简述
输入子系统是为支持输入设备而开发的,能让Linux内核处理各种不同类型的输入设备,比如触摸屏、鼠标、键盘等,而且也支持蜂鸣器、LED等输出设备。输入子系统的作用是为上层提供统一的抽象层,为驱动层程序的实现提供统一的接口,起到承上启下的作用。基本框架如下:
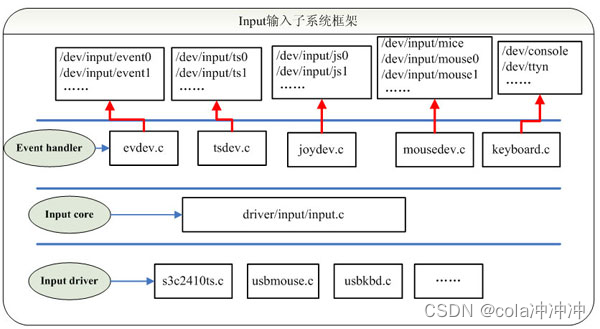
输入子系统框架
以evdev.c为例画一个简单的输入字系统框架
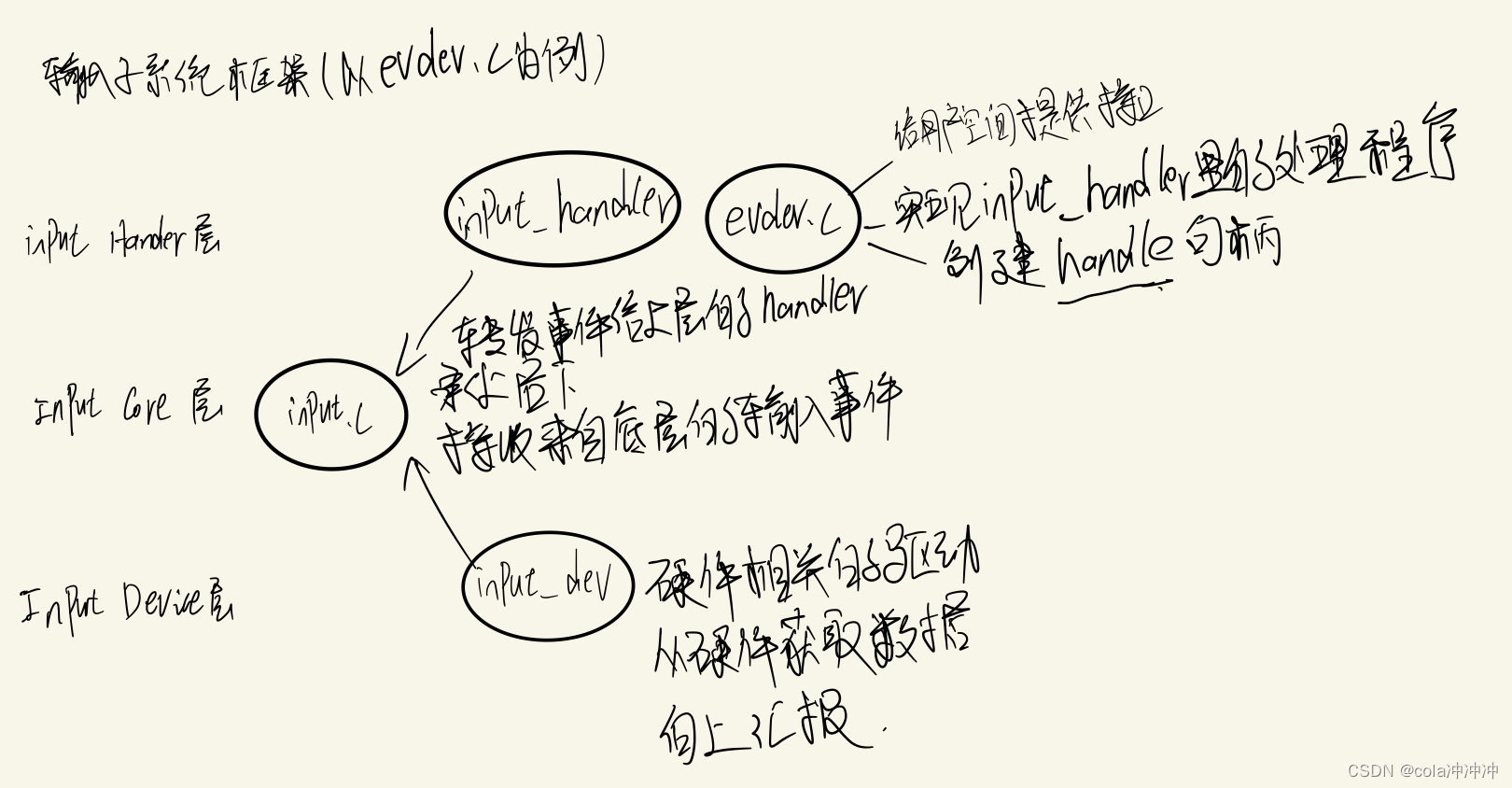
由上述框图可以看出 ,输入子系统由Input Device层(驱动设备层)、Input Core层(核心层)、Input Handler层(事件处理层)三部分组成。
- Input Device层:面向于硬件的驱动程序,负责对硬件设备的读写访问,并通过中断的方式向上层上报事件;该层重要的数据结构为struct input_dev,上报事件所用的接口input_event()。
- Input Core层:承上启下,为驱动层提供统一的接口,接收驱动层上报的输入事件,将事件转发给Input Handler层进行处理;重要的数据成员为input_handler_list、input_dev_list两个链表,重要的数据结构为struct input_handle。
- Input Handler层:处理驱动层提交的数据;为用户空间提供接口;重要的数据结构为struct input_handler 、struct evdev(以evdev.c为例,若是mousedev.c 则是struct mousedev 以此类推)。
输入子系统框架分析
输入子系统是所有输入IO设备的中间层,为上层提供了统一的界面,比如在终端系统中,我们不用管有多少个键盘,多少个鼠标,只需要去输入子系统中去取对应的事件就可以了。
接下来我们从代码的角度出发去分析Input Device层(驱动设备层)、Input Core层(核心层)、Input Handler层(事件处理层)。
- Input Device层(驱动设备层)
- 纯硬件操作层,调用不同的硬件接口去读写硬件,比如(gpio_get_value();
gpio_set_value();)。以中断的方式调用input_event()接口上报事件与传递数据。 - 在硬件相关层,input_dev结构体表示一个输入设备, 对于每种不同的具体硬件操作,都有不同的input_dev结构体与之对应。
- 重点:input_dev结构体里面有一个h_list,指向input_handle。
2. Input Core层(核心层)
- 提供主设备号,主设备号为13。
- 提供input_register_device跟input_register_handler函数分别用于注册input_dev跟input_handler。
