TensorFlow自然语言处理的例子:利用tensorflow实现神经网络进行手写数字识别。
import struct
import gzip
import os
from six.moves.urllib.request import urlretrieve
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class ManualNN:
def __init__(self):
self.WEIGHTS_STRING = 'weights'
self.BIAS_STRING = 'bias'
self.batch_size = 100
img_width = 28
img_height = 28
self.input_size = img_height * img_width
self.num_labels = 10
tf.reset_default_graph()
#下载数据集
def maybe_download(self,url,filename,expected_bytes,force=False):
if force or not os.path.exists(filename):
print('Attempting to download:', filename)
filename,_ = urlretrieve(url+filename,filename)
print('nDownload Complete!')
statInfo = os.stat(filename)
if statInfo.st_size == expected_bytes:
print('Found and verified', filename)
else:
raise Exception(
'Failed to verify ' + filename + '. Can you get to it with a browser?')
return filename
#读取数据
def read_mnist(self,fname_img,fname_lbl):
print('nReading files %s and %s' % (fname_img, fname_lbl))
with gzip.open(fname_img) as fimg:
#采用Big Endian的方式读取四个整数,magic为magic number用于表示文件格式
magic,num,rows,cols = struct.unpack(">IIII", fimg.read(16))
print(num,rows,cols)
#frombuffer将data以流的形式读入转化成ndarray对象
img = (np.frombuffer(fimg.read(num * rows * cols), dtype=np.uint8).reshape(num, rows * cols)).astype(
np.float32)
img = (img - np.mean(img)) / np.std(img)
print(img.shape)
with gzip.open(fname_lbl) as flbl:
# flbl.read(8) reads upto 8 bytes
magic, num = struct.unpack(">II", flbl.read(8))
lbl = np.frombuffer(flbl.read(num), dtype=np.int8)
print('(Labels) Returned a tensor of shape: %s' % lbl.shape)
print('Sample labels: ', lbl[:10])
return img, lbl
def train(self,train_inputs,train_labels,test_inputs,test_labels):
tf_inputs = tf.placeholder(shape=[self.batch_size,self.input_size],dtype=tf.float32,name='inputs')
tf_labels = tf.placeholder(shape=[self.batch_size,self.num_labels],dtype=tf.float32,name='labels')
#定义作用域重用变量
self.define_net_param()
tf_loss = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits=self.inference(tf_inputs), labels=tf_labels))
tf_loss_mini = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(momentum=0.9, learning_rate=0.01).minimize(tf_loss)
tf_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(self.inference(tf_inputs))
NUM_EPOCHS = 50
session = tf.InteractiveSession()
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
test_accuracy_over_time = []
train_loss_over_time = []
for epoch in range(NUM_EPOCHS):
train_loss = []
#每次训练批量的数据,100条
for step in range(train_inputs.shape[0]//self.batch_size):
#[100,10]的标签矩阵
labels_one_hot = np.zeros((self.batch_size,self.num_labels),dtype=np.float32)
#设置每条数据的标签,即取出前100个标签,train_label数据格式[2,3,5,7,8],则根据train_label索引设置每一行何处为1,从而设置标签 labels_one_hot[np.arange(self.batch_size),train_labels[step*self.batch_size:(step+1)*self.batch_size]] = 1.0
if epoch == 0 and step == 0:
print('Sample labels (one-hot)')
print(labels_one_hot[:10])
print()
loss,_ = session.run([tf_loss,tf_loss_mini],feed_dict={
tf_inputs: train_inputs[step * self.batch_size: (step + 1) * self.batch_size, :],
tf_labels: labels_one_hot
})
train_loss.append(loss)
test_accuracy = []
# Testing Phase
for step in range(test_inputs.shape[0] // self.batch_size):
test_predictions = session.run(tf_prediction, feed_dict={
tf_inputs: test_inputs[step * self.batch_size: (step + 1) * self.batch_size, :]})
batch_test_accuracy = self.accuracy(test_predictions,
test_labels[step * self.batch_size: (step + 1) * self.batch_size])
test_accuracy.append(batch_test_accuracy)
print('Average train loss for the %d epoch: %.3fn' % (epoch + 1, np.mean(train_loss)))
train_loss_over_time.append(np.mean(train_loss))
print('tAverage test accuracy for the %d epoch: %.2fn' % (epoch + 1, np.mean(test_accuracy) * 100.0))
