证书和CA指令
- 证书生命周期
- 证书封装类型
- 证书使用
- 证书应用模型
- 证书链
- 用户身份确认
- OpenSSL支持的CA指令
- 申请证书
- req指令
- 生成证书密钥
- 使用RSA密钥生成证书请求
- 使用DSA密钥生成证书请求
- 双证书
- 在证书请求中增加扩展项
- 申请用户证书请求
- 申请 CA 证书请求
- 建立CA
- CA 服务器的基本功能
- CA 服务器的基本要素
- OpenSSL 模拟 CA 服务器结构
- OpenSSl 配置文件
- 建立基于 OpenSSL 的 CA 服务器
- CA 操作
- 指令格式
- 在证书中增加扩展项
- 签发用户证书
- 签发下级 CA 证书
- 建立多级 CA
- 使用证书
- X.509 证书
- CRL
- PCKS#12 证书
- PCKS#7 证书
- 验证证书
- 证书验证过程
- verify 指令介绍
- 在线状态服务程序指令 ocsp
证书生命周期
| 证书生命流程 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 证书申请 | 生成密钥对(使用genrsa、gendsa或req),填写用户信息,并将公钥和用户信息一起交给CA验证 |
| 证书颁发 | 首先验证证书请求上的签名;查阅证书请求用户信息(匹配、支持或可选);签发(ca或x509指令) |
| 证书验证 | 验证CA数字签名、证书的有效期、证书是否被吊销(verify或者ocsp) |
| 证书吊销 | 从CA的证书数据库中删除被吊销的证书;生成和公布证书吊销列表CRL(ca的revoke选项) |
| 证书过期 | 证书过期后,CA需要更新证书库中已经过期的证书的状态(ca指令对应updatedb更新数据库中证书的标记状态) |
证书封装类型
- X.509证书:X.509证书包含的内容主要是用户信息、整数序列号、签发者、有效期、公钥、其他信息及CA的数字签名。如果要在Windows平台查看和管理X.509证书,需要将X.509证书文件后缀名改成cer、der或者crt。OpenSSL本身的ca指令颁发的证书是X.5009标准格式。
- PKCS#12证书:PCKS#12格式证书可以将证书和其相应的私钥封装在一起。PKCS#12采用了PKCS#8的私钥封装格式对私钥进行了基于口令的加密。
- PKCS#7证书:所谓证书链,就是一个用户证书和一系列与其证书相关的CA证书的有序集合。PKCS#7证书可以包含多个证书和CRL。
| 证书类型 | 证书内容 | 适用范围 | OpenSSL支持 | Windows后缀 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X.509 | 用户信息、公钥、序列号、CA签名和其他证书信息 | 用户和被验证用户处于同一个CA域内的验证模型,用户不需要考虑私钥存储的问题 | 生成、适用和其他管理都支持 | der、cer、crt |
| PKCS#12证书 | X.509证书和其相应私钥 | 需要同时使用X.509证书和其私钥的应用,比如导入证书到IE或Netscape浏览器 | 生成、使用和其他管理都基本支持 | pfx、p12 |
| PKCS#7证书 | 多个X.509证书和CRL | 需要同时使用多个用户证书和CRL的验证过程或其他应用 | 生成和管理支持 | p7 |
证书使用
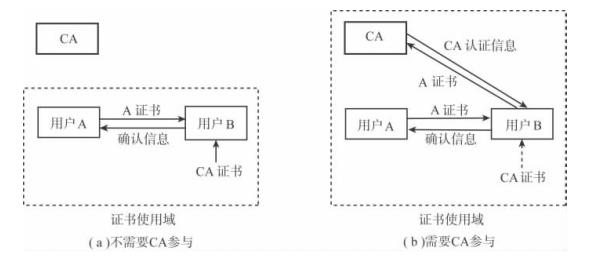
证书应用模型
证书链
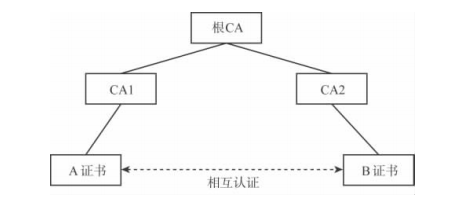
用户A和用户B的证书是不同的CA签发的,CA1和CA2,但具有相同的根证书CA。证书链的认证流程如下:
- A将自己的证书、CA1的证书和根CA证书发送给B;
- B接收到A发送过来的整个证书链后,B从CA1提取公钥,验证用户证书A的合法性和有效性;
- B从根CA提取公钥,验证CA1证书的合法性和有效性;
- B利用根CA的公钥验证根CA证书的合法性和有效新(因为它是一个自签发根证书);
- B查找自己的信任证书库(通常是一些根CA的列表),看看上述通过验证的根CA是否在信任列表中,如果在,那么验证通过,否则验证不通过。
用户身份确认
证书验证通过后,还需要确认用户身份。一般的做法是,提取证书中的公钥并使用公钥加密一个随机数,然后发送给用户,要求用户解密并返回该数据。
OpenSSL支持的CA指令
| 指令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| req | 根据给定的密钥对或者新生成的密钥对按OpenSSL配置文件指定的要求生成符合pkcs#10的证书请求。此外,还支持生成自签名根证书的功能 |
| ca | 该指令模拟了一个ca服务器的功能和操作,包括签发证书、吊销证书、产生CRL等证书相关管理操作 |
| x509 | 该指令是一个显示X.509证书内容和签发证书的工具,具备了使用特定私钥和证书进行证书签发的功能 |
| verify | 验证证书程序 |
| ocsp | 支持在线证书验证协议的指令,可以处理OCSP协议的一些标准格式信息操作,生成OCSP请求发送给其他OCSP服务器,甚至可以自己模拟一个OCSP服务程序 |
| crl | 处理和显示CRL文件信息 |
| crl2pkcs7 | 将CRL和其他证书封装成PKCS#7证书 |
| pkcs12 | 将X.509证书和其相应私钥封装成PKCS#12证书,或者将PKCS#12证书转换位X.509证书 |
| pkcs7 | 处理PKCS#7的证书,并可以将之转换位普通格式证书 |
申请证书
req指令
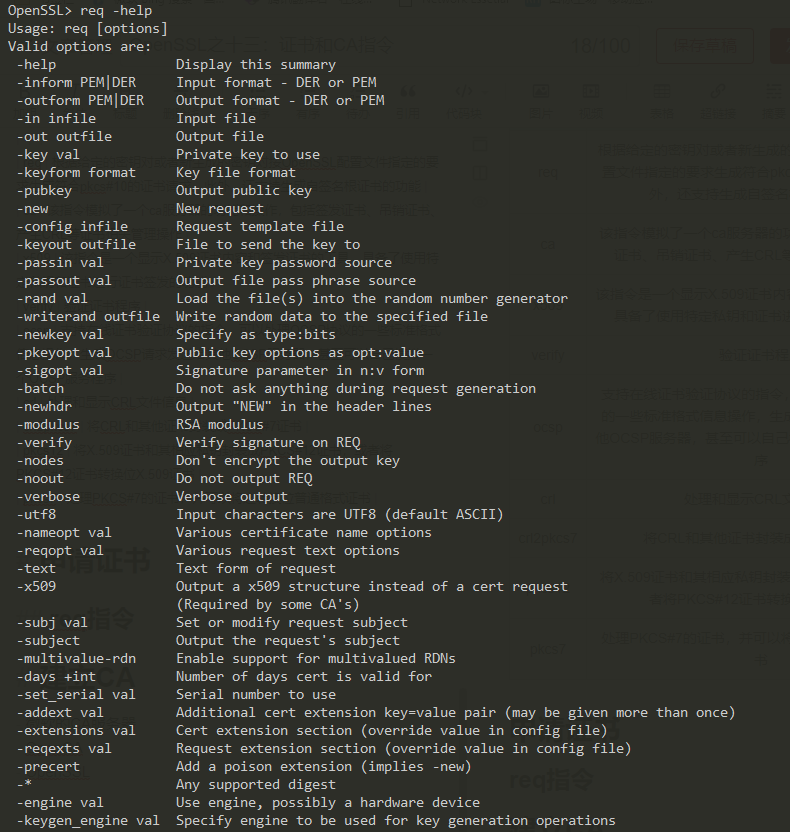
req指令选项:
| 选项 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| in | 指定了保存证书请求的文件名,默认是标准输入 |
| out | 指定了输出文件名,默认是标准输出 |
| key | 指定了输入私钥的文件,该文件内的私钥编码格式由keyform指定 |
| keyout | 指定了新生成的私钥的输入保存文件,默认为OpenSSL配置文件中req字段default_keyfile选项的参数中获取输出私钥文件名 |
| inform | 指定了选项in指定的输入证书请求文件的编码格式 |
| outform | 指定了输出选项out输出的证书请求或自签发证书的编码格式 |
| keyform | 指定了输入选项key指定的密钥编码格式 |
| passin | 指定了读取key选项指定的私钥所需要的解密口令 |
| passout | 指定了使用keyout选项输出私钥时使用的加密口令 |
| pubkey | 指定输出PEM编码公钥到out指定文件中 |
| new | 告诉指令生成新的证书请求操作,此时in选项指定的输入文件会被忽略 |
| newkey | 告诉指令生成一个新的密钥对,该选项只有在没有使用key选项时才有效,newkey选项包含rsa:numbite和dsa:file两种形式 |
| nodes | 告诉指令不对新生成的私钥进行加密保存,此时passout选项会被忽略 |
| x509 | 告诉指令生成一个自签名证书而不是输出一个证书请求 |
| * | 支持的算法类型 |
| subj | 从指令行指定证书的主体名称,没有改选项,req指令默认从主配置文件获取国家代号、省份、单位名称等 |
| days | 设定了生成的自签名根证书的有效期,单位是天,只有在使用x509时才有效 |
| set_serial | 指定了生成的自签名根证书的序列号,默认根序列号时0,只有在使用x509时才有效 |
| config | 指定req指定在生成证书请求的使用使用的OpenSSL配置文件,默认为openssl.cnf |
| extensions | 指定了生成自签名根证书的时候使用的扩展字段,比如openssl.cnf文件中的v3_ca字段 |
| reqexts | 指定了生成证书请求时使用的扩展字段,比如openssl.cnf文件中的v3_req字段 |
| newhdr | 使用该选后将会在输出的PEM编码的证书请求开始和结束行增加“NEW”标记字符串 |
| utf8 | 使用该选项后,输出信息将采用UTF8编码,默认时ASCII编码 |
| noout | 使用该选项后,指令将不会输出编码的证书请求或自签发证书到out选项指定的文件中 |
| subject | 告诉指令输出主题名信息,即使text选项已经输出,该选项还会再次输出 |
