如果不了解FM模型或者FFM模型可以查阅下面两篇文章:
1、推荐系统 | 《Factorization Machines》 | FM模型及python实现
2、《Field-aware Factorization Machines for CTR Prediction》FFM模型整理及python代码
1 DeepFM模型论文原文




2 模型
2.1 CTR预估数据特点:
1、输入中既包含离散型数据(性别),也包含连续型数据(年龄)。离散型数据需要one-hot编码,连续型数据可以先离散化再one-hot编码,也可以直接保留原值。
2、维度非常高, 将one-hot类型的特征输入到DNN中,会导致网络参数太多。
3、数据非常稀疏,one-hot以后,大部分数据都为0。
4、特征按照Field分组
CTR预估重点在于学习低阶与高阶的组合特征。注意,组合特征包括二阶、三阶甚至更高阶的,阶数越高越复杂,越不容易学习。FM模型由于计算复杂度太高,一般只计算到二阶。
根据Google的Wide&Deep模型得出:高阶和低阶的组合特征都非常重要,同时学习到这两种组合特征的性能要比只考虑其中一种的性能要好。
那么关键问题转化成:如何高效的提取这些组合特征。
1、引入领域知识人工进行特征工程。这样做的弊端是高阶组合特征非常难提取,会耗费极大的人力。而且,有些组合特征是隐藏在数据中的,即使是专家也不一定能提取出来,比如著名的“尿布与啤酒”问题。
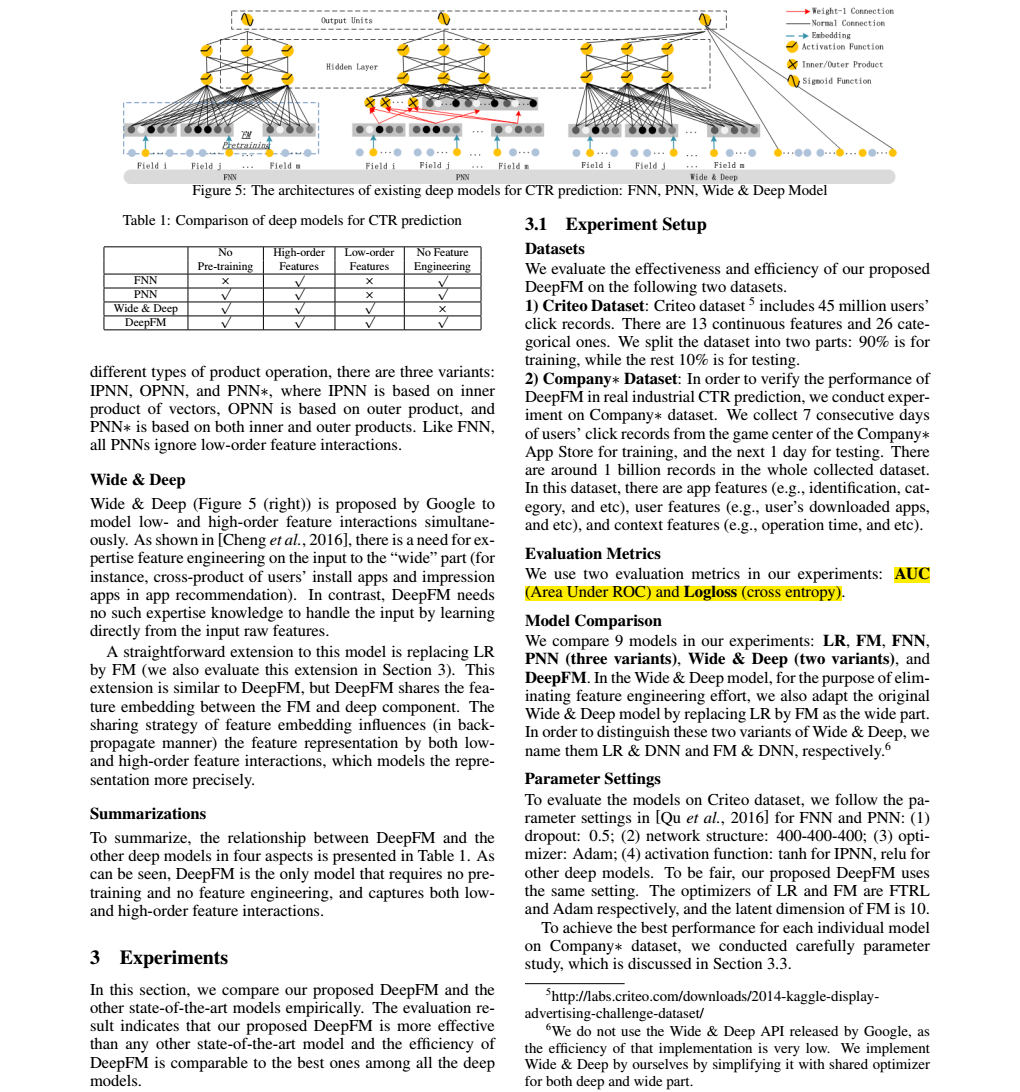
2、将DNN用于高阶的特征组合,是很自然的想法,通过多层的神经网络去解决高阶问题。但是将One-hot类型的特征输入到DNN中,会导致网络参数太多。