- 提供input_register_handle函数用于注册一个事件处理input_handle,代表一个成功配对的input_dev和input_handler,input_handle结构体里存放着配对成功的input_dev与input_handler。
3. Input Handler层(事件处理层)
- 该层是纯软件层,不涉及硬件的操作,用于不同设备的事件处理(比如触摸屏、按键等)。
- 对于不同的设备事件处理,都有一个input_handler结构体与之对应。
- 重点:input_handler结构体里面有一个h_list,指向input_handle。
重要的数据结构
-
input_dev结构体
struct input_dev {
const char *name; //提供给用户的输入设备的名称
const char *phys; //提供给编程者的设备节点的名称
const char *uniq; //指定唯一的ID号,就像MAC地址一样
struct input_id id; //输入设备标识ID,用于和事件处理层进行匹配
unsigned long evbit[NBITS(EV_MAX)]; // 记录设备支持的事件类型
unsigned long keybit[NBITS(KEY_MAX)]; // 记录设备支持的按键类型
unsigned long relbit[NBITS(REL_MAX)]; // 表示能产生哪些相对位移事件, x,y,滚轮
unsigned long absbit[NBITS(ABS_MAX)]; // 表示能产生哪些绝对位移事件, x,y
unsigned long mscbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(MSC_CNT)];
unsigned long ledbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)];
unsigned long sndbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)];
unsigned long ffbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(FF_CNT)];
unsigned long swbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)];
...
struct list_head h_list; //input_handle链表 input_handle里面有支持该设备的
input_handler
struct list_head node;
...