test_accuracy_over_time.append(np.mean(test_accuracy) * 100)
session.close()
#可视化
x_axis = np.arange(len(train_loss_over_time))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2)
fig.set_size_inches(w=25, h=5)
ax[0].plot(x_axis, train_loss_over_time)
ax[0].set_xlabel('Epochs', fontsize=18)
ax[0].set_ylabel('Average train loss', fontsize=18)
ax[0].set_title('Training Loss over Time', fontsize=20)
ax[1].plot(x_axis, test_accuracy_over_time)
ax[1].set_xlabel('Epochs', fontsize=18)
ax[1].set_ylabel('Test accuracy', fontsize=18)
ax[1].set_title('Test Accuracy over Time', fontsize=20)
fig.savefig('mnist_stats.jpg')
def accuracy(self,predictions,labels):
return np.sum(np.argmax(predictions,axis=1).flatten() == labels.flatten()) / self.batch_size
#初始化作用域重用变量layer1/w、layer1/b
def define_net_param(self):
#输入到隐层1
with tf.variable_scope('layer1'):
# tf.get_variable(self.WEIGHT_STRING,shape=[self.input_size,500],initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(0,0.02))
# tf.get_variable(self.BIAS_STRING,shape=[500],initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(0,0.01))
tf.get_variable(self.WEIGHTS_STRING, shape=[self.input_size, 500],
initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(0, 0.02))
tf.get_variable(self.BIAS_STRING, shape=[500],
initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(0, 0.01))
#隐层1到隐层2
with tf.variable_scope('layer2'):
tf.get_variable(self.WEIGHTS_STRING,shape=[500,250],initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(0,0.02))
tf.get_variable(self.BIAS_STRING,shape=[250],initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(0,0.01))
#隐层2到输出层
with tf.variable_scope('output'):
tf.get_variable(self.WEIGHTS_STRING,shape=[250,10],initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(0,0.02))
tf.get_variable(self.BIAS_STRING,shape=[10],initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(0,0.01))
def inference(self,x):
with tf.variable_scope('layer1',reuse=True):
w,b = tf.get_variable(self.WEIGHTS_STRING),tf.get_variable(self.BIAS_STRING)
tf_h1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x,w)+b,name='hidden1')
with tf.variable_scope('layer2',reuse=True):
w,b = tf.get_variable(self.WEIGHTS_STRING),tf.get_variable(self.BIAS_STRING)
tf_h2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(tf_h1,w)+b,name='hidden1')
with tf.variable_scope('output',reuse=True):
w,b = tf.get_variable(self.WEIGHTS_STRING),tf.get_variable(self.BIAS_STRING)
tf_logits = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(tf_h2,w),b,name='logits')
return tf_logits
if __name__ == '__main__':
mn = ManualNN()
# Download data if needed
# url = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/'
# training data
# mn.maybe_download(url, 'train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz', 9912422)
# mn.maybe_download(url, 'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz', 28881)
# testing data
# mn.maybe_download(url, 't10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz', 1648877)
# mn.maybe_download(url, 't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz', 4542)
# Read the training and testing data
train_inputs, train_labels = mn.read_mnist('train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz', 'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz')
test_inputs, test_labels = mn.read_mnist('t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz', 't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz')
mn.train(train_inputs,train_labels,test_inputs,test_labels)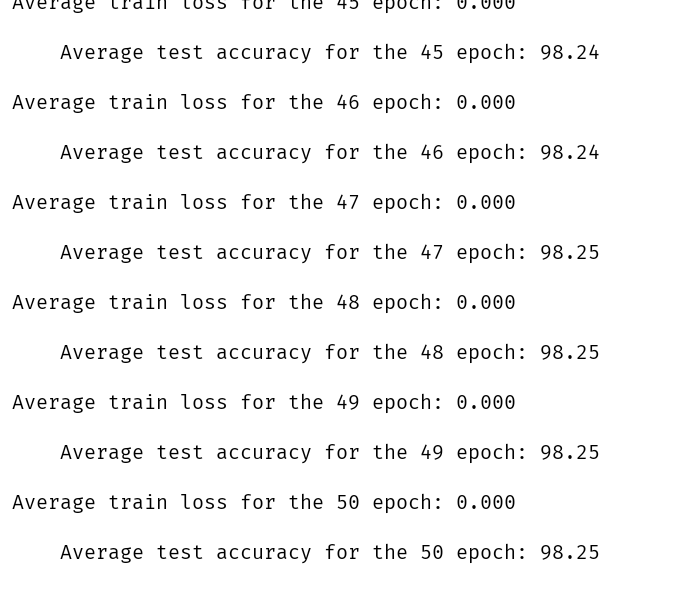
最后
以上就是生动小甜瓜最近收集整理的关于通过tensorflow实现神经网络的全部内容,更多相关通过tensorflow实现神经网络内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复