文章目录
- 禁忌搜索
- 一、局部领域搜索
- 二、TS算法
- 2.1 **通过针对爬山法的分析,提出了TS搜索算法:**
- 2.2 **TS算法的特点:**
- 2.3 **TS算法构成要素:**
- 2.3 禁忌搜索特点
- 三、TS算法举例
- TS解TSP问题
禁忌搜索
适用于离散化变量求解。
一、局部领域搜索
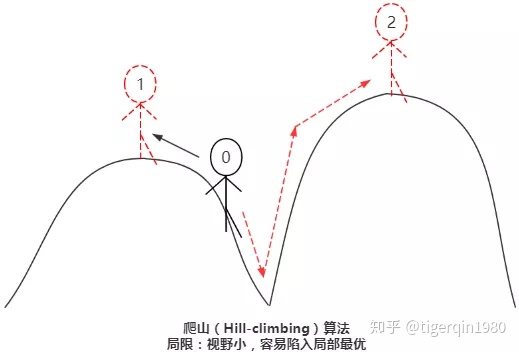
又称爬山启发式算法,从当前的节点开始,和周围的邻居节点的值进行比较。如果当前节点是最大的,那么返回当前节点,作为最大值(即山峰最高点);反之就用最高的邻居节点替换当前节点,从而实现向山峰的高处攀爬的目的。它是禁忌搜索的基础,TS算法是在其上改进而来。
优点:
-
容易理解,容易实现,具有较强的通用性;
-
局部开发能力强,收敛速度很快。
缺点:
-
全局开发能力弱,只能搜索到局部最优解;
-
搜索结果完全依赖于初始解和邻域的映射关系。
二、TS算法
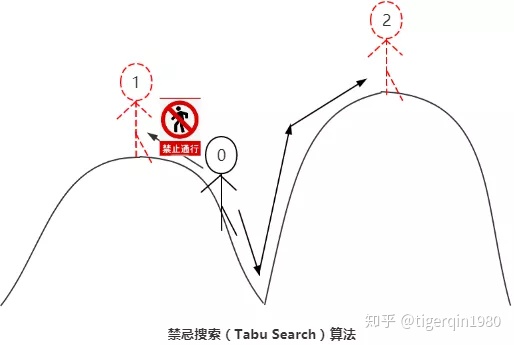
2.1 通过针对爬山法的分析,提出了TS搜索算法:
算法的基本思想:采用邻域选优的搜索方法,为了逃离局部最优解,算法必须能够接受劣解,也就是每一次得到的解不一定优于原来的解。但是,一旦接受了劣解,算法迭代即可能陷入循环。为了避免循环,算法将最近接受的一些移动放在禁忌表中,在以后的迭代中加以禁止。即只有不在禁忌表中的较好解(可能比当前解差)才能接受作为下一代迭代的初始解。随着迭代的进行,禁忌表不断更新,经过一定的迭代次数后,最早进入禁忌表的移动就从禁忌表中解禁退出。
-
改进1:接受劣解。
-
改进2:引入禁忌表。
-
改进3:引入长期表和中期表。
2.2 TS算法的特点:
- 1、基本思想——避免在搜索过程中的循环
- 2、只进不退的原则,通过禁忌表实现
- 3、不以局部最优作为停止准则
- 4、邻域选优的规则模拟了人类的记忆功能
2.3 TS算法构成要素:
(1)编码方式
将不相同的n件物品分为m组,可以用的编码:
a、带分隔符的顺序编码
以自然数1~n分别代表n件物品,n个数加上m-1个分割符号混编在一起,随机排列。 如:1-3-4-0-2-6-7-5-0-8-9b、自然数编码
编码的每一位分别代表一件物品,而每一位的值代表该物品所在的分组。如:1-2-1-1-2-2-2-3-3(2)初始解的获取
可以随机给出初始解,也可以事先使用其他启发式等算法给出一个较好的初始解。
(3)移动邻域
移动是从当前解产生新解的途径,例如上述问题中用移动s产生新解s(x)。
