项目介绍
代码链接
飞桨推出的Paddle-Detection是端到端目标检测开发套件,旨在帮助开发者更快更好地完成检测模型的训练、精度速度优化到部署全流程。PaddleDetection以模块化的设计实现了多种主流目标检测算法,并且提供了丰富的数据增强、网络组件、损失函数等模块,集成了模型压缩和跨平台高性能部署能力。目前基于PaddleDetection已经完成落地的项目涉及工业质检、遥感图像检测、无人巡检等多个领域。
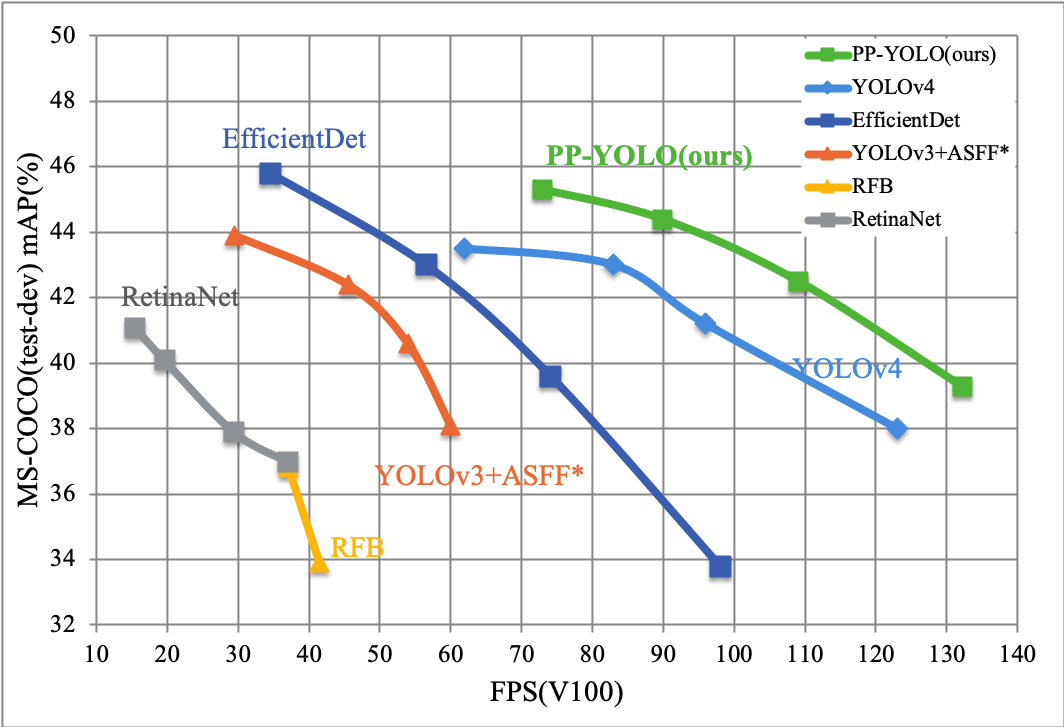
PaddleDetection新发布精度速度领先的PP-YOLO模型,COCO数据集精度达到45.2%,单卡Tesla V100预测速度达到72.9 FPS。从此图可以看出其性能各方面均高于YOLOV4.
环境搭建
1.https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection 进入该链接下载对应操作系统的版本PaddlePaddle Fluid v.1.6。
需要注意的是必须安装好对应的依赖cuda和cudnn:[cuda安装](https://blog.csdn.net/wanzhen4330/article/details/81699769)
CUDA >= 8.0
cuDNN >= 5.0
nccl >= 2.1.2
2.安装COCO-API
git clone https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi.git
cd cocoapi/PythonAPI
# 若Cython未安装,安装Cython
pip install Cython
# 安装至全局site-packages
make install
# 若您没有权限或更倾向不安装至全局site-packages
python setup.py install --user
# 或者使用pip安装
pip install "git+https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi.git#subdirectory=PythonAPI"
3. 通过以下命令克隆PaddleDetection:
cd <path/to/clone/PaddleDetection>
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection.git
4. 安装python依赖包
cd 到指定文件夹
pip install -r requirements.txt
5 简单测试
python ppdet/modeling/tests/test_architectures.py
如下界面即成功安装。
(py36) z@z-SYS-4028GR-TR2:~/zuo/PaddleDetection$ python ppdet/modeling/tests/test_architectures.py
ss..........
