stm32mp157 盘古开发板 Linux内核版本4.19
目录
1、朱有鹏老师的视频课程笔记和应用测试代码:
2、input子系统架构分析
2.1、输入核心层源码分析
2.1.1、首先是核心模块注册input_init
2.1.2、提供给设备驱动层的接口函数input_allocate_device、input_set_capability、input_register_device
2.1.3、handler和device的匹配
2.1.4、事件驱动层的接口函数input_register_handler、input_register_handle
2.2、最上层:输入事件驱动层源码分析
2.3、最下层:输入设备驱动层
1、朱有鹏老师的视频课程笔记和应用测试代码:
***********《朱有鹏老师嵌入式linux核心课程》 ***********
《5.linux驱动开发-第5部分-5.8.input子系统基础之按键》
--------------------------------------------------------
本课程由朱老师物联网大讲堂推出并提供技术支持,课件可打包下载
网盘地址:http://yunpan.cn/cjVy3RAgfDufK 访问密码 4ad7
技术交流QQ群:朱老师物联网讲堂1群 397164505
朱老师个人QQ:1264671872
--------------------------------------------------------
第一部分、章节目录
5.8.1.什么是input子系统
5.8.2.input设备应用层编程实践1
5.8.3.input设备应用层编程实践2
5.8.4.input子系统架构总览1
5.8.5.input子系统架构总览2
5.8.6.输入核心层源码分析1
5.8.7.输入核心层源码分析2
5.8.8.输入事件驱动层源码分析
5.8.9.输入设备驱动层源码分析1
5.8.10.输入设备驱动层源码分析2
5.8.11.中断方式按键驱动实战1
5.8.12.中断方式按键驱动实战2
第二部分、章节介绍
5.8.1.什么是input子系统
本节全面介绍input子系统的概念和来源、解决的主要问题,目的是让大家对linux中输入类设备有一个全面了解
5.8.2.input设备应用层编程实践1
本节实践编写应用层程序,操作键盘和鼠标这些常见input类设备,目的是让大家先学会使用输入类设备,后面再来分析驱动。
5.8.3.input设备应用层编程实践2
本节接着上节对读上来的数据进行解析,分析其规律并且和设备本身特性进行关联分析。
5.8.4.input子系统架构总览1
本节详细介绍input子系统的三层结构以及各层的功能特点。
5.8.5.input子系统架构总览2
本节介绍input子系统下编写驱动的路线和方法。
5.8.6.输入核心层源码分析1
本节分析输入核心层,主要是模块装载和开放给其他层的接口的分析。
5.8.7.输入核心层源码分析2
本节接着分析输入核心层,主要是handler和device的匹配、安装部分的源码分析。
5.8.8.输入事件驱动层源码分析
本节对输入事件层源码分析,主要以evdev.c为例分析了event handler的安装函数、数据上报函数的实现。
5.8.9.输入设备驱动层源码分析1
本节分析输入设备驱动层,以x210自带的按键驱动为例进行分析。
5.8.10.输入设备驱动层源码分析2
本节接着分析按键驱动,主要是一些源码细节探究。
5.8.11.中断方式按键驱动实战1
本节开始按键驱动实战,先找到内核提供的模版,并且对模版程序进行分析讲解。
5.8.12.中断方式按键驱动实战2
本节以模版驱动为基础,结合x210开发板的情况进行驱动移植、编译、测试、修改。
第三部分、随堂记录
5.8.1.什么是input子系统
5.8.1.1、何为输入设备
5.8.1.2、linux中输入设备的编程模型
(1)命令行界面的输入类设备应用接口
(2)GUI界面带来的麻烦、不同的输入类设备也会带来麻烦
(3)struct input_event
5.8.1.3、input子系统简介
(1)linux的input子系统解决了什么问题
(2)input子系统分4个部分:应用层 + input event + input core + 硬件驱动
(3)input子系统如何工作
(4)事件驱动型GUI框架,如QT、VC等。
5.8.2.input设备应用层编程实践1
5.8.2.1、确定设备文件名
(1)应用层操作驱动有2条路:/dev目录下的设备文件,/sys目录下的属性文件
(2)input子系统用的/dev目录下的设备文件,具体一般都是在 /dev/input/eventn
(3)用cat命令来确认某个设备文件名对应哪个具体设备。我在自己的ubuntu中实测的键盘是event1,而鼠标是event3.
