反转链表
反转一个单链表。
输入: 1->2->3->4->5
输出: 5->4->3->2->1
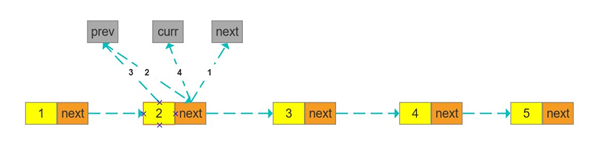
解法1:迭代,重复某一过程,每一次处理结果作为下一次处理的初始值,这些初始值类似于状态、每次处理都会改变状态、直至到达最终状态
从前往后遍历链表,将当前节点的next指向上一个节点,因此需要一个变量存储上一个节点prev,当前节点处理完需要寻找下一个节点,因此需要一个变量保存当前节点curr,处理完后要将当前节点赋值给 prev,并将next指针赋值给curr,因此需要一个变量提前保存下一个节点的指针next
-
将下一个节点指针保存到next变量 next = curr.next
-
将下一个节点的指针指向prev,curr.next = prev
-
准备处理下一个节点,将curr赋值给prev
-
将下一个节点赋值为curr,处理一个节点
解法2:递归:以相似的方法重复,类似于树结构,先从根节点找到叶子节点,从叶子节点开始遍历大的问题(整个链表反转)拆成性质相同的小问题(两个元素反转)curr.next.next = curr 将所有的小问题解决,大问题即解决
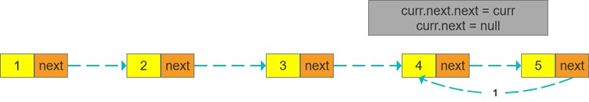
只需每个元素都执行curr.next.next = curr,curr.next = null两个步骤即可为了保证链不断,必须从最后一个元素开始
public class ReverseList {
static class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
public static ListNode iterate(ListNode head){
ListNode prev = null,curr,next;
curr = head;
while(curr != null){
next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
public static ListNode recursion(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead = recursion(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(5,null);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(4,node5);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(3,node4);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(2,node3);
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(1,node2);
//ListNode node = iterate(node1);
ListNode node_1 = recursion(node1);
System.out.println(node_1);
}
}
统计N以内的素数
素数:只能被1和自身整除的数,0、1除外解法一:暴力算法直接从2开始遍历,判断是否能被2到自身之间的数整除
public int countPrimes(int n) {
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
ans += isPrime(i) ? 1 : 0;
}
return ans;
}
//i如果能被x整除,则x/i肯定能被x整除,因此只需判断i和根号x之中较小的即可
public boolean isPrime(int x) {
for (int i = 2; i * i <= x; i++) {
if (x % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
解法2:埃氏筛
利用合数的概念(非素数),素数*n必然是合数,因此可以从2开始遍历,将所有的合数做上标记
public static int eratosthenes(int n) {
boolean[] isPrime = new boolean[n];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
if (!isPrime[i]) {
ans += 1;
for (int j = i * i; j < n; j += i) {
isPrime[j] = true;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
将合数标记为true,j = i * i 从 2 * i 优化而来,系数2会随着遍历递增(j += i,相当于递增了系数2),每一个合数都会有两个比本身要小的因子(0,1除外),2 * i 必然会遍历到这两个因子
当2递增到大于根号n时,其实后面的已经无需再判断(或者只需判断后面一段),而2到根号n、实际上在 i 递增的过程中已经计算过了,i 实际上就相当于根号n 例如:n = 25 会计算以下
-
* 4 = 8
-
* 4 = 12
但实际上8和12已经标记过,在n = 17时已经计算了 3 * 4,2 * 4
寻找数组的中心索引
数组中某一个下标,左右两边的元素之后相等,该下标即为中心索引思路:先统计出整个数组的总和,然后从第一个元素开始叠加总和递减当前元素,叠加递增当前元素,知道两个值相等
public static int pivotIndex(int[] nums) {
int sum1 = Arrays.stream(nums).sum();
int sum2 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<nums.length; i++){
sum2 += nums[i];
