数字IC设计学习笔记
跨时钟域同步问题
1 单比特信号跨时钟域问题
1.1 慢时钟域--> 快时钟域
1.2 快时钟域-->慢时钟域
1 单比特信号跨时钟域问题
1.1 慢时钟域–> 快时钟域
- 方法:两级触发器打两拍;
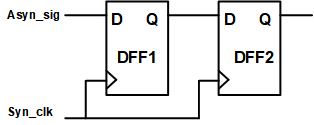
- 注意:
- 第一级寄存器产生亚稳态并经过自身后可以稳定输出的概率为70%~80%左右,第二级寄存器可以稳定输出的概率为99%左右,再后面改善就不明显了,所以数据进来后一般选择打两拍即可。
- 打两拍后虽然能够将数据稳定到0或1,但是0,1的稳定值时随机的,与输入没有必然关系。
- 影响亚稳态的震荡时间的因素:器件的生产工艺,温度,环境,寄存器采集到亚稳态里稳定态的时间,干扰,辐射等。
- Verilog代码
input syn_clk;
input rst_n;
input asyn_sig;
reg syn_reg1;
reg syn_reg2;
always@(posedge syn_clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)begin
syn_reg1 <= 0;
syn_reg2 <= 0;
end else
begin
syn_reg1 <= asyn_sig;
syn_reg2 <= syn_reg1;
end
1.2 快时钟域–>慢时钟域
- 方法1:
- 将脉冲信号在原时钟域(clka)转换为电平信号
- 将电平信号传递到慢时钟域,在慢时钟域(clb)做打两拍处理
- 最后将同步后的信号还原为脉冲信号(边沿检测方法)
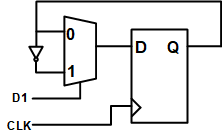
-
缺点:快时钟域产生脉冲信号的周期必须大于慢时钟域的时钟周期,否则慢时钟域依然可能采集不到信号。
-
时序图
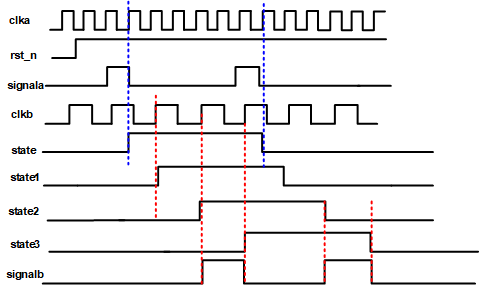
- Verilog代码
//----top module---------------------------------
module fast_to_slow
(
input clka, rsta, clkb,signala,rstb,
output signalb
);
reg sstate,state1, state2, state3;
//----脉冲信号转换沿信号-----------------------
always@(posedge clka or negedge rsta)begin
if(!rsta) state <= 0
else if(signala) state <=~state;
else state <=0;
end
//----沿信号打三拍-----------------------------
always@(posedge clkb or negedge rstb)begin
If(!rst) begin
state1 <= 0;
state2<=0;
state3<=0;
end
else begin
state1<=state;
state2<=state1;
state3<=state2;
end
//----上升沿,下降沿同时检测-------------------
assign signalb = state2 ^ state3;
endmodule
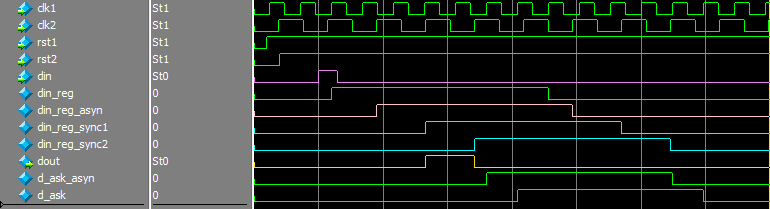
- 方法2:握手信号
慢时钟域从采集到信号以后,反馈给快时钟域一个信号,快时钟域再结束传递数据。
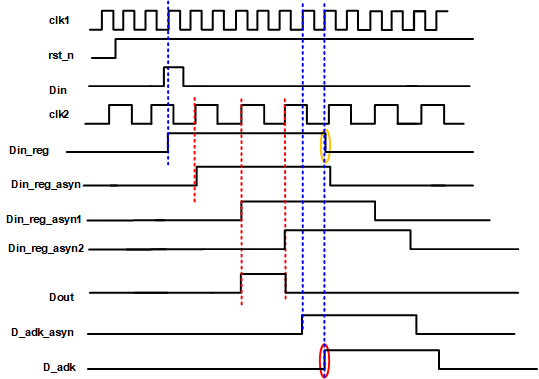
- Verilog代码
// Company:
// Engineer: GloriaHuo
//
// Create Date: 15:26:46 10/20/2020
// Design Name:
// Module Name: shack_hand
// Project Name:
// Target Devices:
// Tool versions:
// Description:
//
// Dependencies:
//
// Revision:
// Revision 0.01 - File Created
// Additional Comments:
//
//
module shack_hand
(
input clk1,
input clk2,
input rst1,
input rst2,
input din,
output dout
);
reg din_reg;
reg din_reg_asyn;
reg din_reg_sync1;
reg din_reg_sync2;
reg d_ask_asyn;
reg d_ask;
//----extend din--------------------//
always@(posedge clk1 or negedge rst1)begin
if(~rst1)
din_reg <= 0;
else if(din==1)
din_reg <= 1;
else if(d_ask == 1)
din_reg <= 0;
end
//----asyn din_reg from clk1 to clk2---//
always@(posedge clk2 or negedge rst2)begin
if(~rst2)
din_reg_asyn <= 0;
else
din_reg_asyn <= din_reg;
end
//----clk2: synchronos process by two DFF-----//
always@(posedge clk2 or negedge rst2)begin
if(~rst2)begin
din_reg_sync1 <= 0;
din_reg_sync2 <= 0;
end else
begin
din_reg_sync1 <= din_reg_asyn;
din_reg_sync2 <= din_reg_sync1;
end
end
//----clk1: d_ask --------------------//
always@(posedge clk1 or negedge rst1)begin
if(~rst1)begin
d_ask_asyn <= 0;
d_ask <= 0;
end else
begin
d_ask_asyn <= din_reg_sync2;
d_ask <= d_ask_asyn;
end
end
//----dout---------------------//
assign dout = din_reg_sync1 & ~din_reg_sync2;
endmodule
—部分内容源自达尔文说公众号,Thanks^^
【注】:个人学习笔记,如有错误,望不吝赐教,这厢有礼了~~~
最后
以上就是无情毛豆最近收集整理的关于数字IC设计学习笔记_跨时钟域同步问题1_单比特信号跨时钟域问题数字IC设计学习笔记的全部内容,更多相关数字IC设计学习笔记_跨时钟域同步问题1_单比特信号跨时钟域问题数字IC设计学习笔记内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复