2 调通框架
2.1 修改的内容
相比上一次实验,本次实验对框架的修改较大,主要在以下几方面:
• 修改了main.cpp,以适应本次实验的测试模型CornellBox
• 修改了Render,以适应CornellBox 并且支持Path Tracing 需要的同一Pixel多次Sample
• 修改了Object,Sphere,Triangle,TriangleMesh,BVH,添加了area 属性与Sample 方法,以实现对光源按面积采样,并在Scene 中添加了采样光源的接口sampleLight
• 修改了Material 并在其中实现了sample, eval, pdf 三个方法用于Path racing
变量的辅助计算
2.2 你需要迁移的内容
你需要从上一次编程练习中直接拷贝以下函数到对应位置:
• Triangle::getIntersection in Triangle.hpp: 将你的光线-三角形相交函数粘贴到此处,请直接将上次实验中实现的内容粘贴在此。
• IntersectP(const Ray& ray, const Vector3f& invDir,const std::array<int, 3>& dirIsNeg) in the Bounds3.hpp: 这个函数的作用是判断包围盒BoundingBox 光线是否相交,请直接将上次实验中实现的内容粘贴在此处,并且注意检查t_enter = t_exit 的时候的判断是否正确。
• getIntersection(BVHBuildNode* node, const Ray ray)in BVH.cpp: BVH查找过程,请直接将上次实验中实现的内容粘贴在此处.
复制部分和作业6一样,需要改的是IntersectP的判断要加等号,不然会导致天花板全黑且物体没有影子。
castRay(const Ray ray, int depth)in Scene.cpp:
简单来说就是①求Intersection判断和场景有没有相交,没有就直接return{};②判断是不是和光源相交③采样光线④计算反射光线生成的L,直接光照⑤轮盘赌⑥计算间接光照(递归)
Vector3f Scene::castRay(const Ray &ray, int depth) const
{
// TO DO Implement Path Tracing Algorithm here
Vector3f L_dir = { 0,0,0 };
Vector3f L_indir = { 0,0,0 };
Intersection intersection = Scene::intersect(ray);
if (!intersection.happened) return {}; // 和场景没有交叉
return intersection.m->getEmission();
if (intersection.m->hasEmission()) {
if (depth == 0) return intersection.m->getEmission(); // 光线打到光源就直接返回光源Emission
else return {};
}
Intersection lightpos;
float lightpdf = 0.0f;
sampleLight(lightpos, lightpdf);
Vector3f collisionlight = lightpos.coords - intersection.coords;
float dis = dotProduct(collisionlight, collisionlight);
Vector3f collisionlightdir = collisionlight.normalized();
Ray objray(intersection.coords, collisionlightdir);
Intersection ishaveobj = Scene::intersect(objray);
if (ishaveobj.distance - collisionlight.norm() > -EPSILON)
L_dir = lightpos.emit *
intersection.m->eval(ray.direction, collisionlightdir, intersection.normal) *
dotProduct(collisionlightdir, intersection.normal) *
dotProduct(-collisionlightdir, lightpos.normal) / dis / lightpdf;
if (get_random_float() > RussianRoulette)
return L_dir; // 俄罗斯轮盘,大于0.8就直接返回