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 12 tests in 3.133s
数据集制作
Pascal VOC 数据集目录结构如下:
dataset/voc/
├── trainval.txt
├── test.txt
├── label_list.txt (optional)
├── VOCdevkit/VOC2007
│ ├── Annotations
│ ├── 001789.xml
│ | ...
│ ├── JPEGImages
│ ├── 001789.jpg
│ | ...
│ ├── ImageSets
│ | ...
├── VOCdevkit/VOC2012
│ ├── Annotations
│ ├── 2011_003876.xml
│ | ...
│ ├── JPEGImages
│ ├── 2011_003876.jpg
│ | ...
│ ├── ImageSets
│ | ...
| ...
coco如下:
dataset/coco/
├── annotations
│ ├── instances_train2014.json
│ ├── instances_train2017.json
│ ├── instances_val2014.json
│ ├── instances_val2017.json
│ | ...
├── train2017
│ ├── 000000000009.jpg
│ ├── 000000580008.jpg
│ | ...
├── val2017
│ ├── 000000000139.jpg
│ ├── 000000000285.jpg
│ | ...
| ...
实现voc-coco的转化:
python tools/x2coco.py
--dataset_type voc
--voc_anno_dir path/to/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/Annotations/
--voc_anno_list path/to/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt
--voc_label_list dataset/voc/label_list.txt
--voc_out_name voc_train.json
对照这个官方给出的代码,在pycharm对照改写如下:
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter)
parser.add_argument('--dataset_type', help='the type of dataset',default='voc')
parser.add_argument('--json_input_dir', help='input annotated directory')
parser.add_argument('--image_input_dir', help='image directory')
parser.add_argument(
'--output_dir', help='output dataset directory', default='')
parser.add_argument(
'--train_proportion',
help='the proportion of train dataset',
type=float,
default=1.0)
parser.add_argument(
'--val_proportion',
help='the proportion of validation dataset',
type=float,
default=0.0)
parser.add_argument(
'--test_proportion',
help='the proportion of test dataset',
type=float,
default=0.0)
parser.add_argument(
'--voc_anno_dir',
help='In Voc format dataset, path to annotation files directory.',
type=str,
default='./VOCdevkit/VOC2007/Annotations/')
parser.add_argument(
'--voc_anno_list',
help='In Voc format dataset, path to annotation files ids list.',
type=str,
default='VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt')
parser.add_argument(
'--voc_label_list',
help='In Voc format dataset, path to label list. The content of each line is a category.',
type=str,
default='./label_list.txt')
parser.add_argument(
'--voc_out_name',
type=str,
default='voc_train.json',
help='In Voc format dataset, path to output json file')
args = parser.parse_args()
运行后会在tools/下生成voc_train.json
过程如下:
Start converting !