if(sum1 == sum2){
return i;
}
sum1 = sum1 - nums[i];
}
return -1;
}
删除排序数组中的重复项
一个有序数组 nums ,原地删除重复出现的元素,使每个元素只出现一次 ,返回删除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,必须在原地修改输入数组并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
双指针算法:
数组完成排序后,我们可以放置两个指针 i 和 j,其中 i 是慢指针,而 j 是快指针。只要 nums[i]=nums[j],我们就增加 j 以跳过重复项。
当遇到 nums[j] != nums[i]时,跳过重复项的运行已经结束,必须把nums[j])的值复制到 nums[i +
1]。然后递增 i,接着将再次重复相同的过程,直到 j 到达数组的末尾为止。
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) return 0;
int i = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[j] != nums[i]) {
i++;
nums[i] = nums[j];
}
}
return i + 1;
}
x的平方根
在不使用 sqrt(x) 函数的情况下,得到 x的平方根的整数部分解法一:二分查找
x的平方根肯定在0到x之间,使用二分查找定位该数字,该数字的平方一定是最接近x的,m平方值如果大于x、则往左边找,如果小于等于x则往右边找找到0和X的最中间的数m,
如果m * m > x,则m取x/2到x的中间数字,直到m * m < x,m则为平方根的整数部分
如果m * m <= x,则取0到x/2的中间值,知道两边的界限重合,找到最大的整数,则为x平方根的整数部分
时间复杂度:O(logN)
public static int binarySearch(int x) {
int l = 0, r = x, index = -1;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if ((long) mid * mid <= x) {
index = mid;
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
return index;
}
解法二:牛顿迭代
假设平方根是 i ,则 i 和 x/i 必然都是x的因子,而 x/i 必然等于 i ,推导出 i + x / i = 2 * i,得出 i = (i + x / i) / 2
由此得出解法,i 可以任选一个值,只要上述公式成立,i 必然就是x的平方根,如果不成立, (i + x / i) /
2得出的值进行递归,直至得出正确解
public static int newton(int x) {
if(x==0) return 0;
return ((int)(sqrts(x,x)));
}
public static double sqrts(double i,int x){
double res = (i + x / i) / 2;
if (res == i) {
return i;
} else {
return sqrts(res,x);
}
}
三个数的最大乘积
一个整型数组 nums ,在数组中找出由三个数字组成的最大乘积,并输出这个乘积。
乘积不会越界
如果数组中全是非负数,则排序后最大的三个数相乘即为最大乘积;如果全是非正数,则最大的三个数相乘同样也为最大乘积。
如果数组中有正数有负数,则最大乘积既可能是三个最大正数的乘积,也可能是两个最小负数(即绝对值最大)与最大正数的乘积。
分别求出三个最大正数的乘积,以及两个最小负数与最大正数的乘积,二者之间的最大值即为所求答案。
解法一:排序
public static int sort(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int n = nums.length;
return Math.max(nums[0] * nums[1] * nums[n - 1], nums[n - 3] * nums[n - 2] *
nums[n - 1]);
}
解法二:线性扫描
public static int getMaxMin(int[] nums) {
// 最小的和第二小的
int min1 = 0, min2 = 0;
// 最大的、第二大的和第三大的
int max1 = 0, max2 = 0, max3 = 0;
for (int x : nums) {
if (x < min1) {
min2 = min1;
min1 = x;
} else if (x < min2) {
min2 = x;
}
if (x > max1) {
max3 = max2;
max2 = max1;
max1 = x;
} else if (x > max2) {
max3 = max2;
max2 = x;
} else if (x > max3) {
max3 = x;
}
}
return Math.max(min1 * min2 * max1, max1 * max2 * max3);
}
两数之和
给定一个升序排列的整数数组 numbers ,从数组中找出两个数满足相加之和等于目标数 target 。
假设每个输入只对应唯一的答案,而且不可以重复使用相同的元素。
返回两数的下标值,以数组形式返回暴力解法
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
return new int[]{i, j};
}
}
}
return new int[0];
}
时间复杂度:O(N的平方)
空间复杂度:O(1)
哈希表:将数组的值作为key存入map,target - num作为key
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
