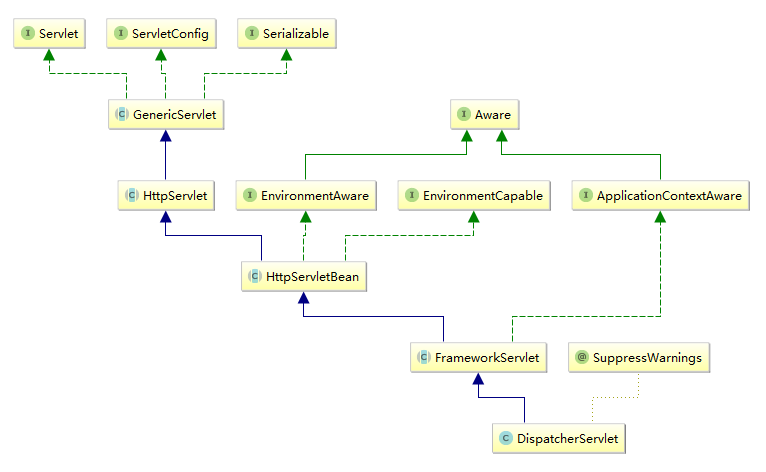
DispatchServlet类图结构
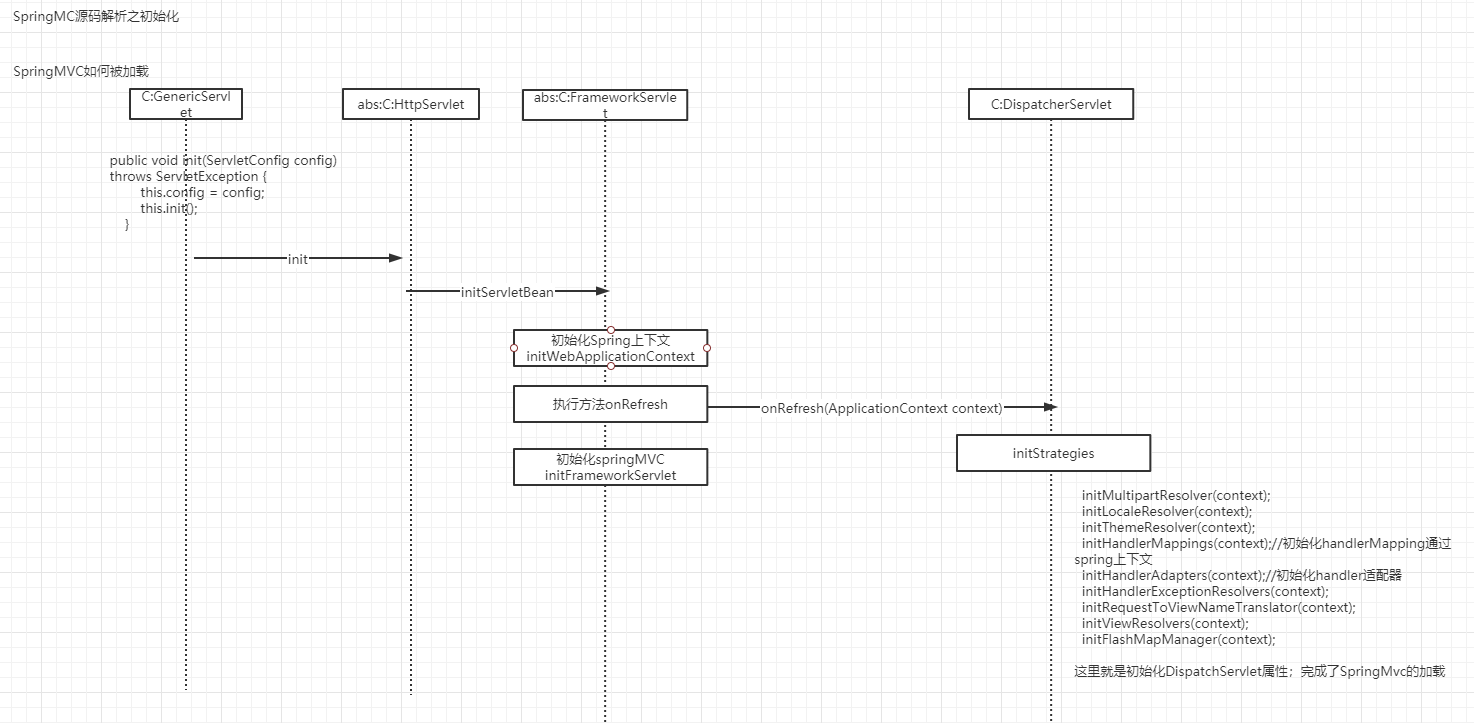
看看调用流程
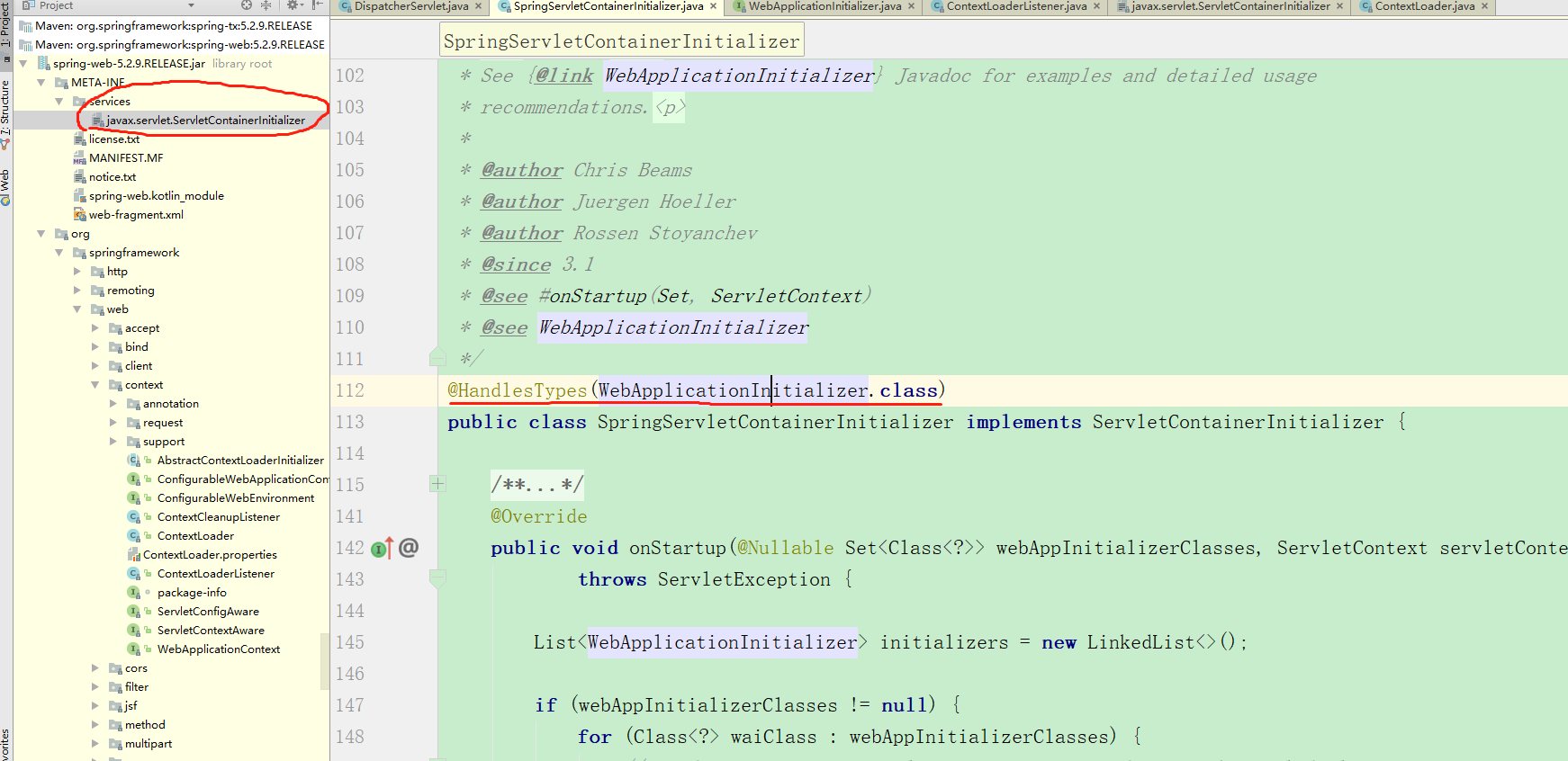
DispatchServlet初始化方式
Spring官网
- 基于Java类初始化
public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) {
// Load Spring web application configuration
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
context.register(AppConfig.class);
// Create and register the DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet servlet = new DispatcherServlet(context);
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet("app", servlet);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping("/app/*");
}
}
- 基于XML
在web.xml中定义
<web-app>