5.8.2.2、标准接口打开并读取文件
5.8.2.3、解析struct input_event
5.8.3.input设备应用层编程实践2
5.8.3.1、解析键盘事件数据
5.8.3.2、解析鼠标事件数据
5.8.4.input子系统架构总览1
5.8.4.1、input子系统分为三层
(1)最上层:输入事件驱动层,evdev.c和mousedev.c和joydev.c属于这一层
(2)中间层:输入核心层,input.c属于这一层
(3)最下层:输入设备驱动层,drivers/input/xxx 文件夹下
5.8.4.2、input类设备驱动开发方法
(1)输入事件驱动层和输入核心层不需要动,只需要编写设备驱动层
(2)设备驱动层编写的接口和调用模式已定义好,驱动工程师的核心工作量是对具体输入设备硬件的操作和性能调优。
(3)input子系统不算复杂,学习时要注意“标准模式”四个字。
5.8.5.input子系统架构总览2
5.8.6.输入核心层源码分析1
5.8.6.1、核心模块注册input_init
(1)class_register
(2)input_proc_init
(3)register_chrdev
5.8.6.2、设备驱动层的接口函数
(1)input_allocate_device
(2)input_set_capability
(3)input_register_device
5.8.7.输入核心层源码分析2
5.8.7.1、handler和device的匹配
(1)input_attach_handler
input_match_device 匹配device和handler
handler->connect(handler, dev, id) 连接device和handler
5.8.7.2、事件驱动层的接口函数
(1)input_register_handler
(2)input_register_handle
5.8.8.输入事件驱动层源码分析
5.8.8.1、input_handler
5.8.8.2、evdev_connect
5.8.8.3、evdev_event
5.8.9_10.输入设备驱动层源码分析1_2
5.8.9.1、先找到bsp中按键驱动源码
(1)锁定目标:板载按键驱动
(2)确认厂家提供的BSP是否已经有驱动
(3)找到bsp中的驱动源码
5.8.9.2、按键驱动源码初步分析
(1)模块装载分析
(2)平台总线相关分析
(3)确定重点:probe函数
5.8.9.3、源码细节实现分析
(1)gpio_request
(2)input_allocate_device
(3)input_register_device
(4)timer
5.8.11.中断方式按键驱动实战1
5.8.11.1、模板
(1)input类设备驱动模式非常固定,用参考模版修改即可
(2)新建驱动项目并粘贴模版内容
5.8.11.2、模板驱动的解析
5.8.11.3、着手移植驱动
5.8.12.中断方式按键驱动实战2
5.8.12.1、驱动移植细节
5.8.12.2、驱动实践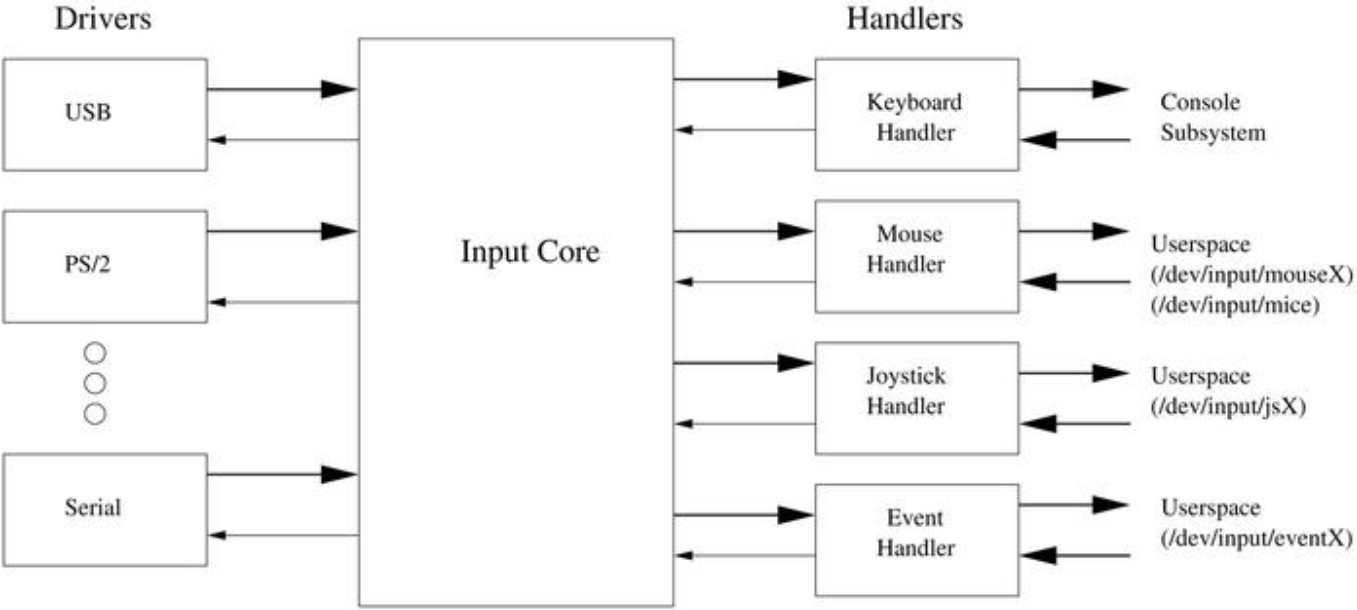
上图即为input子系统架构的三层:drivers(最下层,输入设备驱动层)、core(中间层,核心层)、handlers(最上层,输入事件驱动层)
应用程序测试代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <string.h>
#define DEVICE_KEY "/dev/input/event1"
#define DEVICE_MOUSE "/dev/input/event3"
#define X210_KEY "/dev/input/event1"
int main(void)
{
int fd = -1, ret = -1;
struct input_event ev;
// 第1步:打开设备文件
fd = open(X210_KEY, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
while (1)
{
// 第2步:读取一个event事件包
memset(&ev, 0, sizeof(struct input_event));
ret = read(fd, &ev, sizeof(struct input_event));
if (ret != sizeof(struct input_event))
{
perror("read");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
// 第3步:解析event包,才知道发生了什么样的输入事件
printf("-------------------------n");
printf("type: %hdn", ev.type);
printf("code: %hdn", ev.code);
printf("value: %dn", ev.value);
printf("n");
}
// 第4步:关闭设备
close(fd);
return 0;
}2、input子系统架构分析
2.1、输入核心层源码分析
相关代码linux_kernellinux-stdriversinput目录下input.c
2.1.1、首先是核心模块注册input_init
static int __init input_init(void)
{
int err;
//在/sys/class下面注册一个input类
err = class_register(&input_class);
if (err) {
pr_err("unable to register input_dev classn");
return err;
}
//proc目录下面
err = input_proc_init();
if (err)
goto fail1;
//注册字符设备驱动,主设备号是13
err = register_chrdev_region(MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, 0),
