A summary of speech data augment algorithms
语音数据增强算法汇总
本项目已上传至Github:speech_data_augment
目录
-
音量增强
-
速度增强
-
音调增强
-
移动增强
-
噪声增强
5.1 自然噪声
5.2 人工噪声
-
时域遮掩
-
频域遮掩
1.音量增强
1.1 volume_augment:
在百度DeepSpeech2源码的基础上改进:保持增益前后的数据类型不变
音量增益范围约为【0.316,3.16】,不均匀采样:指数分布,降低幂函数的底10可以缩小范围
使用幂函数可以有更大的概率使增益后的音频接近原始音频
def volume_augment(samples, min_gain_dBFS=-10, max_gain_dBFS=10):
"""
音量增益范围约为【0.316,3.16】,不均匀,指数分布,降低幂函数的底10.可以缩小范围
:param samples: 音频数据,一维
:param min_gain_dBFS:
:param max_gain_dBFS:
:return:
"""
samples = samples.copy() # frombuffer()导致数据不可更改因此使用拷贝
data_type = samples[0].dtype
gain = rng.uniform(min_gain_dBFS, max_gain_dBFS)
gain = 10. ** (gain / 20.)
samples = samples * gain
# improvement:保证输出的音频还是原类型,不然耳朵会聋
samples = samples.astype(data_type)
return samples
1.2 效果展示
gain = 2.4986395586019112
上图/左图为原始数据,下图/右图为增益后数据。下同
1.2.1 波形图
- 原始音频

- 音量扰动(2.49倍)波形

1.2.2 语谱图
-
原始特征

-
音量扰动后特征

1.3 结论
-
波形图上,振幅变化明显
-
特征图上,整体颜色深浅发生细微变化,变化不明显
-
当振幅增益过大时,会出现破音,在波形图上表现为超出振幅范围,在特征图上表现为特征明显的突变。可以模型音频中可能出现的破音现象。
2. 速度增强
2.1 speed_numpy
使用numpy线形插值法
def speed_numpy(samples, min_speed=0.9, max_speed=1.1):
"""
线形插值速度增益
:param samples: 音频数据,一维
:param max_speed: 不能低于0.9,太低效果不好
:param min_speed: 不能高于1.1,太高效果不好
:return:
"""
samples = samples.copy() # frombuffer()导致数据不可更改因此使用拷贝
data_type = samples[0].dtype
speed = rng.uniform(min_speed, max_speed)
old_length = samples.shape[0]
new_length = int(old_length / speed)
old_indices = np.arange(old_length) # (0,1,2,...old_length-1)
new_indices = np.linspace(start=0, stop=old_length, num=new_length) # 在指定的间隔内返回均匀间隔的数字
samples = np.interp(new_indices, old_indices, samples) # 一维线性插值
samples = samples.astype(data_type)
return samples
2.2 librosa
def speed_librosa(samples, min_speed=0.9, max_speed=1.1):
"""
librosa时间拉伸
:param samples: 音频数据,一维
:param max_speed: 不要低于0.9,太低效果不好
:param min_speed: 不要高于1.1,太高效果不好
:return:
"""
samples = samples.copy() # frombuffer()导致数据不可更改因此使用拷贝
data_type = samples[0].dtype
speed = rng.uniform(min_speed, max_speed)
samples = samples.astype(np.float)
samples = librosa.effects.time_stretch(samples, speed)
samples = samples.astype(data_type)
return samples
2.3 效果展示
speed = 2.0,为方便展示设置了较大的速度,实际项目中不应设置过快或过慢
2.3.1 波形图
- 原始波形