| reqopt | 指定text输出的内容 |
| nameopt | 输出字符编码选项,指定了如何显示主体名称和签发者名称,主要用于演示名称后不同编码的内容 |
| verify | 对证书请求的数字签名进行验证操作,并给出失败或者成功的提示信息 |
| rand | 指定了生成密钥对或者其他一些操作需要的随机种子文件 |
| batch | 使用该选项将不在提示用户输入生成证书请求需要的用户信息,而是直接从主 |
| verbose | 输出执行各个操作的详细信息 |
自签名证书:指用一对密钥对的私钥对自己相应的公钥生成的证书请求进行签名而颁发证书,这样证书申请人和签发人都是同一个,所以称为自签名根证书。如果证书不用于根CA,那么一般来说只有测试的意义。
生成证书密钥
使用RSA密钥生成证书请求
#方式1:直接使用req指令生成RSA密钥用于证书请求(缺点是私钥加密只能使用DES3-CBC,输出编码只能是PEM)
OpenSSL> req -new -newkey rsa:1024 -keyout RSAPrivateKey.pem -out RSAReq.pem -passout pass:12345678
#方式2:使用genrsa和req生成证书请求
#第一步
OpenSSL> genrsa -aes256 -passout pass:12345678 -out RSAPrivateKey.pem 1024
#第二步:
OpenSSL> req -new -key RSAPrivateKey.pem -passin pass:12345678 -out RSAReq.pem
使用DSA密钥生成证书请求
#方式1:使用dsaparam和req指令生成DSA密钥用于证书请求(缺点是私钥加密只能使用DES3-CBC,输出编码只能是PEM)
#第一步
OpenSSL> dsaparam -out DSAParam.pem 1024
#第二步
OpenSSL> req -new -newkey dsa:DSAParam.pem -keyout DSAPrivateKey.pem -out DSAReq.pem -passout pass:12345678
#方式2:使用dsaparam、genrsa和req指令生成证书请求
#第一步
OpenSSL> dsaparam -out DSAParam.pem 1024
#第二步
OpenSSL> gendsa -out DSAPrivateKey.pem -aes256 -passout pass:12345678 DSAParam.pem
#第三步
OpenSSL> gendsa -out DSAPrivateKey.pem -aes256 -passout pass:12345678 DSAParam.pem
双证书
一个整数用于密钥交换,一个证书用于数字签名。用于密钥交换的证书其密钥对一般由CA或者RA代替用户产生;而用于数字签名的证书的密钥则由用户自己产生。
在证书请求中增加扩展项
在某些特殊情况下,需要在证书中扩展一些标记以便实现一些特定的功能,比如,你可能需要在给你公司员工发放的证书中增加一项权限的功能,这可能给会给管理带来很大的方便,尤其对于有多个服务器的分布式系统中,这种证书尤其有用。
首先保证 openssl.cnf 文件中 oid_section = new_oids 没有被注释,然后在 [new_oids] 字段中定义一个 OID,其简短名和长名都是 UserRights, OID 为 2.5.4.555:
[ new_oids ]
......
......
UserRights=2.5.4.555
......
......
然后在 [ req_distinguished_name ] 字段中添加自定义配置:
[ req_distinguished_name ]
UserRights = User Rights
UserRights_default = US
UserRights_min = 2
UserRights_max = 2
申请用户证书请求
证书按照其在证书链中的位置分类,一般可以分为两种:终端用户证书和 CA 证书。所谓 CA 证书,是指该证书可以用于签发别的用户证书,也就是说,它可以有下级的证书。终端用户证书则用于具体应用程序或协议中,它不能用来签发别的证书,在证书链中,它处于最末端。
首先保证 openssl.cnf 配置文件中 v3_req 生效:req_extensions = v3_req 没有被注释,然后修改 [ v3_req ] 配置项:
[ v3_req ]
# Extensions to add to a certificate request
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
申请 CA 证书请求
如果你要申请一个临时的 CA 证书,你可能并不需要签发这个证书,只需要生成一个申请一个 CA 证书的请求,然后发给上级 CA,然后等待它的签发就可以了。怎样生成一个 CA 证书请求,而不是用户证书请求呢?首先保证 openssl.cnf 配置文件中 v3_req 生效:req_extensions = v3_req 没有被注释,然后修改 [ v3_req ] 配置项:
[ v3_req ]
# Extensions to add to a certificate request
basicConstraints = CA:TRUE
建立CA
有了 OpenSSl,建立一个 CA 服务器非常简单。这里我们需要直到 CA 服务器只是一个技术上的基础程序,而 CA 则是一个集技术个管理于一体的庞大机构。
CA 服务器的基本功能
- 接受证书请求:在线实时提交、在线非实时提交和本地提交
- 审核证书请求
- 签发证书
- 发布证书,发布对象有两种:一种是申请证书的用户本人,必须让他能够及时获得自己的证书;一种是其他用户,可以向他们提供获得所有用户证书的途径。一般通过 WEB 方式或 LDAP 方式发布。
- 吊销证书
- 生成和发布 CRL
- 证书库管理
CA 服务器的基本要素
- 一个具备基本功(CA 服务器基本功能)能的 CA 应用程序,可以使用 OpenSSL 的 ca 指令作为 CA 应用程序,当然也可以使用微软的CA服务器或 OpenCA。
- 一个 CA 证书和一个其相应的私钥,可能是自签名的根证书,也可能是向另一个 CA 申请的证书。如果我们搭建的 CA 服务自称体系,并不需要上级 CA 支持,那么使用 OpenSSL 的 req 指令生成一个自签名根证书作为 CA 服务器的证书即可;如果需要上级 CA 支持,只需要生成一个 CA 证书请求发送给上级 CA,然后等待上级 CA 签发你的证书。
- 证书数据库,用于存储证书(有时候还包括私钥)。可以使用 Mysql、Oracle、SQLServer 数据库,或自定义的文本数据库。
OpenSSL 模拟 CA 服务器结构
demoCA 根目录
|____newcerts 目录(存放新证书,如 01.pem)
|____cers 目录(存放签发者证书)
|____private 目录(存放私钥文件)
| |____cakey.pem(CA 私钥)
|____crl 目录(存放 CA 的 CRL)
|____cacert.pem 文件(CA 证书)
|____index.txt 文件(文本证书库)
|____serial 文件(序列号文件)
OpenSSl 配置文件
[ CA_default ]
dir = ./demoCA
certs = $dir/certs
crl_dir = $dir/crl
database = $dir/index.txt
new_certs_dir = $dir/newcerts
certificate = $dir/cacert.pem
serial = $dir/serial
crlnumber = $dir/crlnumber
crl = $dir/crl.pem
private_key = $dir/private/cakey.pem
RANDFILE = $dir/private/.rand
建立基于 OpenSSL 的 CA 服务器
- 手动创建一个 CA 目录结构
- 在 OpenSSL 目录下创建 demoCA 目录
- 在 demoCA 目录下创建 newcerts、cers、private、crl 子目录
- 在 demoCA 目录下创建 index.txt 空文件
- 在 demoCA 目录下创建 serial 文件,文件内容为
01 - 将 CA 证书文件转换为 pem 格式,复制到 demoCA 根目录,命名为 cacert.pem