INPUT_MAX_CHAR_DEVICES, "input");
if (err) {
pr_err("unable to register char major %d", INPUT_MAJOR);
goto fail2;
}
return 0;
fail2: input_proc_exit();
fail1: class_unregister(&input_class);
return err;
}
static void __exit input_exit(void)
{
input_proc_exit();
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, 0),
INPUT_MAX_CHAR_DEVICES);
class_unregister(&input_class);
}
subsys_initcall(input_init);
module_exit(input_exit);
2.1.2、提供给设备驱动层的接口函数input_allocate_device、input_set_capability、input_register_device
/**
* input_allocate_device - allocate memory for new input device
*
* Returns prepared struct input_dev or %NULL.
*
* NOTE: Use input_free_device() to free devices that have not been
* registered; input_unregister_device() should be used for already
* registered devices.
*/
//相当于动态申请一个input dev设备变量,并对其进行初步必要的初始化
struct input_dev *input_allocate_device(void)
{
static atomic_t input_no = ATOMIC_INIT(-1);
struct input_dev *dev;
dev = kzalloc(sizeof(*dev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (dev) {
dev->dev.type = &input_dev_type;
dev->dev.class = &input_class;
device_initialize(&dev->dev);
mutex_init(&dev->mutex);
spin_lock_init(&dev->event_lock);
timer_setup(&dev->timer, NULL, 0);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->h_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->node);
dev_set_name(&dev->dev, "input%lu",
(unsigned long)atomic_inc_return(&input_no));
__module_get(THIS_MODULE);
}
return dev;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(input_allocate_device);
/**
* input_register_device - register device with input core
* @dev: device to be registered
*
* This function registers device with input core. The device must be
* allocated with input_allocate_device() and all it's capabilities
* set up before registering.
* If function fails the device must be freed with input_free_device().
* Once device has been successfully registered it can be unregistered
* with input_unregister_device(); input_free_device() should not be
* called in this case.
*
* Note that this function is also used to register managed input devices
* (ones allocated with devm_input_allocate_device()). Such managed input
* devices need not be explicitly unregistered or freed, their tear down
* is controlled by the devres infrastructure. It is also worth noting
* that tear down of managed input devices is internally a 2-step process:
* registered managed input device is first unregistered, but stays in
* memory and can still handle input_event() calls (although events will
* not be delivered anywhere). The freeing of managed input device will
* happen later, when devres stack is unwound to the point where device
* allocation was made.
