决策树是一种基本的分类与回归方法,本人学习的主要为分类的决策树
在分类的过程中,决策树可以表示为基于特征对对象进行分类的过程
在构造决策树的过程中,我们需要经历以下几个步骤:
1.数据收集(构造数据集)
2.构造节点,将数据先存放在根节点,选择一个最优特征,然后以该特征将数据集分割成2部分,接着对子集进行最优特征选择,最终使基本数据得到正确分类,或再无可分特征为止
3.直到每个子集都被分类在叶结点上,决策树构造完成
决策树的基本数据分类判断方式是在这个结点下方先判断数据是否已经为同一类型,若是,则基本数据得到正确分类,该结点为叶节点,若否,则根据尚有的数据进行分类,直到数据类型相同或无法再分而止
一:信息增益
信息熵是度量样本集合纯度最常用的指标,假定当前集合D中第k类样本所占比例为pk(k=1,2,……,|y|) ,则D信息熵的定义为
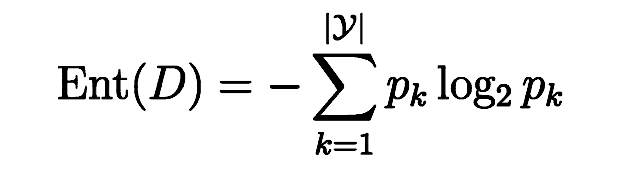
Ent(D)的值越小,则D纯度越高
计算信息熵时约定:若p=0,则plog⒉p=0
Ent(D)最小值为0,最大值为log2|y|
离散性a有v个可能的取值a1,a2……,aV,用a划分,则会产生n个分支节点,其中第n个分支节点包含了D中所有属性在a上取值为aV的样本,记为DV,则可计算出用属性a对样本集D进行划分所得到的信息增益:
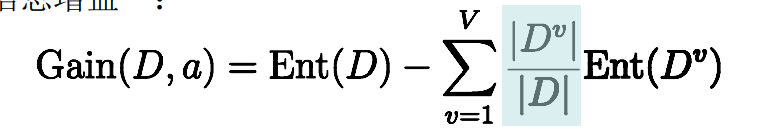
一般而言,信息增益越大,则意味着使用属性a来划分所获得的纯度提升越大
用ID3(迭代二分器)算法构造决策树
1.创建数据集
def createDataSet():
dataSet = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 'no'],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 'no'],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
]
labels = ['main_attribute', 'attack', 'critical_hit', 'critical', 'speed', 'effect_hit', 'resist', 'result']
return dataSet, labels2.计算数据集的熵
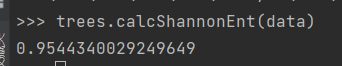
def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
numEntries = len(dataSet)
labelCounts = {}
for featVec in dataSet: #the the number of unique elements and their occurance
currentLabel = featVec[-1]
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1
shannonEnt = 0.0
for key in labelCounts:
prob = float(labelCounts[key])/numEntries
shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob,2) #log base 2
return shannonEnt这段代码将决策属性分别计算信息熵,再将其加在一起得到数据集的信息熵
3.划分数据集
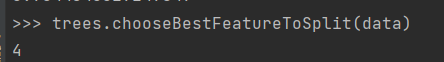
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #the last column is used for the labels
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet)
bestInfoGain = 0.0; bestFeature = -1
for i in range(numFeatures): #iterate over all the features
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]#create a list of all the examples of this feature
