一、前言
Linux内核链表结构是一种双向循环链表结构,与传统的链表结构不同,Linux内核链表结构仅包含前驱和后继指针,不包含数据域。使用链表结构,仅需在结构体成员中包含list_head*成员就行;链表结构的定义在linux/list.h头文件。
二、链表初始化
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name)
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
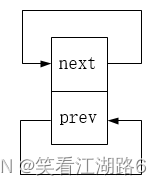
宏LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)和LIST_HEAD(name)的作用在于初始化一个链表头节点,并使其前驱指针和后继指针指向自身;内联函数INIT_LIST_HEAD同理;
三、添加节点
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
prev->next = new;
}
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}
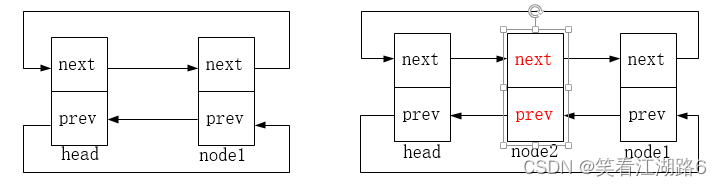
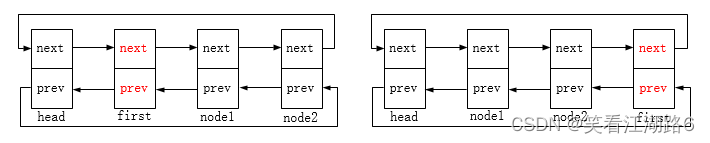
list_add:在头节点后插入节点,图示如下,node2为新增的节点:
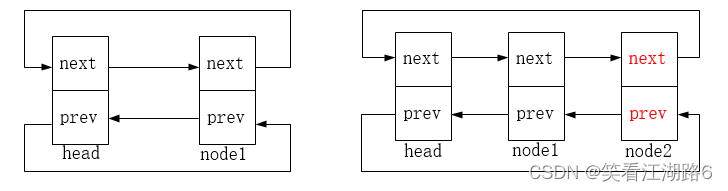
list_add_tail在头节点前插入节点,图示如下,node2为新增的节点:
四、删除节点
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next)
{
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
}
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->next = LIST_POISON1;
entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
}
static inline void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry);
}
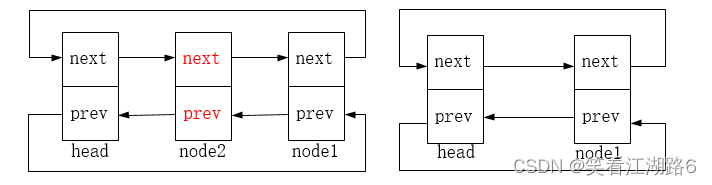
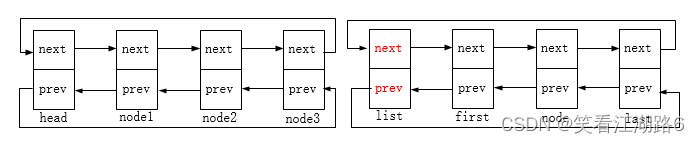
list_del:删除链表中的entry节点,entry节点的前驱后继指针指向LIST_POSITION1和LIST_POSITION2两个特殊值,这样设置是为了保证不在链表中的节点项不可访问,对LIST_POSITION1和LIST_POSITION2的访问都将引起页故障。
list_del_init:删除原链表中的entry节点,然后重新初始化entry节点为头节点(使其前驱后继指针都指向自身)。
/*
* Architectures might want to move the poison pointer offset
* into some well-recognized area such as 0xdead000000000000,
* that is also not mappable by user-space exploits:
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_ILLEGAL_POINTER_VALUE
# define POISON_POINTER_DELTA _AC(CONFIG_ILLEGAL_POINTER_VALUE, UL)
#else
# define POISON_POINTER_DELTA 0
#endif
/*
* These are non-NULL pointers that will result in page faults
* under normal circumstances, used to verify that nobody uses
* non-initialized list entries.
