WEBRTC系列文章:
WEBRTC系列之基于IOS平台编译WEBRTC(一)
WEBRTC AGC 算法原理初识(二)
- 1、AGC 初识
- 2、WEBRTC 的 AGC算法
- 3、主要配置
- 4、主要接口
1、AGC 初识
自动增益控制电路的作用是:当输入信号电压变化很大时,保持接收机输出电压恒定或基本不变。具体地说,当输入信号很弱时,接收机的增益大,自动增益控制电路不起作用;当输入信号很强时,自动增益控制电路进行控制,使接收机的增益减小。这样,当接收信号强度变化时,接收机的输出端的电压或功率基本不变或保持恒定。因此对AGC电路的要求是:在输入信号较小时,AGC电路不起作用,只有当输入信号增大到一定程度后,AGC电路才起控制作用,使增益随输入信号的增大而减少。
为实现上述要求,必须有一个能随外来信号强弱而变化的控制电压或电流信号,利用这个信号对放大器的增益自动进行控制。由上述分析可知,调幅中频信号经幅度检波后,在它的输出中除音频信号外,还含有直流分量。直流分量大小与中频载波的振幅成正比,也即与外来高频信号成正比。因此,可将检波器输出的直流分量作为AGC控制信号。
AGC电路工作原理:可以分为增益受控放大电路和控制电压形成电路。增益受控放大电路位于正向放大通路,其增益随控制电压U0而改变。控制电压形成电路的基本部件是AGC整流器和低通平滑滤波器,有时也包含门电路和直流放大器等部件。
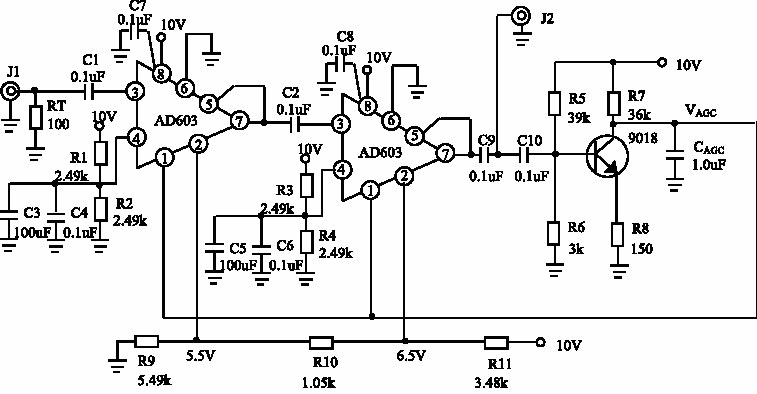
2、WEBRTC 的 AGC算法
