接上一篇: [[ 机器学习项目实战-能源利用率2-建模 ]]
解释模型目录:
- * 导入建模数据
- 七. 解释模型
- 7.1 特征重要性
- 7.1.1 特征重要性排序
- 7.1.2 特征重要性95%
- 7.1.3 根据特征重要性筛选特征
- 7.1.4 检测效果
- 7.2 LIME
- 7.2.1 最差预测的解释
- 7.2.2 最好预测的解释
- 7.3 单棵树模型观察
* 导入建模数据
import warning
warning.filterwarning('ignore')
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
pd.options.mode.chained_assignment = None
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 50)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 24
sns.set(font_scale = 2)
train_features = pd.read_csv('data/training_features.csv')
test_features = pd.read_csv('data/testing_features.csv')
train_labels = pd.read_csv('data/training_labels.csv')
test_labels = pd.read_csv('data/testing_labels.csv')
from sklearn.importer import SimpleImputer
imputer = SimpleImputer(strategy = 'median')
imputer.fit(train_features)
X = imputer.transform(train_features)
X_test = imputer.transform(test_features)
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
minmax_scaler = MinMaxScaler().fit(X)
X = minmax_scaler.transform(X)
X_test = minmax_scaler.transform(X_test)
y = np.array(train_labels).reshape((-1, ))
y_test = np.array(test_labels).reshape((-1, ))
def mae(y_true, y_pred):
return np.mean(abs(y_true - y_pred))
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingRegressor
model = GradientBoostingRegressor(loss = 'lad', max_depth = 6, max_features = None,
min_samples_leaf = 4, min_samples_split = 10, e_estimators = 550, random_state = 42)
model.fit(X, y)
model_pred = model.predict(X_test)
model_mae = mae(y_test, model_pred)
print('Final Model Performance on the test set: MAE = %.4f' % model_mae)
Final Model Performance on the test set: MAE = 9.0963
七. 解释模型
- 特征重要性
- Locally Interpretable Model-agnostic Explainer (LIME)
- 建立一颗树模
7.1 特征重要性
sklearn中特征重要性的计算方法
在所有树模型中平均节点不纯度的减少
7.1.1 特征重要性排序
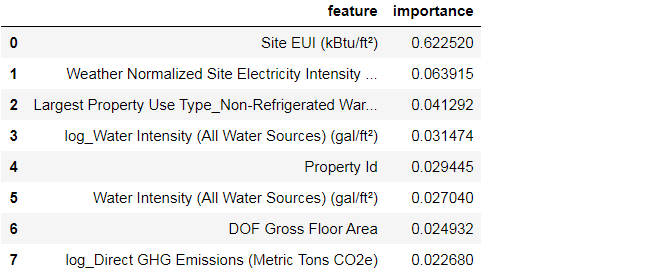
feature_results = pd.DataFrame({'feature': list(train_features.columns),
'importance': model.feature_importances_})
feature_results = feature_results.sort_values('importance', ascending = False).reset_index(drop = True)
feature_results.head(8)
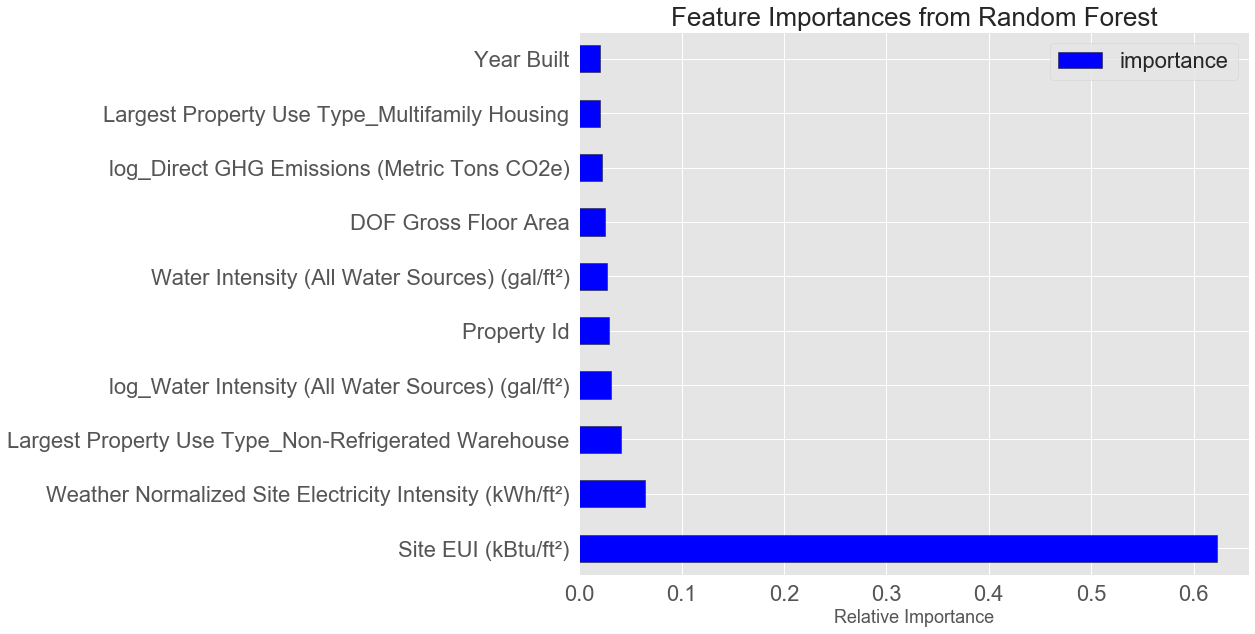
from IPython.core.pylabtools import figsize
figsize(12, 10)
plt.style.use('ggplot')
feature_results.loc[:9, :].plot(x = 'feature', y = 'importance', edgecolor = 'k',
kind = 'barh', color = 'blue')
plt.xlabel('Relative Importance', fontsize = 18); plt.ylabel('')
# plt.yticks(fontsize = 12); plt.xticks(fontsize = 14)
plt.title('Feature Importances from Random Forest', size = 26)
7.1.2 特征重要性95%
cumulative_importances = np.cumsum(feature_results['importance'])