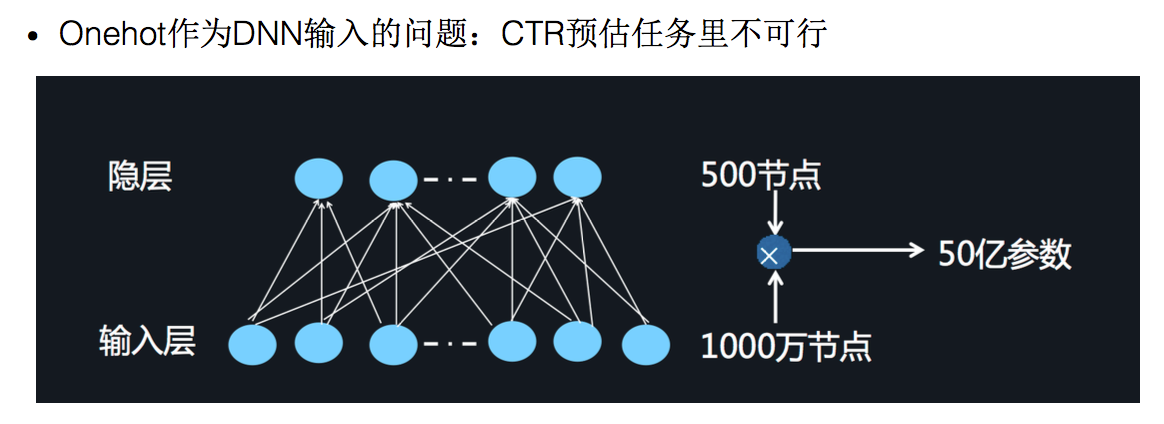
解决思路:将原始数据的one-hot根据不同特征,分别将其编码进行Embedding,这样的可以减少数据稀疏,而且每个feature 在embedding后长度均相同。
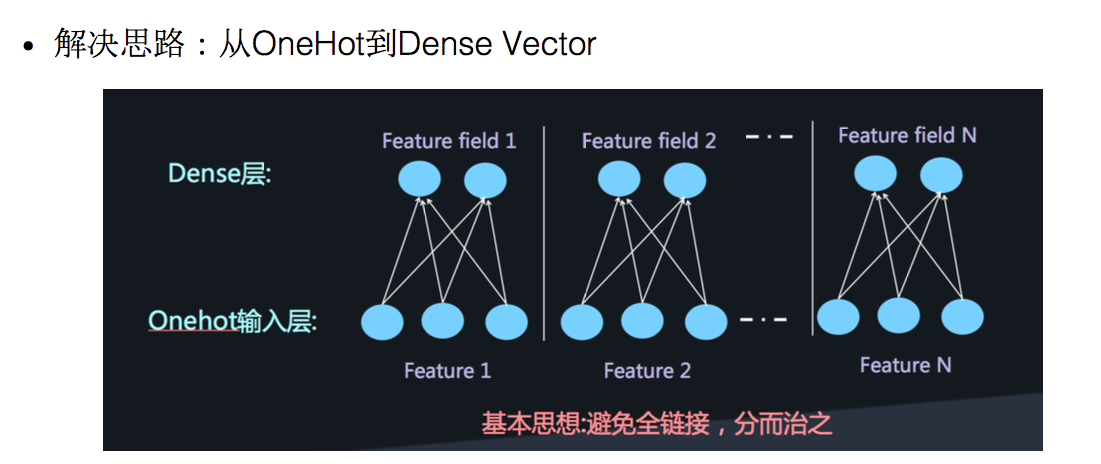
然后。将embedding组合输入到两个隐藏层的神经网络,进行高阶特征的组合。
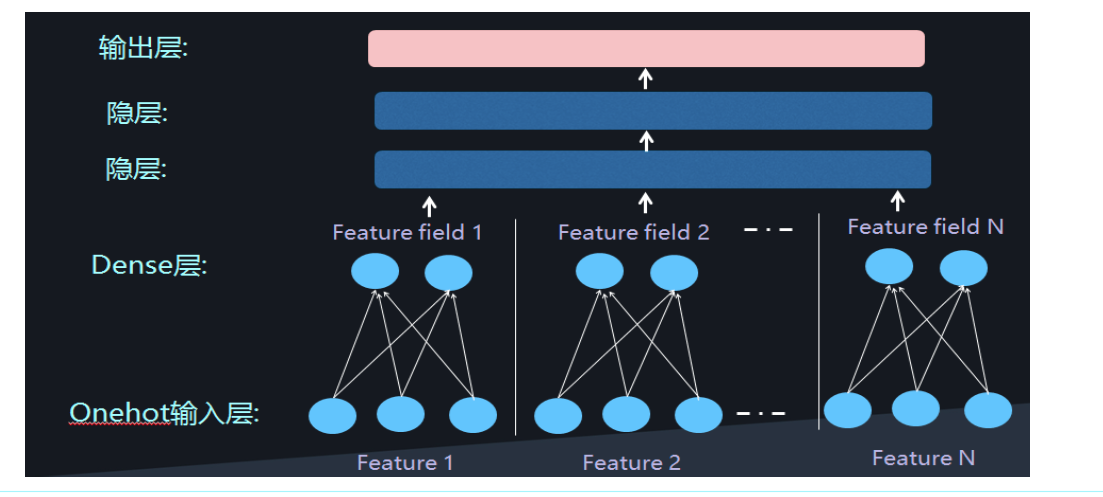
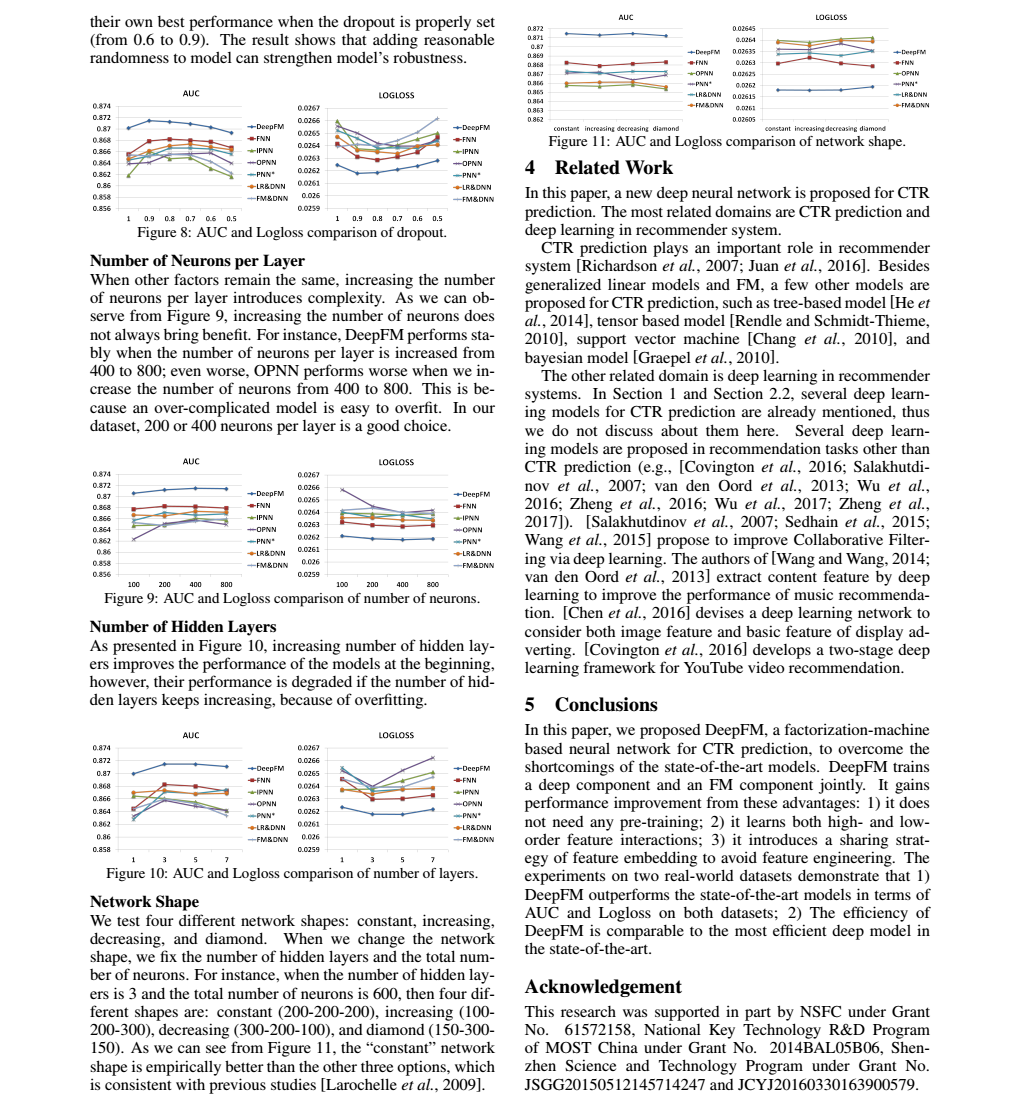
2.2 DeepFM模型介绍
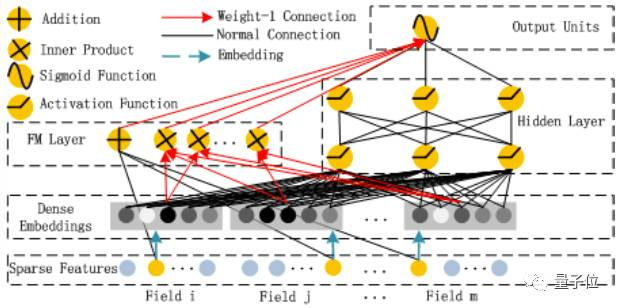
DeepFM有以下特点:
1、FM与DNN并行连接
2、共享embedding
所以DeepFM的输出结果可以表示成 :
y
′
=
s
i
g
m
o
i
d
(
y
F
M
+
y
D
N
N
)
y' = sigmoid(y_{FM} + y_{DNN})
y′=sigmoid(yFM+yDNN)
2.2.1 FM部分介绍
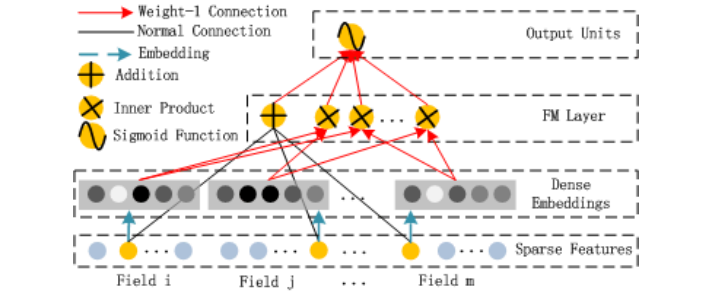
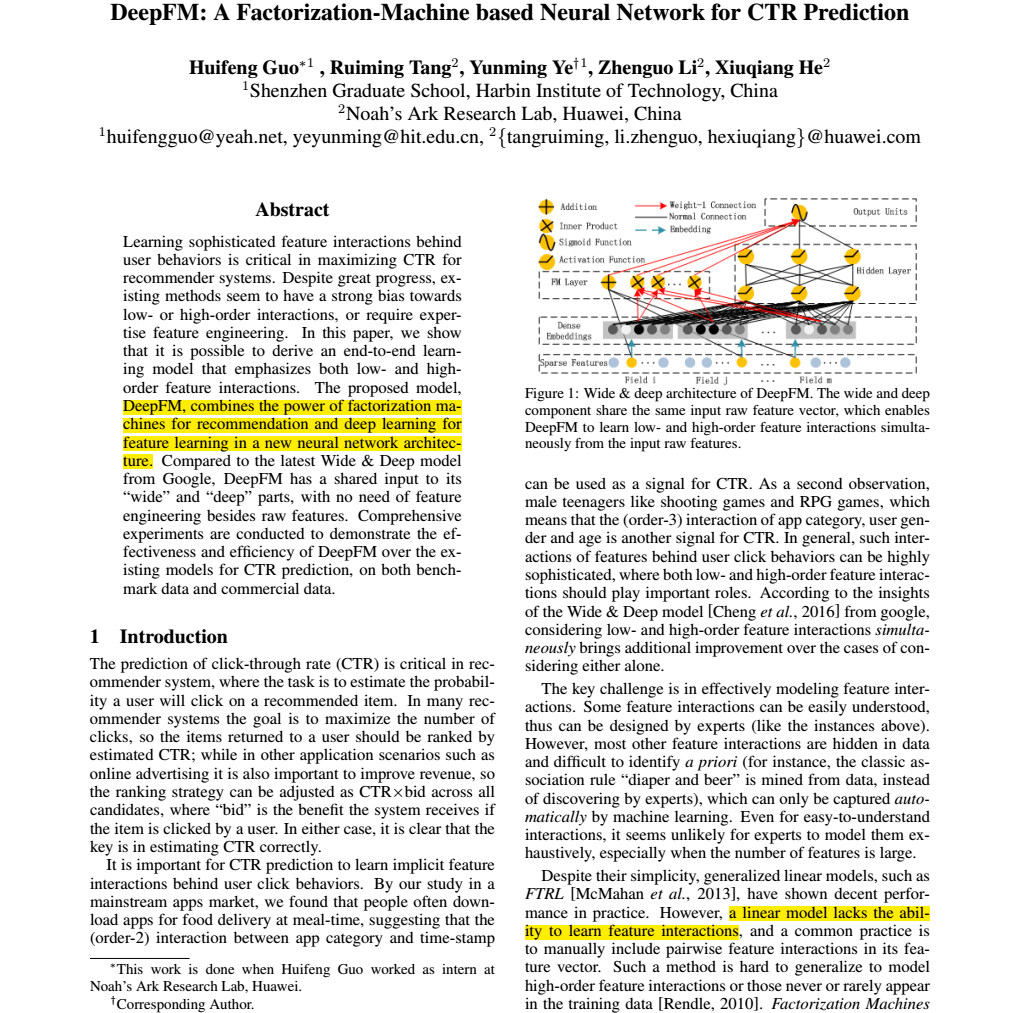
观察上图比较容易发现FM Layer 包含一个Addition 和 多个 Inner Product内积单元。Addition反映的是1阶的特征。内积单元反映的是2阶的组合特征对于预测结果的影响。
