正弦载波有三个参量:幅度、频率、相位。所以调制信号的信息我们可以载荷于这三个参量的变化之中。在调制时,若载波的频率随调制信号变化,则称之为频率调制(FM)。并把FM和PM(相位调制)统称为角度调制。对于角度调制而言,不再是原调制信号频谱的线性搬移,而是非线性变换,会产生新的频率成分,所以又称之为非线性调制。
频率调制FM指的是瞬时频率偏移随调制信号m(t)成比例变化,即
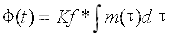
其中,Kf为调频灵敏度(rad/(s·V))。
接下来将通过MATLAB进行模拟:
① 系统参数初始化
% 系统参数初始化
clear;clc;close all;
echo on
t0 = .15; % signal duration
ts = 0.0005; % sampling interval
fc = 200; % carrier frequency
kf = 100; % modulation index
fs = 1/ts; % sampling frequency
t = [0:ts:t0]; % time vector
df = 0.25; % required frequency resolution② 调制信号和FM已调信号的产生
% 调制信号和FM已调信号的产生
% message signal
m = [ones(1,t0 / (3 * ts)),-2 * ones(1,t0 / (3 * ts)),zeros(1,t0 / (3 * ts) + 1)];
int_m(1) = 0;
for i = 1 : length(t) - 1 % integral of m
int_m(i + 1) = int_m(i) + m(i) * ts; % m(i) 是调制信号矩阵的幅值,按顺序将三个阶段排开对应相应的 i
echo off ;
end
echo on ;
u = cos(2*pi * fc * t + 2*pi * kf * int_m); % modulated signal
figure(1);
subplot(2,1,1)
plot(t,m(1 : length(t)))
axis([0 0.15 -2.1 2.1])
xlabel('Time')
title('The message signal')
subplot(2,1,2)
plot(t,u(1 : length(t)))
axis([0 0.15 -2.1 2.1])
xlabel('Time')
title('The modulated signal')③ 调制信号和已调信号的频谱
% 调制信号和已调信号的频谱
[M,m,df1] = fftseq(m,ts,df); % Fourier transform
M = M / fs; % scaling
f = [0 : df1 : df1 * (length(m) - 1)] - fs / 2; % frequency vector
[U,u,df1] = fftseq(u,ts,df); % Fourier transform
U=U / fs; % scaling
figure(2);
subplot(2,1,1)
plot(f,abs(fftshift(M)))
xlabel('Frequency')
title('Magnitude spectrum of the message signal')
subplot(2,1,2)
plot(f,abs(fftshift(U)))
title('Magnitude spectrum of the modulated signal')
xlabel('Frequency')④ FM信号的解调
% 信号的解调
[v,phase] = env_phas(u,ts,200); % demodulation, find phase of u
phi = unwrap(phase); % Restore original phase.
dem = (1 / (2*pi * kf)) * (diff(phi) / ts); % demodulator output, differentiate and scale phase
figure(3)
subplot(2,1,1)
plot(t,m(1:length(t)))
xlabel('Time')
title('The message signal')
subplot(2,1,2)
plot(t,dem(1:length(t)))
xlabel('Time')
title('The demodulated signal')⑤ 四个相关的函数,功能在内容中注释说明
function [M,m,df]=fftseq(m,ts,df)
% [M,m,df]=fftseq(m,ts,df)
% [M,m,df]=fftseq(m,ts)
%FFTSEQ generates M, the FFT of the sequence m.
% The sequence is zero padded to meet the required frequency resolution df.
% 零填充序列,以满足所需的(输入)频率分辨率df
% ts is the sampling interval. The output df is the final frequency resolution.
% ts是采样间隔, 输出的df是 最终的 频率分辨率
% Output m is the zero padded version of input m. M is the FFT.
% 输出m 是 输入m 的零填充版本 M是FFT变化
fs = 1 / ts;
% nargin 针对当前正在执行的函数,返回函数调用中给定函数输入参数的数目。
if nargin == 2 % [M,m,df]=fftseq(m,ts)
n1 = 0;
else % [M,m,df]=fftseq(m,ts,df)
n1 = fs / df;
end
n2 = length(m);
% y = nextpow2(x); 2^y 为 大于等于x 的最小的二的整数次幂的数字 nextpow2(4)=2 nextpow2(5)=3
n = 2^(max(nextpow2(n1),nextpow2(n2)));
M = fft(m,n); % Y = fft(X,n)
% 如果 X 是向量且 X 的长度小于 n,则为 X 补上尾零以达到长度 n
% 如果 X 是向量且 X 的长度大于 n,则对 X 进行截断以达到长度 n
m = [m,zeros(1,n - n2)];
df = fs / n;
function [v,phi]=env_phas(x,ts,f0)
% [v,phi]=env_phas(x,ts,f0)
% v=env_phas(x,ts,f0)
% ENV_PHAS Returns the envelope and the phase of the bandpass signal x.
% 返回带通信号的 包络和相位
% f0 is the center frequency.
% ts is the sampling interval.
% nargin 针对当前正在执行的函数,返回函数调用中给定函数输出参数的数目。
if nargout == 2
z = loweq(x,ts,f0); % 返回 信号x 的低通等效值
phi = angle(z);
end
v = abs(hilbert(x)); % 希尔伯特变换,位移 π/2
function xl=loweq(x,ts,f0)
% xl=loweq(x,ts,f0)
%LOWEQ returns the lowpass equivalent of the signal x
% 返回 信号x 的低通等效值
% f0 is the center frequency.
% ts is the sampling interval.
t = [0 : ts : ts * (length(x)-1)];
z = hilbert(x);
xl = z.* exp(-j * 2 * pi * f0 * t);
function p=spower(x)
% p=spower(x)
%SPOWER returns the power in signal x
% 返回 信号x 的功率
p = (norm(x)^2) / length(x);
% norm(x,1),x是一个向量,norm是对向量中所有值的绝对值求和
% p就是x的平均功率
模拟后,可以通过 调频灵敏度kf 来观察不同的结果,更方便理解FM相关内容。
最后
以上就是兴奋火龙果最近收集整理的关于FM信号的调制与解调的全部内容,更多相关FM信号内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复