- DeepSpeech

- librosa

2.3.2 语谱图
-
原始波形

-
DeepSpeech

-
librosa

2.4 总结
- 听觉效果
- 除语速变化以外,DeepSpeech方法的音调也会发生相应变化。加速时,音调升高,减速时,音调降低。速度变化在【0.9,1.1】范围内时,听觉良好,超过这个范围时,声音(主要是音调)不自然。
- librosa音调不会发生变化,但是声音不清晰
- DeepSpeech方法变换后波形图变化很小,声音特征(语谱图)依然明显,在听觉上清晰,但音调同时发生变化。
- librosa方法变换后波形图变化大,声音特征(语谱图)模糊,在听觉上不清晰。
3. 音调增强
3.1 librosa
def pitch_librosa(samples, sr=16000, ratio=5):
samples = samples.copy() # frombuffer()导致数据不可更改因此使用拷贝
data_type = samples[0].dtype
samples = samples.astype('float')
ratio = random.uniform(-ratio, ratio)
samples = librosa.effects.pitch_shift(samples, sr, n_steps=ratio)
samples = samples.astype(data_type)
return samples
3.2 效果展示
ratio = 5
3.2.1 波形图
-
原始波形(放大局部)
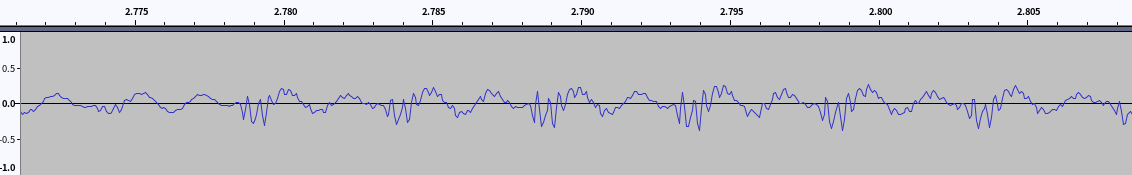
-
音调调整后波形
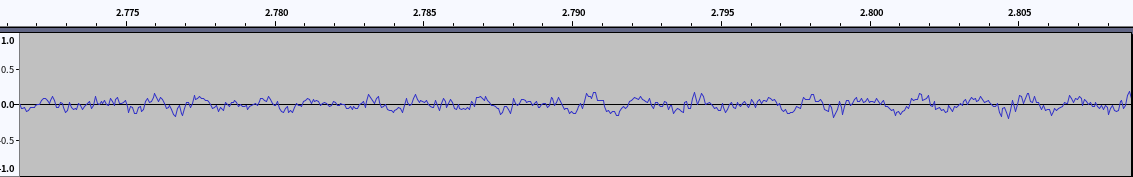
3.2.2 语谱图
-
原始特征

-
音调调整后特征

3.3 结论
- 听觉效果上,音调发生变化,时长保持不变。
- 波形图可以明显看到频率增加(升调)
- 特征图中,声音特征变的模糊(librosa处理音频的通病?是否有利于训练有待测试,可以把应用比例调小)
4. 移动增强
4.1 time_shift
改进:
-
为在一定比例范围内随机偏移,而不是使用固定的时间偏移
-
循环移动,而不是空隙零填充
def time_shift(samples, max_ratio=0.05):
"""
改进:
1.为在一定比例范围内随机偏移,不再需要时间
2.循环移动
:param samples: 音频数据
:param max_ratio:
:return:
"""
samples = samples.copy()
frame_num = samples.shape[0]
max_shifts = frame_num * max_ratio # around 5% shift
shifts_num = np.random.randint(-max_shifts, max_shifts)
print(shifts_num)
if shifts_num > 0:
# time advance
temp = samples[:shifts_num]
samples[:-shifts_num] = samples[shifts_num:]
# samples[-shifts_num:] = 0
samples[-shifts_num:] = temp
elif shifts_num < 0:
# time delay
temp = samples[shifts_num:]
samples[-shifts_num:] = samples[:shifts_num]
# samples[:-shifts_num] = 0
samples[:-shifts_num] = temp
return samples
4.2 numpy
def time_shift_numpy(samples, max_ratio=0.05):
"""
时间变化是在时间轴的±5%范围内的随机滚动。环绕式转换以保留所有信息。
Shift a spectrogram along the frequency axis in the spectral-domain at random
:param max_ratio:
:param samples: 音频数据,一维(序列长度,) 或 特征数据(序列长度,特征维度)
:return:
"""
samples = samples.copy() # frombuffer()导致数据不可更改因此使用拷贝
data_type = samples[0].dtype
frame_num = samples.shape[0]
max_shifts = frame_num * max_ratio # around 5% shift
nb_shifts = np.random.randint(-max_shifts, max_shifts)
samples = np.roll(samples, nb_shifts, axis=0)
samples = samples.astype(data_type)
return samples
4.3 效果展示
偏移量5%
4.3.1 波形图
-
原始波形

