我是靠谱客的博主 糊涂野狼,这篇文章主要介绍HDLBits刷题记录 Circuits—Combinational Logic—Arithmetic Circuits,现在分享给大家,希望可以做个参考。
·Adder
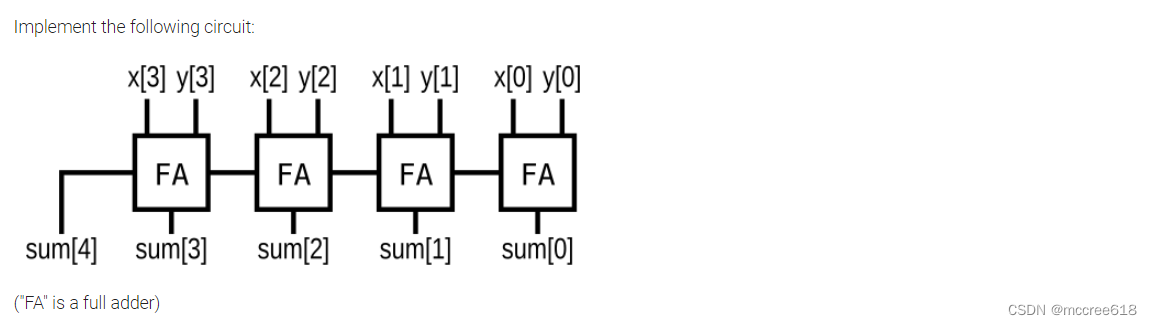
1、typical and fundamental way
module top_module (
input [3:0] x,
input [3:0] y,
output [4:0] sum);
wire cout0, cout1, cout2;
fadder u1(x[0], y[0], 0, sum[0], cout0);
fadder u2(x[1], y[1], cout0, sum[1], cout1);
fadder u3(x[2], y[2], cout1, sum[2], cout2);
fadder u4(x[3], y[3], cout2, sum[3], sum[4]);
endmodule
module fadder(
input a,b,
input cin,
output sum, cout);
assign sum = a ^ b ^ cin;
assign cout = (a&b) | (cin&(a^b));
endmodule
2、more suitable and simple way
module top_module (
input [3:0] x,
input [3:0] y,
output [4:0] sum
);
// This circuit is a 4-bit ripple-carry adder with carry-out.
assign sum = x+y; // Verilog addition automatically produces the carry-out bit.
// Verilog quirk: Even though the value of (x+y) includes the carry-out, (x+y) is still considered to be a 4-bit number (The max width of the two operands).
// This is correct:
// assign sum = (x+y);
// But this is incorrect:
// assign sum = {x+y}; // Concatenation operator: This discards the carry-out
endmodule
最后
以上就是糊涂野狼最近收集整理的关于HDLBits刷题记录 Circuits—Combinational Logic—Arithmetic Circuits的全部内容,更多相关HDLBits刷题记录内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复