100%|██████████| 153/153 [00:00<00:00, 10922.29it/s]
按照同样方法生成voc_test.json和和voc_val.json
然后将其放到上述coco格式中:
即tools/datasets/coco/… 数据集很重要,很多错误都源于这。
选择模型
PaddleDetection中提供了丰富的模型库,具体可在模型库中查看各个模型的指标,可依据实际部署算力的情况,选择合适的模型。
算力资源小时,使用移动端模型,PaddleDetection中的移动端模型经过迭代优化,具有较高性价比。
算力资源强大时,使用服务器端模型,该模型是PaddleDetection提出的面向服务器端实用的目标检测方案。同时也可以根据使用场景不同选择合适的模型。
当小物体检测时,使用两阶段检测模型,比如Faster RCNN系列模型,具体可在模型库中找到。
同时也可以使用PaddleDetection中开发的YOLOv3增强模型、YOLOv4模型与Anchor Free模型等。
选择好模型后,需要在configs目录中找到对应的配置文件,为了在自定义数据集上训练,需要对参数配置做一些修改:
COCO数据集:
dataset:
!COCODataSet
image_dir: val2017 # 图像数据基于数据集根目录的相对路径
anno_path: annotations/instances_val2017.json # 标注文件基于数据集根目录的相对路径
dataset_dir: dataset/coco # 数据集根目录
with_background: true # 背景是否作为一类标签,默认为true。
这里选择的是ppylolo_r18vd.yml,路径和类别修改后,开始训练。
修改最大迭代次数:
max_iters=epoch×训练集数目/2倍的gpu个数
比如训练集200,一个gpu,选取epoch=12时,max_iters=2400/2=1200
尽管我选择的ppylolo_r18vd.yml,但是其基于ppyolo_reader.yml
找到这部分进行修改,不然测试时全是官方类别:
TestReader:
inputs_def:
image_shape: [3, 608, 608]
fields: ['image', 'im_size', 'im_id']
dataset:
!ImageFolder
#anno_path: annotations/instances_val2017.json
#修改
anno_path: dataset/coco/annotations/instances_val2017.json
with_background: false
训练及测试
在pycharm上方参数行输入:
-c /home/z/zuo/PaddleDetection/configs/ppyolo/ppyolo_r18vd.yml --eval
运行结果:
2020-09-26 16:16:06,211-INFO: places would be ommited when DataLoader is not iterable
W0926 16:16:06.233088 11782 device_context.cc:252] Please NOTE: device: 0, CUDA Capability: 61, Driver API Version: 11.0, Runtime API Version: 10.0
W0926 16:16:06.236994 11782 device_context.cc:260] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 7.6.
loading annotations into memory...
Done (t=0.00s)
creating index...
index created!
2020-09-26 16:16:14,963-INFO: places would be ommited when DataLoader is not iterable
I0926 16:16:19.645217 11782 build_strategy.cc:361] set enable_sequential_execution:1
W0926 16:16:19.923936 11782 fuse_all_reduce_op_pass.cc:74] Find all_reduce operators: 88. To make the speed faster, some all_reduce ops are fused during training, after fusion, the number of all_reduce ops is 72.
2020-09-26 16:16:29,817-INFO: iter: 0, lr: 0.000000, 'loss_xy': '1.268840', 'loss_wh': '5.101564', 'loss_obj': '3439.274658', 'loss_cls': '0.728997', 'loss_iou': '5.795195', 'loss': '3452.169189', time: 0.000, eta: 0:00:00
2020-09-26 16:16:43,796-INFO: iter: 20, lr: 0.000020, 'loss_xy': '1.486864', 'loss_wh': '5.368582', 'loss_obj': '527.408203', 'loss_cls': '0.749239', 'loss_iou': '6.396237', 'loss': '540.208008', time: 1.408, eta: 0:46:28
2020-09-26 16:17:00,762-INFO: iter: 40, lr: 0.000040, 'loss_xy': '1.548631', 'loss_wh': '4.606500', 'loss_obj': '14.239037', 'loss_cls': '0.723093', 'loss_iou': '6.582170', 'loss': '27.592823', time: 0.859, eta: 0:28:03
训练完毕后会在当前tools目录下生成output文件夹里面是生成的模型,但不是最后用的模型,需要进行转换。
tools/export_model.py
在pycharm运行参数栏里输入后运行。
-c configs/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x.yml --output_dir=./inference_model
如果有找不到模型的错误,可能需要改config的参数:在weights那行
weights: output/ppyolo_tiny/model_final,
按照提示把最后一个模型文件名给改了,可能是:
weights: output/ppyolo_r18vd/best_model
运行后生成inference_model里面是可用的模型
运行结果如下:
2020-09-24 15:55:40,178-INFO: save_inference_model pruned unused feed variables im_id
2020-09-24 15:55:40,178-INFO: Export inference model to ./inference_model/ppyolo_r18vd, input: ['image', 'im_size'], output: ['matrix_nms_0.tmp_0']...