从当前解可以进行的所有移动构成邻域,也可以理解为从当前解经过“一步”可以到达的区域。(4)禁忌表
禁忌表的作用:防止搜索出现死循环-
记录前若干步走过的点、方向或目标值,禁止返回
-
表是动态更新的
-
表的长度称为Tabu-Size
禁忌表的主要指标(两项指标)
-
**禁忌对象:**禁忌表中被禁的那些变化元素
-
**禁忌长度:**对象的禁忌在多少次迭代后失效。
-
禁忌长度:可以是一个固定的常数(T=c),也可以是动态变化的,可按照某种规则或公式在区间内变化
- 禁忌长度过短,一旦陷入局部最优点,出现循环无法跳出;
- 禁忌长度过长,候选解全部被禁忌,造成计算时间较大,也可能造成计算无法继续下去。
-
禁忌对象(三种变化)
- 以状态本身或者状态的变化作为禁忌对象
- 以状态分量以及分量的变化作为禁忌对象
- 采用类似的等高线做法,以目标值变化作为禁忌对象
-
(5)渴望水平函数
A(x,s)一般为历史上曾经达到的最好目标值,若有C(s(x))<A(x,s)则S(x)是不受T表限制。即使s(x)∈T,仍可取x=s(x)。A(x,s)称为渴望水平函数。
(6)停止准则
(1)给定最大迭代步数(最常用 )
(2)设定某个对象的最大禁忌频率。
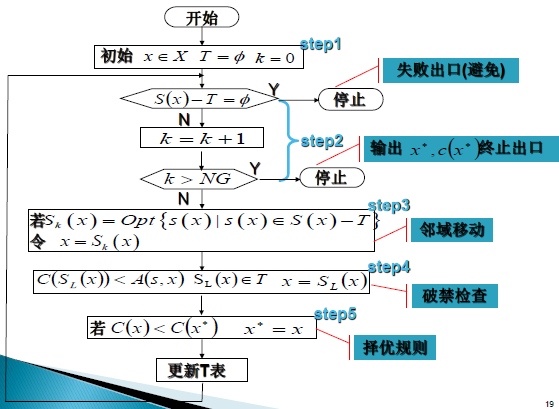
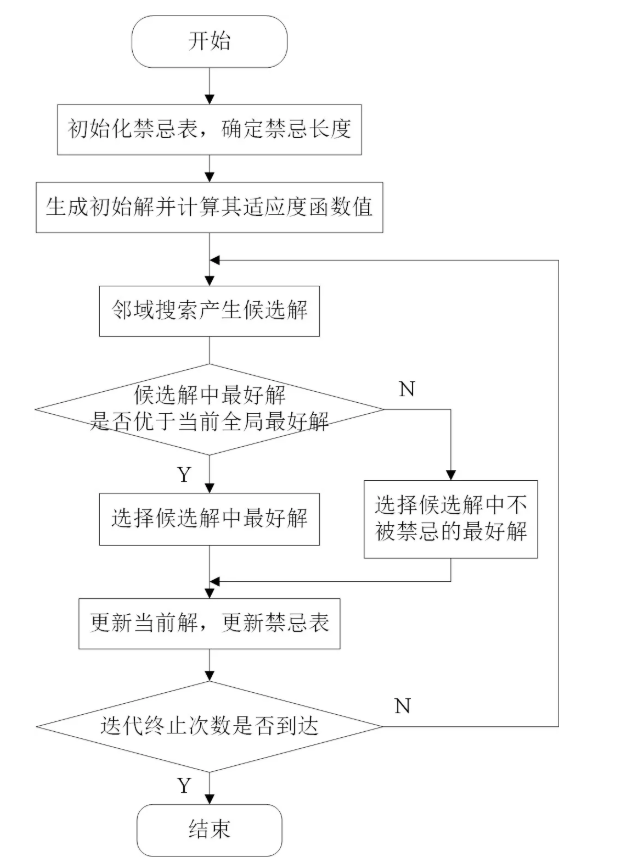
(3)设定适配值的偏离阈值。TS算法流程图:
2.3 禁忌搜索特点
- 禁忌搜索适用于离散优化,不适合实优化
- 局部邻域搜索:贪婪、持续在当前的邻域中搜索,直至领域中没有更好的解
三、TS算法举例
由7层不同的绝缘材料构成的一种绝缘体,应如何排列顺序,可获得最好的绝缘性能。
-
编码方式:顺序编码
-
初始编码:2-5-7-3-4-6-1
-
目标值:极大化目标值。
-
邻域移动:两两交换
-
禁忌表长度(TabuSize):3
-
迭代次数(NG):5
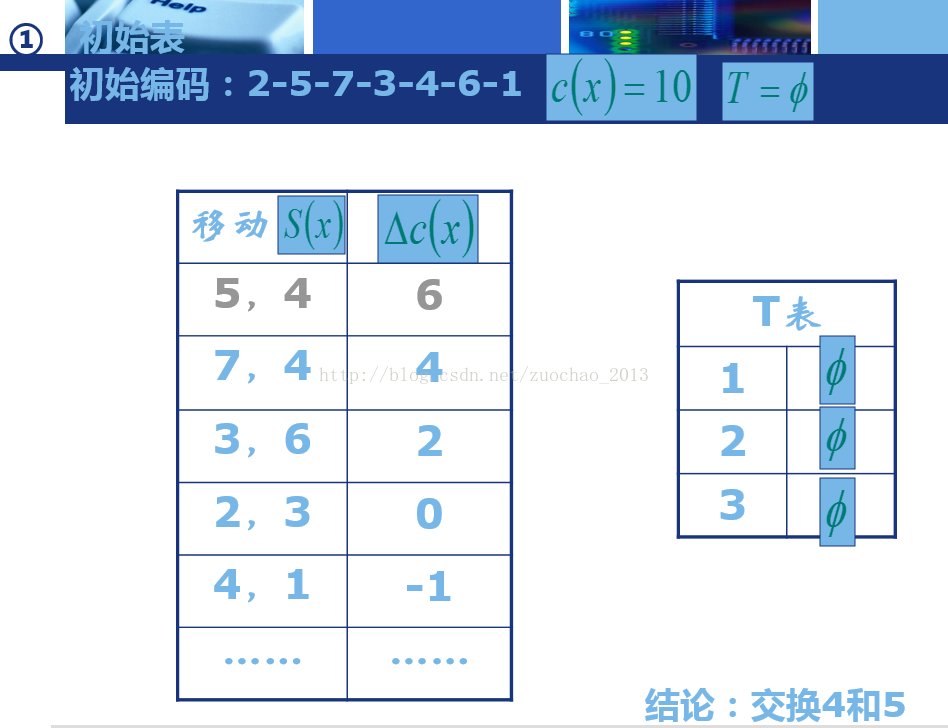
注意:左边的表为候选表,右边的表为禁忌表,若任意两两交换的次数过多可能计算缓慢,因此可以规定候选表的长度,每次随机选择两个交换,直到候选表被填满。
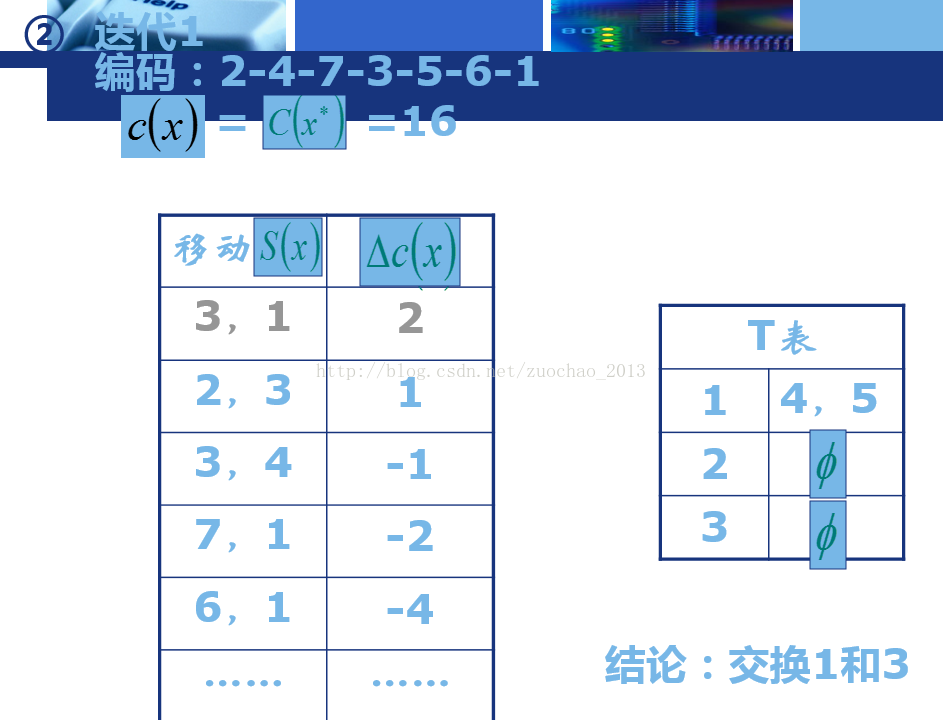
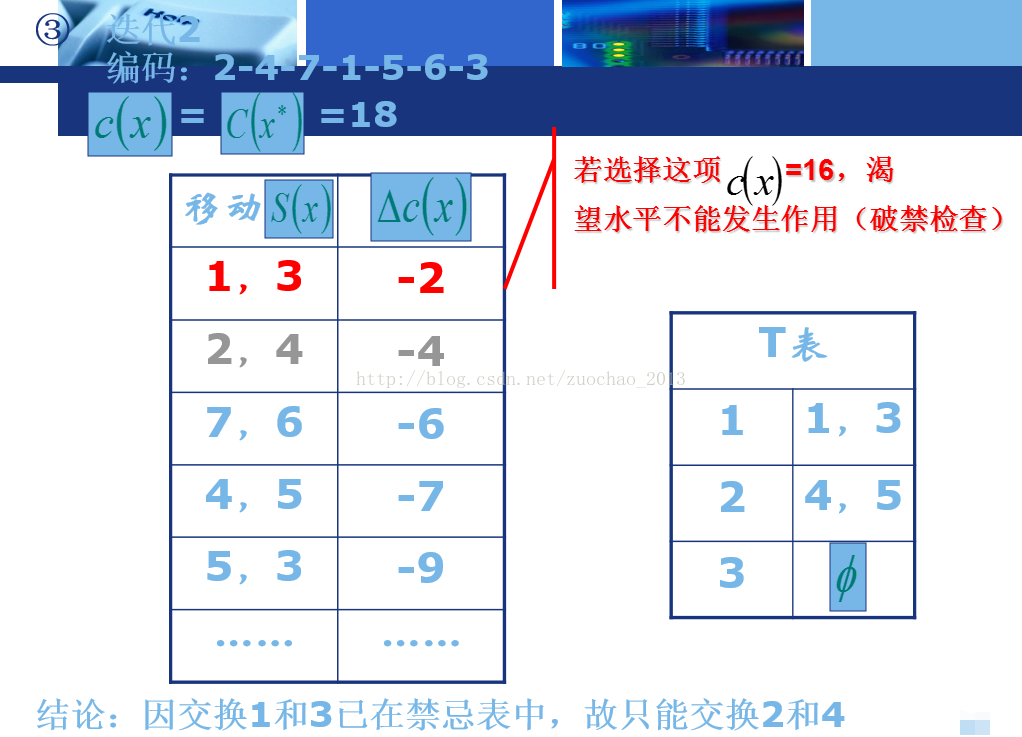
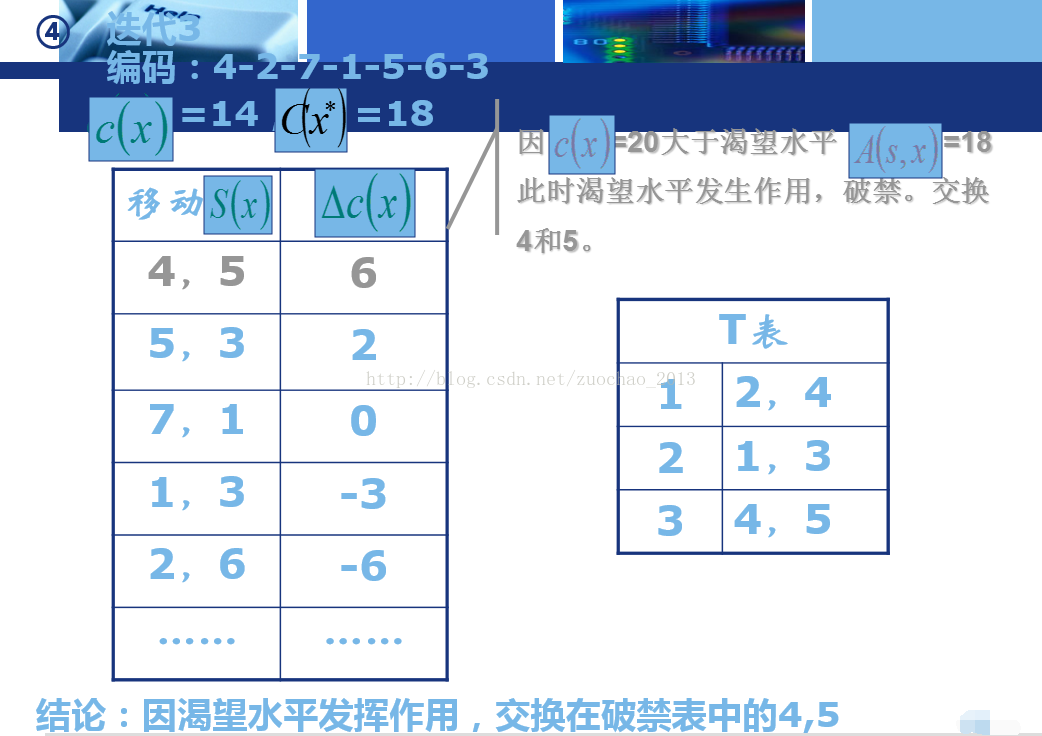
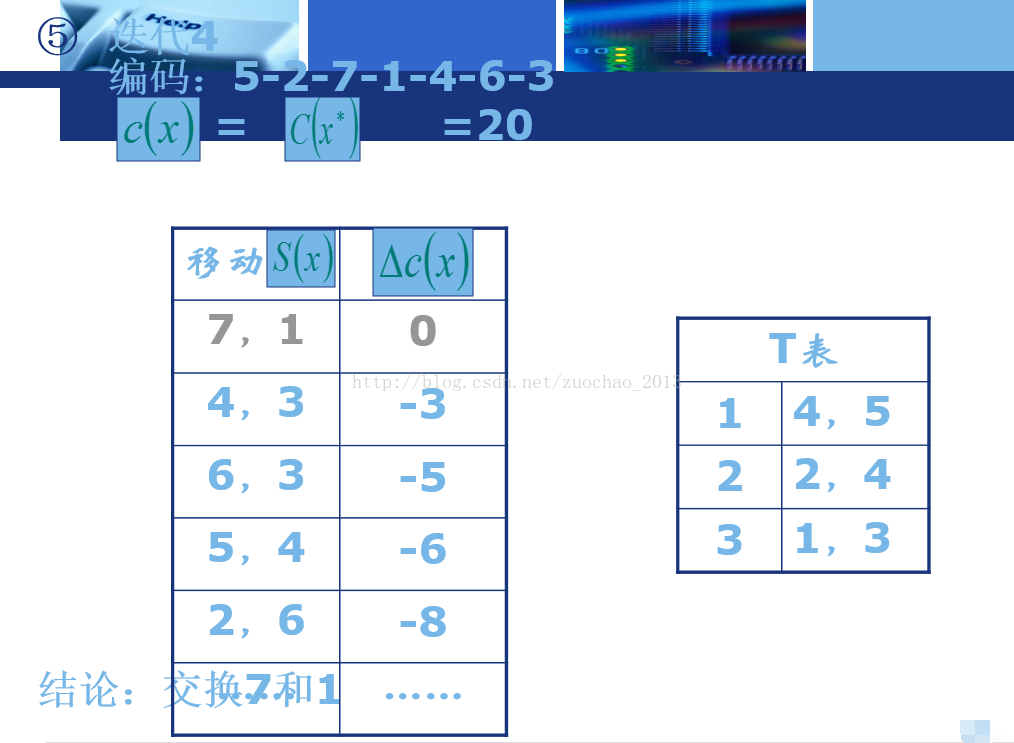