- 将 CA 私钥文件转换为 pem 格式,复制到 demoCA 根目录,命名为 cakey.pem
CA 证书和私钥可以使用自签名证书和私钥,生成命令:
OpenSSL> req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout cakey.pem -out cacert.pem - 自动创建一个 CA 目录结构
将 OpenSSL 的 apps 目录下的 ca.pl 文件赋值到你想创建 CA 目录的目录,然后运行下面的命令:
OpenSSL> perl ca.pl -newca
接下来该指令会提示输入已有的 CA 证书或者直接按 Enter 建创建一个自签名的根证书。执行完成后 CA 的目录结构就会自动创建完成。如果你想使用已经申请到的 CA 证书作为 CA 证书,那么将证书和私钥转换为 pem 格式,并将其替代 CA 目录下的 cacert.pem 和 cakey.pem。
- 指定 OpenSSL 配置文件
- Linux 环境下默认的 OpenSSL 配置文件路径是
/usr/local/ssl/openssl.cnf - Windows 环境下可以通过设置环境变量 OPENSSL_CONF 或 SSLEAY_CONF 来指定 openssl.cnf 的位置,也可直接在指令环境中输入:
OpenSSL> set OPENSSL_CONF=C:OpenSSLopenssl.cnf - 使用 ca 指令的 config 选项来指定
- Linux 环境下默认的 OpenSSL 配置文件路径是
CA 操作
指令格式
C:UsersSunny
λ openssl.exe ca -help
Usage: ca [options]
Valid options are:
-help Display this summary
-verbose Verbose output during processing
-config val A config file
-name val The particular CA definition to use
-subj val Use arg instead of request's subject
-utf8 Input characters are UTF8 (default ASCII)
-create_serial If reading serial fails, create a new random serial
-rand_serial Always create a random serial; do not store it
-multivalue-rdn Enable support for multivalued RDNs
-startdate val Cert notBefore, YYMMDDHHMMSSZ
-enddate val YYMMDDHHMMSSZ cert notAfter (overrides -days)
-days +int Number of days to certify the cert for
-md val md to use; one of md2, md5, sha or sha1
-policy val The CA 'policy' to support
-keyfile val Private key
-keyform format Private key file format (PEM or ENGINE)
-passin val Input file pass phrase source
-key val Key to decode the private key if it is encrypted
-cert infile The CA cert
-selfsign Sign a cert with the key associated with it
-in infile The input PEM encoded cert request(s)
-out outfile Where to put the output file(s)
-outdir dir Where to put output cert
-sigopt val Signature parameter in n:v form
-notext Do not print the generated certificate
-batch Don't ask questions
-preserveDN Don't re-order the DN
-noemailDN Don't add the EMAIL field to the DN
-gencrl Generate a new CRL
-msie_hack msie modifications to handle all those universal strings
-crldays +int Days until the next CRL is due
-crlhours +int Hours until the next CRL is due
-crlsec +int Seconds until the next CRL is due
-infiles The last argument, requests to process
-ss_cert infile File contains a self signed cert to sign
-spkac infile File contains DN and signed public key and challenge
-revoke infile Revoke a cert (given in file)
-valid val Add a Valid(not-revoked) DB entry about a cert (given in file)
-extensions val Extension section (override value in config file)
-extfile infile Configuration file with X509v3 extensions to add
-status val Shows cert status given the serial number
-updatedb Updates db for expired cert
-crlexts val CRL extension section (override value in config file)
-crl_reason val revocation reason
-crl_hold val the hold instruction, an OID. Sets revocation reason to certificateHold
-crl_compromise val sets compromise time to val and the revocation reason to keyCompromise
-crl_CA_compromise val sets compromise time to val and the revocation reason to CACompromise
-rand val Load the file(s) into the random number generator
-writerand outfile Write random data to the specified file
-engine val Use engine, possibly a hardware device
例程:
# 使用 notext,不输出明文信息到证书文件
OpenSSL> ca -in req.pem -out cert.cer -notext
# 生成有效期在2020年9月9日 至 2021年10月10日的证书
OpenSSL> ca -notext -startdata 200909000000Z -enddata 211010000000Z -infiles req1.pem req2.pem
# 使用 Engine 中的私钥签发证书
OpenSSL> ca -in req.pem =out cert.cer -notext -cert pcks11cert.pem -keyfile pkcs11key.pem -keyform e -engine pkcs11
# 吊销证书,并指明吊销原因是密钥泄露
OpenSSL> ca -revoke cert.pem -crl_reason keyCompromise