y
F
M
=
<
w
,
x
>
+
∑
j
1
=
1
d
∑
j
2
=
j
1
+
1
d
<
V
i
,
V
j
>
x
j
1
⋅
x
j
2
y_{FM} = <w,x> + sum_{j_1=1}^dsum_{j_2=j_1+1}^d<V_i, V_j>x_{j_1}cdot x_{j_2}
yFM=<w,x>+j1=1∑dj2=j1+1∑d<Vi,Vj>xj1⋅xj2
d是输入one-hot之后的维度,我们一般称之为feature_size。
1、FM模块图中,黑线部分是一个全连接!W就是里面的权重。把输入X和W相乘就得到了输出。至于Addition Unit,我们就不纠结了,这里并没有做什么加法,就把他当成是反应1阶特征对输出的影响就行了。
2、这里最后的结果中是在[1,K]上的一个求和。 K就是W的列数,就是Embedding后的维度,也就是embedding_size。也就是说,在DeepFM的FM模块中,最后没有对结果从[1,K]进行求和。而是把这K个数拼接起来形成了一个K维度的向量。
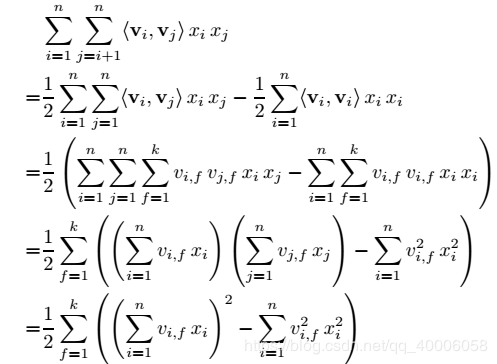
3、FM模块实现了对于1阶(addition)和2阶(inner product)组合特征的建模。
4、FM模型没有进行预训练
5、没有使用人工特征工程
6、embedding矩阵的大小是:特征数量 * 嵌入维度。 然后用一个index表示选择了哪个特征。
7、需要训练的两部分:
1). input_vector和Addition 相连的全连接层,也就是1阶的Embedding矩阵。