*/
#define LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x00100100 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA)
#define LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x00200200 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA)
链表删除的图示如下:
五、节点替换
static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
new->next = old->next;
new->next->prev = new;
new->prev = old->prev;
new->prev->next = new;
}
static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
list_replace(old, new);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);
}
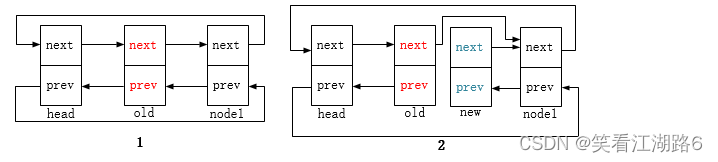
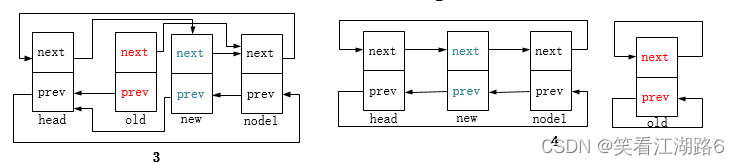
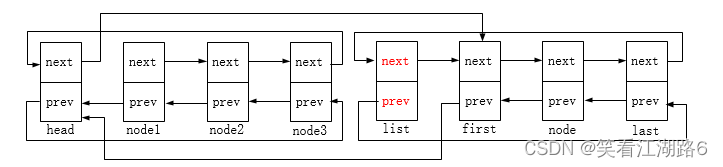
list_replace:将旧节点替换为新节点,函数头两句对应下图2,新节点next指针指向node1,node1节点的prev指针指向新节点。后两句对应图3,新节点prev指针指向head,head节点的next指针指向新节点。此时old节点的next和prev指针指向仍保留着;
list_replace_init:将旧节点替换为新节点,并将旧节点重新初始化为头节点(前驱后继指针指向自身),对应下图4。
六、移动节点
static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del(list->prev, list->next);
list_add(list, head);
}
static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del(list->prev, list->next);
list_add_tail(list, head);
}
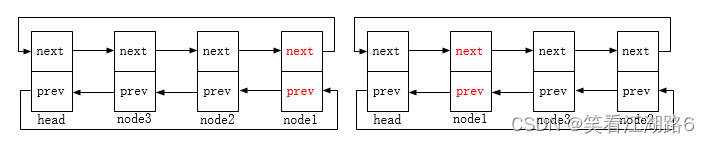
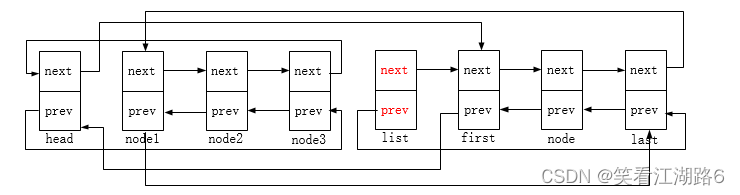
list_move:将list节点移动至head节点后(对应下图示的node1节点移动);
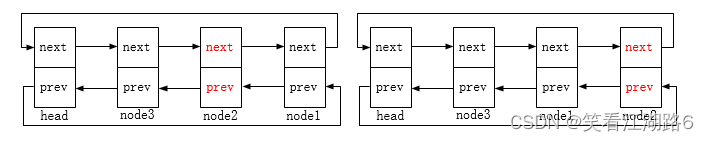
list_move_tail:将list节点移动至head节点前(对应下图示的node2节点移动);
七、尾节点判断
static inline int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list,
const struct list_head *head)
{
return list->next == head;
}
链表的最后一个节点特性:其后继指针next必将指向头节点head
八、链表空判断
static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}
static inline int list_empty_careful(const struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *next = head->next;
return (next == head) && (next == head->prev);
}
list_empty和list_empty_careful都是判断链表是否为空。list_empty判断节点的后继指针next是否指向自身;list_empty_careful判断节点的后继指针和前驱指针是否均指向自身,其可用来判断链表是否为空且当前是否正在被修改。
九、链表旋转
static inline void list_rotate_left(struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *first;
if (!list_empty(head)) {
first = head->next;
list_move_tail(first, head);
}
}
list_rotate_left:链表节点向左移动,原先左边的节点向右移。相当于与前一节点互换位置。图示如下:
十、判断链表是否仅含单个节点
static inline int list_is_singular(const struct list_head *head)
{
return !list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev);
}
判断条件为链表不为空,且头指针的前驱和后继均指向同个节点
十一、合并链表
static inline void __list_splice(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
struct list_head *first = list->next;
struct list_head *last = list->prev;
first->prev = prev;
prev->next = first;
last->next = next;
next->prev = last;
}
/**
* list_splice - join two lists, this is designed for stacks
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void list_splice(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head, head->next);
}
/**
* list_splice_tail - join two lists, each list being a queue
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void list_splice_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);
}
/**
* list_splice_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list.
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list)) {
__list_splice(list, head, head->next);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
}
}
/**
* list_splice_tail_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* Each of the lists is a queue.
