
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
// 初始化Bean的方法
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
// 到这里说明所有的非懒加载的 singleton beans 已经完成了初始化
// 如果定义的 bean 是实现了 SmartInitializingSingleton 接口的,那么在这里得到回调
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
StartupStep smartInitialize = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.beans.smart-initialize")
.tag("beanName", beanName);
SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
smartInitialize.end();
}
}
}
初始化 Bean 的操作就在 getBean() 方法中:
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
直接进入 AbstractBeanFactory 类的 doGetBean 方法:
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
// 获取一个 “正统的” beanName,也就是针对每一个bean都唯一的beanname,无论这个bean出现几次,都是这个name,
// 处理两种情况,一个是FactoryBean(前面带 ‘&’),
// 一个是别名问题,因为这个方法是 getBean,获取 Bean 用的,要是传一个别名进来,是完全可以的
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
// 返回值
Object beanInstance;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
/**
* 检查一下是否已经创建过了
* 先尝试获取一次单例bean,如果能获取到就直接走缓存了
* 包含三级缓存
*/
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
// 如果是为了创建bean,那么args参数就是有用的,
// 也就是说如果 args 不为空的时候,那么意味着调用方不是希望获取 Bean,而是创建 Bean
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
// 包含两种bean:一种原生bean,一种factorybean,后者需要通过getObject方法才能获取到真正的bean
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
//单例bean获取失败,是第一次创建
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
/**
* 不是单例模式
*/
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
// 当前线程已经创建过了此 beanName 的 prototype 类型的 bean,那么抛异常
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
/**
* 检查一下这个 BeanDefinition 在容器中是否存在
* 如果不存在且有父beanFactory则通过父beanFactory创建一次bean
*/
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else if (requiredType != null) {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
else {
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup);
}
}
/**
* 判断是否只是检查类型,如果不是则在创建之前将该bean加入正在创建集合中,及当前创建Bean池,标记该bean正在被创建
*/
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
/**
* 用于记录关于应用程序启动期间发生的特定阶段或操作
*/
StartupStep beanCreation = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.beans.instantiate")
.tag("beanName", name);
/**
* 开始创建bean,对于单例bean,容器中还没有创建过此Bean;
* 对于prototype的Bean,本来就是要创建一个新的Bean
*/
try {
if (requiredType != null) {
beanCreation.tag("beanType", requiredType::toString);
}
// 先合并所有关于此Bean的定义
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
// 先初始化依赖的所有 Bean,这个很好理解。
// 注意,这里的依赖指的是 depends-on 中定义的依赖
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
// 注册一下依赖关系
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
// 先初始化被依赖项
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
//创建单例Bean
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
/**
* 真正创建Bean的方法
*/
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 创建 prototype 的实例
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 如果不是 singleton 和 prototype 的话,需要委托给相应的实现类来处理
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(scopeName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No scope name defined for bean ´" + beanName + "'");
}
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new ScopeNotActiveException(beanName, scopeName, ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
beanCreation.tag("exception", ex.getClass().toString());
beanCreation.tag("message", String.valueOf(ex.getMessage()));
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
finally {
beanCreation.end();
}
}
return adaptBeanInstance(name, beanInstance, requiredType);
}
其中 getSingleton(beanName) 方法涉及到 Spring 三级缓存的概念,不懂得建议百度。代码解析:
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// Quick check for existing instance without full singleton lock
/**
* 先从一级缓存中获取单例bean
* 如果不存在且该bean正在创建中,则从二级缓存中查找该bean
*/
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
/**
* 从二级缓存中获取bean,如果bean不存在且允许循环依赖,则继续查看三级缓存
*/
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Consistent creation of early reference within full singleton lock
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
/**
* 查看三级缓存,若三级缓存中存在则把它放入二级缓存
* 加入singletonFactories三级缓存的前提是执行了构造器,所以构造器的循环依赖没法解决
*/
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
//放入二级缓存
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
//从三级缓存中移除该bean对应的factory
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
然后进入真正创建 bean 的方法,AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 类的 createBean() 方法:
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
// 确保 BeanDefinition 中的 Class 被加载
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
