反射
运行时,区别于翻译时,指的是程序被加载到内存中执行的时候。
反射,reflection,指的是运行时获取类型定义信息。
一个对象能够在运行时,像照镜子一样,反射出其类型信息。简单说,在Python中,能够通过一个对象,找出其type、class、attribute或method的能力,称为反射或自省。
具有反射能力的函数有type(),isinstance(),callable().dir().getattr()等
反射相关的函数和用法
class Point:
def __init__(self,x,y):
self.x=x
self.y=y
def __str__(self):
return "{} and {}".format(self.x,self.y)
def show(self):
print(self.x,self.y)
p=Point(4,5)
print(p)
print(p.__dict__)
p.__dict__['y']=16
print(p.__dict__)
p.z=10
print(p.__dict__)
print(dir(p))
print(sorted(p.__dir__()))

上例通过属性字典__dict__来访问对象的属性,本质上就是利用反射的能力,但是上面的例子中,访问的方式不优雅,Python提供了内置的函数
| 内建函数 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| getattr(object,name[,default]) | 通过name返回object的属性值,当属性不存在,将属性不存在,将使用default返回,如果没有default,则抛出AttributeError,name必须是字符串 |
| setattr(object,name,value) | object的属性,则覆盖,不存在则新增 |
| hasaattr(object,name) | 判断对象是否有这个名字的属性,name必须为字符串 |
class Point:
def __init__(self,x,y):
self.x=x
self.y=y
def __str__(self):
return "{}{}".format(self.x,self.y)
def show(self):
print(self)
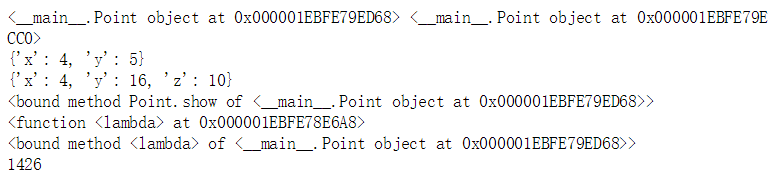
p1=Point(4,5)
p2=Point(10,10)
print(repr(p1),repr(p2))
print(p1.__dict__)
setattr(p1,'y',16)
setattr(p1,'z',10)
print(getattr(p1,'__dict__'))
#动态调用方法
if hasattr(p1,'show'):
print(getattr(p1,'show'))
# 动态增加方法
if not hasattr(Point,'add'):
setattr(Point,'add',lambda self,other: Point(self.x+other.x,self.y+other.y))
print(Point.add)
print(p1.add)
print(p1.add(p2))
#为实例增加方法,
#为实例增加方法,
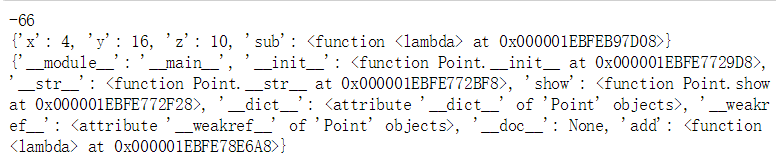
if not hasattr(p1,'sub'):
setattr(p1,'sub',lambda self,other: Point(self.x-other.x,self.y-other.y))
print(p1.sub(p1,p2))
print(p1.__dict__)
print(Point.__dict__)
反射相关的魔术方法
getattr()、setattr()、delattr()这三个魔术方法。
getattr()
class Base:
n = 0
class Point(Base):
z = 6
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
def show(self):
print(self.x, self.y)
def __getattr__(self, item):
return item
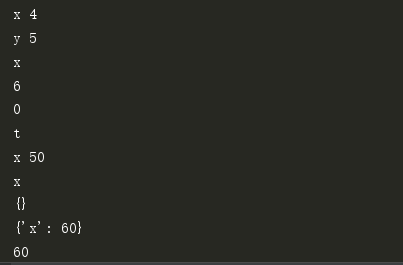
p1=Point(4,5)
print(p1.x)
print(p1.z)
print(p1.n)
print(p1.t)

