迭代器iterator

1.什么是迭代器
迭代器是访问集合的一种方式,可以记住遍历位置的对象,迭代器从集合的第一个元素开始访问,直到所有的元素被访问完才结束,只能往往前,不能后退。
可以直接作用于for循环的数据类型:
-
一类是集合数据类型:如:
list,tuple,dict,set,str等; -
一类是
generator,包括生成器和yield关键字的生成器函数generator function。 -
这些可以直接作用于
for循环的对象统称为可迭代对象:Iterable.
a = (1,) # 元组
b = [1, 2] # 列表
c = {} # 空字典
d = () # 元组
s = set()
s1 = {None} # 集合
print(type(c)) # 空集合 <class 'dict'>
print(type(d)) # <class 'tuple'>
print(type(s)) # 空集合 <class 'set'>
2.Iterable可迭代对象判断
可以使用
instance()判断一个对象是否是Iterable对象。
instance()函数
def isinstance(x, A_tuple): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
Return whether an object is an instance of a class or of a subclass thereof.
(返回一个对象是类的实例还是类的子类。)
A tuple, as in ``isinstance(x, (A, B, ...))``, may be given as the target to
check against. This is equivalent to ``isinstance(x, A) or isinstance(x, B)
or ...`` etc.
(一个元组,如' ' isinstance(x, (A, B,…))' ',可以被指定为目标
核对。这相当于' ' isinstance(x, A)或isinstance(x, B)
or ...`` etc.)
"""
pass
代码实现:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @File : iterable对象判断.py
# @author: Flyme awei
# @email : Flymeawei@163.com
# @Time : 2022/8/20 22:09
from collections.abc import Iterable
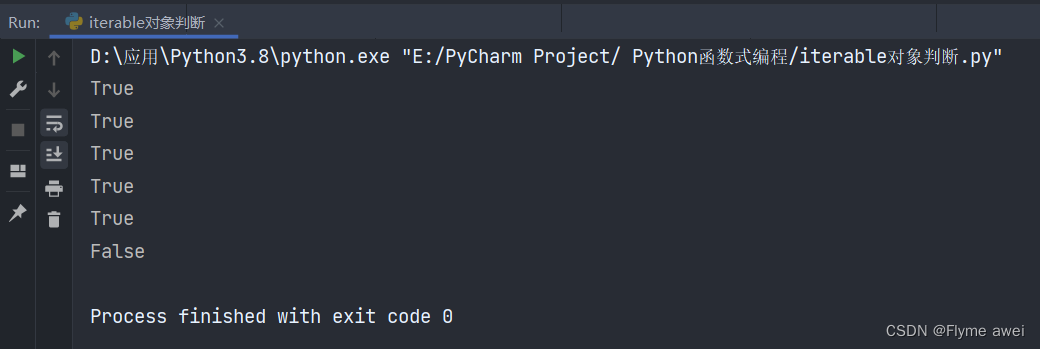
print(isinstance([1], Iterable)) # True
print(isinstance({0, 1}, Iterable)) # True
print(isinstance((1, ''), Iterable)) # True
print(isinstance({1: 10}, Iterable)) # True
print(isinstance((i for i in range(10)), Iterable)) # True
