2021SC@SDUSC
YOLOv3的目标检测源代码,核心的函数包括:
detect_image()
generate()
yolo_eval()
yolo_model()
yolo_boxes_and_scores()
yolo_head()
yolo_correct_boxes()
等
1.算法代码
yolo.py
class YOLO(object):
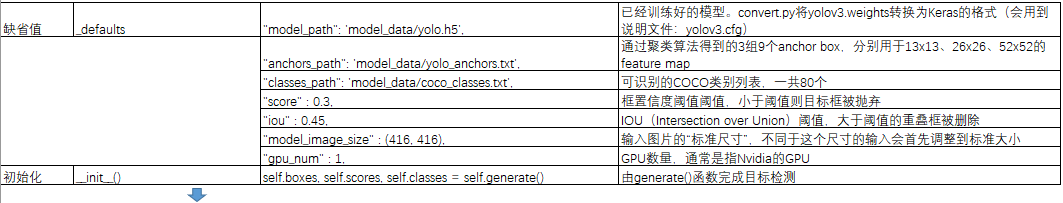
_defaults = {
"model_path": 'model_data/yolo.h5', #已经训练好的模型
"anchors_path": 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt', #通过聚类算法得到的3组9个anchor box,分别用于13x13、26x26、52x52的feature map
"classes_path": 'model_data/coco_classes.txt', #可识别的COCO类别列表,一共80个
"score" : 0.3, #框置信度阈值阈值,小于阈值则目标框被抛弃
"iou" : 0.45, #IOU(Intersection over Union)阈值,大于阈值的重叠框被删除
"model_image_size" : (416, 416), #输入图片的“标准尺寸”,不同于这个尺寸的输入会首先调整到标准大小
"gpu_num" : 1, #GPU数量,通常是指Nvidia的GPU
}
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults) # set up default values
self.__dict__.update(kwargs) # and update with user overrides
self.class_names = self._get_class()
self.anchors = self._get_anchors()
self.sess = K.get_session()
self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes = self.generate() #由generate()函数完成目标检测
def generate(self):
#读取:model路径、anchor box、coco类别,加载模型yolo.h5
model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'
# Load model, or construct model and load weights.
num_anchors = len(self.anchors)
num_classes = len(self.class_names)
is_tiny_version = num_anchors==6 # default setting
try:
self.yolo_model = load_model(model_path, compile=False)
except:
self.yolo_model = tiny_yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//2, num_classes)
if is_tiny_version else yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//3, num_classes)
self.yolo_model.load_weights(self.model_path) # make sure model, anchors and classes match
else:
assert self.yolo_model.layers[-1].output_shape[-1] ==
num_anchors/len(self.yolo_model.output) * (num_classes + 5),
'Mismatch between model and given anchor and class sizes'
print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))
# Generate colors for drawing bounding boxes.
#对于80种coco目标,确定每一种目标框的绘制颜色,即:将(x/80, 1.0, 1.0)的颜色转换为RGB格式,并随机调整颜色以便于肉眼识别,其中:一个1.0表示饱和度,一个1.0表示亮度
hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)
for x in range(len(self.class_names))]
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
self.colors = list(
map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),
self.colors))
np.random.seed(10101) # Fixed seed for consistent colors across runs.
np.random.shuffle(self.colors) # Shuffle colors to decorrelate adjacent classes.
np.random.seed(None) # Reset seed to default.
# Generate output tensor targets for filtered bounding boxes.
self.input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2, ))
#若GPU个数大于等于2,调用multi_gpu_model()
if self.gpu_num>=2:
self.yolo_model = multi_gpu_model(self.yolo_model, gpus=self.gpu_num)
boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(self.yolo_model.output, self.anchors,
len(self.class_names), self.input_image_shape,
score_threshold=self.score, iou_threshold=self.iou)
return boxes, scores, classes
def detect_image(self, image):
#开始计时
start = timer()
#调用letterbox_image()函数,即:先生成一个用“绝对灰”R128-G128-B128“填充的416x416新图片,然后用按比例缩放(采样方法:BICUBIC)后的输入图片粘贴,粘贴不到的部分保留为灰色
if self.model_image_size != (None, None):
assert self.model_image_size[0]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
assert self.model_image_size[1]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, tuple(reversed(self.model_image_size)))
else:
#model_image_size定义的宽和高必须是32的整倍数;若没有定义model_image_size,将输入图片的尺寸调整到32的整倍数,并调用letterbox_image()函数进行缩放
new_image_size = (image.width - (image.width % 32),
image.height - (image.height % 32))
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, new_image_size)
image_data = np.array(boxed_image, dtype='float32')
print(image_data.shape)
image_data /= 255. #将缩放后图片的数值除以255,做归一化
#将(416,416,3)数组调整为(1,416,416,3)元组,满足YOLOv3输入的张量格式
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0) # Add batch dimension.
out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = self.sess.run(
[self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes],
feed_dict={ #输入参数
self.yolo_model.input: image_data, #输入图片
self.input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]], #图片尺寸416x416
K.learning_phase(): 0 #学习模式:0测试/1训练
})
print('Found {} boxes for {}'.format(len(out_boxes), 'img'))
#设置字体
font = ImageFont.truetype(font='font/FiraMono-Medium.otf',
size=np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))
#设置目标框线条的宽度
thickness = (image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // 300
#对于c个目标类别中的每个目标框i,调用Pillow画图
for i, c in reversed(list(enumerate(out_classes))):
predicted_class = self.class_names[c] #目标类别的名字
box = out_boxes[i] #目标框
score = out_scores[i] #目标框的置信度评分
label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image) #输出:绘制输入的原始图片
label_size = draw.textsize(label, font) #返回label的宽和高(多少个pixels).