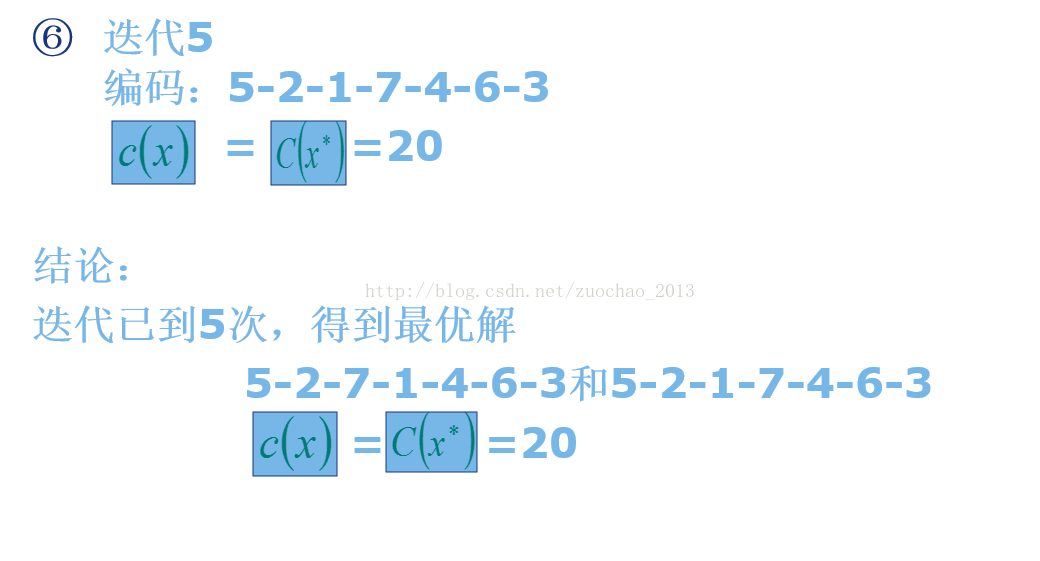
-
TS解TSP问题
TS算法受禁忌表长度、邻域选择方式、以及初始值的影响比较 严重,且经检验极易陷入局部最优值(不知道是不是参数设置原因),且耗时较长。
用python给出TS解TSP问题的代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2022/2/17 15:01
# @Author : Orange
# @File : ts1.py.py
import copy, random, datetime
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
city_list = [[1, (1150.0, 1760.0)], [2, (630.0, 1660.0)], [3, (40.0, 2090.0)], [4, (750.0, 1100.0)],
[5, (750.0, 2030.0)], [6, (1030.0, 2070.0)], [7, (1650.0, 650.0)], [8, (1490.0, 1630.0)],
[9, (790.0, 2260.0)], [10, (710.0, 1310.0)], [11, (840.0, 550.0)], [12, (1170.0, 2300.0)],
[13, (970.0, 1340.0)], [14, (510.0, 700.0)], [15, (750.0, 900.0)], [16, (1280.0, 1200.0)],
[17, (230.0, 590.0)], [18, (460.0, 860.0)], [19, (1040.0, 950.0)], [20, (590.0, 1390.0)],
[21, (830.0, 1770.0)], [22, (490.0, 500.0)], [23, (1840.0, 1240.0)], [24, (1260.0, 1500.0)],
[25, (1280.0, 790.0)], [26, (490.0, 2130.0)], [27, (1460.0, 1420.0)], [28, (1260.0, 1910.0)],
[29, (360.0, 1980.0)]
]
class Taboo_search:
def __init__(self, city_list, candidate_count, taboo_list_length, iteration_count, is_random=True):
