1. 求轮廓
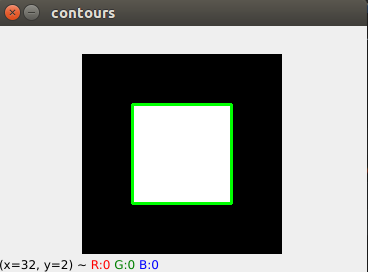
import cv2
import numpy as np
def cal_contours(image, thresh_value=0, mode=cv2.RETR_TREE, method=cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE):
"""
:param image: 单通道图像, 8-bit or 32-bit floating point
:param thresh_value: 二值化单通道图像
:param mode: Contour retrieval mode, eg
cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL:表示只提取最外面的轮廓; cv2.RETR_LIST:表示提取所有轮廓并将其放入列表;
cv2.RETR_CCOMP:表示提取所有轮廓并将组织成一个两层结构,其中顶层轮廓是外部轮廓,第二层轮廓是“洞”的轮廓;
cv2.RETR_TREE:表示提取所有轮廓并组织成轮廓嵌套的完整层级结构
:param method: Contour approximation method, eg
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE:将轮廓中的所有点的编码转换成点;
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE:压缩水平、垂直和对角直线段,仅保留它们的端点
:return:
"""
cv_major_version = int(cv2.__version__.split('.')[0]) # 获取当前版本
# multiple-channel, 8-bit or 32-bit floating point
thresh_value, thresh_img = cv2.threshold(image, thresh_value, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
if cv_major_version >= 4:
# OpenCV 4 or a later version is being used.
# an 8-bit single-channel image. Non-zero pixels are treated as 1's.
contours, hier = cv2.findContours(thresh_img, mode, method)
else:
# OpenCV 3 or an earlier version is being used.
# cv2.findContours has an extra return value.
# The extra return value is the thresholded image, which is
# unchanged, so we can ignore it.
_, contours, hier = cv2.findContours(thresh_img, mode, method)
return contours
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = np.zeros((200, 200), dtype=np.uint8)
img[50:150, 50:150] = 255
cnts = cal_contours(img)
color_img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
img = cv2.drawContours(color_img, cnts, -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow("contours", color_img), cv2.waitKey(), cv2.destroyAllWindows()
2. 求外接矩形
原图: 效果图:

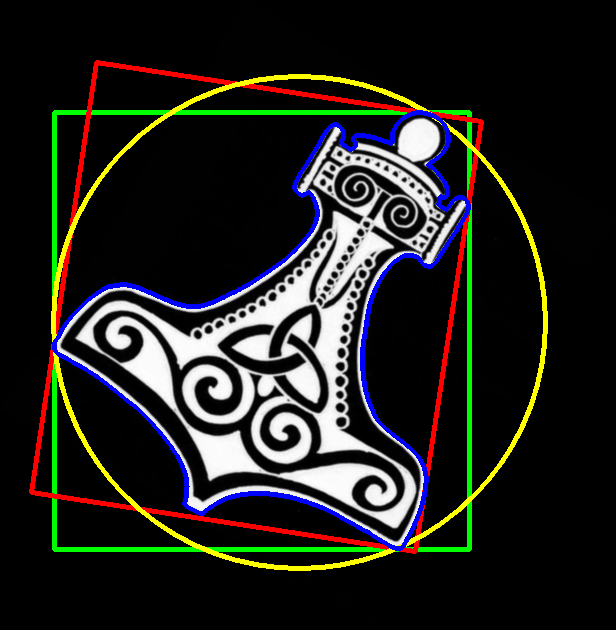
import cv2
import numpy as np
from chapter03.contours import cal_contours
def cal_min_area_rect(contour):
"""
找到最小的带旋转的外接矩形
:param contour:
:return:
"""
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(contour) # Finds a rotated rectangle of the minimum area enclosing the input 2D point set.
# calculate coordinates of the minimum area rectangle
box = cv2.boxPoints(rect) # Finds the four vertices of a rotated rect.
# normalize coordinates to integers
box = np.int0(box) # numpy.int64. four vertices
return box
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = cv2.pyrDown(cv2.imread("hammer.jpg", cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED))
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
contours = cal_contours(gray_img, thresh_value=127, mode=cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, method=cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for c in contours:
# 1, find bounding box coordinates
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c) # 轮廓的外接矩形
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 3) # 没有旋转的外接矩形,绿色
# 2, 找到最小的带旋转的外接矩形
box = cal_min_area_rect(c)
# draw contours
cv2.drawContours(img, [box], 0, (0, 0, 255), 3)
# 3, calculate center and radius of minimum enclosing circle
(x, y), radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(c)
# cast to integers
center = (int(x), int(y))
radius = int(radius)
# draw the circle
img = cv2.circle(img, center, radius, (0, 255, 255), 3)
cv2.drawContours(img, contours, -1, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv2.imshow("contours", img)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
3. 凸包
原图: 效果图:
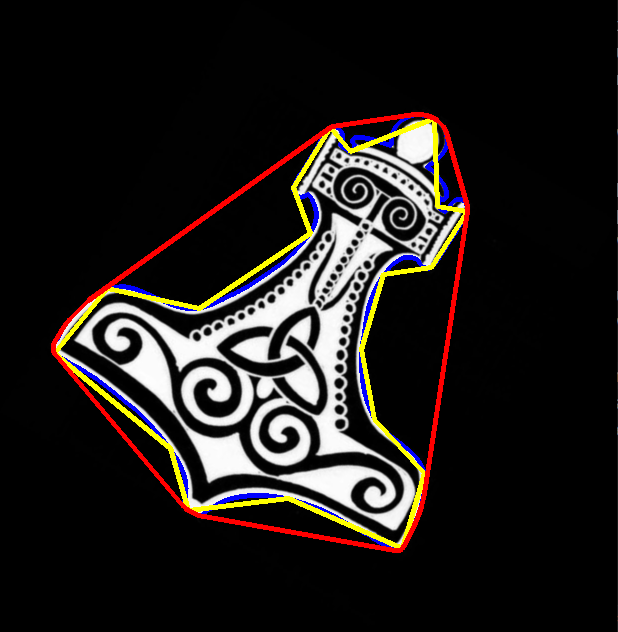


import cv2
import numpy as np
from chapter03.contours import cal_contours
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = cv2.pyrDown(cv2.imread("hammer.jpg", cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED))
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
contours = cal_contours(gray_img, 127, mode=cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, method=cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for cnt in contours: # 只有一个
# 1, 轮廓,蓝色
cv2.drawContours(img, [cnt], -1, (255, 0, 0), 3)
# 2, 多边形,黄色
epsilon = 0.01 * cv2.arcLength(cnt, True) # 0.01 * 周长
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt, epsilon, True) # 以指定的精度近似多边形曲线。 (num, 1, 2)
cv2.drawContours(img, [approx], -1, (0, 255, 255), 3)
# 3, 凸包,红色
hull = cv2.convexHull(cnt) # 轮廓的凸包。(num1, 1, 2)
cv2.drawContours(img, [hull], -1, (0, 0, 255), 3)
cv2.imshow("hull", img)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
最后
以上就是自由水壶最近收集整理的关于opencv 求轮廓、外接矩形、凸包等-06的全部内容,更多相关opencv内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复