# 吊销证书,并指明密钥泄露时间
OpenSSL> ca -revoke cert.pem -crl_compromise 2023210309000000Z
# 生成一个 CRL,并设定 CRL 更新时间为 7 天 7 小时
OpenSSL> ca -gencrl -crldays 7 -crlhours 7 -out crl.crl
# 查询证书号为 1 的证书状态
OpenSSL> ca -gencrl -crldays 7 -crlhours 7 -out crl.crl
# 更新文本证书数据库
OpenSSL> ca -updatedb
在证书中增加扩展项
首先增加 OID,然后在 [ policy_match ] 或 [ policy_anything ] 中添加扩展项。
签发用户证书
可以通过在 OpenSSL 配置文件中的 X.509 v3 扩展项 [ usr_cert ] 字段来告诉 ca 指令签发用户证书:
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
签发下级 CA 证书
首先保证 OpenSSL的 basicConstraints 配置项为 basicConstraints = CA:TRUE。
然后,如果要签发 CA 证书,则使用 extensions 选项指定 X509 v3 扩展字段为 v3_ca:
OpenSSL> ca [其它参数] -extensions v3_ca
或者直接在配置文件中配置:x509_extensions = usr_cert
建立多级 CA
建立多级 CA 的过程总结:
RootCA
________________|________________
| |
SubCA 用户证书 A
|
用户证书 B
- 使用 req 生成一个自签名根证书作为 RootCA 证书,配置 RootCA 配置文件。
- 使用 req 生成一个 CA 证书请求,并使用 RootCA 签发该请求形成 SubCA 的证书,配置 SubCA 配置文件。
- 使用 req 生成一个证书请求,并使用 SubCA 的证书签发该请求形成用户证书 B。
- 使用 req 生成一个证书请求,并使用 RootCA 的证书签发该请求形成用户证书 A。
# Step1:创建 RootCA 目录
C:UsersSunnyDesktop
λ mkdir RootCA
C:UsersSunnyDesktop
λ cd RootCA
C:UsersSunnyDesktopRootCA
λ
# Step2:将 openssl.exe、openssl.cnf、ca.pl 拷贝到 RootCA 目录,创建 demoCA 目录
# RootCA 的配置文件需要支持两个不同的 X.509 v3 扩展项,用于签发用户证书(user_cert)和 CA 证书(ca_v3)
C:UsersSunnyDesktopRootCA
λ perl ca.pl -newca
λ openssl
OpenSSL>
# Step3: 生成一个使用 2048 位密钥的自签名根证书作为 RootCA 的证书
OpenSSL> req -x509 -nerkey rsa:2048 -out rootca_cart.pem -keyout rootca_key.pem -config C:UsersSunnyDesktopRootCAopenssl.cnf
# Step4:将 rootca_cart.pem 命名为 cacert.pem 拷贝到 demoCA 根目录替换原文件,将 rootca_key.pem 命名为 cakey.pem 拷贝到 demoCA/private 目录,替换原文件
# Step5:创建 SubCA 目录
C:UsersSunnyDesktop
λ mkdir SubCA
C:UsersSunnyDesktop
λ cd SubCA
C:UsersSunnyDesktopSubCA
λ
# Step6:将 openssl.exe、openssl.cnf、ca.pl 拷贝到 RootCA 目录,创建 SubCA目录,创建 demoCA 目录
C:UsersSunnyDesktopSubCA
λ perl ca.pl -newca
# Step7:创建由 RootCA 签发的 SubCA 的证书和密钥
OpenSSL> req -new -nerkey rsa:2048 -out subca_req.pem -keyout subca_key.pem -config C:UsersSunnyDesktopSubCAopenssl.cnf
# 此时将 subca_key.pem 文件拷贝到 SubCA/demoCA/prvate 目录下,替换原文件
# Step8:将证书请求提交给 RootCA 签发,首先将 subca_req.pem 拷贝到 RootCA 目录下,执行签发命令
OpenSSL> ca -in subca_req.pem -out subca_cert.pem -notext -extensions v3_ca -config C:UsersSunnyDesktopRootCAopenssl.cnf
# 此时将 subca_cert.pem 文件命名为 cacert.pem,拷贝到 SubCA/demoCA 的根目录下,替换原文件
# 至此,RootCA 和 SubCA 已经配置完成,可以进行签发用户证书了
# Step9:签发用户证书 A,切换到 RootCA 目录下
C:UsersFengGuodongDesktopRootCA
λ openssl
OpenSSL> req -new -newkey rsa:1024 -out userA_req.pem -keyout userA_key.pem -config C:UsersSunnyDesktopRootCAopenssl.cnf
OpenSSL> ca -in userA_req.pem -out userA_cert.pem -notext -config C:UsersSunnyDesktopRootCAopenssl.cnf
# Step10:签发用户证书 B,切换到 SubCA 目录下
C:UsersFengGuodongDesktopSubCA
λ openssl
OpenSSL> req -new -newkey rsa:1024 -out userB_req.pem -keyout userB_key.pem -config C:UsersSunnyDesktopSubCAopenssl.cnf
OpenSSL> ca -in userB_req.pem -out userB_cert.pem -notext -config C:UsersSunnyDesktopSubCAopenssl.cnf
使用证书
X.509 证书
x509 指令格式:
OpenSSL> x509 -help
Usage: x509 [options]
Valid options are:
-help Display this summary
-inform format Input format - default PEM (one of DER or PEM)
-in infile Input file - default stdin
-outform format Output format - default PEM (one of DER or PEM)
-out outfile Output file - default stdout
-keyform PEM|DER|ENGINE Private key format - default PEM
-passin val Private key password/pass-phrase source
-serial Print serial number value
-subject_hash Print subject hash value
-issuer_hash Print issuer hash value
-hash Synonym for -subject_hash
-subject Print subject DN
-issuer Print issuer DN
-email Print email address(es)
-startdate Set notBefore field
-enddate Set notAfter field
-purpose Print out certificate purposes
-dates Both Before and After dates
-modulus Print the RSA key modulus
-pubkey Output the public key