Vector3f w0 = intersection.m->sample(ray.direction, intersection.normal).normalized();
Ray objrayobj(intersection.coords, w0);
Intersection islight = Scene::intersect(objrayobj);
if (islight.happened && !islight.m->hasEmission()) {
float pdf = intersection.m->pdf(ray.direction, w0, intersection.normal);
if (pdf > EPSILON) {
L_indir = castRay(objrayobj, depth + 1) *
intersection.m->eval(ray.direction, w0, intersection.normal) *
dotProduct(w0, intersection.normal) / pdf / RussianRoulette;
}
}
return L_dir + L_indir;
}
渲染质量和Renderer.cpp中的spp参数有关,以下是spp=3的效果: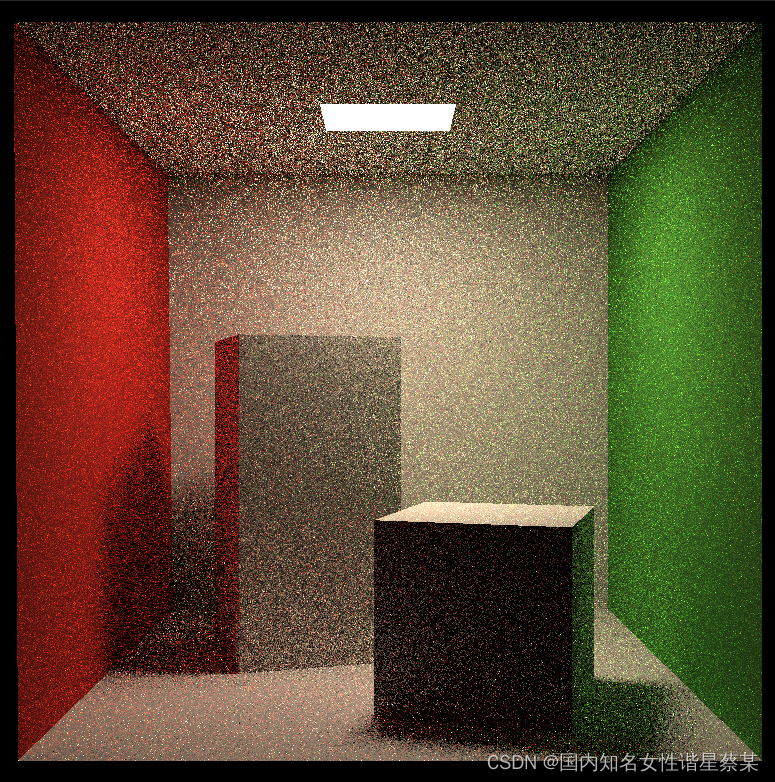
没有采用多线程加速的适合spp=3渲染了四分多钟,用了多线程加速只花了几秒,以下是多线程加速之后的Renderer.cpp,参考了【GAMES101】作业7(提高)多线程、Microfacet(全镜面反射)、抗锯齿:
//
// Created by goksu on 2/25/20.
//
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE
#include <fstream>
#include "Scene.hpp"
#include "Renderer.hpp"
#include <omp.h>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
inline float deg2rad(const float& deg) { return deg * M_PI / 180.0; }
const float EPSILON = 0.0001;
omp_lock_t lock1;
int prog = 0;
std::mutex lock;
void para(Vector3f eye_pos, std::vector<Vector3f>& framebuffer, const Scene& scene, int spp, float imageAspectRatio, float scale, int start, int end) {
int width, height;
width = height = sqrt(spp);
float step = 1.0f / width;
for (uint32_t j = start; j < end; j++) {
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < scene.width; i++) {
for (int k = 0; k < spp; k++) {
float x = (2 * (i + 0.5) / (float)scene.width - 1) *
imageAspectRatio * scale;
float y = (1 - 2 * (j + 0.5) / (float)scene.height) * scale;
Vector3f dir = normalize(Vector3f(-x, y, 1));
framebuffer[j * scene.width + i] += scene.castRay(Ray(eye_pos, dir), 0) / spp;
}
}
/* omp_set_lock(&lock1);
prog++;
UpdateProgress(prog / (float)scene.height);
omp_unset_lock(&lock1);*/
lock.lock();
prog++;
UpdateProgress(prog / (float)scene.height);
lock.unlock();
}
}
// The main render function. This where we iterate over all pixels in the image,
// generate primary rays and cast these rays into the scene. The content of the
// framebuffer is saved to a file.