self.city_list = city_list # 城市列表
self.candidate_count = candidate_count # 候选集合长度
self.taboo_list_length = taboo_list_length # 禁忌长度
self.iteration_count = iteration_count # 迭代次数
self.min_route, self.min_cost = self.random_first_full_road() if is_random else self.greedy_first_full_road() # 最小解;最小目标值
self.taboo_list = [] # 禁忌表
# 计算两城市间的距离
def city_distance(self, city1, city2):
distance = ((float(city1[1][0] - city2[1][0])) ** 2 + (float(city1[1][1] - city2[1][1])) ** 2) ** 0.5
return distance
# 获取当前城市邻居城市中距离最短的一个
def next_shotest_road(self, city1, other_cities):
tmp_min = 999999
tmp_next = None
for i in range(0, len(other_cities)):
distance = self.city_distance(city1, other_cities[i])
# print(distance)
if distance < tmp_min:
tmp_min = distance
tmp_next = other_cities[i]
return tmp_next, tmp_min
# 随机生成初始线路
def random_first_full_road(self):
cities = copy.deepcopy(self.city_list)
cities.remove(cities[0])
route = copy.deepcopy(cities)
random.shuffle(route)
# route = [[6, (1030.0, 2070.0)], [5, (750.0, 2030.0)], [29, (360.0, 1980.0)], [3, (40.0, 2090.0)],
# [26, (490.0, 2130.0)], [9, (790.0, 2260.0)], [12, (1170.0, 2300.0)], [28, (1260.0, 1910.0)],
# [8, (1490.0, 1630.0)], [27, (1460.0, 1420.0)], [24, (1260.0, 1500.0)], [13, (970.0, 1340.0)],
# [16, (1280.0, 1200.0)], [23, (1840.0, 1240.0)], [7, (1650.0, 650.0)], [25, (1280.0, 790.0)],
# [19, (1040.0, 950.0)], [11, (840.0, 550.0)], [22, (490.0, 500.0)], [17, (230.0, 590.0)],
# [14, (510.0, 700.0)], [18, (460.0, 860.0)], [15, (750.0, 900.0)], [4, (750.0, 1100.0)],
# [10, (710.0, 1310.0)], [20, (590.0, 1390.0)], [2, (630.0, 1660.0)],
# [21, (830.0, 1770.0)]] # 将初始值设置为遗传算法的最优值
cost = self.route_cost(route)
return route, cost
# 根据贪婪算法获取初始线路
def greedy_first_full_road(self):
remain_city = copy.deepcopy(self.city_list)
current_city = remain_city[0]
road_list = []
remain_city.remove(current_city)
all_distance = 0
while len(remain_city) > 0:
next_city, distance = self.next_shotest_road(current_city, remain_city)
all_distance += distance
road_list.append(next_city)
remain_city.remove(next_city)
current_city = next_city
all_distance += self.city_distance(self.city_list[0], road_list[-1])
return road_list, round(all_distance, 2)