plt.figure(figsize = (20, 6))
plt.plot(list(range(feature_results.shape[0])), cumulative_importances.values, 'b-')
plt.hlines(y=0.95, xmin=0, xmax=feature_results.shape[0], color='r', linestyles='dashed')
# plt.xticks(list(range(feature_results.shape[0])), feature_results.feature, rotation=60)
plt.xlabel('Feature', fontsize = 18)
plt.ylabel('Cumulative importance', fontsize = 18)
plt.title('Cumulative Importances', fontsize = 26)
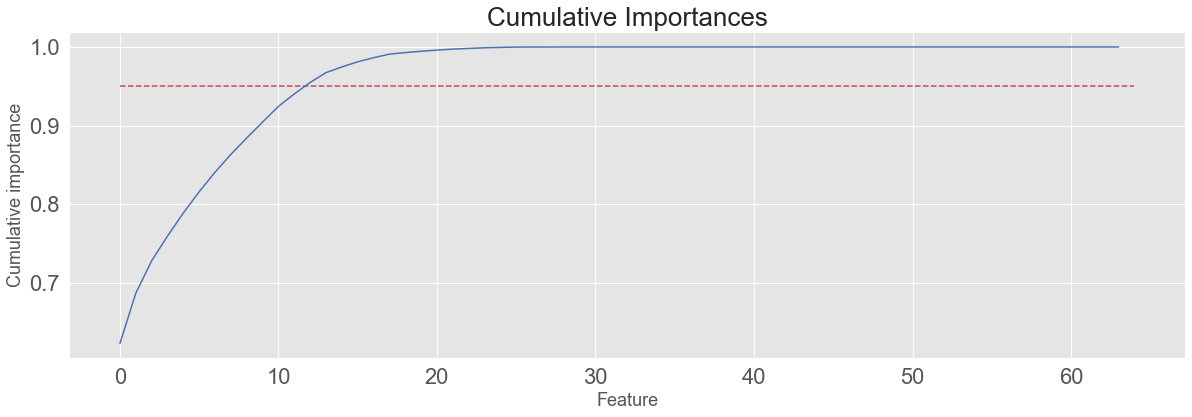
most_num_importances = np.where(cumulative_importances > 0.95)[0][0] + 1
print('Number of features for 95% importance: ', most_num_importances)
Number of features for 95% importance: 13
7.1.3 根据特征重要性筛选特征
most_important_features = feature_results['feature'][:13]
indices = [list(train_features.columns).index(x) for x in most_important_features]
X_reduced = X[:, indices]
X_test_reduced = X_test[:, indices]
pirnt('Most import training features shape: ', X_reduced.shape)
print('Most import testing feature shape: ', X_test_reduced.shape)
Most import training features shape: (6622, 13)
Most import testing features shape: (2839, 13)
7.1.4 检测效果
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
rfr = RandomForestRegressor(random_state = 42)
rfr.fit(X, y)
rfr_full_pred = rfr.predict(X_test)
rfr.fit(X_reduced, y)
rfr_reduced_pred = rfr.predict(X_test_reduced)