AGC是自动增益补偿功能(Automatic Gain Control),AGC可以自动调麦克风的收音量,使与会者收到一定的音量水平,不会因发言者与麦克风的距离改变时,声音有忽大忽小声的缺点。webbrtc中的结构如下:
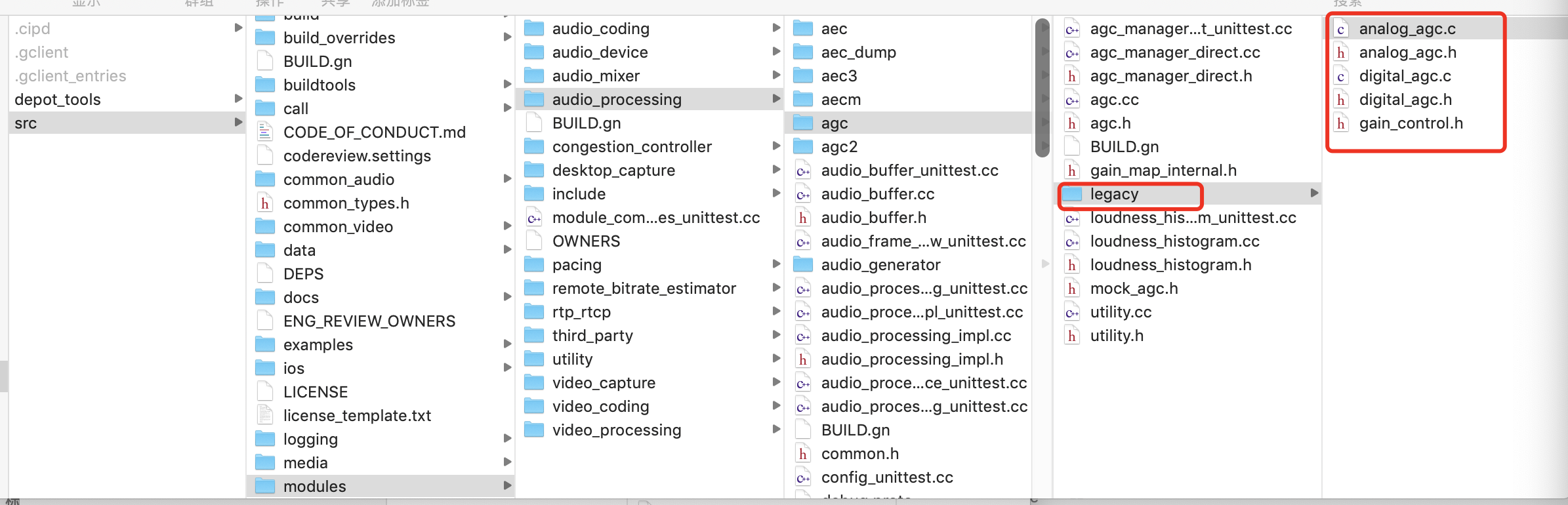
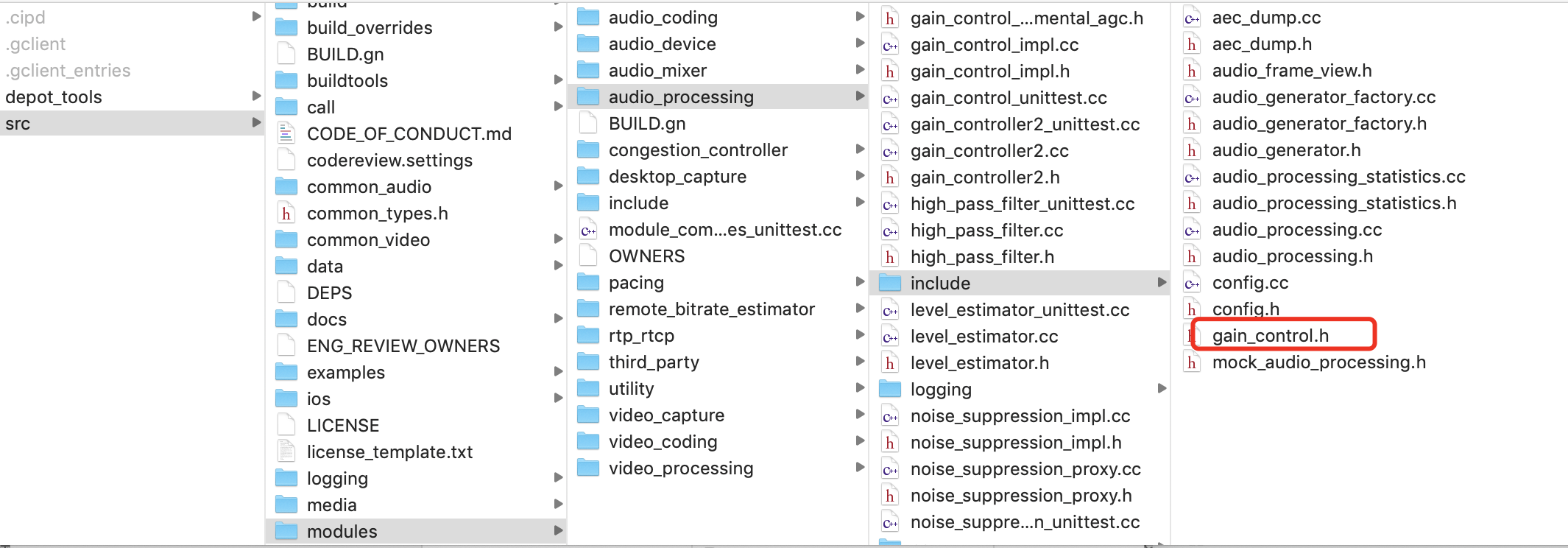
说明:gain_control.h是包装的头文件,在apm里头gain_control_impl调用。主要包括了接口定义函数和参数配置。
3、主要配置
- include/gain_control.h 里面定义了agc的三种模式,kAdaptiveAnalog、kAdaptiveDigital和kFixedDigital。其中,kAdaptiveAnalog带有模拟音量调节的功能。kAdaptiveDigital是可变增益agc,但是不调节系统音量。kFixedDigital是固定增益的agc。
enum Mode {
// Adaptive mode intended for use if an analog volume control is available
// on the capture device. It will require the user to provide coupling
// between the OS mixer controls and AGC through the |stream_analog_level()|
// functions.