# 随机交换2个城市位置
def random_swap_2_city(self, route):
# print(route)
road_list = copy.deepcopy(route)
two_rand_city = random.sample(road_list, 2)
# print(two_rand_city)
index_a = road_list.index(two_rand_city[0])
index_b = road_list.index(two_rand_city[1])
road_list[index_a] = two_rand_city[1]
road_list[index_b] = two_rand_city[0]
return road_list, sorted(two_rand_city)
# 计算线路路径长度
def route_cost(self, route):
road_list = copy.deepcopy(route)
current_city = self.city_list[0]
while current_city in road_list:
road_list.remove(current_city)
all_distance = 0
while len(road_list) > 0:
distance = self.city_distance(current_city, road_list[0])
all_distance += distance
current_city = road_list[0]
road_list.remove(current_city)
all_distance += self.city_distance(current_city, self.city_list[0])
return round(all_distance, 2)
# 获取下一条线路
def single_search(self, route):
# 生成候选集合列表和其对应的移动列表
candidate_list = []
candidate_move_list = []
while len(candidate_list) < self.candidate_count: # 在候选集合里放candidate_count条不重复路径
tmp_route, tmp_move = self.random_swap_2_city(route)
# print("tmp_route:",tmp_route)
if tmp_route not in candidate_list:
candidate_list.append(tmp_route)
candidate_move_list.append(tmp_move)
# 计算候选集合各路径的长度
candidate_cost_list = []
for candidate in candidate_list:
candidate_cost_list.append(self.route_cost(candidate))
# print(candidate_list)
min_candidate_cost = min(candidate_cost_list) # 候选集合中最短路径
min_candidate_index = candidate_cost_list.index(min_candidate_cost)
min_candidate = candidate_list[min_candidate_index] # 候选集合中最短路径对应的线路
move_city = candidate_move_list[min_candidate_index]
if min_candidate_cost < self.min_cost:
# 若满足这个条件不管禁忌对象是否在禁忌表内,都直接更新禁忌表
self.min_cost = min_candidate_cost
self.min_route = min_candidate
if move_city in self.taboo_list: # 破禁法则,当此移动导致的值更优,则无视该禁忌列表
self.taboo_list.remove(move_city)
if len(self.taboo_list) >= self.taboo_list_length: # 判断该禁忌列表长度是否以达到限制,是的话移除最初始的move
self.taboo_list.remove(self.taboo_list[0])
self.taboo_list.append(move_city) # 将该move加入到禁忌列表
return min_candidate
else:
# 当未找到更优路径时,选择次优路线,如果该次优路线在禁忌表里,则更次一层,依次类推,找到一条次优路线
if move_city in self.taboo_list:
tmp_min_candidate = min_candidate
tmp_move_city = move_city
while move_city in self.taboo_list: # 若候选最优禁忌对象已经在T表,寻找次优禁忌对象,若已在T表,.....