print(isinstance(10, Iterable)) # False
⽣成器不但可以作⽤于for循环,还可以被next()函数不断调⽤并返回下⼀个值,直到最后抛出StopIteration错误表示⽆法继续返回下⼀个值了。
可以被
next()函数调⽤并不断返回下⼀个值的对象称为迭代器:Iterator。
可以使⽤
isinstance()判断⼀个对象是 否是Iterator对象,这里就产生一个疑问了,生成器都是Iterator对象,那么list、dict、str是不是Iterator?为什么?。
3.Iterator迭代器判断
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @File : iterator迭代器判断.py
# @author: Flyme awei
# @email : Flymeawei@163.com
# @Time : 2022/8/20 22:40
from collections.abc import Iterator
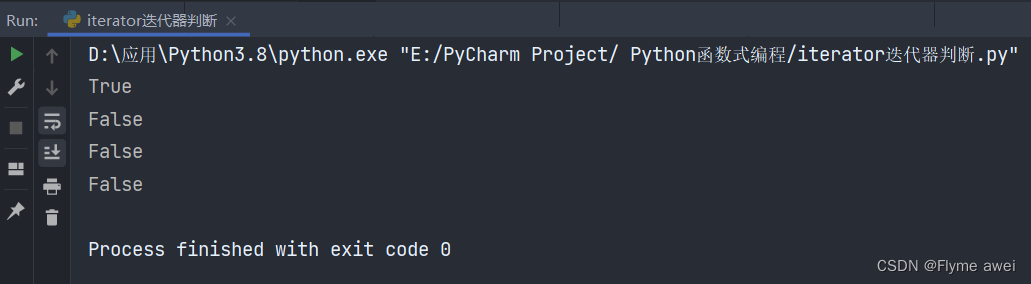
print(isinstance((i for i in range(10) if i % 2 == 0), Iterator)) # True
print(isinstance([], Iterator)) # False
print(isinstance({}, Iterator)) # False
print(isinstance('abc', Iterator)) # False
可以得出
list、dict、str不是Iterator,因为Python的Iterator对象表示的是一个数据流,Iterator对象可以 被next()函数调用并不断返回下一个数据,直到没有数据时抛出StopIteration错误。
可以把这个数据流看做 是一个有序序列,但我们却不能提前知道序列的长度,
只能不断通过next()函数实现按需计算下一个数据,所以Iterator的计算是惰性的,只有在需要返回下一个数据时它才会计算。
Iterator甚至可以表示一个无限大的数据流,例如全体自然数。而使用list是永远不可能存储全体自然数的 那我们还可以通过isinstance()来判断是否是Iterator对象
注意: Iterator 和 Iterable ,一个是迭代器,一个是可迭代对象
但是可以使用
iter()函数将list、dict、str等Iterable变成Iterator。
iter()函数.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @File : iter()函数.py
# @author: Flyme awei
# @email : Flymeawei@163.com
# @Time : 2022/8/20 22:46
from collections.abc import Iterator
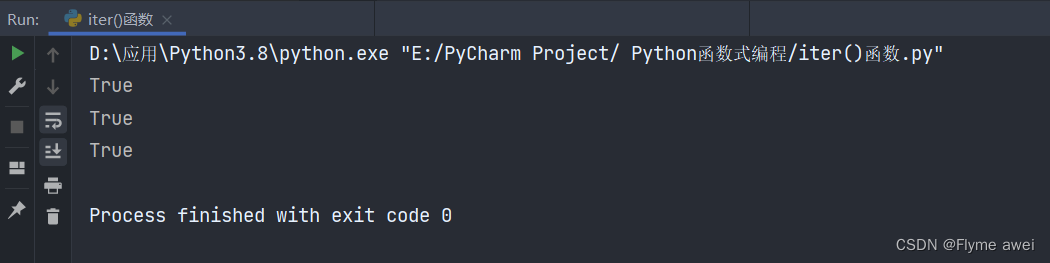
print(isinstance(iter([]), Iterator)) # True
print(isinstance(iter({}), Iterator)) # True