*/
//将input_dev类型的变量注册进系统
int input_register_device(struct input_dev *dev)
{
struct input_devres *devres = NULL;
struct input_handler *handler;
unsigned int packet_size;
const char *path;
int error;
if (test_bit(EV_ABS, dev->evbit) && !dev->absinfo) {
dev_err(&dev->dev,
"Absolute device without dev->absinfo, refusing to registern");
return -EINVAL;
}
if (dev->devres_managed) {
devres = devres_alloc(devm_input_device_unregister,
sizeof(*devres), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!devres)
return -ENOMEM;
devres->input = dev;
}
/* Every input device generates EV_SYN/SYN_REPORT events. */
__set_bit(EV_SYN, dev->evbit);
/* KEY_RESERVED is not supposed to be transmitted to userspace. */
__clear_bit(KEY_RESERVED, dev->keybit);
/* Make sure that bitmasks not mentioned in dev->evbit are clean. */
input_cleanse_bitmasks(dev);
packet_size = input_estimate_events_per_packet(dev);
if (dev->hint_events_per_packet < packet_size)
dev->hint_events_per_packet = packet_size;
dev->max_vals = dev->hint_events_per_packet + 2;
dev->vals = kcalloc(dev->max_vals, sizeof(*dev->vals), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dev->vals) {
error = -ENOMEM;
goto err_devres_free;
}
/*
* If delay and period are pre-set by the driver, then autorepeating
* is handled by the driver itself and we don't do it in input.c.
*/
if (!dev->rep[REP_DELAY] && !dev->rep[REP_PERIOD])
input_enable_softrepeat(dev, 250, 33);
if (!dev->getkeycode)
dev->getkeycode = input_default_getkeycode;
if (!dev->setkeycode)
dev->setkeycode = input_default_setkeycode;
error = device_add(&dev->dev);
if (error)
goto err_free_vals;
path = kobject_get_path(&dev->dev.kobj, GFP_KERNEL);
pr_info("%s as %sn",
dev->name ? dev->name : "Unspecified device",
path ? path : "N/A");
kfree(path);
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex);
if (error)
goto err_device_del;
//添加到输入设备列表里面
list_add_tail(&dev->node, &input_dev_list);
//遍历所有的handler,看哪个和刚注册进来的设备驱动能够匹配,
//如果匹配就会将其绑定,并且生成应用层可以操作的文件接口
list_for_each_entry(handler, &input_handler_list, node)
input_attach_handler(dev, handler);//负责匹配和链接的
//handler和device的挂接是handle结构体,即在handle结构体
//中记录配对的device和handler结构体指针
input_wakeup_procfs_readers();
mutex_unlock(&input_mutex);
if (dev->devres_managed) {
dev_dbg(dev->dev.parent, "%s: registering %s with devres.n",
__func__, dev_name(&dev->dev));
devres_add(dev->dev.parent, devres);
}
return 0;
err_device_del:
device_del(&dev->dev);
err_free_vals:
kfree(dev->vals);
dev->vals = NULL;
err_devres_free:
devres_free(devres);
return error;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(input_register_device);/**
* input_set_capability - mark device as capable of a certain event
* @dev: device that is capable of emitting or accepting event
* @type: type of the event (EV_KEY, EV_REL, etc...)
* @code: event code
*
* In addition to setting up corresponding bit in appropriate capability
* bitmap the function also adjusts dev->evbit.
*/
//声明驱动向上层应用上报哪些信息,在设置驱动向上上报事件的能力
//专用的能力方面设置
void input_set_capability(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code)
{
switch (type) {
case EV_KEY:
__set_bit(code, dev->keybit);
break;
case EV_REL:
__set_bit(code, dev->relbit);
break;
case EV_ABS:
input_alloc_absinfo(dev);
if (!dev->absinfo)
return;
__set_bit(code, dev->absbit);
break;
case EV_MSC:
__set_bit(code, dev->mscbit);
break;
case EV_SW:
__set_bit(code, dev->swbit);
break;
case EV_LED:
__set_bit(code, dev->ledbit);
break;
case EV_SND:
__set_bit(code, dev->sndbit);
break;
case EV_FF:
__set_bit(code, dev->ffbit);
break;
case EV_PWR:
/* do nothing */
break;
default:
pr_err("%s: unknown type %u (code %u)n", __func__, type, code);
dump_stack();
return;
}
__set_bit(type, dev->evbit);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(input_set_capability);static void input_handle_event(struct input_dev *dev,
unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
int disposition = input_get_disposition(dev, type, code, &value);
if (disposition != INPUT_IGNORE_EVENT && type != EV_SYN)
add_input_randomness(type, code, value);
if ((disposition & INPUT_PASS_TO_DEVICE) && dev->event)
dev->event(dev, type, code, value);
if (!dev->vals)
return;
if (disposition & INPUT_PASS_TO_HANDLERS) {
struct input_value *v;
if (disposition & INPUT_SLOT) {
v = &dev->vals[dev->num_vals++];
v->type = EV_ABS;
v->code = ABS_MT_SLOT;
v->value = dev->mt->slot;
}
v = &dev->vals[dev->num_vals++];
v->type = type;
v->code = code;
v->value = value;
}
if (disposition & INPUT_FLUSH) {
if (dev->num_vals >= 2)
input_pass_values(dev, dev->vals, dev->num_vals);
// 最终执行了handle->handler里面的event函数
dev->num_vals = 0;
} else if (dev->num_vals >= dev->max_vals - 2) {
dev->vals[dev->num_vals++] = input_value_sync;
input_pass_values(dev, dev->vals, dev->num_vals);
dev->num_vals = 0;
}
}
/**
* input_event() - report new input event
* @dev: device that generated the event
* @type: type of the event
* @code: event code
* @value: value of the event
*
* This function should be used by drivers implementing various input
* devices to report input events. See also input_inject_event().