print('Random Forest Full Results: MAE = %.4f.' % mae(y_test, rfr_full_pred))
print('Random Forest Reduced Results: MAE = %.4f.' % mae(y_test, rfr_reduced_pred))
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(X, y)
lr_full_pred = lr.predict(X_test)
lr.fit(X_reduced, y)
lr_reduced_pred = lr.predict(X_test_reduced)
print('Linear Regression Full Results: MAE = %.4f.' % mae(y_test, lr_full_pred))
print('Linear Regression Reduced Results: MAE = %.4f.' % mae(y_test, lr_reduced_pred))
Random Forest Full Results: MAE = 9.9025.
Random Forest Reduced Results: MAE = 10.3780.
Linear Regression Full Results: MAE = 13.4651.
Linear Regression Reduced Results: MAE = 14.3103.
- 试验结果发现效果还不如原来
model_reduced = GradientBoostingRegressor(loss = 'lad', max_depth = 6, max_features = None,
min_samples_leaf = 4, min_samples_split = 10,
n_estimators = 550, random_state = 42)
model_reduced.fit(X_reduced, y)
model_reduced_pred = model_reduced.predict(X_test_reduced)
print('Gradient Boosting Reduced Results: MAE = %.4f.' % mae(y_test, model_reduced_pred))
Gradient Boosting Reduced Results: MAE = 9.3899.
- 在GBDT中出现了同样的问题,所以不选择去掉部分小价值特征。
7.2 LIME
Locally Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations
地址:LIME to explain individual predictions
分别选择一个预测最好的和预测最差的来分别解释
7.2.1 最差预测的解释