void Renderer::Render(const Scene& scene)
{
std::vector<Vector3f> framebuffer(scene.width * scene.height);
float scale = tan(deg2rad(scene.fov * 0.5));
float imageAspectRatio = scene.width / (float)scene.height;
Vector3f eye_pos(278, 273, -800);
int m = 0;
int thread_num = 32;
int thread_step = scene.height / thread_num;
std::vector<std::thread> rays;
// change the spp value to change sample ammount
int spp = 1000;
std::cout << "SPP: " << spp << "n";
//for (uint32_t j = 0; j < scene.height; ++j) {
// for (uint32_t i = 0; i < scene.width; ++i) {
// // generate primary ray direction
// float x = (2 * (i + 0.5) / (float)scene.width - 1) *
// imageAspectRatio * scale;
// float y = (1 - 2 * (j + 0.5) / (float)scene.height) * scale;
// Vector3f dir = normalize(Vector3f(-x, y, 1));
// for (int k = 0; k < spp; k++){
// framebuffer[m] += scene.castRay(Ray(eye_pos, dir), 0) / spp;
// }
// m++;
// }
// UpdateProgress(j / (float)scene.height);
//}
//#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < thread_num; i++)
rays.push_back(std::thread(para, eye_pos, std::ref(framebuffer), std::ref(scene),
spp, imageAspectRatio, scale, i * thread_step, (i + 1) * thread_step));
/*para(eye_pos, std::ref(framebuffer), std::ref(scene), spp,
imageAspectRatio, scale, i * thread_step, (i + 1) * thread_step);*/
for (int i = 0; i < thread_num; i++)
rays[i].join();
UpdateProgress(1.f);
// save framebuffer to file
FILE* fp = fopen("binary.ppm", "wb");
(void)fprintf(fp, "P6n%d %dn255n", scene.width, scene.height);
for (auto i = 0; i < scene.height * scene.width; ++i) {
static unsigned char color[3];
color[0] = (unsigned char)(255 * std::pow(clamp(0, 1, framebuffer[i].x), 0.6f));
color[1] = (unsigned char)(255 * std::pow(clamp(0, 1, framebuffer[i].y), 0.6f));
color[2] = (unsigned char)(255 * std::pow(clamp(0, 1, framebuffer[i].z), 0.6f));
fwrite(color, 1, 3, fp);
}
fclose(fp);
}
提高spp到1000后画了半小时,效果如下:
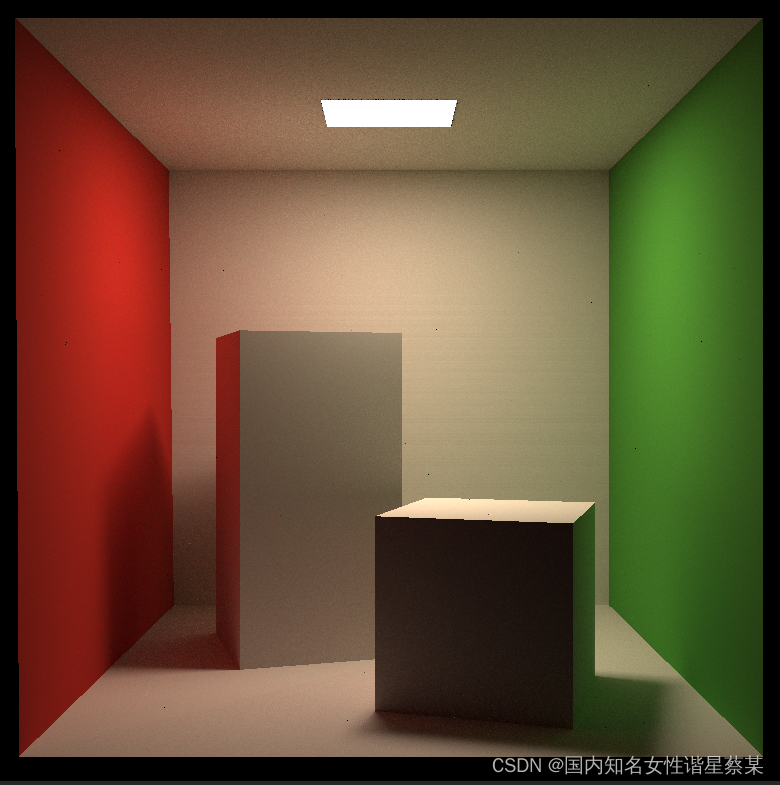
最后
以上就是傻傻小海豚最近收集整理的关于GAMES101-计算机图形学-作业7的全部内容,更多相关GAMES101-计算机图形学-作业7内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复