<!--初始化ContextLoaderListener监听器时,加载-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/app-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>app</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value></param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>app</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/app/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
* 实现servlet的方法
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
}
请求如何被DispatchServlet处理的
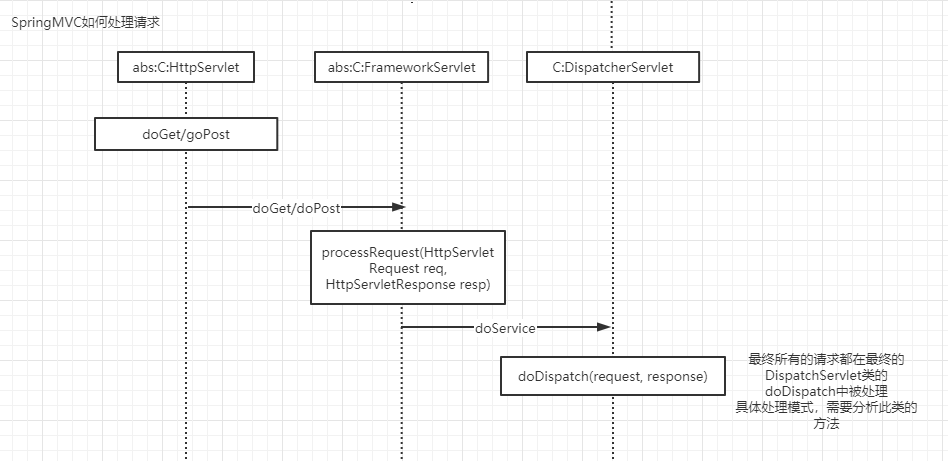
doDispatchServlet
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//请求类型:request.getContentType(), "multipart/" 是否是文件上传,如果是的话,将请求转化成文件上传类请求(StandardMultipartHttpServletRequest)