*
* NOTE: input_event() may be safely used right after input device was
* allocated with input_allocate_device(), even before it is registered
* with input_register_device(), but the event will not reach any of the
* input handlers. Such early invocation of input_event() may be used
* to 'seed' initial state of a switch or initial position of absolute
* axis, etc.
*/
void input_event(struct input_dev *dev,
unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
unsigned long flags;
if (is_event_supported(type, dev->evbit, EV_MAX)) {
spin_lock_irqsave(&dev->event_lock, flags);
input_handle_event(dev, type, code, value); // 上报事件
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&dev->event_lock, flags);
}
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(input_event);2.1.3、handler和device的匹配
input_attach_handler
input_match_device 匹配device和handler
handler->connect(handler, dev, id) 连接device和handler
static int input_attach_handler(struct input_dev *dev, struct input_handler *handler)
{
const struct input_device_id *id;
int error;
//匹配device和handler
id = input_match_device(handler, dev);
if (!id)
return -ENODEV;
//链接device和handler
error = handler->connect(handler, dev, id);
if (error && error != -ENODEV)
pr_err("failed to attach handler %s to device %s, error: %dn",
handler->name, kobject_name(&dev->dev.kobj), error);
return error;
}/**
* struct input_handler - implements one of interfaces for input devices
* @private: driver-specific data
* @event: event handler. This method is being called by input core with
* interrupts disabled and dev->event_lock spinlock held and so
* it may not sleep
* @events: event sequence handler. This method is being called by
* input core with interrupts disabled and dev->event_lock
* spinlock held and so it may not sleep
* @filter: similar to @event; separates normal event handlers from
* "filters".
* @match: called after comparing device's id with handler's id_table
* to perform fine-grained matching between device and handler
* @connect: called when attaching a handler to an input device
* @disconnect: disconnects a handler from input device
* @start: starts handler for given handle. This function is called by
* input core right after connect() method and also when a process
* that "grabbed" a device releases it
* @legacy_minors: set to %true by drivers using legacy minor ranges
* @minor: beginning of range of 32 legacy minors for devices this driver
* can provide
* @name: name of the handler, to be shown in /proc/bus/input/handlers
* @id_table: pointer to a table of input_device_ids this driver can
* handle
* @h_list: list of input handles associated with the handler
* @node: for placing the driver onto input_handler_list
*
* Input handlers attach to input devices and create input handles. There
* are likely several handlers attached to any given input device at the
* same time. All of them will get their copy of input event generated by
* the device.
*
* The very same structure is used to implement input filters. Input core
* allows filters to run first and will not pass event to regular handlers
* if any of the filters indicate that the event should be filtered (by
* returning %true from their filter() method).
*
* Note that input core serializes calls to connect() and disconnect()
* methods.
