import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x_data = [338.,333.,328.,207.,226.,25.,179.,60.,208.,606.] y_data = [640.,633.,619.,393.,428.,27.,193.,66.,226.,1591.] #y_data = w*x_data + b x = np.arange(-200,-100,1)#bias y = np.arange(-5,5,0.1)#weight Z = np.zeros((len(x),len(y))) X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y) for i in range(len(x)): for j in range(len(y)): b = x[i] w = y[j] Z[j][i] = 0 for n in range(len(x_data)): Z[j][i] = Z[j][i] + (y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])**2 Z[j][i] = Z[j][i]/len(x_data) b = -120 #初始化b w = -4 #初始化w lr = 0.0000001 #learning rate iteration = 100000 #作图保留 b_history = [b] w_history = [w] for i in range(iteration): b_grad = 0.0 w_grad = 0.0 for n in range(len(x_data)):#求导的和 b_grad = b_grad - 2.0*(y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])*1.0 w_grad = w_grad - 2.0*(y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])*x_data[n] #update b = b - lr*b_grad w = w - lr*w_grad #store for plotting b_history.append(b) w_history.append(w) #plot plt.contourf(x,y,Z,50,alpha=0.5,cmap=plt.get_cmap('jet')) plt.plot([-188.4],[2.67],'x',ms=12,markeredgewidth=3,color='orange') plt.plot(b_history, w_history, 'o-', ms=3, lw=1.5, color='black') plt.xlim(-200,-100) plt.ylim(-5,5) plt.xlabel(r'$b$', fontsize=16) plt.ylabel(r'$w$', fontsize=16) plt.show()
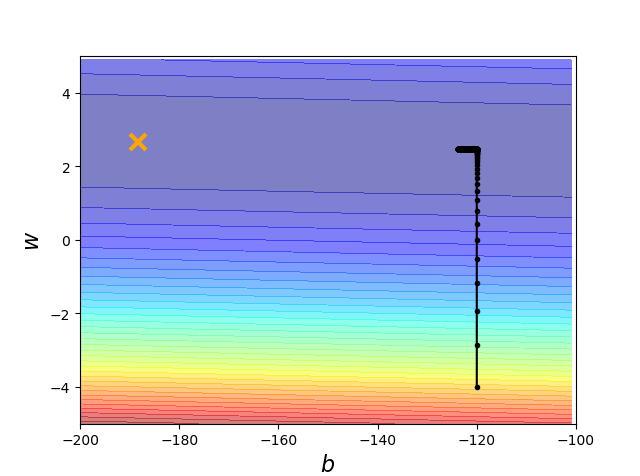
_
显然没有搞好
用adaGrad
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x_data = [338.,333.,328.,207.,226.,25.,179.,60.,208.,606.] y_data = [640.,633.,619.,393.,428.,27.,193.,66.,226.,1591.] #y_data = w*x_data + b #Z是整个data的loss值 x = np.arange(-200,-100,1)#bias y = np.arange(-5,5,0.1)#weight Z = np.zeros((len(x),len(y))) X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y) for i in range(len(x)): for j in range(len(y)): b = x[i] w = y[j] Z[j][i] = 0 for n in range(len(x_data)): Z[j][i] = Z[j][i] + (y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])**2 Z[j][i] = Z[j][i]/len(x_data) b = -120 #初始化b w = -4 #初始化w lr = 1 #learning rate iteration = 100000 #作图保留 b_history = [b] w_history = [w] lr_b = 0 lr_w = 0 for i in range(iteration): b_grad = 0.0 w_grad = 0.0 for n in range(len(x_data)):#求导的和 b_grad = b_grad - 2.0*(y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])*1.0 w_grad = w_grad - 2.0*(y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])*x_data[n] lr_b = lr_b + b_grad ** 2 lr_w = lr_w + w_grad ** 2 #update b = b - lr/np.sqrt(lr_b)*b_grad w = w - lr/np.sqrt(lr_w)*w_grad #store for plotting b_history.append(b) w_history.append(w) #plot plt.contourf(x,y,Z,50,alpha=0.5,cmap=plt.get_cmap('jet')) plt.plot([-188.4],[2.67],'x',ms=12,markeredgewidth=3,color='orange') plt.plot(b_history, w_history, 'o-', ms=3, lw=1.5, color='black') plt.xlim(-200,-100) plt.ylim(-5,5) plt.xlabel(r'$b$', fontsize=16) plt.ylabel(r'$w$', fontsize=16) plt.show()
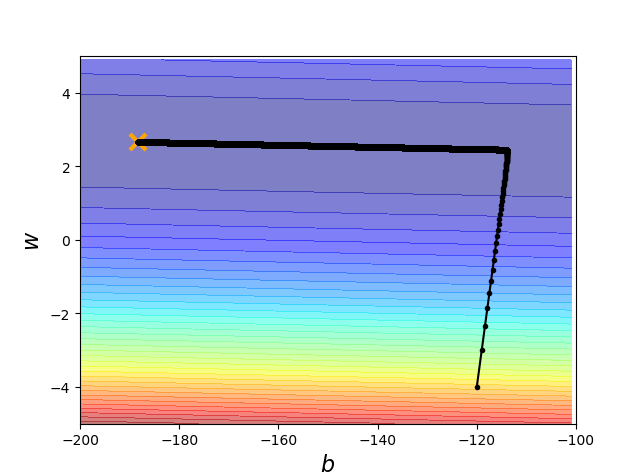
ok
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/cunyusup/p/9565819.html
最后
以上就是顺心花瓣最近收集整理的关于Regression 手动实现Gradient Descent的全部内容,更多相关Regression内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复