新手一枚,记录一下学习的艰辛历程,如果有什么错误,欢迎大家多多指教。根据所学知识,神经网络是允许图片直接输入进行训练的,可是当输入数据集太大时就不大方便啦,一般是生成tfrecords的形式进行训练,实践证明,这样做真的很方便!所以猫狗的识别第一步就是将数据图片生成TF文档。本人使用的是数据集来源于Kaggle,数据集有12500只猫和12500只狗。数据集可以去网站下载~
一 TFrecords的生成
首先下载好的数据集中的train文件夹中的猫狗分开,形成下图中的文件夹
接下来不多说附上程序代码
import os
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
cwd='E:\BaiduNetdiskDownloadkaggle\train\'#上述文件夹地址
classes={'cat','dog'}
writer= tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter("cat_dog.tfrecords")
for index,name in enumerate(classes):
class_path=cwd+name+'/'
for img_name in os.listdir(class_path):
img_path=class_path+img_name
img=Image.open(img_path)
img= img.resize((64,64))
img_raw=img.tobytes()
#plt.imshow(img) # if you want to check you image,please delete '#'
#plt.show()
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
"label": tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[index])),
'img_raw': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[img_raw]))
}))
writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()二 TF文档的读取
新建input_data.py文件,返回图像和标签
import tensorflow as tf
def read_and_decode(tfrecords_file): # read iris_contact.tfrecords
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer([tfrecords_file])# create a queue
#队列生成
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
_, serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue)#return file_name and file
features = tf.parse_single_example(serialized_example,
features={
'label': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'img_raw' : tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
})#return image and label
img = tf.decode_raw(features['img_raw'], tf.uint8)
img = tf.reshape(img, [64, 64, 3]) #reshape image to 512*80*3
img = tf.cast(img, tf.float32) * (1. / 255) - 0.5 #throw img tensor
label = tf.cast(features['label'], tf.float32) #throw label tensor
return img,label
三 训练模型
这个模型并不是固定的,只是用来练习,本人是借助网站上的一个模型
#coding=utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
def inference(images, batch_size, n_classes):
with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope:
# 卷积盒的为 3*3 的卷积盒,图片厚度是3,输出是16个featuremap
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
shape=[3, 3, 3, 16],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
shape=[16],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name)
with tf.variable_scope('pooling1_lrn') as scope:
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME', name='pooling1')
norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75, name='norm1')
with tf.variable_scope('conv2') as scope:
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
shape=[3, 3, 16, 16],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
shape=[16],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name='conv2')
# pool2 and norm2
with tf.variable_scope('pooling2_lrn') as scope:
norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75, name='norm2')
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(norm2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME', name='pooling2')
with tf.variable_scope('local3') as scope:
reshape = tf.reshape(pool2, shape=[batch_size, -1])
dim = reshape.get_shape()[1].value
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
shape=[dim, 128],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005, dtype=tf.float32))
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
shape=[128],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
local3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshape, weights) + biases, name=scope.name)
# local4
with tf.variable_scope('local4') as scope:
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