2020-09-24 15:55:40,495-INFO: Load categories from dataset/coco/annotations/instances_val2017.json
loading annotations into memory...
Done (t=0.00s)
creating index...
index created!
2020-09-24 15:55:40,757-INFO: Export inference config file to ./inference_model/ppyolo_r18vd/infer_cfg.yml
测试时在deploy/python/infer.py
同样在pycharm参数行里输入:
--model_dir=./inference_model//ppyolo_r18vd.yml --image_file=path/to/dataset/2572.jpeg --use_gpu=True
运行结果如下:
image_file: /home/z/zuo/PaddleDetection/tools/dataset/coco/test2017/000001.bmp
model_dir: /home/z/zuo/PaddleDetection/tools/inference_model/ppyolo_r18vd
output_dir: output
run_benchmark: False
run_mode: fluid
threshold: 0.5
use_gpu: True
video_file:
------------------------------------------
----------- Model Configuration -----------
Model Arch: YOLO
Use Padddle Executor: False
Transform Order:
--transform op: Resize
--transform op: Normalize
--transform op: Permute
--------------------------------------------
Inference: 6.660938262939453 ms per batch image
class_id:0, confidence:0.9825,left_top:[471.25,312.21], right_bottom:[689.18,330.45]
save result to: output/000001.bmp
批量测试
修改infer.py
也可以将infer.py程序复制到新建的程序后再改:
防止改不错了
1.找到此行,输入待测试图片文件夹路径
parser.add_argument(
"--image_file", type=str, default='/home/z/zuo/PaddleDetection/tools/dataset/coco/test2017', help="Path of image file.")
2.修改函数def predict_image()
def predict_image():
# 批量测试:
detector = Detector(
FLAGS.model_dir, use_gpu=FLAGS.use_gpu, run_mode=FLAGS.run_mode)
if FLAGS.run_benchmark:
##### 加
for filename in os.listdir(FLAGS.image_file):
path=FLAGS.image_file+'/'+filename
detector.predict(
path,
FLAGS.threshold,
warmup=100,
repeats=100,
run_benchmark=True)
#detector.predict(
#FLAGS.image_file,
#FLAGS.threshold,
#warmup=100,
#repeats=100,
#run_benchmark=True)
else:
for filename in os.listdir(FLAGS.image_file):
path=FLAGS.image_file+'/'+filename
results = detector.predict(path, FLAGS.threshold)
visualize(
path,
results,
detector.config.labels,
mask_resolution=detector.config.mask_resolution,
output_dir=FLAGS.output_dir)
同样在pycharm参数行输入:
--model_dir=/home/z/zuo/PaddleDetection/tools/inference_model/ppyolo_r18vd
测试效果:截取一部分
Inference: 6.028890609741211 ms per batch image
class_id:0, confidence:0.9979,left_top:[405.45,265.05], right_bottom:[423.90,274.10]
class_id:0, confidence:0.9970,left_top:[81.94,309.99], right_bottom:[109.75,319.11]
class_id:0, confidence:0.9920,left_top:[329.64,352.03], right_bottom:[358.91,361.85]
save result to: output/000476.bmp
Inference: 5.766630172729492 ms per batch image
class_id:0, confidence:0.9989,left_top:[239.34,320.03], right_bottom:[310.86,330.82]
class_id:0, confidence:0.9966,left_top:[65.20,318.06], right_bottom:[92.88,327.04]
class_id:0, confidence:0.9843,left_top:[435.73,322.93], right_bottom:[467.24,332.08]
class_id:0, confidence:0.9819,left_top:[339.03,321.02], right_bottom:[371.97,330.75]
save result to: output/000462.bmp
Inference: 5.4779052734375 ms per batch image
class_id:0, confidence:0.9977,left_top:[240.46,323.91], right_bottom:[299.29,334.81]
class_id:0, confidence:0.9958,left_top:[182.27,328.96], right_bottom:[212.92,335.92]
class_id:0, confidence:0.9956,left_top:[383.70,326.88], right_bottom:[409.83,335.94]
class_id:0, confidence:0.9884,left_top:[117.74,327.63], right_bottom:[152.39,335.65]
