本文基于dubbo v2.6.x
1. API方式使用dubbo
我们可以看下dubbo官网api使用方式使用dubbo,地址:链接,我们可以在文档的服务消费者模块看到
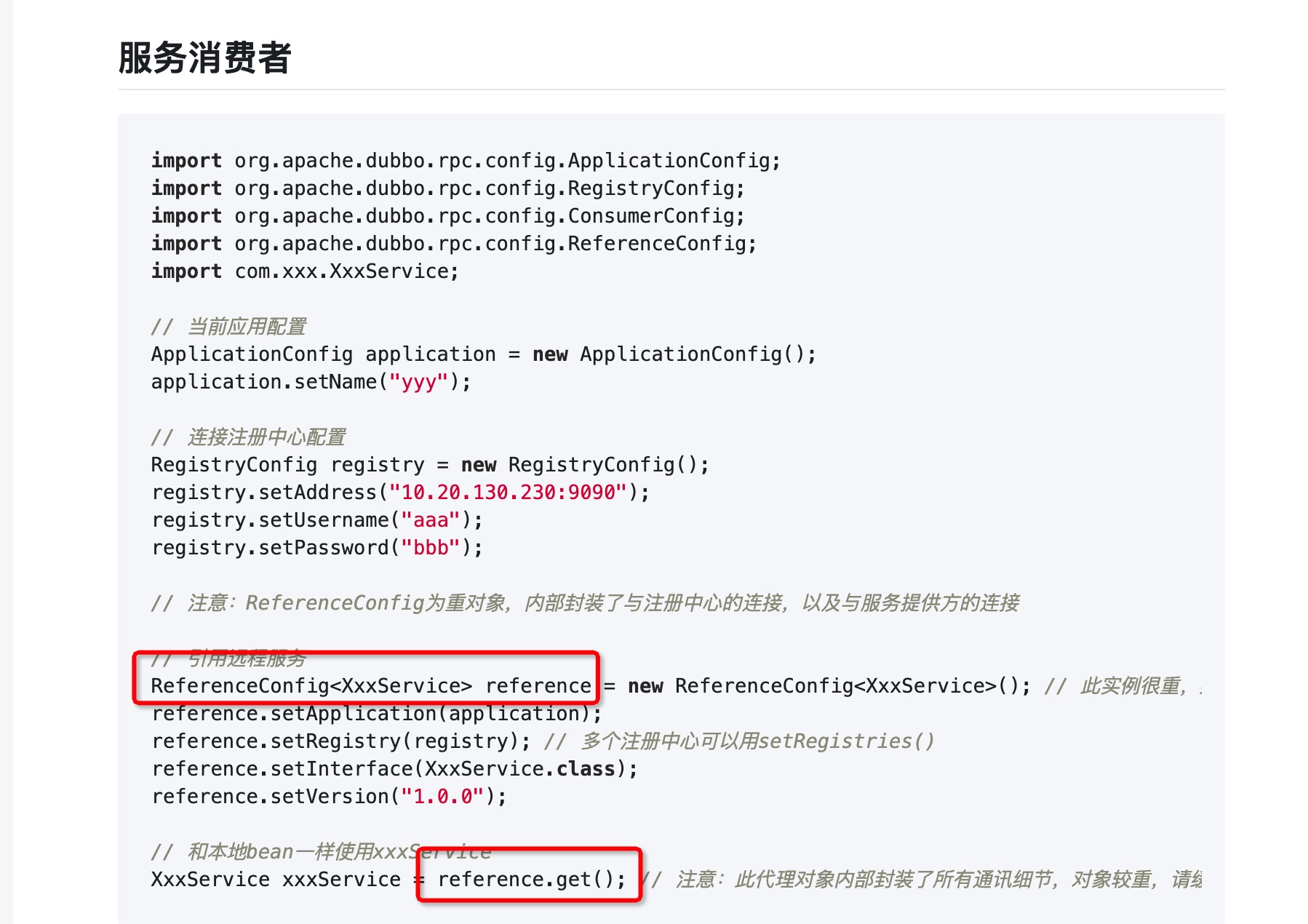
new了一个ReferenceConfig 然后通过get方法获取xxx接口的实现类,也就是服务代理。接下来我们就看这个com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#get
2.com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#get
// 获取
public synchronized T get() {
// 已经销毁
if (destroyed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Already destroyed!");
}
// 还没有初始化的时候进行初始化
if (ref == null) {
// 初始化
init();
}
return ref;
}
首先是该方法synchronized 修饰,然后判断销毁标识,判断ref 是否是空,这个ref其实就是ReferenceConfig范型的实现类,也就是下图的xxxService

如果是null的话就走init方法,第一次的话肯定是要走这里的。我们看下这个init方法。
3.com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#init
该方法前面是一些参数的配置有判断,我们主要是把目光放到后半部分
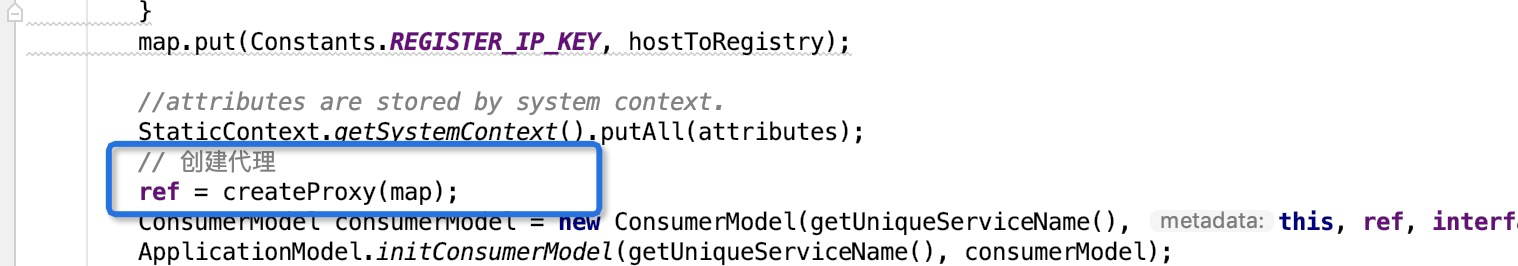
后面有个createProxy(map)方法,然后返回了一个该接口的实现类,也就是我们的代理类。
4.com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy
URL tmpUrl = new UR("temp", "localhost", 0, map);
final boolean isJvmRefer;
if (isInjvm() == null) {// 如果配置里面没有配置这个scope 或者injvm
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { // if a url is specified, don't do local reference
isJvmRefer = false;
} else if (InjvmProtocol.getInjvmProtocol().isInjvmRefer(tmpUrl)) {
// by default, reference local service if there is
isJvmRefer = true;
} else {
isJvmRefer = false;
}
} else {
isJvmRefer = isInjvm().booleanValue();
}
if (isJvmRefer) {// jvm
URL url = new URL(Constants.LOCAL_PROTOCOL, NetUtils.LOCALHOST, 0, interfaceClass.getName()).addParameters(map);
invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Using injvm service " + interfaceClass.getName());
}
} else {
...