return new int[]{map.get(target - nums[i]), i};
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[0];
}
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(N)
解法一:二分查找
先固定一个值(从下标0开始),再用二分查找查另外一个值,找不到则固定值向右移动,继续二分查找
public int[] twoSearch(int[] numbers, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; ++i) {
int low = i, high = numbers.length -1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (high - low) / 2 + low;
if (numbers[mid] == target - numbers[i]) {
return new int[]{i, mid};
} else if (numbers[mid] > target - numbers[i]) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
}
}
时间复杂度:O(N * logN)
空间复杂度:O(1)
解法二:双指针
左指针指向数组head,右指针指向数组tail,head+tail > target 则tail 左移,否则head右移
public int[] twoPoint(int[] numbers, int target) {
int low = 0, high = numbers.length - 1;
while (low < high) {
int sum = numbers[low] + numbers[high];
if (sum == target) {
return new int[]{low + 1, high + 1};
} else if (sum < target) {
++low;
} else {
--high;
}
}
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
时间复杂度:O(N) 空间复杂度:O(1)
斐波那契数列
求取斐波那契数列第N位的值。
斐波那契数列:每一位的值等于他前两位数字之和。前两位固定 0,1,1,2,3,5,8。。。。
解法一:暴力递归
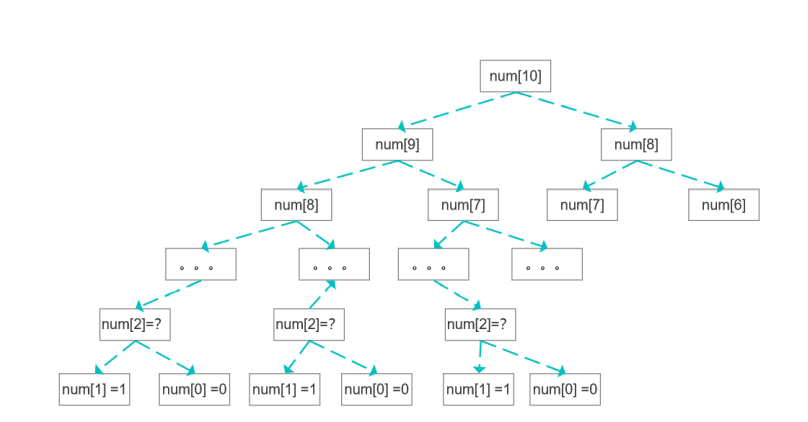
public static int calculate(int num){
if(num == 0 ){
return 0;
}
if(num == 1){
return 1;
}
return calculate(num-1) + calculate(num-2);
}
解法二:去重递归
递归得出具体数值之后、存储到一个集合(下标与数列下标一致),后面递归之前先到该集合查询一次,如果查到则无需递归、直接取值。查不到再进行递归计算
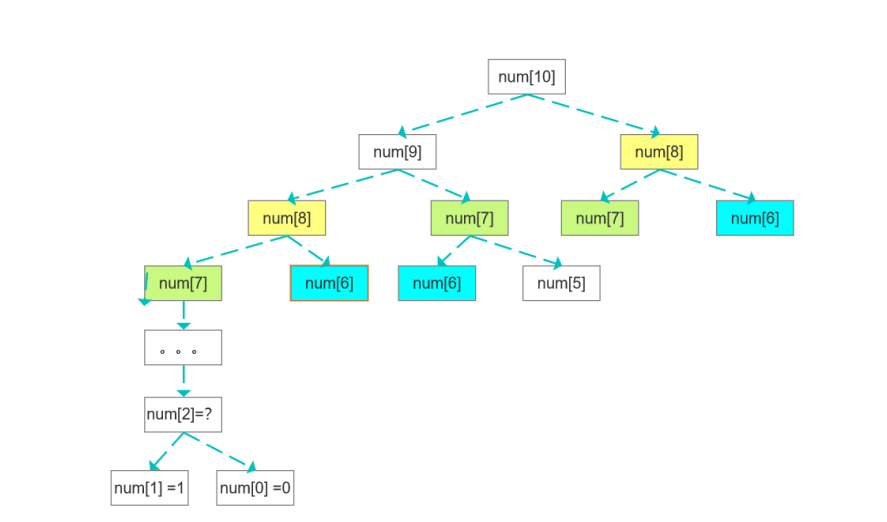
public static int calculate2(int num){
int[] arr = new int[num+1];
return recurse(arr,num);
}
private static int recurse(int[] arr, int num) {
if(num == 0 ){
return 0;
}
if(num == 1){
return 1;
}
if(arr[num] != 0){
return arr[num];
}
arr[num] = recurse(arr,num-1) + recurse(arr,num-2);
return arr[num];
}
解法三:双指针迭代
基于去重递归优化,集合没有必要保存每一个下标值,只需保存前两位即可,向后遍历,得出N的值

public static int iterate(int num){
if(num == 0 ){
return 0;
}
if(num == 1){
return 1;
}
int low = 0,high = 1;
for(int i=2; i<= num; i++){
int sum = low + high;
low = high;
high = sum;
}
return high;
}
环形链表
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达该节点,则链表中存在环如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
解法一:哈希表
public static boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> seen = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while (head != null) {
if (!seen.add(head)) {
return true;
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
解法二:双指针
public static boolean hasCycle2(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (slow != fast) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
排列硬币
总共有 n 枚硬币,将它们摆成一个阶梯形状,第 k 行就必须正好有 k 枚硬币。
给定一个数字 n,找出可形成完整阶梯行的总行数。 n 是一个非负整数,并且在32位有符号整型的范围内解法一:迭代