save result to: output/000770.bmp
Inference: 8.993148803710938 ms per batch image
class_id:0, confidence:0.9973,left_top:[591.84,326.17], right_bottom:[662.69,335.04]
class_id:0, confidence:0.9960,left_top:[441.39,322.97], right_bottom:[543.67,336.99]
save result to: output/000290.bmp
Process finished with exit code 0
如果需要生成txt文档,则需要更改visualize的一些代码:
# coding: utf-8
# copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserve.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from __future__ import division
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
def visualize_box_mask(pic_path, results, labels, mask_resolution=14):
"""
Args:
im (str/np.ndarray): path of image/np.ndarray read by cv2
results (dict): include 'boxes': np.ndarray: shape:[N,6], N: number of box,
matix element:[class, score, x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max]
MaskRCNN's results include 'masks': np.ndarray:
shape:[N, class_num, mask_resolution, mask_resolution]
labels (list): labels:['class1', ..., 'classn']
mask_resolution (int): shape of a mask is:[mask_resolution, mask_resolution]
Returns:
im (PIL.Image.Image): visualized image
"""
if isinstance(pic_path, str):
im = Image.open(pic_path).convert('RGB')
else:
im = Image.fromarray(pic_path)
if 'masks' in results and 'boxes' in results:
im = draw_mask(
im,
results['boxes'],
results['masks'],
labels,
resolution=mask_resolution)
if 'boxes' in results:
im = draw_box(im,pic_path,results['boxes'], labels)
return im
def get_color_map_list(num_classes):
"""
Args:
num_classes (int): number of class
Returns:
color_map (list): RGB color list
"""
color_map = num_classes * [0, 0, 0]
for i in range(0, num_classes):
j = 0
lab = i
while lab:
color_map[i * 3] |= (((lab >> 0) & 1) << (7 - j))
color_map[i * 3 + 1] |= (((lab >> 1) & 1) << (7 - j))
color_map[i * 3 + 2] |= (((lab >> 2) & 1) << (7 - j))
j += 1
lab >>= 3
color_map = [color_map[i:i + 3] for i in range(0, len(color_map), 3)]
return color_map
def expand_boxes(boxes, scale=0.0):
"""
Args:
boxes (np.ndarray): shape:[N,4], N:number of box,
matix element:[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max]
scale (float): scale of boxes
Returns:
boxes_exp (np.ndarray): expanded boxes
"""
w_half = (boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]) * .5
h_half = (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]) * .5
x_c = (boxes[:, 2] + boxes[:, 0]) * .5
y_c = (boxes[:, 3] + boxes[:, 1]) * .5
w_half *= scale
h_half *= scale
boxes_exp = np.zeros(boxes.shape)
boxes_exp[:, 0] = x_c - w_half
boxes_exp[:, 2] = x_c + w_half
boxes_exp[:, 1] = y_c - h_half
boxes_exp[:, 3] = y_c + h_half
return boxes_exp
def draw_mask(im, np_boxes, np_masks, labels, resolution=14, threshold=0.5):
"""
Args:
im (PIL.Image.Image): PIL image
np_boxes (np.ndarray): shape:[N,6], N: number of box,
matix element:[class, score, x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max]
np_masks (np.ndarray): shape:[N, class_num, resolution, resolution]
labels (list): labels:['class1', ..., 'classn']
resolution (int): shape of a mask is:[resolution, resolution]
threshold (float): threshold of mask
Returns:
im (PIL.Image.Image): visualized image
"""
color_list = get_color_map_list(len(labels))