-
移动后波形

4.3.2 特征图
-
原始特征

-
移动后特征

4.4 总结
- 改进百度的方法后,两个方法的移动效果相同,仅实现方式不同,因此可以只测试运行速度
- 移动时应只移动空白段,而不应该移动语音段,移动语音段会丢失或扰乱语音的顺序性,因此应设置很小的移动帧数
- 此移动干扰对语音段的特征不会造成任何影响
- 理论上,移动干扰对语音识别效果提升很小
5. 噪声增强
5.1 自然噪声
需要大量噪声音频文件
- 优势:可以覆盖更多的场景,如公园、人声、电流声等
- 缺点:需要大量噪声数据,数据不足会影响泛化能力
def noise_augmentation(samples, noise_list, max_db=0.5):
"""
叠加自然噪声
:param samples: 语音采样
:param noise_list:噪声文件列表
:param max_db:最大噪声增益
:return:
"""
samples = samples.copy() # frombuffer()导致数据不可更改因此使用拷贝
data_type = samples[0].dtype
noise_path = np.random.choice(noise_list)
# 随机音量
db = np.random.uniform(low=0.1, high=max_db)
aug_noise, fs = read_wave_from_file(noise_path)
# 噪声片段增长
while len(aug_noise) <= len(samples):
aug_noise = np.concatenate((aug_noise, aug_noise), axis=0)
# 随机位置开始截取与语音数据等长的噪声数据
diff_len = len(aug_noise) - len(samples)
start = np.random.randint(0, diff_len)
end = start + len(samples)
# 叠加
samples = samples + db * aug_noise[start:end]
samples = samples.astype(data_type)
return samples
5.2 人工噪声
- 优点:可随机生成,不需要大规模数据集
- 缺点:在人工噪声上表现良好的方法,在现实世界的噪声数据集上效果可能并不理想
5.2.1 高斯白噪声
白噪声是随机样本按一定的间隔分布,均值为0,标准差为1。
def gaussian_white_noise_numpy(samples, min_db=10, max_db=500):
"""
高斯白噪声
噪声音量db
db = 10, 听不见
db = 100,可以听见,很小
db = 500,大
人声都很清晰
:param samples:
:param max_db:
:param min_db:
:return:
"""
samples = samples.copy() # frombuffer()导致数据不可更改因此使用拷贝
data_type = samples[0].dtype
db = np.random.randint(low=min_db, high=max_db)
noise = db * np.random.normal(0, 1, len(samples)) # 高斯分布
print(db)
samples = samples + noise
samples = samples.astype(data_type)
return samples
5.2.2 均匀白噪声
def uniform_white_noise_numpy(samples, min_db=10, max_db=500):
"""
均匀白噪声
:param samples:
:param max_db:
:param min_db:
:return:
"""
samples = samples.copy() # frombuffer()导致数据不可更改因此使用拷贝
data_type = samples[0].dtype
db = np.random.randint(low=min_db, high=max_db)
noise = np.random.uniform(low=-db, high=db, size=len(samples)) # 高斯分布
print(db)
samples = samples + noise
samples = samples.astype(data_type)
return samples
5.3 效果展示
自然噪声:db = 0.5
合成噪声db = 500,实际使用时不要太大。
5.3.1 波形图
-
原始波形

-
自然噪声

-
自然噪声叠加

-
高斯白噪声

-
均匀白噪声

5.3.2 语谱图
-
原始特征

-
自然噪声

-
自然噪声叠加

-
高斯白噪声

-
均匀白噪声

5.4 结论
- 人工噪声和自然噪声可以混合使用
6. 时域遮掩
6.1 Google
def time_mask_augment(inputs, max_mask_time=5, mask_num=10):
"""
时间遮掩,
:param inputs: 三维numpy或tensor,(batch, time_step, feature_dim)
:param max_mask_time:
:param mask_num:
:return:
"""
time_len = inputs.shape[1]
for i in range(mask_num):
t = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=max_mask_time)
t = int(t)
t0 = random.randint(0, time_len - t)
inputs[:, t0:t0 + t, :] = 0
return inputs
6.2 效果展示
6.2.1 特征图
-
原始特征

-
时域掩码

7. 频域遮掩
7.1 Google
def frequency_mask_augment(inputs, max_mask_frequency=5, mask_num=10):
"""
:param inputs: 三维numpy或tensor,(batch, time_step, feature_dim)
:param max_mask_frequency:
:param mask_num:
:return:
"""
feature_len = inputs.shape[2]
for i in range(mask_num):
f = np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=max_mask_frequency)
f = int(f)
f0 = random.randint(0, feature_len - f)
inputs[:, :, f0:f0 + f] = 0
return inputs
7.2 效果展示
7.2.1 特征图
-
原始特征

-
频率遮掩

参考资料
[1]DeepSpeech2(音量扰动、速度扰动、移动扰动、在线贝叶斯归一化、加噪、脉冲响应
[2]GithubCSDN——声音数据增强(时间、音调)
[3]CSDN——音频数据增强处理(时间、音调、随机高斯噪声)
[4]CSDN——Python音频的数据扩充,你知道怎么用吗?(裁减、旋转、调音、加噪)
[5]Github——pydub(压缩、均衡器EQ、变速、正弦、方波、锯齿、白噪声等、静音检测)、CSDN——pydub的中文文档(含API)
[6]博客园——音频数据增强及python实现 - 凌逆战(加噪、波形位移、波形拉伸、音高修正)
[7]知乎——音频信号中做数据增强及部分代码实现(叠加、加噪、时移、音高、其他资料)
[8]利用python进行音频数据增强(加噪、时移、变速、音高)
最后
以上就是粗心橘子最近收集整理的关于语音数据增强算法汇总(附代码)的全部内容,更多相关语音数据增强算法汇总(附代码)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复