*/
struct input_handler {
void *private;
//负责将底层的数据放到某个缓冲区,等待应用层来取数据
void (*event)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
void (*events)(struct input_handle *handle,
const struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count);
bool (*filter)(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
// dev和handler匹配
bool (*match)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev);
// 将dev和handler链接
int (*connect)(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev, const struct input_device_id *id);
void (*disconnect)(struct input_handle *handle);
void (*start)(struct input_handle *handle);
bool legacy_minors;
int minor;
const char *name;
const struct input_device_id *id_table;
struct list_head h_list;
struct list_head node;
};struct input_dev {
const char *name;
const char *phys;
const char *uniq;
struct input_id id;
unsigned long propbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(INPUT_PROP_CNT)];
// BITS_TO_LONGS的作用是计算EV_CNT这么多需要多少个32位的bit来存放记录
// 用来标注自己的驱动有哪些没有哪些,比如只有3个按键...但是系统支持的有很多
// 比如鼠标、触摸屏、键盘等,想鼠标的左右击也需要标注,这就是用其中的一个bit
// 来标注。 去标注自己支持的事件
unsigned long evbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(EV_CNT)];
unsigned long keybit[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];
unsigned long relbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(REL_CNT)];
unsigned long absbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(ABS_CNT)];
unsigned long mscbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(MSC_CNT)];
unsigned long ledbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)];
unsigned long sndbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)];
unsigned long ffbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(FF_CNT)];
unsigned long swbit[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)];
unsigned int hint_events_per_packet;
unsigned int keycodemax;
unsigned int keycodesize;
void *keycode;
int (*setkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev,
const struct input_keymap_entry *ke,
unsigned int *old_keycode);
int (*getkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev,
struct input_keymap_entry *ke);
struct ff_device *ff;
unsigned int repeat_key;
struct timer_list timer;
int rep[REP_CNT];
struct input_mt *mt;
struct input_absinfo *absinfo;
unsigned long key[BITS_TO_LONGS(KEY_CNT)];
unsigned long led[BITS_TO_LONGS(LED_CNT)];
unsigned long snd[BITS_TO_LONGS(SND_CNT)];
unsigned long sw[BITS_TO_LONGS(SW_CNT)];
int (*open)(struct input_dev *dev);
void (*close)(struct input_dev *dev);
int (*flush)(struct input_dev *dev, struct file *file);
int (*event)(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
struct input_handle __rcu *grab;
spinlock_t event_lock;
struct mutex mutex;
unsigned int users;
bool going_away;
struct device dev;
struct list_head h_list;
struct list_head node;
unsigned int num_vals;
unsigned int max_vals;
struct input_value *vals;
bool devres_managed;
};2.1.4、事件驱动层的接口函数input_register_handler、input_register_handle
/**
* input_register_handler - register a new input handler
* @handler: handler to be registered
*
* This function registers a new input handler (interface) for input
* devices in the system and attaches it to all input devices that
* are compatible with the handler.
*/
int input_register_handler(struct input_handler *handler)
{
struct input_dev *dev;
int error;
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex);
if (error)
return error;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&handler->h_list);
list_add_tail(&handler->node, &input_handler_list);
list_for_each_entry(dev, &input_dev_list, node)
input_attach_handler(dev, handler);
input_wakeup_procfs_readers();
mutex_unlock(&input_mutex);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(input_register_handler);
/**
* input_register_handle - register a new input handle
* @handle: handle to register
*
* This function puts a new input handle onto device's
* and handler's lists so that events can flow through
* it once it is opened using input_open_device().
*
* This function is supposed to be called from handler's
* connect() method.
*/
int input_register_handle(struct input_handle *handle)
{
struct input_handler *handler = handle->handler;
struct input_dev *dev = handle->dev;
int error;
/*
* We take dev->mutex here to prevent race with
* input_release_device().
*/
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&dev->mutex);
if (error)
return error;
/*
* Filters go to the head of the list, normal handlers
* to the tail.
*/
if (handler->filter)
list_add_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list);
else
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->d_node, &dev->h_list);
mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex);
/*
* Since we are supposed to be called from ->connect()
* which is mutually exclusive with ->disconnect()
* we can't be racing with input_unregister_handle()
* and so separate lock is not needed here.
*/
list_add_tail_rcu(&handle->h_node, &handler->h_list);
if (handler->start)
handler->start(handle);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(input_register_handle);即在input_handle中记录input_handler和dev的配对情况,民政局。
总结,核心层主要的功能是为设备驱动层(drivers层)和输入事件驱动层(handler层)提供注册接口,同时将这两层能够配对的设备做好配对绑定,然后提供从drivers到handlers数据传输通道,即将dev的数据直接传输给已经配对的handle。
2.2、最上层:输入事件驱动层源码分析
这一层的相关代码linux_kernellinux-stdriversinput目录下evdev.c和joydev.c
evdev.c文件里面,首先是模块的注册:
static struct input_handler evdev_handler = {
.event = evdev_event,
.events = evdev_events,//将数据事件数据放进buffer以及发信号通知应用层,都是这里面做的
.connect = evdev_connect,
.disconnect = evdev_disconnect,
.legacy_minors = true,
//次设备号的基地址,有8个,均是32的整数倍,一个handler对应
//多个dev的时候,第一个dev的次设备号是32*n,第二个是32*n+1...