scale = (resolution + 2.0) / resolution
im_w, im_h = im.size
w_ratio = 0.4
alpha = 0.7
im = np.array(im).astype('float32')
rects = np_boxes[:, 2:]
expand_rects = expand_boxes(rects, scale)
expand_rects = expand_rects.astype(np.int32)
clsid_scores = np_boxes[:, 0:2]
padded_mask = np.zeros((resolution + 2, resolution + 2), dtype=np.float32)
clsid2color = {}
for idx in range(len(np_boxes)):
clsid, score = clsid_scores[idx].tolist()
clsid = int(clsid)
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = expand_rects[idx].tolist()
w = xmax - xmin + 1
h = ymax - ymin + 1
w = np.maximum(w, 1)
h = np.maximum(h, 1)
padded_mask[1:-1, 1:-1] = np_masks[idx, int(clsid), :, :]
resized_mask = cv2.resize(padded_mask, (w, h))
resized_mask = np.array(resized_mask > threshold, dtype=np.uint8)
x0 = min(max(xmin, 0), im_w)
x1 = min(max(xmax + 1, 0), im_w)
y0 = min(max(ymin, 0), im_h)
y1 = min(max(ymax + 1, 0), im_h)
im_mask = np.zeros((im_h, im_w), dtype=np.uint8)
im_mask[y0:y1, x0:x1] = resized_mask[(y0 - ymin):(y1 - ymin), (
x0 - xmin):(x1 - xmin)]
if clsid not in clsid2color:
clsid2color[clsid] = color_list[clsid]
color_mask = clsid2color[clsid]
for c in range(3):
color_mask[c] = color_mask[c] * (1 - w_ratio) + w_ratio * 255
idx = np.nonzero(im_mask)
color_mask = np.array(color_mask)
im[idx[0], idx[1], :] *= 1.0 - alpha
im[idx[0], idx[1], :] += alpha * color_mask
return Image.fromarray(im.astype('uint8'))
def draw_box(im, pic_path,np_boxes, labels):
"""
Args:
im (PIL.Image.Image): PIL image
np_boxes (np.ndarray): shape:[N,6], N: number of box,
matix element:[class, score, x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max]
labels (list): labels:['class1', ..., 'classn']
Returns:
im (PIL.Image.Image): visualized image
"""
draw_thickness = min(im.size) // 320
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(im)
clsid2color = {}
color_list = get_color_map_list(len(labels))
for dt in np_boxes:
clsid, bbox, score = int(dt[0]), dt[2:], dt[1]
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = bbox
w = xmax - xmin
h = ymax - ymin
if clsid not in clsid2color:
clsid2color[clsid] = color_list[clsid]
color = tuple(clsid2color[clsid])
# draw bbox
draw.line(
[(xmin, ymin), (xmin, ymax), (xmax, ymax), (xmax, ymin),
(xmin, ymin)],
width=draw_thickness,
fill=color)
# draw label
text = "{} {:.4f}".format(labels[clsid], score)
tw, th = draw.textsize(text)
draw.rectangle(
[(xmin + 1, ymin - th), (xmin + tw + 1, ymin)], fill=color)
draw.text((xmin + 1, ymin - th), text, fill=(255, 255, 255))
#jia-txt
obj_list=[pic_path[-10:],score,xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax,labels[clsid]]
print(obj_list)
with open('./test.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write('{:s} {:.3f} {:.1f} {:.1f} {:.1f} {:.1f} {:s}n'.format(obj_list[0], float(obj_list[1]),float(obj_list[2]), float(obj_list[3]),float(obj_list[4]),float(obj_list[5]),obj_list[6]))
return im
结果如下:
000262.bmp 0.997 627.8 334.9 718.2 349.0 lf
000245.bmp 0.999 147.9 405.0 192.1 417.0 lf
000236.bmp 0.998 143.9 289.0 208.0 300.0 lf
000236.bmp 0.992 95.5 253.0 136.9 260.8 lf
最后
以上就是傻傻小霸王最近收集整理的关于基于PaddleDetection的PP-YOLO开源代码复现-训练-测试-以及测试时类别为官方标签解决-附加批量测试程序的全部内容,更多相关基于PaddleDetection内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复