-fingerprint Print the certificate fingerprint
-alias Output certificate alias
-noout No output, just status
-nocert No certificate output
-ocspid Print OCSP hash values for the subject name and public key
-ocsp_uri Print OCSP Responder URL(s)
-trustout Output a trusted certificate
-clrtrust Clear all trusted purposes
-clrext Clear all certificate extensions
-addtrust val Trust certificate for a given purpose
-addreject val Reject certificate for a given purpose
-setalias val Set certificate alias
-days int How long till expiry of a signed certificate - def 30 days
-checkend intmax Check whether the cert expires in the next arg seconds
Exit 1 if so, 0 if not
-signkey val Self sign cert with arg
-x509toreq Output a certification request object
-req Input is a certificate request, sign and output
-CA infile Set the CA certificate, must be PEM format
-CAkey val The CA key, must be PEM format; if not in CAfile
-CAcreateserial Create serial number file if it does not exist
-CAserial val Serial file
-set_serial val Serial number to use
-text Print the certificate in text form
-ext val Print various X509V3 extensions
-C Print out C code forms
-extfile infile File with X509V3 extensions to add
-rand val Load the file(s) into the random number generator
-writerand outfile Write random data to the specified file
-extensions val Section from config file to use
-nameopt val Various certificate name options
-certopt val Various certificate text options
-checkhost val Check certificate matches host
-checkemail val Check certificate matches email
-checkip val Check certificate matches ipaddr
-CAform PEM|DER CA format - default PEM
-CAkeyform PEM|DER|ENGINE CA key format - default PEM
-sigopt val Signature parameter in n:v form
-force_pubkey infile Force the Key to put inside certificate
-next_serial Increment current certificate serial number
-clrreject Clears all the prohibited or rejected uses of the certificate
-badsig Corrupt last byte of certificate signature (for test)
-* Any supported digest
-subject_hash_old Print old-style (MD5) issuer hash value
-issuer_hash_old Print old-style (MD5) subject hash value
-engine val Use engine, possibly a hardware device
-preserve_dates preserve existing dates when signing
例程:
# 查看证书内容
OpenSSL> x509 -in cert.pem -noout -text
# 查看证书序列号
OpenSSL> x509 -in cert.pem -noout -setial
# 查看证书 HASH 值
OpenSSL> x509 -in cert.pem -noout -hash
# 查看 MD5 指纹信息
OpenSSL> x509 -in cert.pem -noout -fingerprint
# PEM 格式转 DER
OpenSSL> x509 -in cert.pem inform PEM -out cert.der -outform DER
# 将证书转换为证书请求
OpenSSL> x509 -x509toreq -in cert.pem -out req.pem -signkey key.pem
CRL
所谓 CRL,即为一系列已经被吊销的证书的序列号文件。
crl 指令格式:
OpenSSL> crl -help
Usage: crl [options]
Valid options are:
-help Display this summary
-inform PEM|DER Input format; default PEM
-in infile Input file - default stdin
-outform PEM|DER Output format - default PEM
-out outfile output file - default stdout
-keyform PEM|DER Private key file format (PEM or ENGINE)
-key infile CRL signing Private key to use
-issuer Print issuer DN
-lastupdate Set lastUpdate field
-nextupdate Set nextUpdate field
-noout No CRL output
-fingerprint Print the crl fingerprint
-crlnumber Print CRL number
-badsig Corrupt last byte of loaded CRL signature (for test)
-gendelta infile Other CRL to compare/diff to the Input one
-CApath dir Verify CRL using certificates in dir
-CAfile infile Verify CRL using certificates in file name
-no-CAfile Do not load the default certificates file
-no-CApath Do not load certificates from the default certificates directory
-verify Verify CRL signature
-text Print out a text format version
-hash Print hash value
-nameopt val Various certificate name options
-* Any supported digest
-hash_old Print old-style (MD5) hash value
