下文默认已导入tensorflow并重命名为tf。
axis
在一个二维张量或数组中,可以通过调整axis等于0或1控制执行维度。
axis=0代表跨行(经度,down), 而axis=1代表跨列 (纬度,across)
如果不指定axis,则所有元素参与计算。
TF常用函数
强制tensor转换为该数据类型
tf.cast (张量名,dtype= 数据类型)
计算张量维度上元素的最小值
tf.reduce_ min (张量名)
计算张量维度上元素的最大值
tf.reduce_ max (张量名)
x1 = tf.constant([1., 2., 3.], dtype=tf.float64)
print("x1:", x1)
x2 = tf.cast(x1, tf.int32)#强制转换
print("x2", x2)
print("minimum of x2:", tf.reduce_min(x2))#计算很张量维度上元素最小值
print("maxmum of x2:", tf.reduce_max(x2))#计算很张量维度上元素最大值
输出:

计算张量沿着指定维度的平均值
tf.reduce_ mean (张量名,axis=操作轴)
计算张量沿着指定维度的和
tf.reduce_ sum (张量名,axis=操作轴)
x = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3], [2, 2, 3]])
print("x:", x)
print("mean of x:", tf.reduce_mean(x)) # 求x中所有数的均值
print("sum of x:", tf.reduce_sum(x, axis=1)) # 求每一行的和
输出:

TF中的数学运算
对应元素的四则运算: tf.add, tf.subtract, tf.multiply, tf.divide(维度相同的张量才可以做四则运算。)
平方、次方与开方: tf.square, tf.pow, tf.sqrt
矩阵乘: tf.matmul
示例如下:
a = tf.ones([1, 3])
b = tf.fill([1, 3], 3.)
print("a:", a)
print("b:", b)
print("a+b:", tf.add(a, b))
print("a-b:", tf.subtract(a, b))
print("a*b:", tf.multiply(a, b))
print("b/a:", tf.divide(b, a))
输出:
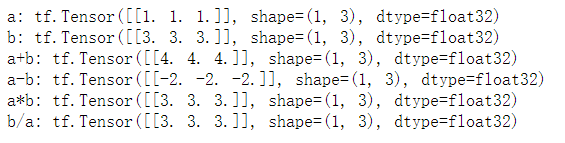
a = tf.fill([1, 2], 3.)
print("a:", a)
print("a的立方:", tf.pow(a, 3))
print("a的平方:", tf.square(a))
print("a的开方:", tf.sqrt(a))
输出:

a = tf.ones([3, 2])
b = tf.fill([2, 3], 3.)
print("a:", a)
print("b:", b)
print("a*b:", tf.matmul(a, b))
输出:

tf.data.Dataset.from tensor_ slices:切分传入张量的第一维度, 生成输入特征标签对,构建数据集data = tf.data.Dataset.from tensor_ slices((输 入特征,标签)) (Numpy和Tensor格式都可用该语句读入数据)
features = tf.constant([12, 23, 10, 17])#特征张量
labels = tf.constant([0, 1, 1, 0])#标签张量
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((features, labels))#(特征,标签)配对
for element in dataset:
print(element)
输出:

tf.GradientTape():实现某个函数对指定参数的求导运算。with结构记录计算过程,gradient求出张量的梯度。利用这个函数可以实现损失函数loss对参数w的求导运算。
通常的形式如下:
with tf.GradientTape( ) as tape:
若干个计算过程
grad=tape.gradient(函数,对谁求导)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
x = tf.Variable(tf.constant(3.0))
y = tf.pow(x, 2)
grad = tape.gradient(y, x)
print(grad)
输出:
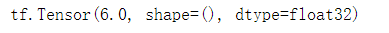
enumerate是python的内建函数,它可遍历每个元素(如列表、元组
或字符串),组合为:索引 元素,常在for循环中使用。
enumerate(列表名)
seq = ['one', 'two', 'three']
for i, element in enumerate(seq):#i是索引,element是元素
print(i, element)
输出:
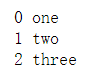
tf.one_ hot:独热编码(one-hot encoding) :在分类问题中,常用独热码做标签,标记类别: 1表示是,0表示非。
tf.one_ hot()函数将待转换数据,转换为one-hot形式的数据输出。
tf.one_ hot (待转换数据,depth=几分类)
classes = 3
labels = tf.constant([1, 0, 2]) # 输入的元素值最小为0,最大为2
output = tf.one_hot(labels, depth=classes)
print("result of labels1:", output)
print("n")
输出:

对于分类问题,神经网络完成前向传播计算出了每种类型的可能性大小,但这些数字只有符合了概率分布后才可以与独热码的标签进行比较,要通过公式将这些数字转换成相应的概率(转换后的概率和为1)。
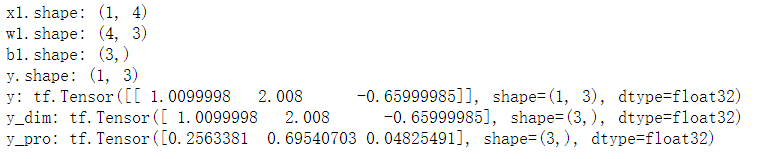
x1 = tf.constant([[5.8, 4.0, 1.2, 0.2]]) # 5.8,4.0,1.2,0.2(0)
w1 = tf.constant([[-0.8, -0.34, -1.4],
[0.6, 1.3, 0.25],
[0.5, 1.45, 0.9],
[0.65, 0.7, -1.2]])
b1 = tf.constant([2.52, -3.1, 5.62])
y = tf.matmul(x1, w1) + b1
print("x1.shape:", x1.shape)
print("w1.shape:", w1.shape)
print("b1.shape:", b1.shape)
print("y.shape:", y.shape)
print("y:", y)
#####以下代码可将输出结果y转化为概率值#####
y_dim = tf.squeeze(y) # 去掉y中纬度1(观察y_dim与 y 效果对比)
y_pro = tf.nn.softmax(y_dim) # 使y_dim符合概率分布,输出为概率值了
print("y_dim:", y_dim)
print("y_pro:", y_pro)
#请观察打印出的shape
输出:
我们可以使用tf.nn.softmax使输出符合概率分布。
当n分类的n个输出(yo, y…1)通过softmax( )函数,便符合概率分布了。
y = tf.constant([1.01, 2.01, -0.66])
y_pro = tf.nn.softmax(y)
print("After softmax, y_pro is:", y_pro) # y_pro 符合概率分布
print("The sum of y_pro:", tf.reduce_sum(y_pro)) # 通过softmax后,所有概率加起来和为1
输出:

assign_ sub:赋值操作,更新(减去)参数的值(需指定)并返回。
调用assign_ sub前,先用 tf.Variable 定义变量w为可训练(可自更新)。
tf.Variable ()将变量标记为“可训练”,被标记的变量会在反向传播
中记录梯度信息。神经网络训练中,常用该函数标记待训练参数。
w.assign_ sub (w要自减的内容)
sub表示subtract,减去的意思。
x = tf.Variable(4)
x.assign_sub(1)
print("x:", x) # 4-1=3
输出:
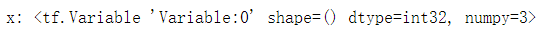
tf.argmax:返回张量沿指定维度最大值的索引号
tf.argmax (张量名,axis=操作轴)
import numpy as np
test = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [2, 3, 4], [5, 4, 3], [8, 7, 2]])
print("test:n", test)
print("每一列的最大值的索引:", tf.argmax(test, axis=0)) # 返回每一列最大值的索引号
print("每一行的最大值的索引", tf.argmax(test, axis=1)) # 返回每一行最大值的索引号
输出:

最后
以上就是飞快巨人最近收集整理的关于TensorFlow2.1(Anaconda)学习笔记三之TF常用函数的全部内容,更多相关TensorFlow2内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。







![[442]tf.Graph().as_default()](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg5.png)
发表评论 取消回复