import lime
import lime.lime_tabular
residuals = abs(model_reduced_pred - y_test) # 残差
wrong = X_test_reduced[np.argmax(residuals), :] # 最差的预测
right = X_test_reduced[np.argmin(residuals), :] # 最好的预测
# 最差预测位置的预测值与真实值
print('Prediction: %.4f' % model_reduced.predict(wrong.reshape(1, -1)))
print('Actual Value: %.4f' % y_test[np.argmax(residuals)])
# Create a lime explainer object
explainer = lime.lime_tabular.LimeTabularExplainer(training_data = X_reduced, mode = 'regression',
training_labels = y, feature_names = list(most_important_features))
# 最差预测的解释
wrong_exp = explainer.explain_instance(data_row = wrong, predict_fn = model_reduced.predict)
# 预测的解释画图
wrong_exp.as_pyplot_figure()
plt.title('Explanation of Prediction', fontsize = 24)
plt.xlabel('Effect on Prediction', fontsize = 20)
Prediction: 11.6612
Actual Value: 96.0000
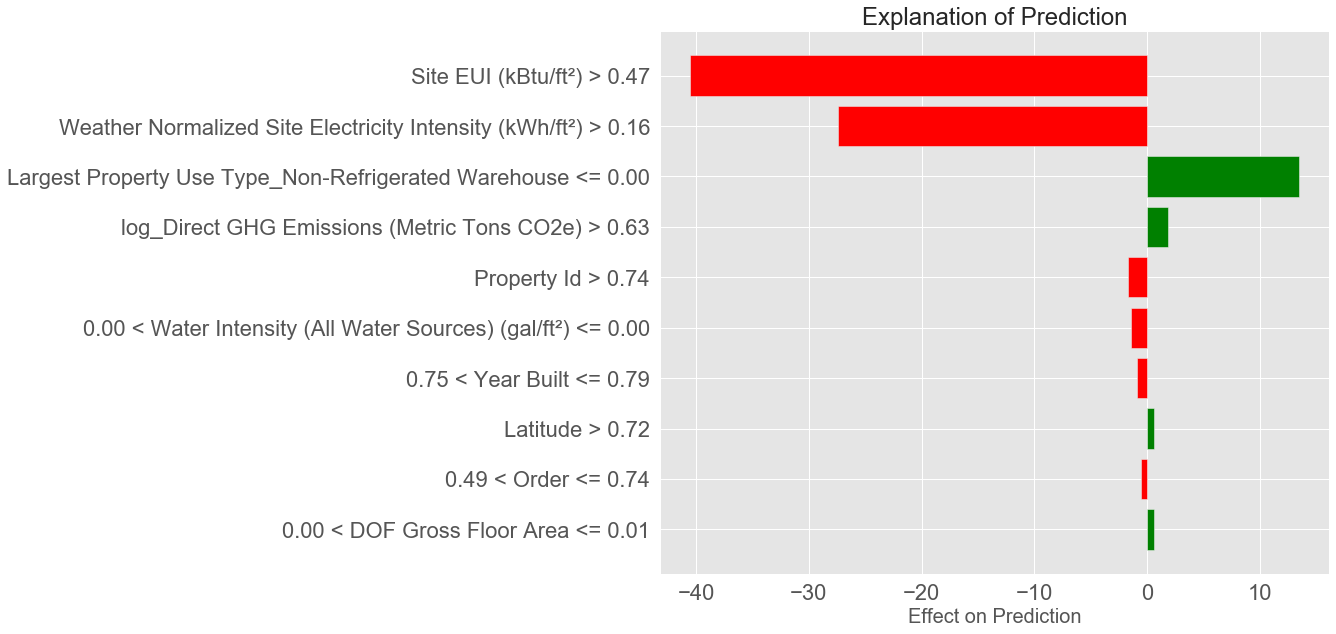
wrong_exp.show_in_notebook(show_predicted_value = False)

预测值:11.66 实际值:96。这里面差距实在太大了,会不会存在什么问题呢?
上图展示了各个特征对结果的贡献程度,其中Site EUI使得结果值大大下降,由于该值(归一化后) 大于0.47了,正常情况下是能源利用率较低了,但是这里反而标签的得分很高,所以有理由认为,该数据点标签值存在问题。
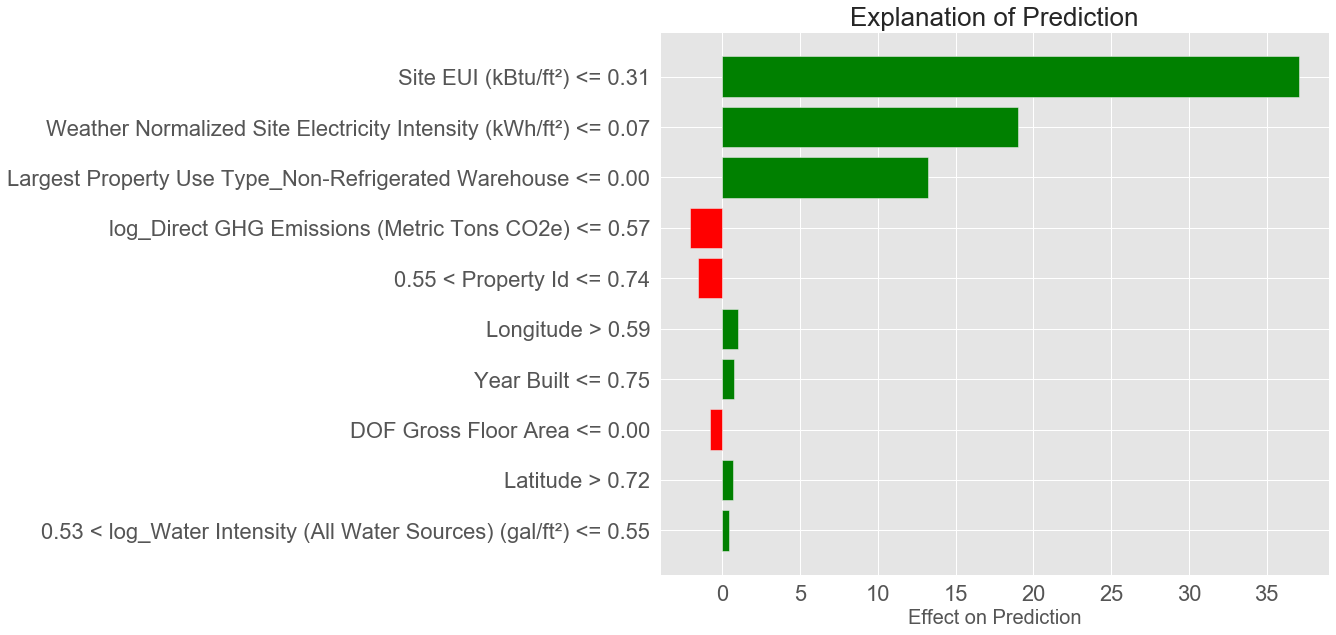
7.2.2 最好预测的解释
# 最好预测位置的预测值与真实值
print('Prediction: %0.4f' % model_reduced.predict(right.reshape(1, -1)))
print('Actual Value: %0.4f' % y_test[np.argmin(residuals)])