shape=[128, 128],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005, dtype=tf.float32))
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
shape=[128],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
local4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(local3, weights) + biases, name='local4')
# softmax
with tf.variable_scope('softmax_linear') as scope:
weights = tf.get_variable('softmax_linear',
shape=[128, n_classes],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005, dtype=tf.float32))
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
shape=[n_classes],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
softmax_linear = tf.add(tf.matmul(local4, weights), biases, name='softmax_linear')
return softmax_linear
def losses(logits, labels):
with tf.variable_scope('loss') as scope:
cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits
(logits=logits, labels=labels, name='xentropy_per_example')
loss = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='loss')
tf.summary.scalar(scope.name + '/loss', loss)
return loss
def trainning(loss, learning_rate):
with tf.name_scope('optimizer'):
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate= learning_rate)
global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss, global_step= global_step)
return train_op
def evaluation(logits, labels):
with tf.variable_scope('accuracy') as scope:
correct = tf.nn.in_top_k(logits, labels, 1)
correct = tf.cast(correct, tf.float16)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(correct)
tf.summary.scalar(scope.name + '/accuracy', accuracy)
return accuracy 四 训练
import os
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import input_data
import model
N_CLASSES = 2 # 2个输出神经元,[1,0] 或者 [0,1]猫和狗的概率
batch_size = 32 #每批数据的大小
capacity=2000
MAX_STEP = 15000 # 训练的步数,应当 >= 10000
learning_rate = 0.0001 # 学习率,建议刚开始的 learning_rate <= 0.0001
min_after_dequeue=1000
def run_training():
#logs_train_dir 存放训练模型的过程的数据,在tensorboard 中查看
logs_train_dir = 'F:\ok\log\'
# 自己生成的TF文档
tfrecords_file='F:\ok\cat_dog.tfrecords'
# 生成批次
image,label=input_data.read_and_decode(tfrecords_file)
train_batch, train_label_batch =tf.train.shuffle_batch([image, label],
batch_size, capacity,min_after_dequeue)
# 进入模型
train_logits = model.inference(train_batch, batch_size, N_CLASSES)
# 获取 loss
train_loss = model.losses(train_logits, train_label_batch)
# 训练
train_op = model.trainning(train_loss, learning_rate)
# 获取准确率
train__acc = model.evaluation(train_logits, train_label_batch)
# 合并 summary
summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
sess = tf.Session()
# 保存summary
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logs_train_dir, sess.graph)
saver = tf.train.Saver()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
try:
for step in np.arange(MAX_STEP):
if coord.should_stop():
break
_, tra_loss, tra_acc = sess.run([train_op, train_loss, train__acc])
if step % 50 == 0:
print('Step %d, train loss = %.2f, train accuracy = %.2f%%' %(step, tra_loss, tra_acc*100.0))
summary_str = sess.run(summary_op)
train_writer.add_summary(summary_str, step)
if step % 2000 == 0 or (step + 1) == MAX_STEP:
# 每隔2000步保存一下模型,模型保存在 checkpoint_path 中
checkpoint_path = os.path.join(logs_train_dir, 'model.ckpt')
saver.save(sess, checkpoint_path, global_step=step)
except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError:
print('Done training -- epoch limit reached')
finally:
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
sess.close()
# train
run_training()以上就完成了猫狗识别的训练过程。
打开tensoboard 看到模型结构如下图
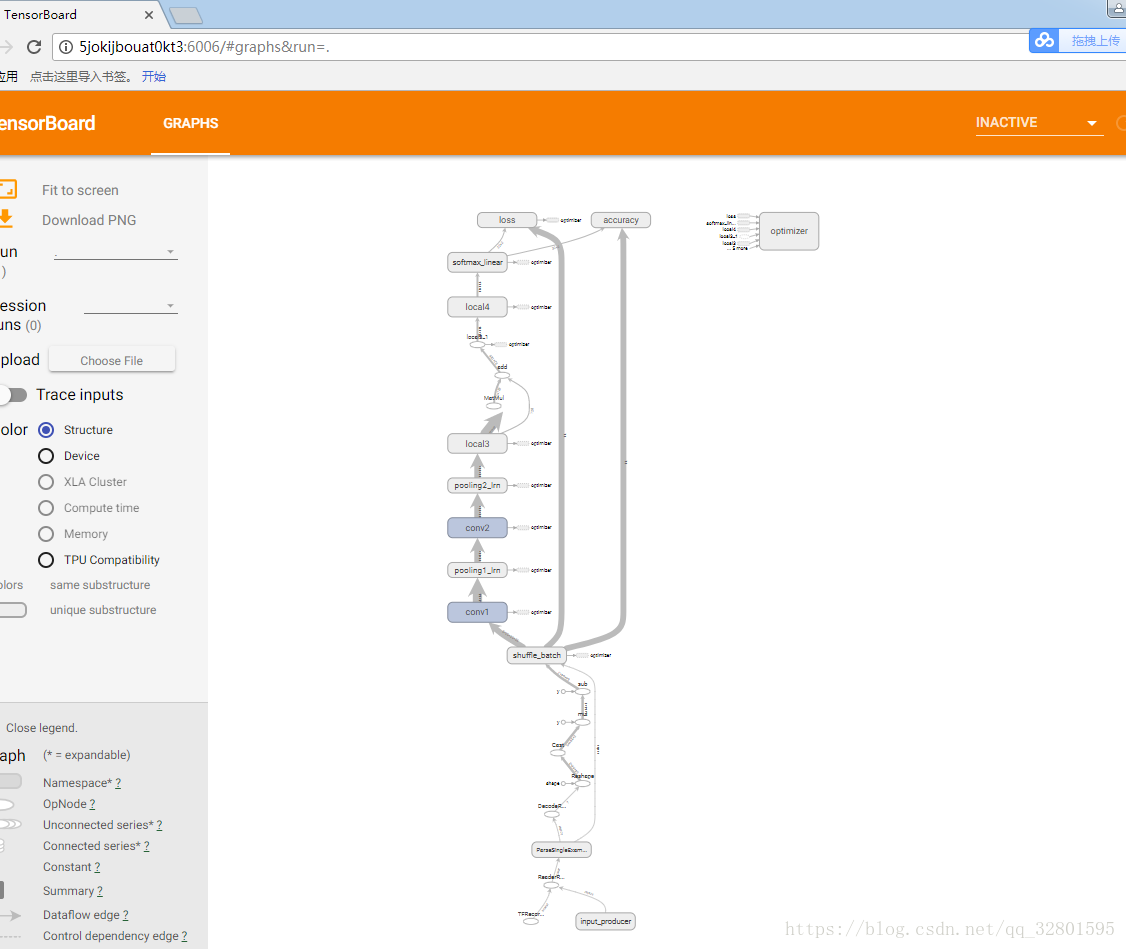
最后
以上就是落后白昼最近收集整理的关于#猫狗大战——TensorFlow的实现一 TFrecords的生成二 TF文档的读取三 训练模型的全部内容,更多相关#猫狗大战——TensorFlow的实现一内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复