2). Sparse Feature到Dense Embedding的Embedding矩阵,中间也是全连接。
2.2.2 DNN部分介绍
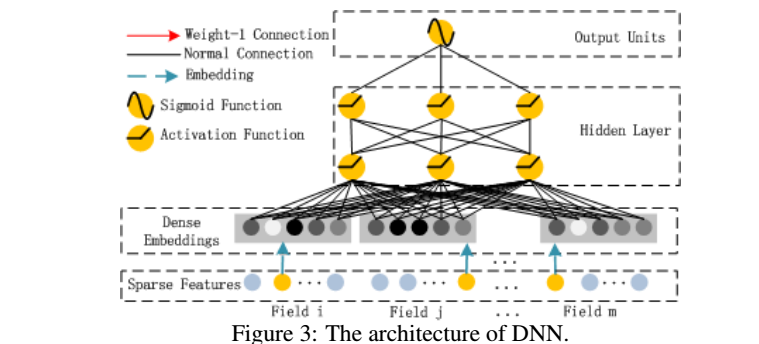
由于CTR或推荐系统的输入数据在one-hot编码之后特别稀疏,如果直接放入到DNN中,会导致网络参数非常多,。所以增加了一个Embedding层,用于降低纬度.embedding层结构如下:
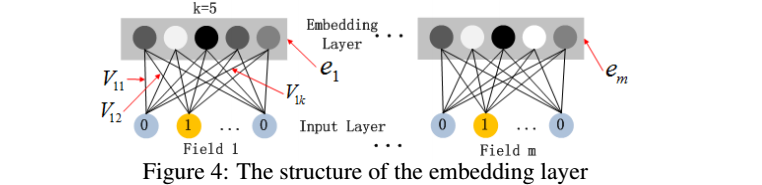
embedding层的两个特点(原文也已经标出):
1、尽管输入的长度不同,但是映射后长度都是相同的.embedding_size 或 k
2、embedding层的参数其实是全连接的Weights,是通过神经网络自己学习到的。
2.2.3 特点
没有预训练(no pre-training)
共享Feature Embedding,没有特征工程(no feature engineering)
同时学习低阶和高阶组合特征(capture both low-high-order interaction features)
3 python 实践
代码就不多做解释了。。。代码来源参考文献已经给出。
3.1 没看懂的部分
1、下面代码如何保证每个特征的embedding都相同?
self.embeddings = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.weights["feature_embeddings"],
self.feat_index) # None * F * K
feat_value = tf.reshape(self.feat_value, shape=[-1, self.field_size, 1])
self.embeddings = tf.multiply(self.embeddings, feat_value)
2、embeddings就是 v i , f x i v_{i,f}x_i vi,fxi么?为什么呀?
self.summed_features_emb = tf.reduce_sum(self.embeddings, 1) # None * K
self.summed_features_emb_square = tf.square(self.summed_features_emb) # None * K
# square_sum part
self.squared_features_emb = tf.square(self.embeddings)
self.squared_sum_features_emb = tf.reduce_sum(self.squared_features_emb, 1) # None * K
如果有大神看到忘请指导,谢谢 !!!
谢谢
谢谢
谢谢
3.2 全部代码
"""
Tensorflow implementation of DeepFM [1]
Reference:
[1] DeepFM: A Factorization-Machine based Neural Network for CTR Prediction,
Huifeng Guo, Ruiming Tang, Yunming Yey, Zhenguo Li, Xiuqiang He.