# 最好预测的解释
right_exp = explainer.explain_instance(data_row = right, predict_fn = model_reduced.predict, num_features = 10)
# 预测的解释画图
right_exp.as_pyplot_figure()
plt.title('Explanation of Prediction', size = 26)
plt.xlabel('Effect on Prediction', size = 20)
Prediction: 99.9975
Actual Value: 100.0000
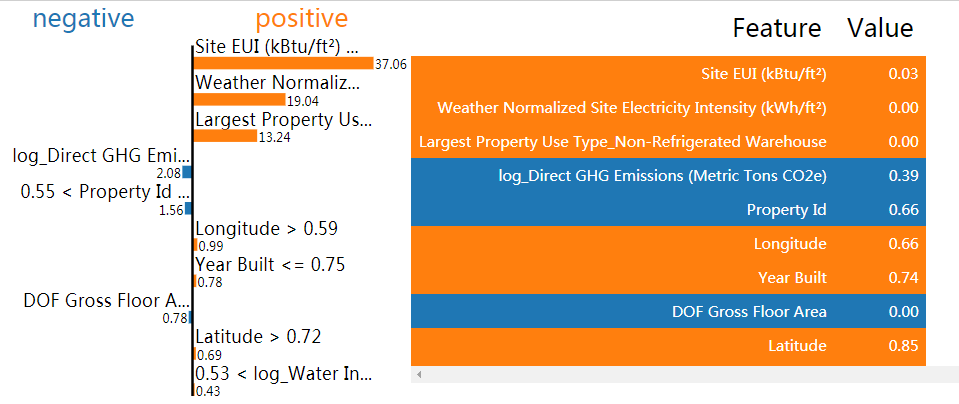
right_exp.show_in_notebook(show_predicted_value = False)
7.3 单棵树模型观察
from sklearn import tree
import pydotplus
from IPython.display import display, Image
single_tree = model_reduced.estimators_[100][0]
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(single_tree, out_file = None, rounded = True,
feature_names = most_important_features, filled = True)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
graph.write_png('sigle_tree.png')
display(Image(graph.creat_png()))
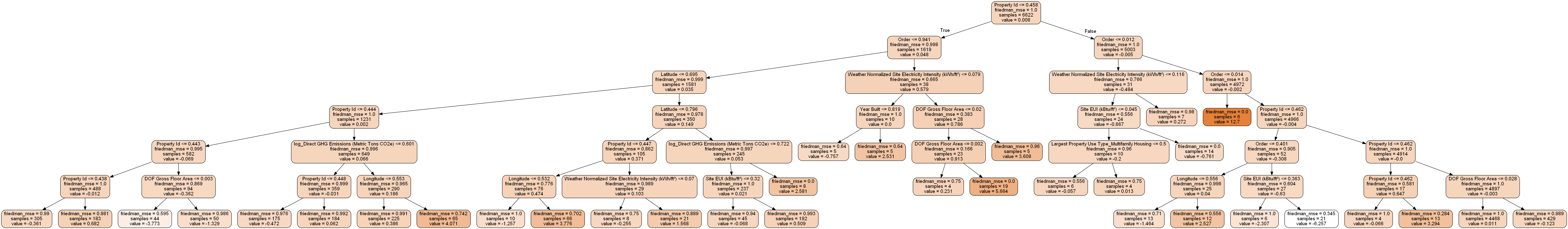
- 太密集了,限制下深度
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(single_tree, out_file = None, rounded = True,
max_depth = 3, feature_names = most_important_features, filled = True)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
graph.write_png('sigle_tree.png')
display(Image(graph.create_png()))
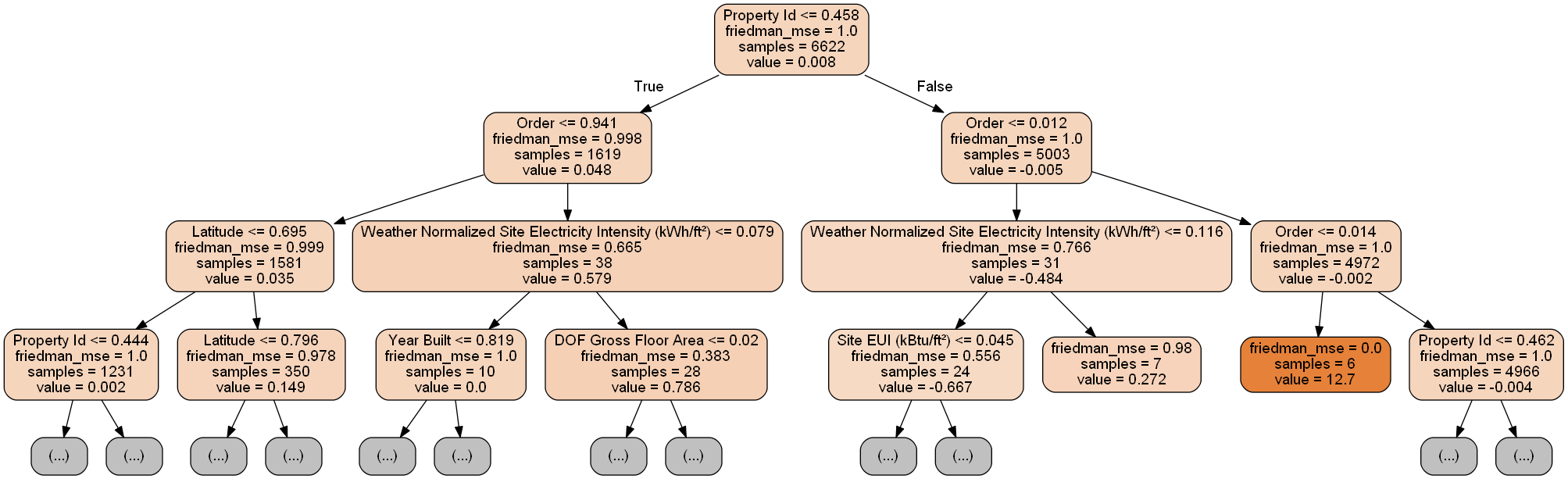
最后
以上就是饱满咖啡豆最近收集整理的关于机器学习项目实战-能源利用率3-分析的全部内容,更多相关机器学习项目实战-能源利用率3-分析内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复