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static inline void list_splice_tail_init(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list)) {
__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
}
}
链表初始状态:
first->prev = prev;
prev->next = first;
这里prev即head节点
last->next = next;
next->prev = last;
这里next即node1节点
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
最后一步,把list节点重新初始化为头节点,使其前驱后继指针指向自身。
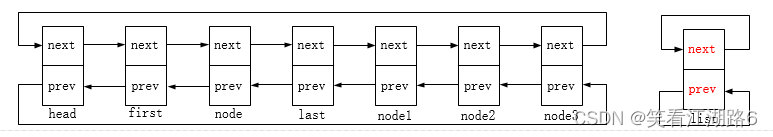
上述图示描述了list_splice_init的链表合并过程,函数的作用是把list链表(除list节点自身)插入到head节点后(即head和head->next之间),并重新初始化list节点;
list_splice_tail_init则是与list_splice_init的区别仅是插入的位置不同,其是插入到head节点之前(即head->prev和head之间)。
linux中定义了很多优美的宏,值得我们深入学习。如下:
一、container_of和offsetof
首先介绍两个很好用的宏container_of和offsetof。offsetof宏用于计算结构体成员基于结构体首地址的偏移量,container_of宏用于获取结构体首地址(根据成员指针)。
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
offsetof宏接受两个入参,分别为结构体类型和结构体成员名,该宏将0强制转换成结构体类型的指针,并取其成员的地址。结构体首地址为0,对应成员的地址即成员相对结构体首地址的偏移量。
/**
* container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structure
* @ptr: the pointer to the member.
* @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the member within the struct.
*
*/
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({
const typeof(((type *)0)->member) * __mptr = (ptr);
(type *)((char *)__mptr - offsetof(type, member)); })
container_of宏接受三个入参,指向结构体成员的指针ptr,结构体类型type,结构体成员名member。该宏首先定义一个结构体成员类型的指针_mptr,类型的获取通过typeof,_mptr = ptr,并将_mptr强转为char*型,减去offsetof计算的偏移量,即得到结构体首地址。
二、list_entry
/**
* list_entry - get the struct for this entry
* @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member)
container_of(ptr, type, member)
list_entry即根据结构体成员指针ptr取得结构体首地址,如下例子使用:
/** 结构体定义 **/
struct student{
int id;
char name[20];
list_head node;
};
struct student stu;
char* ptr = &stu.node;
/** 宏使用如下 **/
struct student* s = list_entry(ptr, struct student, node);
三、list_first_entry
/**
* list_first_entry - get the first element from a list
* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*
* Note, that list is expected to be not empty.
*/
#define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member)
list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)
ptr为链表头节点指针,type为结构体类型,member为结构体内成员名(结构体的链表成员)。list_first_entry宏取得链表首个节点的结构体首地址(头节点不算在内)。
四、list_for_each
#define list_for_each(pos, head)
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
从链表首节点(不包含头节点)开始往后遍历。
六、list_for_each_prev
#define list_for_each_prev(pos, head)
for (pos = (head)->prev; pos != (head); pos = pos->prev)
从链表首节点(不包含头节点)开始往前遍历。
七、list_for_each_safe
/**
* list_for_each_safe - iterate over a list safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head)
for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head);
pos = n, n = pos->next)
list_for_each的加强版,支持遍历过程的节点删除操作,提高安全性。使用变量n提前保存节点pos的后继,避免遍历过程pos节点删除后,指向错误。
八、list_for_each_prev_safe
/**
* list_for_each_prev_safe - iterate over a list backwards safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each_prev_safe(pos, n, head)
for (pos = (head)->prev, n = pos->prev;
pos != (head);
pos = n, n = pos->prev)
list_for_each_prev的加强版,支持遍历过程的节点删除操作。
九、list_for_each_entry
/**
* list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member)
for (pos = list_first_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member);
&pos->member != (head);
pos = list_next_entry(pos, member))
/**
* list_for_each_entry_reverse - iterate backwards over list of given type.
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member)
for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member);
prefetch(pos->member.prev), &pos->member != (head);
pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member))
list_for_each_entry:从链表首节点(不包含头节点)开始往后遍历,pos指向的是结构体,而不是结构体内的链表节点成员。与list_for_each不同,list_for_each遍历的是链表节点,而list_for_each_entry遍历的是由链表节点串起来的结构体链表。
list_for_each_entry_reverse:与list_for_each_entry相反,是往前遍历。
最后
以上就是优秀百褶裙最近收集整理的关于Linux内核--链表结构的全部内容,更多相关Linux内核--链表结构内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复