例程:
# CRL 文件 PEM 格式转换为 DER
OpenSSL> crl -in crl.pem -outform DER -out crl.der
# 输出 DER 格式编码的证书吊销列表的文本
OpenSSL> crl -in crl.der -text -noout
PCKS#12 证书
pkcs12 指令格式:
OpenSSL> pkcs12 -help
Usage: pkcs12 [options]
Valid options are:
-help Display this summary
-nokeys Don't output private keys
-keyex Set MS key exchange type
-keysig Set MS key signature type
-nocerts Don't output certificates
-clcerts Only output client certificates
-cacerts Only output CA certificates
-noout Don't output anything, just verify
-info Print info about PKCS#12 structure
-chain Add certificate chain
-twopass Separate MAC, encryption passwords
-nomacver Don't verify MAC
-descert Encrypt output with 3DES (default RC2-40)
-certpbe val Certificate PBE algorithm (default RC2-40)
-export Output PKCS12 file
-noiter Don't use encryption iteration
-maciter Use MAC iteration
-nomaciter Don't use MAC iteration
-nomac Don't generate MAC
-LMK Add local machine keyset attribute to private key
-nodes Don't encrypt private keys
-macalg val Digest algorithm used in MAC (default SHA1)
-keypbe val Private key PBE algorithm (default 3DES)
-rand val Load the file(s) into the random number generator
-writerand outfile Write random data to the specified file
-inkey val Private key if not infile
-certfile infile Load certs from file
-name val Use name as friendly name
-CSP val Microsoft CSP name
-caname val Use name as CA friendly name (can be repeated)
-in infile Input filename
-out outfile Output filename
-passin val Input file pass phrase source
-passout val Output file pass phrase source
-password val Set import/export password source
-CApath dir PEM-format directory of CA's
-CAfile infile PEM-format file of CA's
-no-CAfile Do not load the default certificates file
-no-CApath Do not load certificates from the default certificates directory
-* Any supported cipher
-engine val Use engine, possibly a hardware device
例程:
# 生成一个 PKCS#12 证书
OpenSSL> pkcs12 -export -in Mycert.pem -inkey Mykey.pem -out file.p12 -name "MyCert"
# 添加额外证书
OpenSSL> pkcs12 -export -in Mycert.pem -inkey Mykey.pem -out file.p12 -name "MyCert" -certfile Mycert1.pem
# 查看证书结构和信息
OpenSSL> pkcs12 -in file.p12 -info -noout
# 分解证书
OpenSSL> pkcs12 -in file.p12 -out file.pem
# 分解得到客户证书信息
OpenSSL> pkcs12 -in file.p12 -clcerts -out file.pem
PCKS#7 证书
pkcs7 指令格式:
OpenSSL> pkcs7 -help
Usage: pkcs7 [options]
Valid options are:
-help Display this summary
-inform PEM|DER Input format - DER or PEM
-in infile Input file
-outform PEM|DER Output format - DER or PEM
-out outfile Output file
-noout Don't output encoded data
-text Print full details of certificates
-print Print out all fields of the PKCS7 structure
-print_certs Print_certs print any certs or crl in the input
-engine val Use engine, possibly a hardware device
例程:
# PEM 转 DER
OpenSSL> pkcs7 -in file.pem -outform DER -out file.der
# 输出文件中的所有证书
OpenSSL> pkcs7 -in file.pem -print_certs -out certs.pem
验证证书
证书验证过程
- 确认证书内容正确完整,没有被篡改,CA 签名是正确的。
- 确认证书有效,在有效期内没有被吊销(证书序列号不在 CRL 中)。
- 确认 CA 证书是可被信任的,如果 CA 证书不是根证书,还要继续对 CA 证书进行验证。
- 通过与用户交互,基于证书中的公钥和公开密钥算法确认用户身份:
(1)被验证方发送自己的证书给验证方。
(2)验证方提前证书中的公钥,并产生一个随机数 Rp,使用该公钥加密随机数得到加密的随机数 Re,并发给被验证方。
(3)被验证方使用自己的私钥解密 Re 得到 Rep 并返回给验证方。
(4)验证方对比 Rp 和 Rep,如果一致,则验证通过,否则,验证不通过。
verify 指令介绍
指令格式:
OpenSSL> verify -help
Usage: verify [options] cert.pem...
Valid options are:
-help Display this summary
-verbose Print extra information about the operations being performed.
-CApath dir A directory of trusted certificates
-CAfile infile A file of trusted certificates
-no-CAfile Do not load the default certificates file
-no-CApath Do not load certificates from the default certificates directory
-untrusted infile A file of untrusted certificates
-trusted infile A file of trusted certificates
