Spring的基础知识
前言
坊间有传言,java程序员实际上是spring程序员,spring是每个java开发者必须掌握的技术。由此可见,spring的影响之大,说spring是java技术的集大成者一点也不为过。从某种角度来说,java和spring已经是互相成就的关系了,java的迭代推动了spring强大,spring的广泛使用也推动java的迭代。
说了那么多,简言之,学java,那就学spring,spring的深度和广度都值得每一个java开发者去研究。
本人在学习和使用spring框架一段时间后,用本系列记录和总结自己的使用心得,通过知识点配合代码的方式来呈现,目的是加深理解,方便回忆,最好能让没接触过spring的小伙伴照着学习后,也能够快速入门。
spring是什么
spring一般说的是spring framework,它是spring家族强大生态下的一个项目,其他的还有诸如springboot,springcloud等等,本文用spring代指spring framework。作为系列的开篇,只展开介绍spring的核心部分,
即spring作为容器的部分。
spring作为容器
几乎每篇介绍spring的文章都会提到spring作为IOC容器的特性,可见,这必是spring的核心所在。把组件交给spring管理,spring把组件存起来,如同一个容器一般。这很好理解,但是,从源码角度直观的感受下:
类DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
public class DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry extends SimpleAliasRegistry implements SingletonBeanRegistry {
/**
* Internal marker for a null singleton object:
* used as marker value for concurrent Maps (which don't support null values).
*/
protected static final Object NULL_OBJECT = new Object();
/** Logger available to subclasses */
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(256);
/** Cache of singleton factories: bean name --> ObjectFactory */
private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<String, ObjectFactory<?>>(16);
/** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap<String, Object>(16);
/** Set of registered singletons, containing the bean names in registration order */
private final Set<String> registeredSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<String>(256);
/** Names of beans that are currently in creation */
private final Set<String> singletonsCurrentlyInCreation =
Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Boolean>(16));
/** Names of beans currently excluded from in creation checks */
private final Set<String> inCreationCheckExclusions =
Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Boolean>(16));
/** List of suppressed Exceptions, available for associating related causes */
private Set<Exception> suppressedExceptions;
/** Flag that indicates whether we're currently within destroySingletons */
private boolean singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = false;
/** Disposable bean instances: bean name --> disposable instance */
private final Map<String, Object> disposableBeans = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
/** Map between containing bean names: bean name --> Set of bean names that the bean contains */
private final Map<String, Set<String>> containedBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Set<String>>(16);
/** Map between dependent bean names: bean name --> Set of dependent bean names */
private final Map<String, Set<String>> dependentBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Set<String>>(64);
/** Map between depending bean names: bean name --> Set of bean names for the bean's dependencies */
private final Map<String, Set<String>> dependenciesForBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Set<String>>(64);
//.......................................
//.......................................
}
由此可见,容器就是通过一个个map来保存组件的。
为什么是DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry这个类来保存组件的呢?
其中的设计思想我不理解,但是这里通过源码角度分析下其继承关系
一般而言,我们通过注解方式来使用spring,使用的上下文是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext这个类
这个类的继承关系如下:
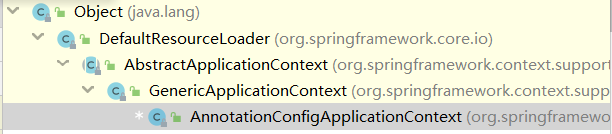
当我们启动容器的时候,会经历刷新容器的阶段,其中有一个步骤是获bean factory:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 关键在这一步获取容器
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//.............................
//...............................
}
获取bean factory实际就是获取父类GenericApplicationContext的成员变量bean factory,其所属类是DefaultListableBeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory的继承关系如下
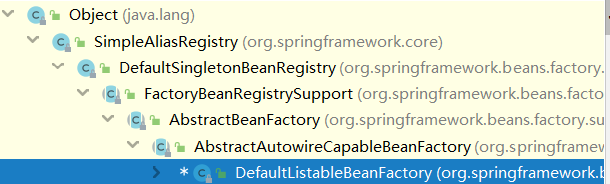
DefaultListableBeanFactory是DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry的一个子类。
由此可见,总结一下:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext这个是实际使用的上下文,其有着成员变量DefaultListableBeanFactory,这个成员变量是DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry的子类。DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry有着许多的map来存放组件,所以最终得出AnnotationConfigApplicationContext也是通过这些map来存放组件的。
IOC容器使用实战
接下来是如何使用spring作为ioc容器,从以下几个方面记录下:
- 作为IOC容器是怎么使用的
- 怎么将类交给spring管理
- spring管理的组件怎么赋值,怎么解决依赖问题
注意:本文使用注解方式使用spring,spring的版本为4.3.12
spring管理组件
为了演示这个功能,创建三个类:测试类,配置类,实体类
使用@Bean方式
//----------实体类-----------------
public class Person {
private String name;
private String age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + ''' +
", age='" + age + ''' +
'}';
}
}
//---------------配置类-----------------
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
@Bean
public Person person() {
return new Person();
}
}
//--------------测试类------------------
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
public void testIOC() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
System.out.println("容器种所有的组件名称如下:");
List<String> names = Arrays.asList(definitionNames);
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println("------------------------");
System.out.println("获取person组件");
Person person = applicationContext.getBean("person", Person.class);
System.out.println("person = " + person);
}
}
//-----------控制台输出---------------------
容器种所有的组件名称如下:
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalRequiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
mainConfig
person
------------------------
获取person组件
person = Person{name='null', age='null'}
从控制台输出可以看出,spring容器会自己注入一些组件
使用扫描注解@ComponenScan
在实体类上标上@Component
@Component
public class Person {
//....................