};-
input_handler结构体
struct input_handler {
void *private;
void (*event)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value); //如果没有events,则使用event一个一个处理
void (*events)(struct input_handle *handle,
const struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count);//如果没被过滤,优先调用
//events接口处理多个事件
bool (*filter)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value); //硬件产生数据时优先调用filter函数过滤
bool (*match)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev);//用来匹配是否支持
//注册的input_dev
int (*connect)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, const struct input_device_id *id); //若input_handler与input_dev匹配,则调用该接口将两者建立联系
void (*disconnect)(struct input_handle *handle);
void (*start)(struct input_handle *handle); //建立联系后start
bool legacy_minors; //connet函数根据该参数来决定是否使用minor创建设备节点
int minor;
const char *name;
const struct input_device_id *id_table; //用于判断能否支持注册的input_dev
struct list_head h_list; //input_handle链表 input_handle里面有支持该设备的input_dev
struct list_head node;
};-
input_handle结构体
struct input_handle {
void *private;
int open;
const char *name;
struct input_dev *dev; //与input_handler匹配成功的input_dev
struct input_handler *handler; //与input_dev匹配成功的input_handler
struct list_head d_node; //存放input_dev_list链表
struct list_head h_node; //存放input_handler_list链表
};重点:两条链表一个结构
-
对于handler和device,分别用链表input_handler_list和input_device_list进行维护,
当handler或者device增加或减少的时候,分别往这两链表增加或删除节点,这两条都是全局链表。 -
input_handle 结构体代表一个成功配对的input_dev和input_handler。input_hande 没有一个全局的链表,它注册的时候将自己分别挂在了input_device_list和 input_handler_list的h_list上了;同时,input_handle的成员
.*dev,关联到input_dev结构,.*handler关联到input_handler结构 。从此,建立好了三者的铁三角关系,通过任何一方,都可以找到彼此。
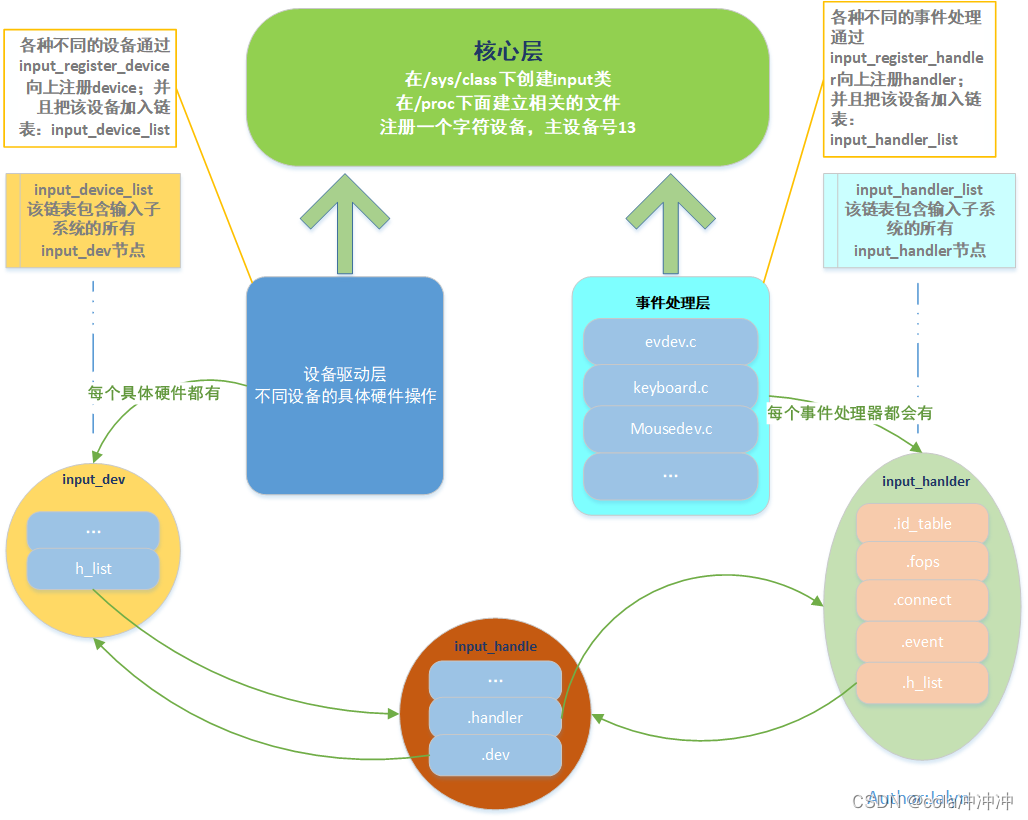
注册输入设备的流程
- 注册input_dev:input_register_device
- 把input_dev放入input.c的input_dev_list链表
- 对于input.c的input_handler_list链表中的每一个input_handler,一一比较
- 如果匹配则调用input_handler.connect
- 判断input_dev和input_handler是否匹配
- input_handler中有一个id_table,表示它支持哪类设备
- input_handler有一个match函数,可以用来进行复杂的判断
- 如果有match函数:input_dev先跟id_table比较,成功后再用match函数再次判断
- 如果没有match函数:input_dev跟id_table比较即可
- 匹配后建立调用input_handler里的connect函数建立联系
- 创建一个input_handle,把input_dev, input_handler放在里面
类似: evdev->handle.dev = input_get_device(dev); evdev->handle.handler = handler; error = input_register_handle(&evdev->handle); - 调用input_register_handle函数注册input_handle
- 注册函数里将input_handle放入input_dev和input_handler结构体的h_list链表中