// 准备方法覆盖
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
// 让 BeanPostProcessor 在这一步有机会返回代理,而不是 bean 实例
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
/**
* 创建Bean
*/
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}
进入 doCreateBean 方法:
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 能到这,说明不是factoryBean,在这里实例化bean
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
// 解决循环依赖的问题
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
/**
* 将能获取到该bean的ObjectFactory放入三级缓存中,通过getEarlyBeanReference方法可以处理AOP动态代理,获取到的直接就是代理类
*/
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
/**
* 填充属性,解决@Autowired依赖,因为前面的实例只是实例化了,并没有设值,这里就是设值
*/
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
/**
* 执行初始化回调方法
* 处理 bean 初始化完成后的各种回调
*/
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
最终创建 bean 实例的方法在 createBeanInstance() 中:
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
// 校验一下这个类的访问权限
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
// 返回一个回调函数来创建bean,如果有的话
Supplier<?> instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
}
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
// 通过工厂方法创建bean,注意与FactoryBean.getObject()区分
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
// 如果不是第一次创建,比如第二次创建 prototype bean。
// 这种情况下,可以从第一次创建知道,采用无参构造函数,还是构造函数依赖注入 来完成实例化
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
if (resolved) {
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// Candidate constructors for autowiring?
// 判断是否采用有参构造函数
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
// 使用有参构造函数创建 bean 实例
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// Preferred constructors for default construction?
ctors = mbd.getPreferredConstructors();
if (ctors != null) {
// 使用默认构造的首选构造函数创建 bean 实例
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, null);
}
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
// 使用无参构造函数创建 bean 实例
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
到这 bean 已经初始化完成,实例也被创建成功,但是并没有设置属性值,设置属性值在方法 populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper) 中:
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
// 到这步的时候,bean 实例化完成(通过工厂方法或构造方法),但是还没开始属性设值,
// InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的实现类可以在这里对 bean 进行状态修改
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
if (!bp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
// bean 实例的所有属性都在这里
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
// 通过名字找到所有属性值,如果是 bean 依赖,先初始化依赖的 bean。记录依赖关系
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
PropertyValues pvsToUse = bp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = bp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
设置完属性之后 bean 就算被构建完成了,但是别忘了还有各种 bean 后置处理器没有执行,所以要通过initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd) 方法执行各种回调:
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 如果 bean 实现了 BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware 或 BeanFactoryAware 接口,回调
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 执行所有 BeanPostProcessor 的前置回调方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 处理 bean 中定义的 init-method,
// 或者如果 bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,调用 afterPropertiesSet() 方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 执行所有 BeanPostProcessor 的后置回调方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
至此,bean初始化的全过程已经结束,然后回到 AbstractBeanFactory 的 doGetBean 方法,具体如图:
进入此 getSingleton 方法
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) {
throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName,
"Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " +
"(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
/**
* 创建bean之前先把该bean放入正在创建的缓存集合中,标记该bean正在创建
*/
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
try {
// 会调用实现类的createBean()方法
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
/**
* bean创建完成后,从正在创建的缓存集合中移除该bean
*/
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
if (newSingleton) {
/**
* bean对象创建完成,注册到一级缓存中,从二、三及缓存中删除该bean
*/
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
}
会发现在 bean 对象完全创建成功后会将该 bean 添加至一级缓存 singletonObjects 中,同时从二级缓存 earlySingletonObjects 和三级缓存 earlySingletonObjects 移除该 bean,并将该 bean 添加至已注册 Singleton Bean 列表 registeredSingletons 中。
至此,spring 容器加载的全过程已经结束,中间部分方法代码未展开,若想完整理清整个流程,最好的方式是自己编写测试用例,通过 debug 跟随程序执行不断熟悉代码,最终弄懂弄透。
撰写本文时参考了很多此链接的内容:
参考:https://javadoop.com/post/spring-ioc
最后
以上就是柔弱小丸子最近收集整理的关于spring启动全过程写在前面开始源码分析的全部内容,更多相关spring启动全过程写在前面开始源码分析内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复