注:本文章基于学校优化计算方法选修课程的实验内容,可供研究相关领域的初学者作为入门学习以及编程实现的案例参照。
一. 非对称TSP问题:
旅行商问题,即TSP问题(Traveling Salesman Problem)又译为旅行推销员问题、货郎担问题,是数学领域中著名问题之一。假设有一个旅行商人要拜访n个城市,他必须选择所要走的路径,路径的限制是每个城市只能拜访一次,而且最后要回到原来出发的城市。路径的选择目标是要求得的路径路程为所有路径之中的最小值。(定义摘自百度百科~)
非对称TSP问题的特殊之处在于两个城市的往与返成本是不同的,因为本文章所采用的禁忌搜索算法在对称与非对称的两种问题求解实现上差别不大,因此这里不做深入探究。
二. 禁忌搜索算法:
这里仅列出禁忌搜索算法设计的关键步骤,感兴趣的同学可以查询相书籍或博客以做深入了解。
①已知当前解以及当前解的函数值。
②创建可进行邻域移动的解集、初始化禁忌表。
③判断当前解集中的最优移动是否在禁忌表中。若不在禁忌表中则将此移动作为当前解;若在禁忌表中,则判断此移动能否打破禁忌(在TSP中则将当前解的函数值由于历史最优解的函数值视为打破禁忌),若不能打破禁忌,则舍弃此移动方式,继续判断次优移动是否满足条件,依此类推,直到找到满足条件的邻域移动方式。
④更新当前函数值f,历最优值A。
⑤判断是否达到最大迭代次数,达到则结束算法,否则回到步骤②。
三. 编程实现
1. 编程环境:
Java1.8、maven
2. 数据:
实验课提供的矩阵。
3. 代码奉上:
① 定义Ts算法的主体实现类:
public class Ts {
private int A, f; //历史最优A,当前目标函数值f
private int gen, T_size, cnum; // 迭代次数gen,禁忌表长度T_size,城市数量cnum
private ArrayList<MoveNeigbor> tab = new ArrayList<>(); // tab是邻域表,用顺序表实现
private LimitedQueue<MoveNeigbor> T; // T是禁忌表,用固定长度队列实现
private Route s_; //最优路径s_
private Route s; //当前路径s
private String csvPath = "/Users/Henry/Desktop/task/data/data.csv";
private int[][] dis= new int[this.cnum][this.cnum];
// 迭代求解
public void iterate(){
initial();
// 获取所有可行的邻域移动方式
getTab();
for (int i = 0; i < this.gen; i++) {
// 第一步先排序
this.tab.sort(new Comparator<MoveNeigbor>() {
// 重写比较器的比较方法
@Override
public int compare(MoveNeigbor o1, MoveNeigbor o2) {
return get_f(o1) - get_f(o2);
}
});
// 第二步循环,从头到尾看tab中的邻域移动方式是否在禁忌表中,
// 若该移动方式在禁忌表中,则判断该方式是否能打破禁忌(f > A),
// 若能打破禁忌,则取该种方式;若无法打破禁忌,则继续搜索,直到
// 搜索到不在禁忌表中的移动方式或是能够打破禁忌的移动方式,采取
// 该方式,break停止循环,并更新T(禁忌表)以及f(当前最优)。
for (MoveNeigbor moveNeigbor : this.tab) {
if (this.T.contains(moveNeigbor)) {
if (get_f(moveNeigbor) < this.A) {
this.s.makeAMove(moveNeigbor);
// this.T.add(moveNeigbor);
this.f = get_f(moveNeigbor);
break;
}
} else {
this.s.makeAMove(moveNeigbor);
this.T.add(moveNeigbor);
this.f = get_f(moveNeigbor);
break;
}
}
// 第三步,更新s_(最优路径)、更新A(历史最优)
if (this.f < this.A) {
this.A = this.f;
s_ = new Route(this.s.getRt());
}
// 打印日志
if(i % 10 == 0){
System.out.println("第" + i + "代————" + "历史最优A:" + this.A + " 当前优化f:" + this.f);
}
}
}
// 构造方法
public Ts(int t_size, int gen,int cnum) {
this.gen = gen;
this.T_size = t_size;
this.cnum = cnum;
this.T = new LimitedQueue<>(T_size);
}
// 初始化解集状态
public void initial(){
ReadCsv cr = new ReadCsv(this.csvPath);
this.dis = cr.getArray(this.cnum);
this.s = setRandS();
this.s_ = new Route(this.s.getRt());
this.f = getF(this.s.getRt());
this.A = this.f;
}
// setS方法用于生成随机顺序的初始解
public Route setRandS(){
ArrayList<Double> arr1 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Double> arr2 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
// 初始化arr
for (int i = 0; i < this.cnum; i++) {
arr.add(i);
}
// 随机初始化arr1
for (int i = 0; i < this.cnum; i++) {
arr1.add(Math.random());
}
// copy arr1给arr2
for (int i = 0; i < this.cnum; i++) {
arr2.add(arr1.get(i));
}
arr2.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder());
for (int i = 0; i < this.cnum; i++) {
int idx = arr2.indexOf(arr1.get(i));
arr.set(idx, i);
}
return new Route(arr);
}
// 创建方法获取某一状态的目标函数值