从第一行开始排列,排完一列、计算剩余硬币数,排第二列,直至剩余硬币数小于或等于行数
public static int arrangeCoins(int n) {
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
n = n-i;
if (n <= i){
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
解法二:二分查找
假设能排 n 行,计算 n 行需要多少硬币数,如果大于 n,则排 n/2行,再计算硬币数和 n 的大小关系
public static int arrangeCoins2(int n) {
int low = 0, high = n;
while (low <= high) {
long mid = (high - low) / 2 + low;
long cost = ((mid + 1) * mid) / 2;
if (cost == n) {
return (int)mid;
} else if (cost > n) {
high = (int)mid - 1;
} else {
low = (int)mid + 1;
}
}
return high;
}
解法三:牛顿迭代
使用牛顿迭代求平方根,(x + n/x)/2
假设能排 x 行 则 1 + 2 + 3 + …+ x = n,即 x(x+1)/2 = n 推导出 x = 2n - x
public static double sqrts(double x,int n){
double res = (x + (2*n-x) / x) / 2;
if (res == x) {
return x;
} else {
return sqrts(res,n);
}
}
合并两个有序数组
两个有序整数数组 nums1 和 nums2,将 nums2 合并到 nums1 中,使 nums1 成为一个有序数组。
初始化 nums1 和 nums2 的元素数量分别为 m 和 n 。假设 nums1 的空间大小等于 m + n,这样它就有足够的空间保存来自 nums2 的元素。
解法一:合并后排序
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
System.arraycopy(nums2, 0, nums1, m, n);
Arrays.sort(nums1);
}
时间复杂度 : O((n+m)log(n+m))。
空间复杂度 : O(1)。
解法二:双指针 从前往后
将两个数组按顺序进行比较,放入新的数组
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int [] nums1_copy = new int[m];
System.arraycopy(nums1, 0, nums1_copy, 0, m);//拷贝数组1
int p1 = 0;//指向数组1的拷贝
int p2 = 0;//指向数组2
int p = 0;//指向数组1
//将数组1当成空数组,比较数组1的拷贝和数组2,将较小的放入空数组
while ((p1 < m) && (p2 < n))
nums1[p++] = (nums1_copy[p1] < nums2[p2]) ? nums1_copy[p1++] :
nums2[p2++];
//数组2和数组1不等长,将多出的元素拷贝
if (p1 < m)
System.arraycopy(nums1_copy, p1, nums1, p1 + p2, m + n - p1 - p2);
if (p2 < n)
System.arraycopy(nums2, p2, nums1, p1 + p2, m + n - p1 - p2);
}
时间复杂度 : O(n + m)。
空间复杂度 : O(m)。
解法三:双指针优化
从后往前
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int p1 = m - 1;
int p2 = n - 1;
int p = m + n - 1;
while ((p1 >= 0) && (p2 >= 0))
nums1[p--] = (nums1[p1] < nums2[p2]) ? nums2[p2--] : nums1[p1--];
System.arraycopy(nums2, 0, nums1, 0, p2 + 1);
}
时间复杂度 : O(n + m)。
空间复杂度 : O(1)。
子数组最大平均数
给一个整数数组,找出平均数最大且长度为 k 的下标连续的子数组,并输出该最大平均数。
滑动窗口:
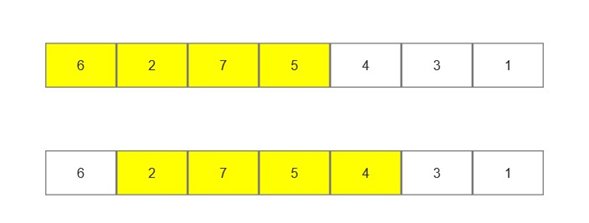
窗口移动时,窗口内的和等于sum加上新加进来的值,减去出去的值
public double findMaxAverage(int[] nums, int k) {
int sum = 0;
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
sum += nums[i];
}
int maxSum = sum;
for (int i = k; i < n; i++) {
sum = sum - nums[i - k] + nums[i];
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, sum);
}
return 1.0 * maxSum / k;
}
二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
解法一:深度优先
遍历整颗数,找到每一个叶子节点,从叶子节点往上开始计算,左右子节点都为空则记录深度为1
左右子节点只有一边,深度记录为子节点深度+1
左右两边都有子节点,则记录左右子节点的深度较小值+1
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return 1;
}