.minor = EVDEV_MINOR_BASE,
.name = "evdev",
.id_table = evdev_ids,
};
static int __init evdev_init(void)
{
//将上面声明的handler注册到核心层
return input_register_handler(&evdev_handler);
}
static void __exit evdev_exit(void)
{
input_unregister_handler(&evdev_handler);
}
module_init(evdev_init);
module_exit(evdev_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("Vojtech Pavlik <vojtech@ucw.cz>");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Input driver event char devices");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
/*
* Create new evdev device. Note that input core serializes calls
* to connect and disconnect.
*/
static int evdev_connect(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev,
const struct input_device_id *id)
{
struct evdev *evdev;
int minor;
int dev_no;
int error;
minor = input_get_new_minor(EVDEV_MINOR_BASE, EVDEV_MINORS, true);
if (minor < 0) {
error = minor;
pr_err("failed to reserve new minor: %dn", error);
return error;
}
evdev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct evdev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!evdev) {
error = -ENOMEM;
goto err_free_minor;
}
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&evdev->client_list);
spin_lock_init(&evdev->client_lock);
mutex_init(&evdev->mutex);
init_waitqueue_head(&evdev->wait);
evdev->exist = true;
dev_no = minor;
/* Normalize device number if it falls into legacy range */
if (dev_no < EVDEV_MINOR_BASE + EVDEV_MINORS)
dev_no -= EVDEV_MINOR_BASE;
// 设备文件名的产生,event0,event1...次设备号是32*n+event后面的数字
dev_set_name(&evdev->dev, "event%d", dev_no);
// dev和handler配对时,需要先到handle这里登记,相当于民政局
evdev->handle.dev = input_get_device(dev);
evdev->handle.name = dev_name(&evdev->dev);
evdev->handle.handler = handler;
evdev->handle.private = evdev;
// 这里的主设备是13,次设备号是32*n+minor,moinor在上面有赋值计算
evdev->dev.devt = MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, minor);
evdev->dev.class = &input_class;
evdev->dev.parent = &dev->dev;
evdev->dev.release = evdev_free;
device_initialize(&evdev->dev);// 这个函数和下面的cdev_device_add函数一起构成device_register函数
// device_register就是注册设备,在input.c中class_register是注册class下面的input类
// 这里是注册input类里面的设备,如event1 , event2 , ...
error = input_register_handle(&evdev->handle); // 注册handle,民政局的登记册
if (error)
goto err_free_evdev;
cdev_init(&evdev->cdev, &evdev_fops);
error = cdev_device_add(&evdev->cdev, &evdev->dev);
if (error)
goto err_cleanup_evdev;
return 0;
err_cleanup_evdev:
evdev_cleanup(evdev);
input_unregister_handle(&evdev->handle);
err_free_evdev:
put_device(&evdev->dev);
err_free_minor:
input_free_minor(minor);
return error;
}static const struct file_operations evdev_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = evdev_read, // 应用层调用的read,其实就是这个read
// 这个evdev_read里面调用了capy_to_user
// 传到用户空间
.write = evdev_write,
.poll = evdev_poll,
.open = evdev_open,
.release = evdev_release,
.unlocked_ioctl = evdev_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = evdev_ioctl_compat,
#endif
.fasync = evdev_fasync,
.flush = evdev_flush,
.llseek = no_llseek,
};static ssize_t evdev_read(struct file *file, char __user *buffer,
size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
struct evdev_client *client = file->private_data;
struct evdev *evdev = client->evdev;
struct input_event event;
size_t read = 0;
int error;
if (count != 0 && count < input_event_size())
return -EINVAL;
for (;;) {
if (!evdev->exist || client->revoked)
return -ENODEV;
if (client->packet_head == client->tail &&
(file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK))
return -EAGAIN;
/*
* count == 0 is special - no IO is done but we check
* for error conditions (see above).
