
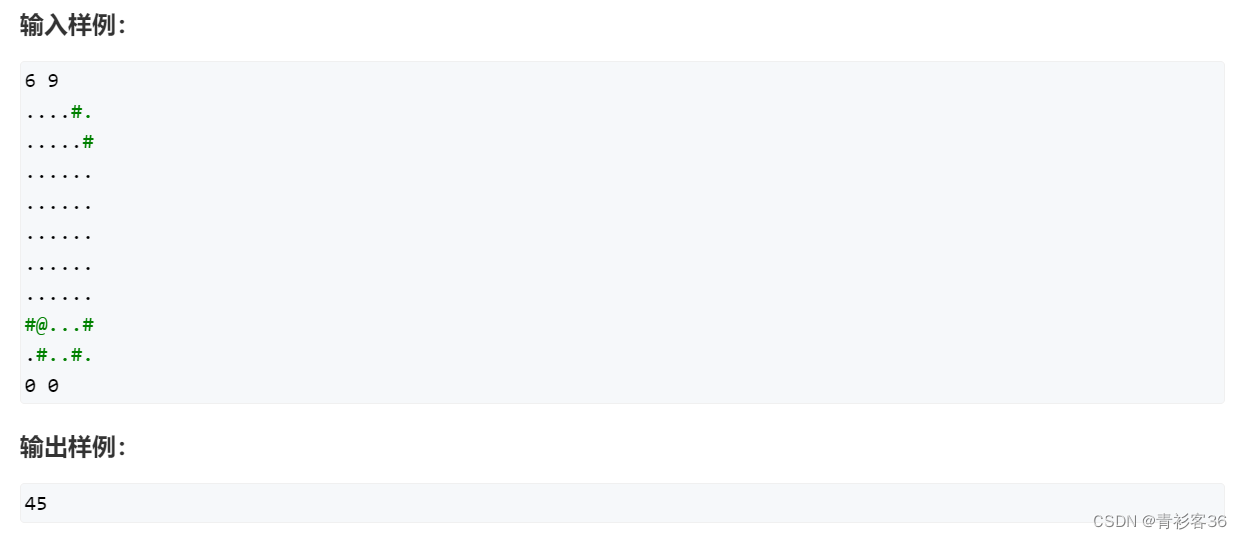
DFS解法:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 25;
char g[N][N];
bool st[N][N];
int w, h, res;
int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
void dfs(int x, int y)
{
if (g[x][y] == '#') return ;
st[x][y] = true;
res ++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++ i)
{
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if (a < 0 || a >= h || b < 0 || b >= w || st[a][b]) continue;
dfs(a, b);
}
}
int main()
{
while (cin >> w >> h && w && h)
{
memset(st, 0, sizeof(st));
for (int i = 0; i < h; ++ i) cin >> g[i];
res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < h; ++ i)
for (int j = 0; j < w; ++ j)
if (g[i][j] == '@') dfs(i, j);
printf("%dn", res);
}
return 0;
}BFS解法:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 25;
char g[N][N];
queue<PII> q;
int w, h;
int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int dfs(int x, int y)
{
int res = 0;
q.push({x, y});
g[x][y] = '#';
while (q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
res ++;
int x = t.first, y = t.second;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++ i)
{
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if (a < 0 || a >= h || b < 0 || b >= w || g[a][b] == '#') continue;
g[a][b] = '#';
q.push({a, b});
}
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
while (cin >> w >> h, w || h)
{
for (int i = 0; i < h; ++ i) cin >> g[i];
for (int i = 0; i < h; ++ i)
for (int j = 0; j < w; ++ j)
if (g[i][j] == '@') cout << dfs(i, j) << endl;
}
return 0;
}最后
以上就是热情早晨最近收集整理的关于Acwing-1113. 红与黑的全部内容,更多相关Acwing-1113.内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复