"""
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
from time import time
from tensorflow.contrib.layers.python.layers import batch_norm as batch_norm
from yellowfin import YFOptimizer
class DeepFM(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):
def __init__(self, feature_size, field_size,
embedding_size=8, dropout_fm=[1.0, 1.0],
deep_layers=[32, 32], dropout_deep=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
deep_layers_activation=tf.nn.relu,
epoch=10, batch_size=256,
learning_rate=0.001, optimizer_type="adam",
batch_norm=0, batch_norm_decay=0.995,
verbose=False, random_seed=2016,
use_fm=True, use_deep=True,
loss_type="logloss", eval_metric=roc_auc_score,
l2_reg=0.0, greater_is_better=True):
assert (use_fm or use_deep)
assert loss_type in ["logloss", "mse"],
"loss_type can be either 'logloss' for classification task or 'mse' for regression task"
self.feature_size = feature_size # denote as M, size of the feature dictionary
self.field_size = field_size # denote as F, size of the feature fields
self.embedding_size = embedding_size # denote as K, size of the feature embedding
self.dropout_fm = dropout_fm
self.deep_layers = deep_layers
self.dropout_deep = dropout_deep
self.deep_layers_activation = deep_layers_activation
self.use_fm = use_fm
self.use_deep = use_deep
self.l2_reg = l2_reg
self.epoch = epoch
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.optimizer_type = optimizer_type
self.batch_norm = batch_norm
self.batch_norm_decay = batch_norm_decay
self.verbose = verbose
self.random_seed = random_seed
self.loss_type = loss_type
self.eval_metric = eval_metric
self.greater_is_better = greater_is_better
self.train_result, self.valid_result = [], []
self._init_graph()
def _init_graph(self):
self.graph = tf.Graph()
with self.graph.as_default():
tf.set_random_seed(self.random_seed)
self.feat_index = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, None],
name="feat_index") # None * F
self.feat_value = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, None],
name="feat_value") # None * F
self.label = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 1], name="label") # None * 1
self.dropout_keep_fm = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None], name="dropout_keep_fm")
self.dropout_keep_deep = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None], name="dropout_keep_deep")
self.train_phase = tf.placeholder(tf.bool, name="train_phase")
self.weights = self._initialize_weights()
# model
self.embeddings = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.weights["feature_embeddings"],
self.feat_index) # None * F * K
feat_value = tf.reshape(self.feat_value, shape=[-1, self.field_size, 1])
self.embeddings = tf.multiply(self.embeddings, feat_value)
# ---------- first order term ----------
self.y_first_order = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.weights["feature_bias"], self.feat_index) # None * F * 1
self.y_first_order = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(self.y_first_order, feat_value), 2) # None * F
self.y_first_order = tf.nn.dropout(self.y_first_order, self.dropout_keep_fm[0]) # None * F
# ---------- second order term ---------------
# sum_square part
self.summed_features_emb = tf.reduce_sum(self.embeddings, 1) # None * K
self.summed_features_emb_square = tf.square(self.summed_features_emb) # None * K
# square_sum part
self.squared_features_emb = tf.square(self.embeddings)
self.squared_sum_features_emb = tf.reduce_sum(self.squared_features_emb, 1) # None * K
# second order
self.y_second_order = 0.5 * tf.subtract(self.summed_features_emb_square, self.squared_sum_features_emb) # None * K
self.y_second_order = tf.nn.dropout(self.y_second_order, self.dropout_keep_fm[1]) # None * K
# ---------- Deep component ----------
self.y_deep = tf.reshape(self.embeddings, shape=[-1, self.field_size * self.embedding_size]) # None * (F*K)
self.y_deep = tf.nn.dropout(self.y_deep, self.dropout_keep_deep[0])
for i in range(0, len(self.deep_layers)):
self.y_deep = tf.add(tf.matmul(self.y_deep, self.weights["layer_%d" %i]), self.weights["bias_%d"%i]) # None * layer[i] * 1
if self.batch_norm:
self.y_deep = self.batch_norm_layer(self.y_deep, train_phase=self.train_phase, scope_bn="bn_%d" %i) # None * layer[i] * 1
self.y_deep = self.deep_layers_activation(self.y_deep)
self.y_deep = tf.nn.dropout(self.y_deep, self.dropout_keep_deep[1+i]) # dropout at each Deep layer
# ---------- DeepFM ----------
if self.use_fm and self.use_deep:
concat_input = tf.concat([self.y_first_order, self.y_second_order, self.y_deep], axis=1)
elif self.use_fm:
concat_input = tf.concat([self.y_first_order, self.y_second_order], axis=1)
elif self.use_deep:
concat_input = self.y_deep
self.out = tf.add(tf.matmul(concat_input, self.weights["concat_projection"]), self.weights["concat_bias"])
# loss
if self.loss_type == "logloss":
self.out = tf.nn.sigmoid(self.out)
self.loss = tf.losses.log_loss(self.label, self.out)
elif self.loss_type == "mse":
self.loss = tf.nn.l2_loss(tf.subtract(self.label, self.out))
# l2 regularization on weights
if self.l2_reg > 0:
self.loss += tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(
self.l2_reg)(self.weights["concat_projection"])