}
配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.hhdd.bean"})
public class MainConfig2 {
}
测试类
@org.junit.Test
public void test2(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
System.out.println("容器种所有的组件名称如下:");
List<String> names = Arrays.asList(definitionNames);
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println("------------------------");
System.out.println("获取person组件");
Person person = applicationContext.getBean("person", Person.class);
System.out.println("person = " + person);
}
//----------控制台输出----------------
容器种所有的组件名称如下:
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalRequiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
mainConfig
person
------------------------
获取person组件
person = Person{name='null', age='null'}
@import方式
直接引入类
@Configuration
@Import({Person.class})
public class MainConfig3 {
}
此时就不需要在Person类上标注@Component注解了
测试类
@org.junit.Test
public void test3() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig3.class);
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
System.out.println("容器种所有的组件名称如下:");
List<String> names = Arrays.asList(definitionNames);
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println("------------------------");
System.out.println("获取person组件");
Person person = applicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println("person = " + person);
}
}
//---------控制台输出------------
容器种所有的组件名称如下:
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalRequiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
mainConfig3
com.hhdd.bean.Person
------------------------
获取person组件
person = Person{name='null', age='null'}
可见,通过这种方式,注入的组件名称是全路径类名com.hhdd.bean.Person
importSelector方式
实现这个接口,返回需要导入的组件的全类名
public class MyImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return new String[]{"com.hhdd.bean.Person"};
}
}
@org.junit.Test
public void test4() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig4.class);
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
System.out.println("容器种所有的组件名称如下:");
List<String> names = Arrays.asList(definitionNames);
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println("------------------------");
System.out.println("获取person组件");
Person person = applicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println("person = " + person);
}
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
实现这个接口,直接拿registrar给容器种注册对象
public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
boolean res = registry.containsBeanDefinition("person");
if (!res) {
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(Person.class);
registry.registerBeanDefinition("person", beanDefinition);
}
}
}
/**
* 注册组件,@import方式之使用ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
*/
@org.junit.Test
public void test5() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig5.class);
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
System.out.println("容器种所有的组件名称如下:");
List<String> names = Arrays.asList(definitionNames);
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println("------------------------");
System.out.println("获取person组件");
Person person = applicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println("person = " + person);
}
总结
以上就是spring注入bean的最最基本也最常见的几种方式,更多信息请查阅spring的官方文档
给组件赋值
@Value
此注解可以给组件的基本成员变量赋值
@Component
public class Person2 {
@Value("${person.name}")
private String name;
@Value("#{20-2}")
private String age;
@Value("male")
private String sex;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person2{" +
"name='" + name + ''' +
", age='" + age + ''' +
", sex='" + sex + ''' +
'}';
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.hhdd.bean")
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:/person.properties"})
public class DIConfig {
}
测试类
/**
* 测试组件的属性赋值,基本类型赋值
*/
@org.junit.Test
public void test6(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DIConfig.class);
System.out.println("--------获取Person2组件-----------");
Person2 person = applicationContext.getBean(Person2.class);
System.out.println("person = " + person);
}
@AutoWired
spring利用依赖注入DI,完成对ioc容器中各个组件依赖关系的赋值
@Autowired 注入的基本规则
-
默认优先按照类型去容器中找对应的组件
-
如果找到多个相同类型的组件,再将属性名称作为组件id去容器中找
-
@Qualifier(BeanId)明确指出要装配的bean
-
自动装配默认必须要在容器中找到依赖,否则报错;可通过属性required = false取消这个特性
-
这个注解可以在的位置:构造器,参数,方法,属性
示例,假设有实体类Student Money Dog Book
@Component
public class Student {
//属性注入方式
@Autowired
private Book book;
private Dog dog;
private Money money;
//构造器注入
@Autowired
public Student(Money money){
this.money = money;
}
public Book getBook() {
return book;
}
public void setBook(Book book) {
this.book = book;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
//setter注入
@Autowired
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
public Money getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Money money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"book=" + book +
", dog=" + dog +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
测试类
/**
* 测试属性赋值,autowired注入
*/
@org.junit.Test
public void test7(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DIConfig.class);
System.out.println("-------获取student组件-----------");
Student student = applicationContext.getBean(Student.class);
System.out.println("student = " + student);
}
//--------------控制台输出------------------
-------获取student组件-----------
student = Student{book=com.hhdd.bean.Book@163e4e87, dog=com.hhdd.bean.Dog@56de5251, money=com.hhdd.bean.Money@419c5f1a}
最后
本文简单示例介绍了spring中管理组件和给组件赋值的功能,所有的示例代码已经放在github地址:spring-practice
有任何问题欢迎评论区留言,本人创建了一个java交流群:624017389,任何热爱技术的小伙伴都可以加入探讨技术。
后期,会继续更新spring系列的笔记总结,会更加深入,主要是原理方向的东西了。
最后
以上就是踏实夏天最近收集整理的关于Spring的基础知识Spring的基础知识的全部内容,更多相关Spring内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复