*/
if (count == 0)
break;
while (read + input_event_size() <= count &&
evdev_fetch_next_event(client, &event)) {
//写到用户空间
if (input_event_to_user(buffer + read, &event))
return -EFAULT;
read += input_event_size();
}
if (read)
break;
if (!(file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)) {
error = wait_event_interruptible(evdev->wait, //阻塞等待有数据产生
client->packet_head != client->tail ||
!evdev->exist || client->revoked);
if (error)
return error;
}
}
return read;
}总结,这一层主要向应用层提供操作接口。
2.3、最下层:输入设备驱动层
代码目录linux-stdriversinputkeyboard gpio_keys.c
static struct platform_driver gpio_keys_device_driver = {
.probe = gpio_keys_probe,
.driver = {
.name = "gpio-keys",
.pm = &gpio_keys_pm_ops,
.of_match_table = gpio_keys_of_match,
}
};
static int __init gpio_keys_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&gpio_keys_device_driver);
}
static void __exit gpio_keys_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&gpio_keys_device_driver);
}
late_initcall(gpio_keys_init);
module_exit(gpio_keys_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("Phil Blundell <pb@handhelds.org>");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Keyboard driver for GPIOs");
MODULE_ALIAS("platform:gpio-keys");
static const struct of_device_id gpio_keys_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "gpio-keys", },
{ },
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, gpio_keys_of_match);static int gpio_keys_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct device *dev = &pdev->dev;
const struct gpio_keys_platform_data *pdata = dev_get_platdata(dev);
struct fwnode_handle *child = NULL;
struct gpio_keys_drvdata *ddata;
struct input_dev *input;
size_t size;
int i, error;
int wakeup = 0;
if (!pdata) {
pdata = gpio_keys_get_devtree_pdata(dev);
if (IS_ERR(pdata))
return PTR_ERR(pdata);
}
size = sizeof(struct gpio_keys_drvdata) +
pdata->nbuttons * sizeof(struct gpio_button_data);
ddata = devm_kzalloc(dev, size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ddata) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to allocate staten");
return -ENOMEM;
}
ddata->keymap = devm_kcalloc(dev,
pdata->nbuttons, sizeof(ddata->keymap[0]),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ddata->keymap)
return -ENOMEM;
// input.c中给input_dev分配内存的函数
input = devm_input_allocate_device(dev);
if (!input) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to allocate input devicen");
return -ENOMEM;
}
ddata->pdata = pdata;
ddata->input = input;
mutex_init(&ddata->disable_lock);
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, ddata);
input_set_drvdata(input, ddata);
input->name = pdata->name ? : pdev->name;
input->phys = "gpio-keys/input0";
input->dev.parent = dev;
input->open = gpio_keys_open;
input->close = gpio_keys_close;
input->id.bustype = BUS_HOST;
input->id.vendor = 0x0001;
input->id.product = 0x0001;
input->id.version = 0x0100;
input->keycode = ddata->keymap;
input->keycodesize = sizeof(ddata->keymap[0]);
input->keycodemax = pdata->nbuttons;
/* Enable auto repeat feature of Linux input subsystem */
if (pdata->rep)
__set_bit(EV_REP, input->evbit);
// 设置input里面的evbit支持EV_REP事件
for (i = 0; i < pdata->nbuttons; i++) {
const struct gpio_keys_button *button = &pdata->buttons[i];
if (!dev_get_platdata(dev)) {
// 从设备树取出对应的节点
child = device_get_next_child_node(dev, child);
if (!child) {
dev_err(dev,
"missing child device node for entry %dn",
i);
return -EINVAL;
}
}
// 设置相关的按键引脚,在这里面有中断设置
error = gpio_keys_setup_key(pdev, input, ddata,
button, i, child);
if (error) {
fwnode_handle_put(child);
return error;
}
if (button->wakeup)
wakeup = 1;
}
fwnode_handle_put(child);
error = devm_device_add_group(dev, &gpio_keys_attr_group);
if (error) {
dev_err(dev, "Unable to export keys/switches, error: %dn",
error);
return error;
}
error = input_register_device(input); // 注册设备
if (error) {
dev_err(dev, "Unable to register input device, error: %dn",
error);
return error;
}
device_init_wakeup(dev, wakeup);
return 0;
}// 上报事件
static void gpio_keys_gpio_report_event(struct gpio_button_data *bdata)
{
const struct gpio_keys_button *button = bdata->button;
struct input_dev *input = bdata->input;
unsigned int type = button->type ?: EV_KEY;
int state;
state = gpiod_get_value_cansleep(bdata->gpiod);
if (state < 0) {
dev_err(input->dev.parent,
"failed to get gpio state: %dn", state);
return;
}
if (type == EV_ABS) {
if (state)
input_event(input, type, button->code, button->value);// 上报事件
} else {
input_event(input, type, *bdata->code, state);
}
input_sync(input);
}
最后
以上就是美满红酒最近收集整理的关于Linux驱动分析——input输入子系统1、朱有鹏老师的视频课程笔记和应用测试代码:2、input子系统架构分析的全部内容,更多相关Linux驱动分析——input输入子系统1、朱有鹏老师内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复