//
// It consists of an analog gain prescription for the audio device and a
// digital compression stage.
kAdaptiveAnalog,
// Adaptive mode intended for situations in which an analog volume control
// is unavailable. It operates in a similar fashion to the adaptive analog
// mode, but with scaling instead applied in the digital domain. As with
// the analog mode, it additionally uses a digital compression stage.
kAdaptiveDigital,
// Fixed mode which enables only the digital compression stage also used by
// the two adaptive modes.
//
// It is distinguished from the adaptive modes by considering only a
// short time-window of the input signal. It applies a fixed gain through
// most of the input level range, and compresses (gradually reduces gain
// with increasing level) the input signal at higher levels. This mode is
// preferred on embedded devices where the capture signal level is
// predictable, so that a known gain can be applied.
kFixedDigital
};
- analog_agc.h 定义了配置targetLevelDbfs和compressionGaindB用于调节agc的动态范围
typedef struct {
// Configurable parameters/variables
uint32_t fs; // Sampling frequency
int16_t compressionGaindB; // Fixed gain level in dB
int16_t targetLevelDbfs; // Target level in -dBfs of envelope (default -3)
int16_t agcMode; // Hard coded mode (adaptAna/adaptDig/fixedDig)
uint8_t limiterEnable; // Enabling limiter (on/off (default off))
WebRtcAgcConfig defaultConfig;
WebRtcAgcConfig usedConfig;
// General variables
int16_t initFlag;
int16_t lastError;
// Target level parameters
// Based on the above: analogTargetLevel = round((32767*10^(-22/20))^2*16/2^7)
int32_t analogTargetLevel; // = RXX_BUFFER_LEN * 846805; -22 dBfs
int32_t startUpperLimit; // = RXX_BUFFER_LEN * 1066064; -21 dBfs
int32_t startLowerLimit; // = RXX_BUFFER_LEN * 672641; -23 dBfs
int32_t upperPrimaryLimit; // = RXX_BUFFER_LEN * 1342095; -20 dBfs
int32_t lowerPrimaryLimit; // = RXX_BUFFER_LEN * 534298; -24 dBfs
int32_t upperSecondaryLimit; // = RXX_BUFFER_LEN * 2677832; -17 dBfs
int32_t lowerSecondaryLimit; // = RXX_BUFFER_LEN * 267783; -27 dBfs
uint16_t targetIdx; // Table index for corresponding target level
#ifdef MIC_LEVEL_FEEDBACK
uint16_t targetIdxOffset; // Table index offset for level compensation
#endif
int16_t analogTarget; // Digital reference level in ENV scale
// Analog AGC specific variables
int32_t filterState[8]; // For downsampling wb to nb
int32_t upperLimit; // Upper limit for mic energy
int32_t lowerLimit; // Lower limit for mic energy
int32_t Rxx160w32; // Average energy for one frame
int32_t Rxx16_LPw32; // Low pass filtered subframe energies
int32_t Rxx160_LPw32; // Low pass filtered frame energies
int32_t Rxx16_LPw32Max; // Keeps track of largest energy subframe
int32_t Rxx16_vectorw32[RXX_BUFFER_LEN]; // Array with subframe energies
int32_t Rxx16w32_array[2][5]; // Energy values of microphone signal
int32_t env[2][10]; // Envelope values of subframes
int16_t Rxx16pos; // Current position in the Rxx16_vectorw32
int16_t envSum; // Filtered scaled envelope in subframes
int16_t vadThreshold; // Threshold for VAD decision
int16_t inActive; // Inactive time in milliseconds
int16_t msTooLow; // Milliseconds of speech at a too low level
int16_t msTooHigh; // Milliseconds of speech at a too high level
int16_t changeToSlowMode; // Change to slow mode after some time at target
int16_t firstCall; // First call to the process-function
int16_t msZero; // Milliseconds of zero input
int16_t msecSpeechOuterChange; // Min ms of speech between volume changes
int16_t msecSpeechInnerChange; // Min ms of speech between volume changes
