人脸识别这个领域这两年非常火,公司有个产品也用到了相关技术,用于司机人脸打卡,虽然最终选用了face++的webAPI的方式实现,但这里还是讲一下在本地实现人脸识别系统的主要流程和相关代码。
为了建立我们的人脸识别系统,我们将首先进行人脸检测,利用深度学习从每个人脸中提取人脸嵌入,在嵌入上训练人脸识别模型,然后用OpenCV最终识别图像和视频流中的人脸。
你可以在相应的目录下添加你想要识别的图片进行训练,只要不破坏目录结构,你就会得到你想要的模型。
使用tree命令查看本实验的目录文件。
.
├── dataset
│ ├── hepburn
│ │ ├── 1.jpg
│ │ ├── 2.jpg
│ │ ├── 3.jpg
│ │ ├── 4.jpg
│ │ ├── 5.jpg
│ │ ├── 6.jpg
│ │ ├── 7.jpg
│ │ ├── 8.jpg
│ │ └── 9.jpg
│ ├── nini
│ │ ├── 11.jpg
│ │ ├── 12.jpg
│ │ ├── 1.jpg
│ │ ├── 2.jpg
│ │ ├── 3.jpg
│ │ ├── 4.jpg
│ │ ├── 5.jpg
│ │ ├── 6.jpg
│ │ └── 7.jpg
│ ├── unknown
│ │ ├── alan_grant.jpg
│ │ ├── claire_dearing.jpg
│ │ ├── ellie_sattler.jpg
│ │ ├── ian_malcolm.jpg
│ │ ├── john_hammond.jpg
│ │ ├── me1.jpg
│ │ ├── me2.jpg
│ │ ├── me3.jpg
│ │ ├── me4.jpg
│ │ ├── me5.jpg
│ │ └── own_grady.jpg
│ └── wife
│ ├── 11.jpg
│ ├── 12.jpg
│ ├── 13.jpg
│ ├── 14.jpg
│ ├── 15.jpg
│ ├── 1.jpg
│ ├── 2.jpg
│ ├── 3.jpg
│ ├── 4.jpg
│ ├── 5.jpg
│ ├── 6.jpg
│ └── 7.jpg
├── extract_embeddings.py
├── face_detection_model
│ ├── deploy.prototxt
│ └── res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel
├── images
│ ├── hepburn1.jpg
│ ├── hepburn2.jpg
│ ├── hepburn3.jpg
│ ├── hepburn4.jpg
│ ├── nini.jpg
│ ├── wife2.jpg
│ └── wife.jpg
├── openface_nn4.small2.v1.t7
├── output
│ ├── embeddings.pickle
│ ├── le.pickle
│ └── recognizer.pickle
├── recognize.py
├── recognize_video.py
└── train_model.py
8 directories, 58 files
做一个人脸识别系统共分4步:
1、探测人脸
2、计算128维的人脸嵌入来量化一个人脸
3、基于人脸嵌入训练支持向量机(SVM)
4、在图像和视频流中识别人脸
流程如图所示:
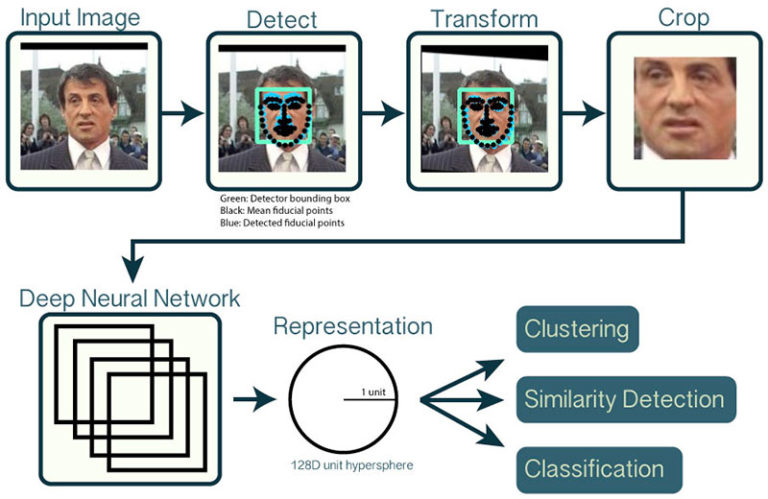
注:要了解128维的人脸嵌入相关原理,请查看之前的博客。
接下来看代码:
提取人脸嵌入:
# USAGE
# python extract_embeddings.py --dataset dataset --embeddings output/embeddings.pickle
# --detector face_detection_model --embedding-model openface_nn4.small2.v1.t7
# import the necessary packages
from imutils import paths
import numpy as np
import argparse
import imutils
import pickle
import cv2
import os
# construct the argument parser and parse the arguments
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-i", "--dataset", required=True,
help="path to input directory of faces + images")
ap.add_argument("-e", "--embeddings", required=True,
help="path to output serialized db of facial embeddings")
ap.add_argument("-d", "--detector", required=True,
help="path to OpenCV's deep learning face detector")
ap.add_argument("-m", "--embedding-model", required=True,
help="path to OpenCV's deep learning face embedding model")
ap.add_argument("-c", "--confidence", type=float, default=0.5,
help="minimum probability to filter weak detections")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
# load our serialized face detector from disk
print("[INFO] loading face detector...")