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.(确定当前请求的处理程序)
//获取请求Controller
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
//获取请求适配器(具体的)
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}通过请求这里拿到的是一个Handler链,链条里面具体包含请求handler,通过调试可以看见具体的handler就是我们实际的controller
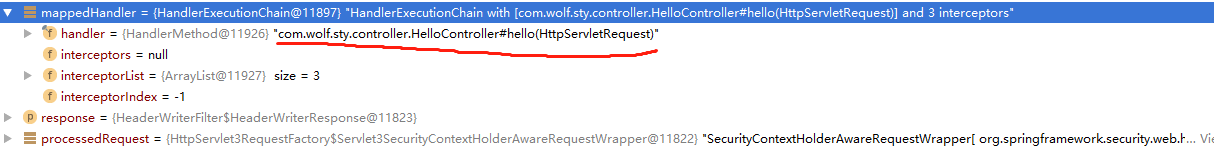
SpringMVC的处理流程
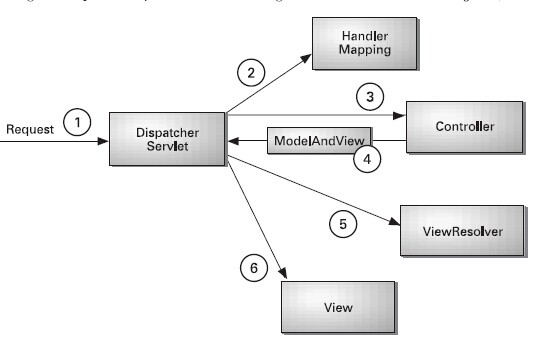
①:DispatcherServlet是springmvc中的前端控制器(front controller),负责接收request并将request转发给对应的处理组件.
②:HanlerMapping是springmvc中完成url到controller映射的组件.DispatcherServlet接收request,然后从HandlerMapping查找处理request的controller.
③:Cntroller处理request,并返回ModelAndView对象,Controller是springmvc中负责处理request的组件(类似于struts2中的Action),ModelAndView是封装结果视图的组件.
④ ⑤ ⑥:视图解析器解析ModelAndView对象并返回对应的视图给客户端.