int16_t activeSpeech; // Milliseconds of active speech
int16_t muteGuardMs; // Counter to prevent mute action
int16_t inQueue; // 10 ms batch indicator
// Microphone level variables
int32_t micRef; // Remember ref. mic level for virtual mic
uint16_t gainTableIdx; // Current position in virtual gain table
int32_t micGainIdx; // Gain index of mic level to increase slowly
int32_t micVol; // Remember volume between frames
int32_t maxLevel; // Max possible vol level, incl dig gain
int32_t maxAnalog; // Maximum possible analog volume level
int32_t maxInit; // Initial value of "max"
int32_t minLevel; // Minimum possible volume level
int32_t minOutput; // Minimum output volume level
int32_t zeroCtrlMax; // Remember max gain => don't amp low input
int32_t lastInMicLevel;
int16_t scale; // Scale factor for internal volume levels
#ifdef MIC_LEVEL_FEEDBACK
int16_t numBlocksMicLvlSat;
uint8_t micLvlSat;
#endif
// Structs for VAD and digital_agc
AgcVad vadMic;
DigitalAgc digitalAgc;
#ifdef WEBRTC_AGC_DEBUG_DUMP
FILE* fpt;
FILE* agcLog;
int32_t fcount;
#endif
int16_t lowLevelSignal;
} LegacyAgc;
相关源代码如下:
int GainControlImpl::AnalyzeCaptureAudio(AudioBuffer* audio) {
if (!enabled_) {
return AudioProcessing::kNoError;
}
RTC_DCHECK(num_proc_channels_);
RTC_DCHECK_GE(AudioBuffer::kMaxSplitFrameLength,
audio->num_frames_per_band());
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(audio->num_channels(), *num_proc_channels_);
RTC_DCHECK_LE(*num_proc_channels_, gain_controllers_.size());
int16_t split_band_data[AudioBuffer::kMaxNumBands]
[AudioBuffer::kMaxSplitFrameLength];
int16_t* split_bands[AudioBuffer::kMaxNumBands] = {
split_band_data[0], split_band_data[1], split_band_data[2]};
if (mode_ == kAdaptiveAnalog) {
int capture_channel = 0;
for (auto& gain_controller : gain_controllers_) {
gain_controller->set_capture_level(analog_capture_level_);
audio->ExportSplitChannelData(capture_channel, split_bands);
int err =
WebRtcAgc_AddMic(gain_controller->state(), split_bands,
audio->num_bands(), audio->num_frames_per_band());
audio->ImportSplitChannelData(capture_channel, split_bands);
if (err != AudioProcessing::kNoError) {
return AudioProcessing::kUnspecifiedError;
}
++capture_channel;
}
} else if (mode_ == kAdaptiveDigital) {
int capture_channel = 0;
for (auto& gain_controller : gain_controllers_) {
int32_t capture_level_out = 0;
audio->ExportSplitChannelData(capture_channel, split_bands);
int err =
WebRtcAgc_VirtualMic(gain_controller->state(), split_bands,
audio->num_bands(), audio->num_frames_per_band(),
analog_capture_level_, &capture_level_out);
audio->ImportSplitChannelData(capture_channel, split_bands);
gain_controller->set_capture_level(capture_level_out);
if (err != AudioProcessing::kNoError) {
return AudioProcessing::kUnspecifiedError;
}
++capture_channel;
}
}
return AudioProcessing::kNoError;
}
4、主要接口
analog_agc.h包括模拟的agc结构体声明,而gain_control.h中的接口函数在analog_agc.c中实现。
WebRtcAgc_AddFarend 计算远端信号的语音活度VAD
WebRtcAgc_AddMic 计算麦克风输入的语音活度,对于非常小的信号会乘增益系数
WebRtcAgc_VirtualMic 用虚拟的麦克风音量来调节幅度
WebRtcAgc_Process vad核心处理
WebRtcAgc_set_config 设置VAD参数
在analog_agc.c还包括以下函数:
WebRtcAgc_UpdateAgcThresholds
WebRtcAgc_SaturationCtrl
WebRtcAgc_ZeroCtrl
WebRtcAgc_SpeakerInactiveCtrl
WebRtcAgc_ExpCurve
WebRtcAgc_ProcessAnalog
digital_agc.h包括数字的agc结构体声明,Vad结构声明,而gain_control.h中的接口函数在analog_agc.c中实现。
WebRtcAgc_ProcessDigital
WebRtcAgc_AddFarendToDigital
WebRtcAgc_InitVad
WebRtcAgc_ProcessVad
WebRtcAgc_CalculateGainTable
欢迎关注公众号“音视频开发之旅”,一起学习成长。
最后
以上就是拉长草莓最近收集整理的关于WEBRTC AGC 算法原理初识(二)1、AGC 初识2、WEBRTC 的 AGC算法3、主要配置4、主要接口的全部内容,更多相关WEBRTC内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复