uniqueVals = set(featList) #get a set of unique values
newEntropy = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value)
prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #calculate the info gain; ie reduction in entropy
if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): #compare this to the best gain so far
bestInfoGain = infoGain #if better than current best, set to best
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature #returns an integer该代码用于选择最好的数据集的划分方式,先遍历当前所有特征,计算数据集的新熵值,比较所有特征的熵值,该处熵值用于度量数据无序度的减少,所以熵越大,则信息增益越大,所以以我的数据集在这里特征4是最好用于划分数据集的特征
4.递归构建决策树
def createTree(dataSet,labels):
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList):
return classList[0]#stop splitting when all of the classes are equal
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: #stop splitting when there are no more features in dataSet
return majorityCnt(classList)
bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet)
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat]
myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}}
del(labels[bestFeat])
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featValues)
for value in uniqueVals:
subLabels = labels[:] #copy all of labels, so trees don't mess up existing labels
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value),subLabels)
return myTree 递归构造树形结构方法
用上述划分数据集的方法将当前递归层数据集划分,也是当前结点的2个分支结点,递归直到没有分支结点或全部数据类型相同则递归返回,构造决策树
然而字典树的形式并不便于理解,所以我们使用matplotlib绘制树形图
5.绘制树形图
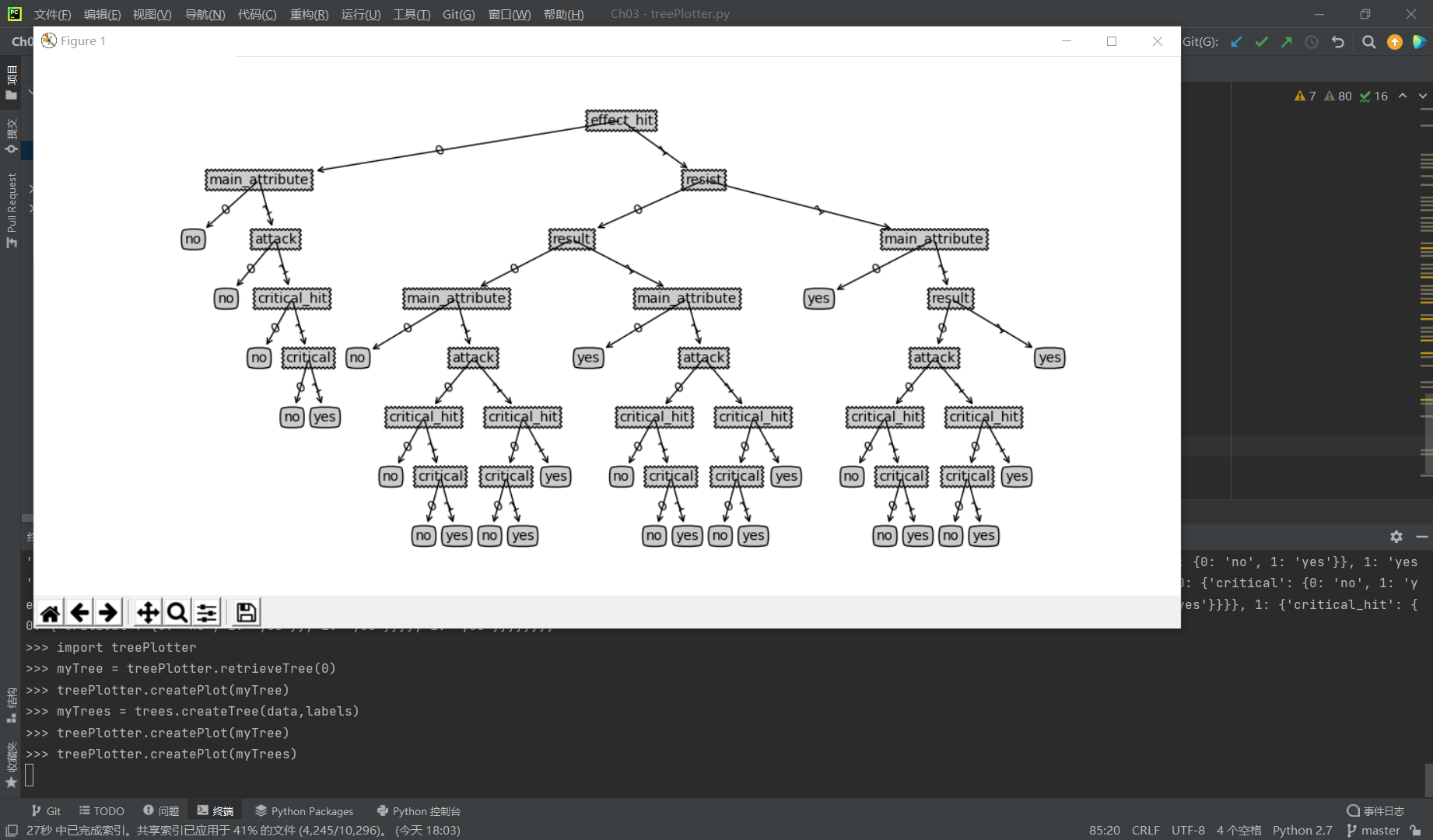
至此,使用信息熵构造决策树全部执行完毕
总结:
在构造过程中,数据集我用真值表方式构造,保证每个数据的不同,但同时也增加了决策树的熵,分类条件也更多更复杂了
在创建树的过程中,需要遍历所有特征,并返回出现次数最多的特征来构造当前分支函数,也导致了树形结构的复杂性,因为时间问题没调整剪枝代码所以树形结构完整但复杂
数据增益构造的决策树需要理解树形结构的形式并遍历特征调整分支属性,计算复杂度不高,但遇到特征过多或数据量过少的情况可能会产生过度匹配问题
最后
以上就是生动白开水最近收集整理的关于机器学习——决策树的全部内容,更多相关机器学习——决策树内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复