int min_depth = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (root.left != null) {
min_depth = Math.min(minDepth(root.left), min_depth);
}
if (root.right != null) {
min_depth = Math.min(minDepth(root.right), min_depth);
}
return min_depth + 1;
}
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(logN) 取决于树的高度
解法二:广度优先
从上往下,找到一个节点时,标记这个节点的深度。查看该节点是否为叶子节点,如果是直接返回深度如果不是叶子节点,将其子节点标记深度(在父节点深度的基础上加1),再判断该节点是否为叶子节点
class QueueNode {
TreeNode node;
int depth;
public QueueNode(TreeNode node, int depth) {
this.node = node;
this.depth = depth;
}
}
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<QueueNode> queue = new LinkedList<QueueNode>();
queue.offer(new QueueNode(root, 1));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
QueueNode nodeDepth = queue.poll();
TreeNode node = nodeDepth.node;
int depth = nodeDepth.depth;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
return depth;
}
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(new QueueNode(node.left, depth + 1));
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(new QueueNode(node.right, depth + 1));
}
}
return 0;
}
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(N)
最长连续递增序列
给定一个未经排序的整数数组,找到最长且连续递增的子序列,并返回该序列的长度。
序列的下标是连续的
贪心算法
从0开始寻找递增序列,并将长度记录,记录递增序列的最后一个下标,然后从该下标继续寻找,记录长度,取长度最大的即可
public static int findLength(int[] nums) {
int ans = 0;
int start = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i > 0 && nums[i] <= nums[i - 1]) {
start = i;
}
ans = Math.max(ans, i - start + 1);
}
return ans;
}
柠檬水找零
在柠檬水摊上,每一杯柠檬水的售价为 5 美元。
顾客排队购买你的产品,一次购买一杯。
每位顾客只买一杯柠檬水,然后向你付 5 美元、10 美元或 20 美元。必须给每个顾客正确找零注意,一开始你手头没有任何零钱。
如果你能给每位顾客正确找零,返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
输入:[5,5,5,10,20]
输出:true
输入:[10,10]
输出:false
贪心:
public boolean lemonadeChange(int[] bills) {
int five = 0, ten = 0;
for (int bill : bills) {
if (bill == 5) {
five++;
} else if (bill == 10) {
if (five == 0) {
return false;
}
five--;
ten++;
} else {
if (five > 0 && ten > 0) {
five--;
ten--;
} else if (five >= 3) {
five -= 3;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
三角形的最大周长
给定由一些正数(代表长度)组成的数组 A,返回由其中三个长度组成的、面积不为零的三角形的最大周长。
如果不能形成任何面积不为零的三角形,返回 0。
贪心:
先小到大排序,假设最长边是最后下标,另外两条边是倒数第二和第三下标,则此时三角形周长最大
n < (n-1) + (n-2),如果不成立,意味着该数组中不可能有另外两个值之和大于n,此时将n左移,重新计算
public int largestPerimeter(int[] A) {
Arrays.sort(A);
for (int i = A.length - 1; i >= 2; --i) {
if (A[i - 2] + A[i - 1] > A[i]) {
return A[i - 2] + A[i - 1] + A[i];
}
}
return 0;
}
最后
以上就是洁净小白菜最近收集整理的关于leetcode算法反转链表统计N以内的素数寻找数组的中心索引删除排序数组中的重复项x的平方根三个数的最大乘积两数之和斐波那契数列环形链表排列硬币合并两个有序数组子数组最大平均数二叉树的最小深度最长连续递增序列柠檬水找零三角形的最大周长的全部内容,更多相关leetcode算法反转链表统计N以内内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复