-CRLfile infile File containing one or more CRL's (in PEM format) to load
-crl_download Attempt to download CRL information for this certificate
-show_chain Display information about the certificate chain
-nameopt val Various certificate name options
-policy val adds policy to the acceptable policy set
-purpose val certificate chain purpose
-verify_name val verification policy name
-verify_depth int chain depth limit
-auth_level int chain authentication security level
-attime intmax verification epoch time
-verify_hostname val expected peer hostname
-verify_email val expected peer email
-verify_ip val expected peer IP address
-ignore_critical permit unhandled critical extensions
-issuer_checks (deprecated)
-crl_check check leaf certificate revocation
-crl_check_all check full chain revocation
-policy_check perform rfc5280 policy checks
-explicit_policy set policy variable require-explicit-policy
-inhibit_any set policy variable inhibit-any-policy
-inhibit_map set policy variable inhibit-policy-mapping
-x509_strict disable certificate compatibility work-arounds
-extended_crl enable extended CRL features
-use_deltas use delta CRLs
-policy_print print policy processing diagnostics
-check_ss_sig check root CA self-signatures
-trusted_first search trust store first (default)
-suiteB_128_only Suite B 128-bit-only mode
-suiteB_128 Suite B 128-bit mode allowing 192-bit algorithms
-suiteB_192 Suite B 192-bit-only mode
-partial_chain accept chains anchored by intermediate trust-store CAs
-no_alt_chains (deprecated)
-no_check_time ignore certificate validity time
-allow_proxy_certs allow the use of proxy certificates
-engine val Use engine, possibly a hardware device
Recognized usages:
sslclient SSL client
sslserver SSL server
nssslserver Netscape SSL server
smimesign S/MIME signing
smimeencrypt S/MIME encryption
crlsign CRL signing
any Any Purpose
ocsphelper OCSP helper
timestampsign Time Stamp signing
Recognized verify names:
default
pkcs7
smime_sign
ssl_client
ssl_server
例程:
penSSL> verify -CApath C:cacert.pem -verbose cert1.pem -verbose cert1.pem
在线状态服务程序指令 ocsp
OCSP(Online Certificate Status Protocol),在线证书状态协议,用于确定证书状态,比如是否被吊销等。OCSP 响应器通常返回给客户端的状态信息包括三种:良好、吊销和未知。
安全起见,每个 OSCP 信息都必须签名,所有用于必须对每一个回应信息进行验证。在 OpenSSL 的实践中,签名者可以是:被验证证书的 CA、被验证证书的 CA特殊授权的 OCSP 响应器、被信任的 OCSP 响应器。
命令格式:
OpenSSL> ocsp -help
Usage: ocsp [options]
Valid options are:
-help Display this summary
-out outfile Output filename
-timeout +int Connection timeout (in seconds) to the OCSP responder
-url val Responder URL
-host val TCP/IP hostname:port to connect to
-port +int Port to run responder on
-ignore_err Ignore error on OCSP request or response and continue running
-noverify Don't verify response at all
-nonce Add OCSP nonce to request
-no_nonce Don't add OCSP nonce to request
-resp_no_certs Don't include any certificates in response
-resp_key_id Identify response by signing certificate key ID
-no_certs Don't include any certificates in signed request
-no_signature_verify Don't check signature on response
-no_cert_verify Don't check signing certificate
-no_chain Don't chain verify response
-no_cert_checks Don't do additional checks on signing certificate
-no_explicit Do not explicitly check the chain, just verify the root
-trust_other Don't verify additional certificates
-no_intern Don't search certificates contained in response for signer
-badsig Corrupt last byte of loaded OSCP response signature (for test)
-text Print text form of request and response
-req_text Print text form of request
-resp_text Print text form of response
-reqin val File with the DER-encoded request
-respin val File with the DER-encoded response
-signer infile Certificate to sign OCSP request with
-VAfile infile Validator certificates file