print(isinstance(iter('abc'), Iterator)) # True
4.迭代器与可迭代对象
所有可以作用于
for循环的对象都是Iterable可迭代对象类型;
可以作用于
next()函数的对象都是itreator迭代器类型,他们表示一个惰性计算序列;
集合数据类型
list,dict,str等是Iterable但不是Iterator,不过可以通过iter()函数获得一个Iterator对象。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @File : 迭代器和可迭代对象.py
# @author: Flyme awei
# @email : Flymeawei@163.com
# @Time : 2022/8/20 23:00
# 迭代器 可以被next()函数调⽤并不断返回下⼀个值的对象称为迭代器:Iterator。
from collections.abc import Iterator, Iterable
# iterable 可迭代对象
# iterator 迭代器
a = (1,) # 元组
b = [1, 2] # 列表
c = {} # 空字典
d = () # 元组
s = set()
s1 = {None} # 集合
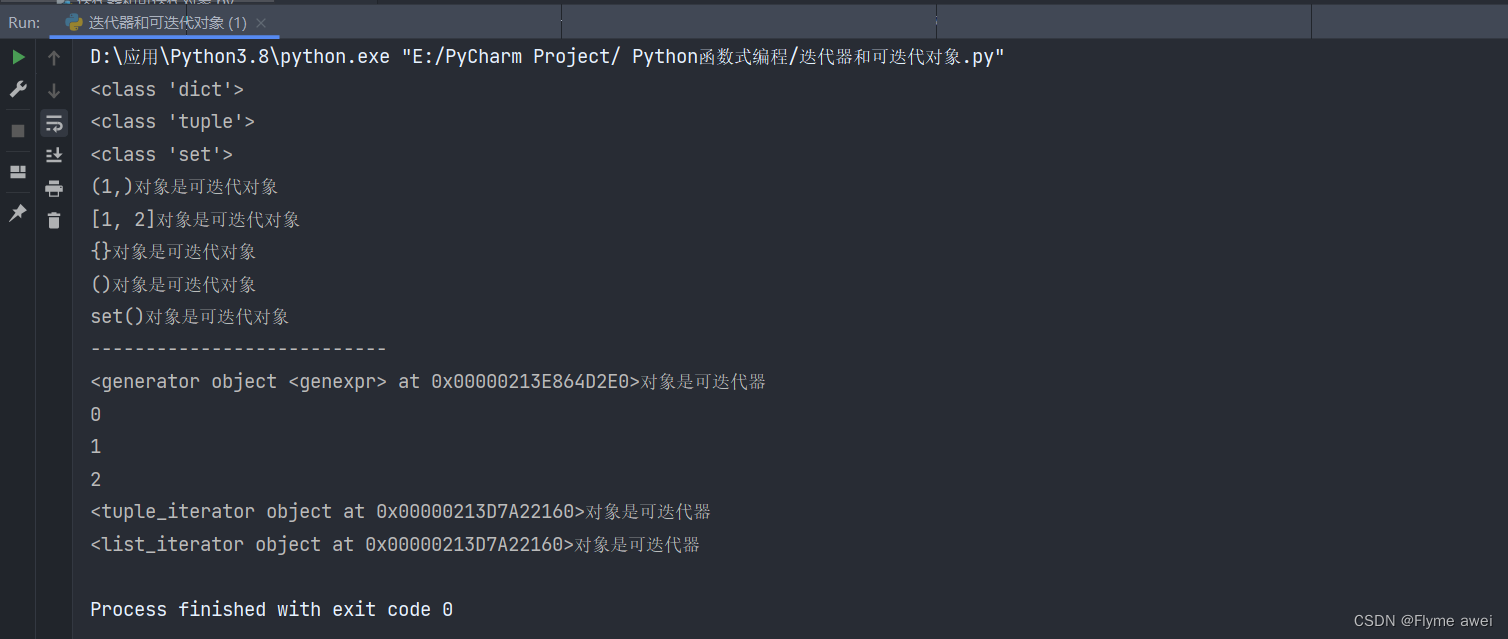
print(type(c)) # 空集合 <class 'dict'>
print(type(d)) # <class 'tuple'>
print(type(s)) # 空集合 <class 'set'>
# isinstance判断
# 可作用于for循环的对象都是iterable类型
def fun(args):
if isinstance(args, Iterable):
print(f'{args}对象是可迭代对象')
else:
print(f'{args}对象不是可迭代对象')
fun(a) # 函数调用
fun(b)
fun(c)
fun(d)
fun(s)
print('---------------------------')
# 渴作用与next()函数的对象都是iterator类型,他们表示一个惰性计算的序列
def fun1(args):
if isinstance(args, Iterator):
print(f'{args}对象是可迭代器')
else:
print(f'{args}对象不是可迭代器')
g = (i for i in range(10))
fun1(g)
print(next(g))
print(next(g))
print(next(g))
# 用python内置函数iter()函数 把list dict str等 iterable变成iterator迭代器
fun1(iter(a))
fun1(iter(b))
最后
以上就是活力电话最近收集整理的关于【Python高级语法】——迭代器 (Iterator)迭代器iterator的全部内容,更多相关【Python高级语法】——迭代器内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复