protoPath = os.path.sep.join([args["detector"], "deploy.prototxt"])
modelPath = os.path.sep.join([args["detector"],
"res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel"])
detector = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(protoPath, modelPath)
# load our serialized face embedding model from disk
print("[INFO] loading face recognizer...")
embedder = cv2.dnn.readNetFromTorch(args["embedding_model"])
# grab the paths to the input images in our dataset
print("[INFO] quantifying faces...")
imagePaths = list(paths.list_images(args["dataset"]))
# initialize our lists of extracted facial embeddings and
# corresponding people names
knownEmbeddings = []
knownNames = []
# initialize the total number of faces processed
total = 0
# loop over the image paths
for (i, imagePath) in enumerate(imagePaths):
# extract the person name from the image path
print("[INFO] processing image {}/{}".format(i + 1,
len(imagePaths)))
name = imagePath.split(os.path.sep)[-2]
# load the image, resize it to have a width of 600 pixels (while
# maintaining the aspect ratio), and then grab the image
# dimensions
image = cv2.imread(imagePath)
image = imutils.resize(image, width=600)
(h, w) = image.shape[:2]
# construct a blob from the image
imageBlob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(
cv2.resize(image, (300, 300)), 1.0, (300, 300),
(104.0, 177.0, 123.0), swapRB=False, crop=False)
# apply OpenCV's deep learning-based face detector to localize
# faces in the input image
detector.setInput(imageBlob)
detections = detector.forward()
# ensure at least one face was found
if len(detections) > 0:
# we're making the assumption that each image has only ONE
# face, so find the bounding box with the largest probability
i = np.argmax(detections[0, 0, :, 2])
confidence = detections[0, 0, i, 2]
# ensure that the detection with the largest probability also
# means our minimum probability test (thus helping filter out
# weak detections)
if confidence > args["confidence"]:
# compute the (x, y)-coordinates of the bounding box for
# the face
box = detections[0, 0, i, 3:7] * np.array([w, h, w, h])
(startX, startY, endX, endY) = box.astype("int")
# extract the face ROI and grab the ROI dimensions
face = image[startY:endY, startX:endX]
(fH, fW) = face.shape[:2]
# ensure the face width and height are sufficiently large
if fW < 20 or fH < 20:
continue
# construct a blob for the face ROI, then pass the blob
# through our face embedding model to obtain the 128-d
# quantification of the face
faceBlob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(face, 1.0 / 255,
(96, 96), (0, 0, 0), swapRB=True, crop=False)
embedder.setInput(faceBlob)
vec = embedder.forward()
# add the name of the person + corresponding face
# embedding to their respective lists
knownNames.append(name)
knownEmbeddings.append(vec.flatten())
total += 1
# dump the facial embeddings + names to disk
print("[INFO] serializing {} encodings...".format(total))
data = {"embeddings": knownEmbeddings, "names": knownNames}
f = open(args["embeddings"], "wb")
f.write(pickle.dumps(data))
f.close()
训练人脸识别模型:这里选用SVM实现
# USAGE
# python train_model.py --embeddings output/embeddings.pickle
# --recognizer output/recognizer.pickle --le output/le.pickle
# import the necessary packages
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import argparse
import pickle
# construct the argument parser and parse the arguments
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-e", "--embeddings", required=True,
help="path to serialized db of facial embeddings")
ap.add_argument("-r", "--recognizer", required=True,
help="path to output model trained to recognize faces")
ap.add_argument("-l", "--le", required=True,
help="path to output label encoder")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
# load the face embeddings
print("[INFO] loading face embeddings...")
data = pickle.loads(open(args["embeddings"], "rb").read())
# encode the labels
print("[INFO] encoding labels...")
le = LabelEncoder()
labels = le.fit_transform(data["names"])
# train the model used to accept the 128-d embeddings of the face and
# then produce the actual face recognition
print("[INFO] training model...")