candidate_list.remove(min_candidate)
candidate_cost_list.remove(min_candidate_cost)
candidate_move_list.remove(move_city)
min_candidate_cost = min(candidate_cost_list) # 候选集合中次优路径
min_candidate_index = candidate_cost_list.index(min_candidate_cost)
min_candidate = candidate_list[min_candidate_index] # 候选集合中最短路径对应的线路
move_city = candidate_move_list[min_candidate_index]
if len(candidate_list) < 10: # 防止陷入死循环,在候选集个数小于10的时候跳出
min_candidate = tmp_min_candidate
move_city = tmp_move_city
if len(self.taboo_list) >= self.taboo_list_length: # 判断该禁忌列表长度是否以达到限制,是的话移除最初始的move
self.taboo_list.remove(self.taboo_list[0])
self.taboo_list.append(move_city)
return min_candidate
# 进行taboo_search直到达到终止条件:循环100次
def taboo_search(self):
route = copy.deepcopy(self.min_route)
for i in range(self.iteration_count):
route = self.single_search(route)
new_route = [self.city_list[0]]
new_route.extend(self.min_route)
new_route.append(self.city_list[0]) # 前后插入首个城市信息
return new_route, self.min_cost
# 画线路图
def draw_line_pic(route, cost, duration, desc):
x = []
y = []
for item in route:
x.append(item[1][0])
y.append(item[1][1])
x_org = []
y_org = []
point_org = []
for item in city_list:
x_org.append(item[1][0])
y_org.append(item[1][1])
point_org.append(item[0])
x0 = [x[0], ]
y0 = [y[0], ]
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.scatter(x_org, y_org, marker="o", c='g')
plt.scatter(x0, y0, marker="o", c="r")
for i in range(len(city_list)):
plt.text(x_org[i], y_org[i], point_org[i], ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10)
plt.title("Taboo_Search(" + desc + ": " + str(cost) + ")")
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
ts_random = Taboo_search(city_list=city_list, candidate_count=40, taboo_list_length=3, iteration_count=4000)
ts_greedy = Taboo_search(city_list, candidate_count=40, taboo_list_length=3, iteration_count=4000,
is_random=False)
start_time1 = datetime.datetime.now()
route_random, cost_random = ts_random.taboo_search()
end_time1 = datetime.datetime.now()
duration1 = (end_time1 - start_time1).seconds
route_greedy, cost_greedy = ts_greedy.taboo_search()
end_time2 = datetime.datetime.now()
duration2 = (end_time2 - end_time1).seconds
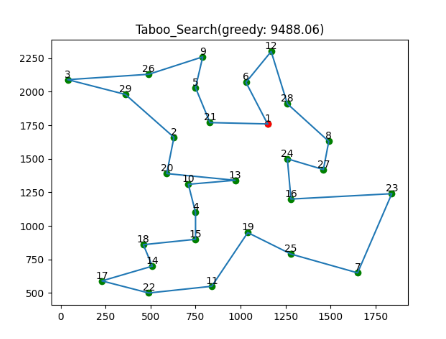
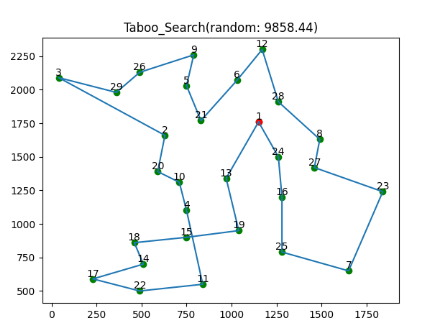
draw_line_pic(route_random, cost_random, duration1, "random")
print("最优路径:", route_random)
print("最短距离:", cost_random)
print("随机TS耗时:",end_time1-start_time1)
draw_line_pic(route_greedy, cost_greedy, duration2, "greedy")
参考:【1】禁忌搜索
最后
以上就是细心花瓣最近收集整理的关于禁忌搜索算法及TS解TSP问题禁忌搜索三、TS算法举例TS解TSP问题的全部内容,更多相关禁忌搜索算法及TS解TSP问题禁忌搜索三、TS算法举例TS解TSP问题内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复