if self.use_deep:
for i in range(len(self.deep_layers)):
self.loss += tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(
self.l2_reg)(self.weights["layer_%d"%i])
# optimizer
if self.optimizer_type == "adam":
self.optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=self.learning_rate, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999,
epsilon=1e-8).minimize(self.loss)
elif self.optimizer_type == "adagrad":
self.optimizer = tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(learning_rate=self.learning_rate,
initial_accumulator_value=1e-8).minimize(self.loss)
elif self.optimizer_type == "gd":
self.optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=self.learning_rate).minimize(self.loss)
elif self.optimizer_type == "momentum":
self.optimizer = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(learning_rate=self.learning_rate, momentum=0.95).minimize(
self.loss)
elif self.optimizer_type == "yellowfin":
self.optimizer = YFOptimizer(learning_rate=self.learning_rate, momentum=0.0).minimize(
self.loss)
# init
self.saver = tf.train.Saver()
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
self.sess = self._init_session()
self.sess.run(init)
# number of params
total_parameters = 0
for variable in self.weights.values():
shape = variable.get_shape()
variable_parameters = 1
for dim in shape:
variable_parameters *= dim.value
total_parameters += variable_parameters
if self.verbose > 0:
print("#params: %d" % total_parameters)
def _init_session(self):
config = tf.ConfigProto(device_count={"gpu": 0})
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
return tf.Session(config=config)
def _initialize_weights(self):
weights = dict()
# embeddings
weights["feature_embeddings"] = tf.Variable(
tf.random_normal([self.feature_size, self.embedding_size], 0.0, 0.01),
name="feature_embeddings") # feature_size * K
weights["feature_bias"] = tf.Variable(
tf.random_uniform([self.feature_size, 1], 0.0, 1.0), name="feature_bias") # feature_size * 1
# deep layers
num_layer = len(self.deep_layers)
input_size = self.field_size * self.embedding_size
glorot = np.sqrt(2.0 / (input_size + self.deep_layers[0]))
weights["layer_0"] = tf.Variable(
np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=glorot, size=(input_size, self.deep_layers[0])), dtype=np.float32)
weights["bias_0"] = tf.Variable(np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=glorot, size=(1, self.deep_layers[0])),
dtype=np.float32) # 1 * layers[0]
for i in range(1, num_layer):
glorot = np.sqrt(2.0 / (self.deep_layers[i-1] + self.deep_layers[i]))
weights["layer_%d" % i] = tf.Variable(
np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=glorot, size=(self.deep_layers[i-1], self.deep_layers[i])),
dtype=np.float32) # layers[i-1] * layers[i]
weights["bias_%d" % i] = tf.Variable(
np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=glorot, size=(1, self.deep_layers[i])),
dtype=np.float32) # 1 * layer[i]
# final concat projection layer
if self.use_fm and self.use_deep:
input_size = self.field_size + self.embedding_size + self.deep_layers[-1]
elif self.use_fm:
input_size = self.field_size + self.embedding_size
elif self.use_deep:
input_size = self.deep_layers[-1]
glorot = np.sqrt(2.0 / (input_size + 1))
weights["concat_projection"] = tf.Variable(
np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=glorot, size=(input_size, 1)),
dtype=np.float32) # layers[i-1]*layers[i]
weights["concat_bias"] = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.01), dtype=np.float32)
return weights
def batch_norm_layer(self, x, train_phase, scope_bn):
bn_train = batch_norm(x, decay=self.batch_norm_decay, center=True, scale=True, updates_collections=None,
is_training=True, reuse=None, trainable=True, scope=scope_bn)
bn_inference = batch_norm(x, decay=self.batch_norm_decay, center=True, scale=True, updates_collections=None,
is_training=False, reuse=True, trainable=True, scope=scope_bn)
z = tf.cond(train_phase, lambda: bn_train, lambda: bn_inference)
return z
def get_batch(self, Xi, Xv, y, batch_size, index):
start = index * batch_size
end = (index+1) * batch_size
end = end if end < len(y) else len(y)
return Xi[start:end], Xv[start:end], [[y_] for y_ in y[start:end]]
# shuffle three lists simutaneously
def shuffle_in_unison_scary(self, a, b, c):
rng_state = np.random.get_state()
np.random.shuffle(a)
np.random.set_state(rng_state)
np.random.shuffle(b)
np.random.set_state(rng_state)
np.random.shuffle(c)
def fit_on_batch(self, Xi, Xv, y):
feed_dict = {self.feat_index: Xi,
self.feat_value: Xv,
self.label: y,
self.dropout_keep_fm: self.dropout_fm,
self.dropout_keep_deep: self.dropout_deep,
self.train_phase: True}
loss, opt = self.sess.run((self.loss, self.optimizer), feed_dict=feed_dict)
return loss
def fit(self, Xi_train, Xv_train, y_train,
Xi_valid=None, Xv_valid=None, y_valid=None,
early_stopping=False, refit=False):
"""
:param Xi_train: [[ind1_1, ind1_2, ...], [ind2_1, ind2_2, ...], ..., [indi_1, indi_2, ..., indi_j, ...], ...]
indi_j is the feature index of feature field j of sample i in the training set
:param Xv_train: [[val1_1, val1_2, ...], [val2_1, val2_2, ...], ..., [vali_1, vali_2, ..., vali_j, ...], ...]