recognizer = SVC(C=1.0, kernel="linear", probability=True)
recognizer.fit(data["embeddings"], labels)
# write the actual face recognition model to disk
f = open(args["recognizer"], "wb")
f.write(pickle.dumps(recognizer))
f.close()
# write the label encoder to disk
f = open(args["le"], "wb")
f.write(pickle.dumps(le))
f.close()识别人脸:
# USAGE
# python recognize.py --detector face_detection_model
# --embedding-model openface_nn4.small2.v1.t7
# --recognizer output/recognizer.pickle
# --le output/le.pickle --image images/adrian.jpg
# import the necessary packages
import numpy as np
import argparse
import imutils
import pickle
import cv2
import os
# construct the argument parser and parse the arguments
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required=True,
help="path to input image")
ap.add_argument("-d", "--detector", required=True,
help="path to OpenCV's deep learning face detector")
ap.add_argument("-m", "--embedding-model", required=True,
help="path to OpenCV's deep learning face embedding model")
ap.add_argument("-r", "--recognizer", required=True,
help="path to model trained to recognize faces")
ap.add_argument("-l", "--le", required=True,
help="path to label encoder")
ap.add_argument("-c", "--confidence", type=float, default=0.5,
help="minimum probability to filter weak detections")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
# load our serialized face detector from disk
print("[INFO] loading face detector...")
protoPath = os.path.sep.join([args["detector"], "deploy.prototxt"])
modelPath = os.path.sep.join([args["detector"],
"res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel"])
detector = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(protoPath, modelPath)
# load our serialized face embedding model from disk
print("[INFO] loading face recognizer...")
embedder = cv2.dnn.readNetFromTorch(args["embedding_model"])
# load the actual face recognition model along with the label encoder
recognizer = pickle.loads(open(args["recognizer"], "rb").read())
le = pickle.loads(open(args["le"], "rb").read())
# load the image, resize it to have a width of 600 pixels (while
# maintaining the aspect ratio), and then grab the image dimensions
image = cv2.imread(args["image"])
image = imutils.resize(image, width=600)
(h, w) = image.shape[:2]
# construct a blob from the image
imageBlob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(
cv2.resize(image, (300, 300)), 1.0, (300, 300),
(104.0, 177.0, 123.0), swapRB=False, crop=False)
# apply OpenCV's deep learning-based face detector to localize
# faces in the input image
detector.setInput(imageBlob)
detections = detector.forward()
# loop over the detections
for i in range(0, detections.shape[2]):
# extract the confidence (i.e., probability) associated with the
# prediction
confidence = detections[0, 0, i, 2]
# filter out weak detections
if confidence > args["confidence"]:
# compute the (x, y)-coordinates of the bounding box for the
# face
box = detections[0, 0, i, 3:7] * np.array([w, h, w, h])
(startX, startY, endX, endY) = box.astype("int")
# extract the face ROI
face = image[startY:endY, startX:endX]
(fH, fW) = face.shape[:2]
# ensure the face width and height are sufficiently large
if fW < 20 or fH < 20:
continue
# construct a blob for the face ROI, then pass the blob
# through our face embedding model to obtain the 128-d
# quantification of the face
faceBlob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(face, 1.0 / 255, (96, 96),
(0, 0, 0), swapRB=True, crop=False)
embedder.setInput(faceBlob)
vec = embedder.forward()
# perform classification to recognize the face
preds = recognizer.predict_proba(vec)[0]
j = np.argmax(preds)
proba = preds[j]
name = le.classes_[j]
# draw the bounding box of the face along with the associated
# probability
text = "{}: {:.2f}%".format(name, proba * 100)
y = startY - 10 if startY - 10 > 10 else startY + 10
cv2.rectangle(image, (startX, startY), (endX, endY),
(0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(image, text, (startX, y),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.45, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# show the output image
cv2.imshow("Image", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)上面这个代码是识别一张静态图片中的人脸,下面这个程序用于识别视频流中的人脸
# USAGE
# python recognize_video.py --detector face_detection_model
# --embedding-model openface_nn4.small2.v1.t7
# --recognizer output/recognizer.pickle
# --le output/le.pickle
# import the necessary packages
from imutils.video import VideoStream
from imutils.video import FPS
import numpy as np
import argparse
import imutils
import pickle
import time
import cv2
import os
# construct the argument parser and parse the arguments
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-d", "--detector", required=True,
help="path to OpenCV's deep learning face detector")
ap.add_argument("-m", "--embedding-model", required=True,
help="path to OpenCV's deep learning face embedding model")
ap.add_argument("-r", "--recognizer", required=True,
help="path to model trained to recognize faces")
ap.add_argument("-l", "--le", required=True,
help="path to label encoder")
ap.add_argument("-c", "--confidence", type=float, default=0.5,
help="minimum probability to filter weak detections")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
# load our serialized face detector from disk
print("[INFO] loading face detector...")