-sign_other infile Additional certificates to include in signed request
-verify_other infile Additional certificates to search for signer
-CAfile infile Trusted certificates file
-CApath infile Trusted certificates directory
-no-CAfile Do not load the default certificates file
-no-CApath Do not load certificates from the default certificates directory
-validity_period ulong Maximum validity discrepancy in seconds
-status_age +int Maximum status age in seconds
-signkey val Private key to sign OCSP request with
-reqout val Output file for the DER-encoded request
-respout val Output file for the DER-encoded response
-path val Path to use in OCSP request
-issuer infile Issuer certificate
-cert infile Certificate to check
-serial val Serial number to check
-index infile Certificate status index file
-CA infile CA certificate
-nmin +int Number of minutes before next update
-nrequest +int Number of requests to accept (default unlimited)
-ndays +int Number of days before next update
-rsigner infile Responder certificate to sign responses with
-rkey infile Responder key to sign responses with
-rother infile Other certificates to include in response
-rmd val Digest Algorithm to use in signature of OCSP response
-rsigopt val OCSP response signature parameter in n:v form
-header val key=value header to add
-* Any supported digest algorithm (sha1,sha256, ... )
-policy val adds policy to the acceptable policy set
-purpose val certificate chain purpose
-verify_name val verification policy name
-verify_depth int chain depth limit
-auth_level int chain authentication security level
-attime intmax verification epoch time
-verify_hostname val expected peer hostname
-verify_email val expected peer email
-verify_ip val expected peer IP address
-ignore_critical permit unhandled critical extensions
-issuer_checks (deprecated)
-crl_check check leaf certificate revocation
-crl_check_all check full chain revocation
-policy_check perform rfc5280 policy checks
-explicit_policy set policy variable require-explicit-policy
-inhibit_any set policy variable inhibit-any-policy
-inhibit_map set policy variable inhibit-policy-mapping
-x509_strict disable certificate compatibility work-arounds
-extended_crl enable extended CRL features
-use_deltas use delta CRLs
-policy_print print policy processing diagnostics
-check_ss_sig check root CA self-signatures
-trusted_first search trust store first (default)
-suiteB_128_only Suite B 128-bit-only mode
-suiteB_128 Suite B 128-bit mode allowing 192-bit algorithms
-suiteB_192 Suite B 192-bit-only mode
-partial_chain accept chains anchored by intermediate trust-store CAs
-no_alt_chains (deprecated)
-no_check_time ignore certificate validity time
-allow_proxy_certs allow the use of proxy certificates
例程:
# 创建一个 ocsp 请求,并把它写入文件
OpenSSL> ocsp -issure issure.pem -cert c1.pem -cert c2.pem -reqout req.der
# 发送一个查询到 OCSP 响应器,保存返回响应到文件中,并以文本格式打印
OpenSSL> ocsp -issure issure.pem -cert c1.pem -cert c2.pem -url http://ocsp.host.com/ -resp_text -respout resp.der
# 读一个 ocsp 响应,并以文本格式打印出来
penSSL> ocsp -respin resp.der -text
# OCSP 服务使用 8888 端口,安装标准 CA 配置并使用独立响应者证书,所有的响应和请求以文本格式写入指定输出文件
OpenSSL> ocsp index index.txt -port 888 -resigner rcert.pem -CA cacert.pem -text -out log.txt
# OCSP 服务使用 8888 端口,安装标准 CA 配置并使用独立响应者证书,但处理一个 OCSP 请求后立即退出
OpenSSL> ocsp index index.txt -port 888 -resigner rcert.pem -CA cacert.pem -nrequest 1
# 从指令行产生一个 OCSP 请求,并实时到 OCSP 服务查询其状态信息
OpenSSL> ocsp index index.txt -resigner rcert.pem -CA cacert.pem -issuer cacert.pem -serial 1
最后
以上就是淡定故事最近收集整理的关于OpenSSL之十三:证书和CA指令证书生命周期证书封装类型证书使用OpenSSL支持的CA指令申请证书建立CACA 操作使用证书验证证书的全部内容,更多相关OpenSSL之十三:证书和CA指令证书生命周期证书封装类型证书使用OpenSSL支持的CA指令申请证书建立CACA内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复