public int getF(ArrayList<Integer> rt_){
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < this.cnum; i++) {
sum = sum + this.dis[rt_.get(i)][rt_.get((i + 1) % this.cnum)];
}
return sum;
}
// 定义评估当前路径进行进行某种路径移动后的目标函数值的方法
public int get_f(MoveNeigbor m){
ArrayList<Integer> rt_ = (ArrayList<Integer>) this.s.getRt().clone();
ArrayList<Integer> loc = m.getLoc();
int idx1 = rt_.indexOf(loc.get(0));
int idx2 = rt_.indexOf(loc.get(1));
Integer tempVar = rt_.get(idx1);
rt_.set(idx1, rt_.get(idx2));
rt_.set(idx2, tempVar);
return getF(rt_);
}
// 得到当前解的所有邻域
public void getTab(){
for (int i = 0; i < this.cnum; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < this.cnum; j++) {
this.tab.add(new MoveNeigbor(i, j));
}
}
}
}②定义描述邻域移动行为的类,这里使用2-opt领域移动方式:
class MoveNeigbor {
// movm代表交换i和j的动作
public HashSet<Integer> movm = new HashSet<>();
// 通过构造方法设置movm属性
public MoveNeigbor(Integer i, Integer j) {
this.movm.add(i);
this.movm.add(j);
}
// 重写equals方法
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
MoveNeigbor that = (MoveNeigbor) o;
return that.movm.equals(this.movm);
}
// 定义方法将movm转为顺序表并返回
public ArrayList<Integer> getLoc() {
Iterator it = this.movm.iterator();
Integer loc1 = (Integer) it.next();
Integer loc2 = (Integer) it.next();
ArrayList<Integer> loc = new ArrayList<>();
loc.add(loc1);
loc.add(loc2);
return loc;
}
}③定义描述当前路径的类:
class Route {
// 属性rt描述当前路径
private ArrayList<Integer> rt = new ArrayList<>();
public ArrayList<Integer> getRt() {
return (ArrayList<Integer>) rt.clone();
}
// 构造方法
public Route(ArrayList<Integer> rt) {
this.rt = (ArrayList<Integer>) rt.clone();
}
// 定义对当前路径进行邻域移动的方法
public void makeAMove(MoveNeigbor m){
ArrayList<Integer> loc = m.getLoc();
int idx1 = rt.indexOf(loc.get(0));
int idx2 = rt.indexOf(loc.get(1));
Integer tempVar = this.rt.get(idx1);
this.rt.set(idx1, this.rt.get(idx2));
this.rt.set(idx2, tempVar);
}
// 定义获取指定索引值的方法
public Integer get(int i){
return this.rt.get(i);
}
}④固定长度队列数据结构的实现:
class LimitedQueue<E> extends LinkedList<E> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final int size;
public LimitedQueue(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
@Override
public boolean add(E o) {
super.add(o);
while (size() > size) {
super.remove();
}
return true;
}
}⑤定义csv文件读取器,需要用到opencsv:
class ReadCsv {
// 定义构造方法,传入文件路径
private String path;
public ReadCsv(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
// 定义方法得到文件解析后的数组
public int[][] getArray(int y){
int[][] arr = new int[y][y];
CSVReader reader = null;
int x = 0;
try {
reader = new CSVReader(new FileReader(path));
String[] line;
while ((line = reader.readNext()) != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < y; i++) {
arr[x][i] = Integer.parseInt(line[i]);
}
x++;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return arr;
}
}4. 运行效果:
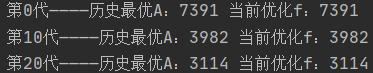
四. 后记
博客是心血来潮写的,代码能力是半吊子的。希望能够为翻到这篇博客的有缘人产生价值。
最后
以上就是专一外套最近收集整理的关于非对称TSP问题的禁忌搜索算法求解的Java实现一. 非对称TSP问题:二. 禁忌搜索算法:三. 编程实现 四. 后记的全部内容,更多相关非对称TSP问题的禁忌搜索算法求解的Java实现一.内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复