vali_j is the feature value of feature field j of sample i in the training set
vali_j can be either binary (1/0, for binary/categorical features) or float (e.g., 10.24, for numerical features)
:param y_train: label of each sample in the training set
:param Xi_valid: list of list of feature indices of each sample in the validation set
:param Xv_valid: list of list of feature values of each sample in the validation set
:param y_valid: label of each sample in the validation set
:param early_stopping: perform early stopping or not
:param refit: refit the model on the train+valid dataset or not
:return: None
"""
has_valid = Xv_valid is not None
for epoch in range(self.epoch):
t1 = time()
self.shuffle_in_unison_scary(Xi_train, Xv_train, y_train)
total_batch = int(len(y_train) / self.batch_size)
for i in range(total_batch):
Xi_batch, Xv_batch, y_batch = self.get_batch(Xi_train, Xv_train, y_train, self.batch_size, i)
self.fit_on_batch(Xi_batch, Xv_batch, y_batch)
# evaluate training and validation datasets
train_result = self.evaluate(Xi_train, Xv_train, y_train)
self.train_result.append(train_result)
if has_valid:
valid_result = self.evaluate(Xi_valid, Xv_valid, y_valid)
self.valid_result.append(valid_result)
if self.verbose > 0 and epoch % self.verbose == 0:
if has_valid:
print("[%d] train-result=%.4f, valid-result=%.4f [%.1f s]"
% (epoch + 1, train_result, valid_result, time() - t1))
else:
print("[%d] train-result=%.4f [%.1f s]"
% (epoch + 1, train_result, time() - t1))
if has_valid and early_stopping and self.training_termination(self.valid_result):
break
# fit a few more epoch on train+valid until result reaches the best_train_score
if has_valid and refit:
if self.greater_is_better:
best_valid_score = max(self.valid_result)
else:
best_valid_score = min(self.valid_result)
best_epoch = self.valid_result.index(best_valid_score)
best_train_score = self.train_result[best_epoch]
Xi_train = Xi_train + Xi_valid
Xv_train = Xv_train + Xv_valid
y_train = y_train + y_valid
for epoch in range(100):
self.shuffle_in_unison_scary(Xi_train, Xv_train, y_train)
total_batch = int(len(y_train) / self.batch_size)
for i in range(total_batch):
Xi_batch, Xv_batch, y_batch = self.get_batch(Xi_train, Xv_train, y_train,
self.batch_size, i)
self.fit_on_batch(Xi_batch, Xv_batch, y_batch)
# check
train_result = self.evaluate(Xi_train, Xv_train, y_train)
if abs(train_result - best_train_score) < 0.001 or
(self.greater_is_better and train_result > best_train_score) or
((not self.greater_is_better) and train_result < best_train_score):
break
def training_termination(self, valid_result):
if len(valid_result) > 5:
if self.greater_is_better:
if valid_result[-1] < valid_result[-2] and
valid_result[-2] < valid_result[-3] and
valid_result[-3] < valid_result[-4] and
valid_result[-4] < valid_result[-5]:
return True
else:
if valid_result[-1] > valid_result[-2] and
valid_result[-2] > valid_result[-3] and
valid_result[-3] > valid_result[-4] and
valid_result[-4] > valid_result[-5]:
return True
return False
def predict(self, Xi, Xv):
"""
:param Xi: list of list of feature indices of each sample in the dataset
:param Xv: list of list of feature values of each sample in the dataset
:return: predicted probability of each sample
"""
# dummy y
dummy_y = [1] * len(Xi)
batch_index = 0
Xi_batch, Xv_batch, y_batch = self.get_batch(Xi, Xv, dummy_y, self.batch_size, batch_index)
y_pred = None
while len(Xi_batch) > 0:
num_batch = len(y_batch)
feed_dict = {self.feat_index: Xi_batch,
self.feat_value: Xv_batch,
self.label: y_batch,
self.dropout_keep_fm: [1.0] * len(self.dropout_fm),
self.dropout_keep_deep: [1.0] * len(self.dropout_deep),
self.train_phase: False}
batch_out = self.sess.run(self.out, feed_dict=feed_dict)
if batch_index == 0:
y_pred = np.reshape(batch_out, (num_batch,))
else:
y_pred = np.concatenate((y_pred, np.reshape(batch_out, (num_batch,))))
batch_index += 1
Xi_batch, Xv_batch, y_batch = self.get_batch(Xi, Xv, dummy_y, self.batch_size, batch_index)
return y_pred
def evaluate(self, Xi, Xv, y):
"""
:param Xi: list of list of feature indices of each sample in the dataset
:param Xv: list of list of feature values of each sample in the dataset
:param y: label of each sample in the dataset
:return: metric of the evaluation
"""
y_pred = self.predict(Xi, Xv)
return self.eval_metric(y, y_pred)
巨人肩膀
1、原文链接:https://www.ijcai.org/proceedings/2017/239
2、FM、DeepFM、PNN、FNN介绍:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Hb6tKk1sw9pZ7qysO765nw
3、DeepFM模型理论和实践:https://www.jianshu.com/p/6f1c2643d31b
4、论文源码: https://github.com/ChenglongChen/tensorflow-DeepFM/blob/master/DeepFM.py
最后
以上就是玩命墨镜最近收集整理的关于《DeepFM: A Factorization-Machine based Neural Network for CTR Prediction》 DeepFM 模型及python代码1 DeepFM模型论文原文2 模型3 python 实践巨人肩膀的全部内容,更多相关《DeepFM:内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复