top, left, bottom, right = box
#目标框的上、左两个坐标小数点后一位四舍五入
top = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32'))
left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32'))
#目标框的下、右两个坐标小数点后一位四舍五入,与图片的尺寸相比,取最小值
bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32'))
right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))
print(label, (left, top), (right, bottom))
#确定标签(label)起始点位置:左、下
if top - label_size[1] >= 0:
text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])
else:
text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])
# My kingdom for a good redistributable image drawing library.
#画目标框,线条宽度为thickness
for i in range(thickness):
draw.rectangle(
[left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],
outline=self.colors[c])
#画标签框
draw.rectangle(
[tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)],
fill=self.colors[c])
#填写标签内容
draw.text(text_origin, label, fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
del draw
#结束计时
end = timer()
print(end - start)
return image
yolo3model.py
def yolo_head(feats, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, calc_loss=False):
#feats,即:feature maps
"""Convert final layer features to bounding box parameters."""
num_anchors = len(anchors) #num_anchors = 3
# Reshape to batch, height, width, num_anchors, box_params.
anchors_tensor = K.reshape(K.constant(anchors), [1, 1, 1, num_anchors, 2])
grid_shape = K.shape(feats)[1:3] # height, width #13x13或26x26或52x52
#通过arange、reshape、tile的组合,根据grid_shape(13x13、26x26或52x52)创建y轴的0~N-1的组合grid_y,再创建x轴的0~N-1的组合grid_x,将两者拼接concatenate,形成NxN的grid(13x13、26x26或52x52)
grid_y = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[0]), [-1, 1, 1, 1]),
[1, grid_shape[1], 1, 1])
grid_x = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[1]), [1, -1, 1, 1]),
[grid_shape[0], 1, 1, 1])
grid = K.concatenate([grid_x, grid_y])
grid = K.cast(grid, K.dtype(feats))
#从待处理的feature map的最后一维数据中,先将num_anchors这个维度与num_classes+5这个维度的数据分离,再取出4个框值tx、ty(最后一维数据的0:1)、tw和th(最后一维数据的2:3)
feats = K.reshape(
feats, [-1, grid_shape[0], grid_shape[1], num_anchors, num_classes + 5])
# Adjust preditions to each spatial grid point and anchor size.
#用sigmoid()函数计算目标框的中心点box_xy,用exp()函数计算目标框的宽和高box_wh
#使用特征图尺寸(如:13x13、26x26或52x52)在水平x、垂直y两个维度对box_xy进行归一化,确定目标框的中心点的相对位置
#使用标准图片尺寸(416x416)在宽和高两个维度对box_wh(因为,3组9个anchor box是基于416x416尺寸定义的)进行归一化,确定目标框的高和宽的相对位置
box_xy = (K.sigmoid(feats[..., :2]) + grid) / K.cast(grid_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats))
box_wh = K.exp(feats[..., 2:4]) * anchors_tensor / K.cast(input_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats))
#用sigmoid()函数计算目标框的置信度box_confidence
box_confidence = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 4:5])
#用sigmoid()函数计算目标框的类别置信度box_class_probs
box_class_probs = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 5:])
if calc_loss == True:
return grid, feats, box_xy, box_wh
return box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs
def yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape):
'''Get corrected boxes'''
#将box_xy, box_wh转换为输入图片上的真实坐标,输出boxes是框的左下、右上两个坐标(y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max)
#np.array[i:j:s],当s<0时,i缺省时,默认为-1;j缺省时,默认为-len(a)-1;所以array[::-1]相当于array[-1:-len(a)-1:-1],也就是从最后一个元素到第一个元素复制一遍,即倒序
box_yx = box_xy[..., ::-1]
box_hw = box_wh[..., ::-1]
input_shape = K.cast(input_shape, K.dtype(box_yx))
image_shape = K.cast(image_shape, K.dtype(box_yx))
new_shape = K.round(image_shape * K.min(input_shape/image_shape))
offset = (input_shape-new_shape)/2./input_shape
scale = input_shape/new_shape
box_yx = (box_yx - offset) * scale
box_hw *= scale
box_mins = box_yx - (box_hw / 2.)
box_maxes = box_yx + (box_hw / 2.)
boxes = K.concatenate([
yolo3utils.py
def letterbox_image(image, size):
'''resize image with unchanged aspect ratio using padding'''
#先生成一个用“绝对灰”R128-G128-B128“填充的416x416新图片,然后用按比例缩放(采样方法:BICUBIC)后的输入图片粘贴,粘贴不到的部分保留为灰色
iw, ih = image.size
w, h = size
scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)
nw = int(iw*scale)
nh = int(ih*scale)
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
new_image = Image.new('RGB', size, (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, ((w-nw)//2, (h-nh)//2))
return new_image
(二)代码分析
YOLOv3的目标识别的源代码流程大致如下:
(1)设置缺省值并初始化:
(2)detect_image()将图片缩放成416x416大小,调用yolo_model(),生成13x13、26x26与52x52等3个feature map的输出,对这3个feature map进行预测,调用yolo_eval()函数得到目标框、目标框得分和类别,然后使用Pillow对发现的每一类对象的每一个目标框,绘制标签、框和文字:
剩余部分下周讲解
最后
以上就是坦率月饼最近收集整理的关于PaddleDetection算法分析(3)2021SC@SDUSC的全部内容,更多相关PaddleDetection算法分析(3)2021SC@SDUSC内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。






![assert all(tensors[0].size(0) == tensor.size(0) for tensor in tensors) AssertionError](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg12.png)

发表评论 取消回复