实例属性会按照继承关系寻找,如果找不到,就会执行__getattr__()方法,如果没有这个方法,就会抛出AttributeError异常标识找不到属性
查找属性顺序为:
instance__dict__---->instance.class.dict---->继承的祖先类(直到object)的__dict__—>找不到—>调用setattr()
class Base:
n = 0
class Point(Base):
z = 6
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
def show(self):
print(self.x, self.y)
def __getattr__(self, item):
return item
def __setattr__(self, key, value):
print(key,value)
p1=Point(4,5)
print(p1.x)
print(p1.z)
print(p1.n)
print(p1.t)
p1.x=50
print(p1.x)
print(p1.__dict__)
p1.__dict__['x']=60
print(p1.__dict__)
print(p1.x)
实例通过.点号设置属性,例如self.x=x,就会代用__setattr__(),属性要加到实例的__dict__中,就需要自己完成。
setattr()方法,可以拦截堆实例属性的增加,修改操作,如果要设置生效,需要自己操作实例的__dict__
class Base:
n = 200
class A(Base):
z = 100
d={}
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
setattr(self,'y',y)
self.__dict__['a']=5
def __getattr__(self, item):
print(item)
return self.d[item]
def __setattr__(self, key, value):
print(key,value)
self.d[key]=value
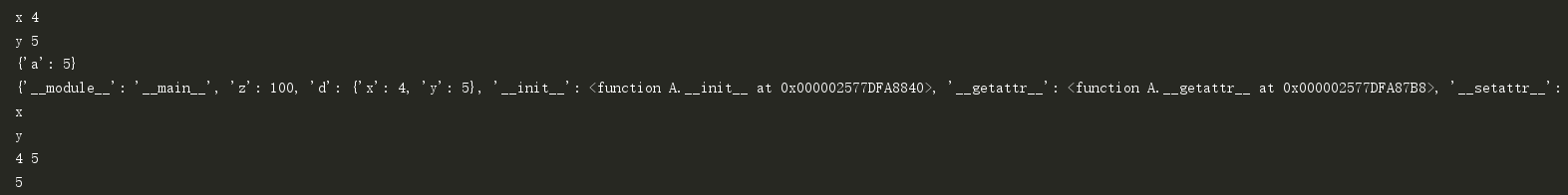
a=A(4,5)
print(a.__dict__)
print(A.__dict__)
print(a.x,a.y)
print(a.a)
delattr()
class Point:
z=5
def __init__(self,x,y):
self.x=x
self.y=y
def __delattr__(self,item):
print(item) p=Point(14,5)
del p.x
p.z=15
del p.z
del p.Z
print(Point.__dict__)

可以阻止通过实例来删除属性的操作
getattribute
class Base:
n=0
class Point(Base):
z=6
def __init__(self,x,y):
self.x=x
self.y=y
def __getattr__(self,item):
return item
def __getattribute__(self,item):
return item
p1=Point(4,5)
print(p1.__dict__)
print(p1.x)
print(p1.z)
print(p1.n)
print(p1.t)
print(Point.__dict__)
print(Point.z)

实例的所有的属性访问,第一个都会调用__getattribute__方法,它阻止了属性的查找,该方法应该返回值或者抛出一个AttributeError异常
- 它的return值将作为属性查找的结果
- 如果抛出AttributeError异常,则会直接调用__getattr__方法,因为属性没有找到
__getattribute__方法中为了避免在该方法中无线递归,它的实现应该永远调用基类的同名方法以访问需要的任何属性,需要注意的是,除非明确知道__getattrtbute__方法用来做什么,否则不要使用
| 魔术方法 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| getattr() | 当通过搜索实例,实例的类及祖先类查找不到属性,就会调用此方法 |
| setattr() | 通过.访问实例属性,进行增加、修改都要调用它 |
| delattr() | 当通过实例来删除属性时调用此方法 |
| getattribute | 实例所有的属性都从这个方法开始 |
属性查找顺序:
实例调用__getattribute__()—>instance.dict–>instance.class.dict–>继承的祖先类(直到object)的__dict__–>调用__getattr__()
最后
以上就是机灵鸵鸟最近收集整理的关于Python中反射的全部内容,更多相关Python中反射内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复