protoPath = os.path.sep.join([args["detector"], "deploy.prototxt"])
modelPath = os.path.sep.join([args["detector"],
"res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel"])
detector = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(protoPath, modelPath)
# load our serialized face embedding model from disk
print("[INFO] loading face recognizer...")
embedder = cv2.dnn.readNetFromTorch(args["embedding_model"])
# load the actual face recognition model along with the label encoder
recognizer = pickle.loads(open(args["recognizer"], "rb").read())
le = pickle.loads(open(args["le"], "rb").read())
# initialize the video stream, then allow the camera sensor to warm up
print("[INFO] starting video stream...")
vs = VideoStream(src=1).start()
time.sleep(2.0)
# start the FPS throughput estimator
fps = FPS().start()
# loop over frames from the video file stream
while True:
# grab the frame from the threaded video stream
frame = vs.read()
# resize the frame to have a width of 600 pixels (while
# maintaining the aspect ratio), and then grab the image
# dimensions
frame = imutils.resize(frame, width=600)
(h, w) = frame.shape[:2]
# construct a blob from the image
imageBlob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(
cv2.resize(frame, (300, 300)), 1.0, (300, 300),
(104.0, 177.0, 123.0), swapRB=False, crop=False)
# apply OpenCV's deep learning-based face detector to localize
# faces in the input image
detector.setInput(imageBlob)
detections = detector.forward()
# loop over the detections
for i in range(0, detections.shape[2]):
# extract the confidence (i.e., probability) associated with
# the prediction
confidence = detections[0, 0, i, 2]
# filter out weak detections
if confidence > args["confidence"]:
# compute the (x, y)-coordinates of the bounding box for
# the face
box = detections[0, 0, i, 3:7] * np.array([w, h, w, h])
(startX, startY, endX, endY) = box.astype("int")
# extract the face ROI
face = frame[startY:endY, startX:endX]
(fH, fW) = face.shape[:2]
# ensure the face width and height are sufficiently large
if fW < 20 or fH < 20:
continue
# construct a blob for the face ROI, then pass the blob
# through our face embedding model to obtain the 128-d
# quantification of the face
faceBlob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(face, 1.0 / 255,
(96, 96), (0, 0, 0), swapRB=True, crop=False)
embedder.setInput(faceBlob)
vec = embedder.forward()
# perform classification to recognize the face
preds = recognizer.predict_proba(vec)[0]
j = np.argmax(preds)
proba = preds[j]
name = le.classes_[j]
# draw the bounding box of the face along with the
# associated probability
text = "{}: {:.2f}%".format(name, proba * 100)
y = startY - 10 if startY - 10 > 10 else startY + 10
cv2.rectangle(frame, (startX, startY), (endX, endY),
(0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, text, (startX, y),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.45, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# update the FPS counter
fps.update()
# show the output frame
cv2.imshow("Frame", frame)
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
# if the `q` key was pressed, break from the loop
if key == ord("q"):
break
# stop the timer and display FPS information
fps.stop()
print("[INFO] elasped time: {:.2f}".format(fps.elapsed()))
print("[INFO] approx. FPS: {:.2f}".format(fps.fps()))
# do a bit of cleanup
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
vs.stop()
看下效果:


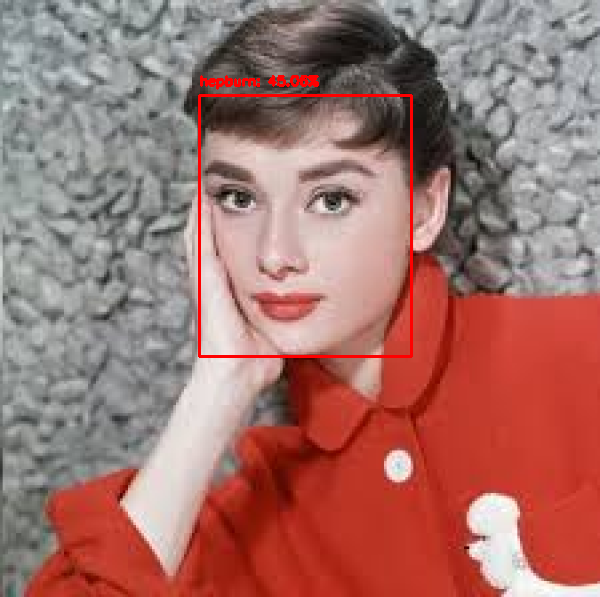
想详细了解这个实验的朋友请参考:https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2018/09/24/opencv-face-recognition/
最后
以上就是淡然煎蛋最近收集整理的关于基于opencv实现人脸识别的全部内容,更多相关基于opencv实现人脸识别内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复