DispatchServlet
private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings//如何被初始化的
先看看调用链
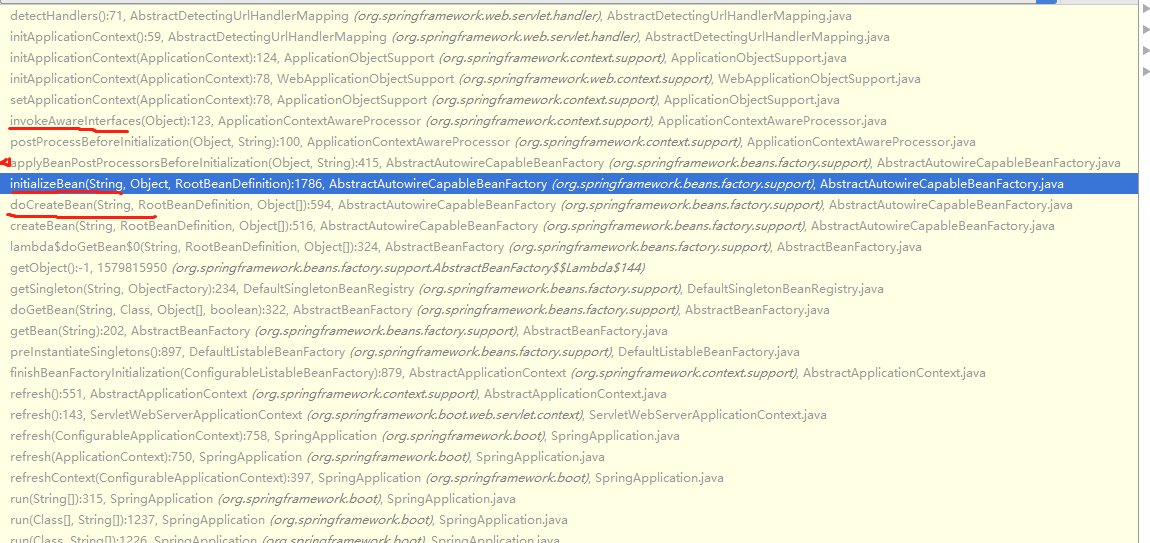
1、spring创建beanName=beanNameHandlerMapping的时候
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
//设置beanName,只要实现了Aware接口(具体的有BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAware)
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//在bean实例化之前调用BeanPostProcessor
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
class ApplicationContextAwareProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
private final ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext;
private final StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver;
/**
* Create a new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor for the given context.
*/
public ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
this.embeddedValueResolver = new EmbeddedValueResolver(applicationContext.getBeanFactory());
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (!(bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware ||
bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware ||
bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware)){
return bean;
}
//非分析的信息删除掉了
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
return bean;
}
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
//这个也就是如果是ApplicationContextAware的实例时,把当前spring上下文设置进去
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);//这里其实调用了ApplicationObjectSupport.setApplicationContext方法,因为他是一个ApplicationContextAware的实例
}
}
}
public abstract class ApplicationObjectSupport implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Override
public final void setApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
//其他代码删除
initApplicationContext(context);
}
}
AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping.initApplicationContext
AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping extends AbstractUrlHandlerMapping
@Override
public void initApplicationContext() throws ApplicationContextException {
super.initApplicationContext();
detectHandlers();
}
protected void detectHandlers() throws BeansException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = obtainApplicationContext();
//在spring上下文中找
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlersInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, Object.class) :
//在spring上下文中获取Object类型的bean然后加载处理
applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
// 遍历beanNames,并找到这些bean对应的url
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
找bean上的所有url(controller上的url+方法上的url),该方法由对应的子类实现--this=beanNameHandlerMapping
String[] urls = determineUrlsForHandler(beanName);//beanNameHandlerMapping.determineUrlsForHandler
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urls)) {
// URL paths found: Let's consider it a handler.
// 保存urls和beanName的对应关系,put it to Map<urls,beanName>,该方法在父类AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中实现
registerHandler(urls, beanName);
}
}
}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
//在创建这个beanName之前,首先先调用
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null) { return result; } result = current; }
我们首先看第一个步骤,也就是建立Map<url,controller>关系的部分.第一部分的入口类为ApplicationObjectSupport的setApplicationContext方法.setApplicationContext方法中核心部分就是初始化容器initApplicationContext(context),子类AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping实现了该方法,所以我们直接看子类中的初始化容器方法.
最后
以上就是傲娇天空最近收集整理的关于Spring-MVC源码分析之DispatchServlet初始化DispatchServlet类图结构DispatchServlet的全部内容,更多相关Spring-MVC源码分析之DispatchServlet初始化DispatchServlet类图结构DispatchServlet内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复