✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,matlab项目合作可私信。
????个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
????个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击????
智能优化算法 神经网络预测 雷达通信 无线传感器
信号处理 图像处理 路径规划 元胞自动机 无人机 电力系统
⛄ 内容介绍
该工具允许使用 MIMO 系统的复杂频率响应函数 (FRF) 来识别模态参数、特征频率、模态阻尼因子和模态留数。使用基于fft的正规方程的快速实现来解决最小二乘问题,以提高算法的效率。
⛄ 部分代码
function [fn, xin, frfnumtot, FST, FF, XIXI, MATHP] = lscf(w, frf, n)
% Linear Square Complex Frequency estimator using discrete-time z-model
%
% k=n
% -----
% k
% . A z
% /
% -----
% k=0 j k w dt
% H(z) = -------------------------, z = e
% k=n
% -----
% k
% . B z
% /
% -----
% k=0
%
% the frequency axis between f0 and fend is shifted using
%
% 1
% dt = --------------
% 2 (fend - f0)
%
% w = 2 pi (f - f0)
%
% w natural frequency vector in rad/s
% frf complex frequency response function matrix
% each column corresponds to one FRF between one sensor
% and one actuator
% n [nmin : nmax] identification using stabilization chart
%
% fn eigen frequency in Hz
% xin modal damping factor
% frfnumtot matrix with numerical identified complex frequency response
% function using discrete-time z-model
% FST cell array with frequency of stable poles in frequency and damping
% FF cell array with frequency of stable poles in frequency
% XIXI cell array with frequency of stable poles in damping
% MATHP cell array with frequency of mathematical poles
%
% References:
% H. Van der Auweraer, P. Guillaume, P. Verboven and S. Vanlanduit, Application
% of a Fast-Stabilizing Frequency Domain Parameter Estimation Method,
%Journal of Dynamics Systems, Measurement and Control, 123, pp 651-658, 2001.
%
%% Parameters and frequency shift
w0 = w ; % natural frequency in rad/s
L = length(w) ; % length of the signal
f = w/(2*pi) ; % frequency in Hz
yfrftot = 20*log10(abs(frf)) ;
f0 = min(f) ;
fend = max(f) ;
w = 2*pi*(f-f0) ; % shifted natural frequency
dt = 1/(2*(fend-f0)) ; % sample time
[L , noni] = size(frf) ; % noni: number output * number input
% cell array to save frequency of stable poles in frequency and damping
% at each iteration
FST = {} ; FF = {}; XIXI = {}; MATHP = {} ;
frfnumtot = zeros(L, noni) ;
disp('-----------------------------------------')
disp(['Identification between order ',num2str(n(1)),' and ',num2str(n(end))])
disp('-----------------------------------------')
n_min = min(n) ;
n_max = max(n) ;
Ptot = zeros(L, n_max+1) ;
for k=1:n_max+1
% matrix P for normal equations using z-domain model
Ptot(:, k) = zdomain(w, dt, k-1) ;
end
ip = 0 ;
iFST = 1 ;
%% fast implementation of normal equations using fft
% fft are padded with zeros because 2*L > L and dt=1/(2(fend-f0))
X1 = fft(frf, 2*L) ;
X2 = fft(conj(frf), 2*L) ;
% correction to avoid warning on the first term of the toeplitz matrices
X2(1,:)= X1(1,:) ;
Y1 = fft(ones(L,1), 2*L) ;
Z1 = fft(abs(frf).^2, 2*L) ;
%% calcul between n_min and n_max
P = Ptot(:, 1:n_min) ;
for p = n_min:n_max
fn = [] ;
xin = [] ;
ff = [] ;
xixi = [] ;
mathp = [] ;
P = cat(2, P, Ptot(:,p+1)) ;
Xtot = {} ;
Ytot = {} ;
Ztot = {} ;
Atot = {} ;
M = zeros(p+1, p+1) ;
% fast implementation using toeplitz matrix
for ifrf = 1:noni
X = toeplitz(-real(X1(1:p+1, ifrf)), -real(X2(1:p+1, ifrf).')) ;
Y = toeplitz(real(Y1(1:p+1))) ;
Z = toeplitz(real(Z1(1:p+1, ifrf))) ;
Xtot{ifrf} = X ; Ytot{ifrf} = Y ; Ztot{ifrf} = Z ;
Mifrf = Z - X'*Y^(-1)*X ;
M = M + Mifrf ;
end
M = 2*M ;
B = lsqminnorm(-M(1:p, 1:p), M(1:p, p+1)) ;
B = [B; 1] ;
% calcul of frfnumtot only for the last iteration
if p == n_max
for ifrf = 1:1:noni
Atot{ifrf} = -lsqminnorm(Ytot{ifrf},(Xtot{ifrf}*B)) ;
frfnumtot(:,ifrf) = (P*Atot{ifrf})./(P*B) ;
end
end
% solve eigenvalue problem using companion matrix
poles = companion2poles(B, p, dt) ;
% modal parameters
wp = abs(poles) ;
% correction of the shift frequency
wp = wp+2*pi*f0 ;
xip = -real(poles)./wp ;
% reorganize modal parameters
[wp, iwp] = sort(wp) ;
xip = xip(iwp) ;
fp = wp/(2*pi) ;
% stabilization chart
if ip == 0
fmin1 = fp ;
ximin1 = xip ;
elseif ip > 0
[fn, xin, ff, xixi, mathp] = stabchart(fp, xip, fmin1, ximin1, ...
f, fn, xin, ff, xixi, mathp, p) ;
xin = xin' ;
fmin1 = fp ;
ximin1 = xip ;
FST{iFST} = fn ; FF{iFST} = ff ; XIXI{iFST} = xixi ;
MATHP{iFST} = mathp ;
iFST = iFST+1 ;
end
ip = ip+1 ;
end
%% axes, label of the figure
xlim([f0 fend*(1+5/100)])
ylim([min(min(yfrftot)) max(max(yfrftot))])
xlabel('Frequency (Hz)')
ylabel('FRF (dB)')
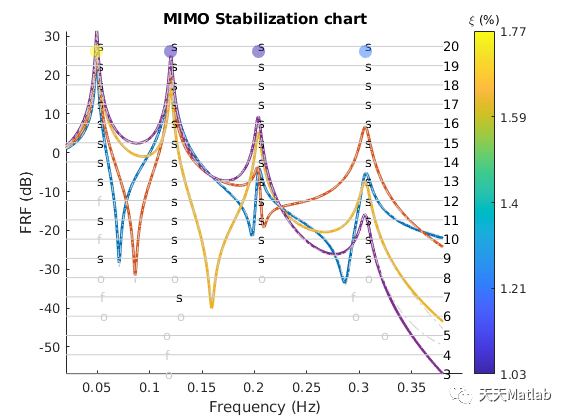
⛄ 运行结果
⛄ 参考文献
[1]王艺衡. 基于MIMO-OFDM系统的信道估计算法研究与实现[D]. 西安电子科技大学.
⛄ Matlab代码关注
❤️部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
❤️ 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料
最后
以上就是炙热康乃馨最近收集整理的关于基于LSCF和LSFD算法在频域中识别快速实现的MIMO研究附Matlab代码的全部内容,更多相关基于LSCF和LSFD算法在频域中识别快速实现内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复