/* * Filters go to the head of the list, normal handlers * to the tail. */ if (handler->filter) list_add_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list); else list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list); /* * Since we are supposed to be called from ->connect() * which is mutually exclusive with ->disconnect() * we can't be racing with input_unregister_handle() * and so separate lock is not needed here. */ list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->h_node, &handler->h_list); - 注册字符设备驱动程序
cdev_init(&evdev->cdev, &evdev_fops); error = cdev_device_add(&evdev->cdev, &evdev->dev);
应用层读取输入设备数据流程
- 应用层调用open函数打开输入设备,在input_handler层会创建一个evdev_client,表示一个"客户"。
- 应用层调用read/poll读取、等待数据。
static ssize_t evdev_read(struct file *file, char __user *buffer, size_t count, loff_t *ppos) { struct evdev_client *client = file->private_data; struct evdev *evdev = client->evdev; struct input_event event; size_t read = 0; int error; if (count != 0 && count < input_event_size()) return -EINVAL; for (;;) { if (!evdev->exist || client->revoked) return -ENODEV; /*如果client的环形缓冲区中没有数据并且是非阻塞的,那么返回-EAGAIN,也就是try again*/ if (client->packet_head == client->tail && (file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)) return -EAGAIN; /* * count == 0 is special - no IO is done but we check * for error conditions (see above). */ if (count == 0) break; /*调用evdev_fetch_next_event,如果获得了数据则取出来*/ while (read + input_event_size() <= count && evdev_fetch_next_event(client, &event)) { /*input_event_to_user调用copy_to_user传入用户程序中,这样读取完成*/ if (input_event_to_user(buffer + read, &event)) return -EFAULT; read += input_event_size(); } if (read) break; /*如果没有数据,并且是阻塞的,则在等待队列上等待*/ if (!(file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)) { error = wait_event_interruptible(evdev->wait, client->packet_head != client->tail || !evdev->exist || client->revoked); if (error) return error; } } return read; }当没有数据时休眠,wait_event_interruptible(),等待唤醒。
唤醒流程
- 用户点击、操作输入设备,产生中断
- 在中断服务程序里 从硬件读取到数据,使用以下函数上报数据
void input_event(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value); static inline void input_sync(struct input_dev *dev); // 实质也是 input_event - 在input_event函数里:
从dev->h_list中取出input_handle,从input_handle取出input_handler
优先调用input_handler->filter来处理
如果没有input_handler->filter或者没处理成功
· 调用input_handler->events
· 没有input_handler->events的话,调用input_handler->event
· 最终调用wake_up_interruptible() 唤醒应用层
input_event( )函数里调用流程:input_event(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value) ---> input_handle_event ---> input_pass_values ---> input_to_handler ---> if (handler->filter) handler->filter() ;return 0 ---> if (handler->events) handler->events; else if (handler->event) handler->event ---> evdev_pass_values ---> wake_up_interruptible
最后
以上就是害羞玉米最近收集整理的关于Linux驱动-Input子系统的全部内容,更多相关Linux驱动-Input子系统内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复