}
第一行new 了一个tempUrl,后面的就是判断要不要injvm,也就是本地引用,如果我们这里配置了scope=injvm或者injvm=true就会执行到isJvmRefer = isInjvm().booleanValue(); 也就isJvmRefer 这个变量设置成true。
接着就是执行进isJvmRefer =true这个代码段中,首先是封装一个url,其中protocol是injvm,host是127.0.0.1。接着调用invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url);这句,我们先看下这个refprotocol 对象,
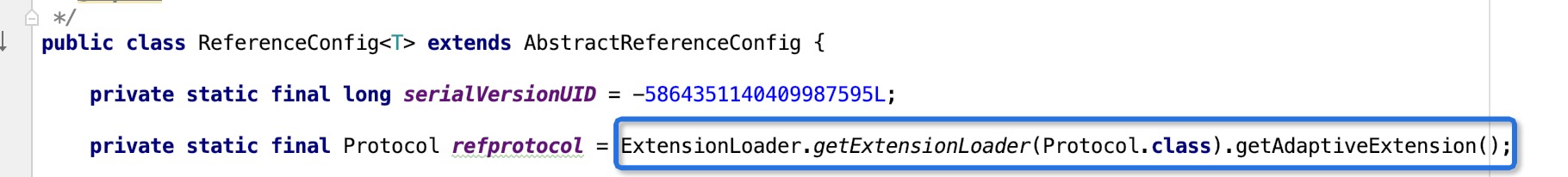
很显然是Protocol接口对象,根据dubbo spi 扩展点的自适应特性,会在url找protocol属性的值,这里url的protocol属性值是injvm,也就是
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.injvm.InjvmProtocol
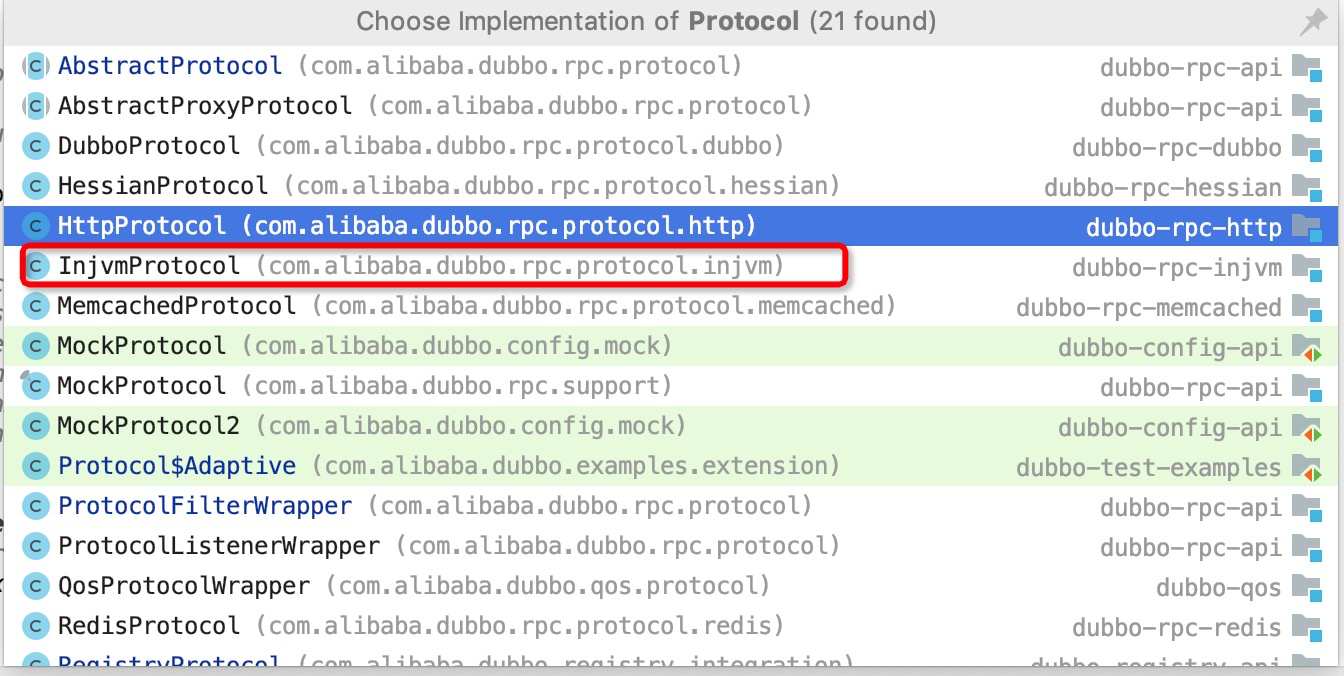
我们接着看下com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.injvm.InjvmProtocol 的refer方法
5. com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.injvm.InjvmProtocol#refer
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
return new InjvmInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, url.getServiceKey(), exporterMap);
}
这里new了一个InjvmInvoker 类并且返回 ,参数分别是 1.咱们那个接口class 类,2.url ,3. 接口的全类名,4. exporterMap 缓存了本地暴露的服务,这个exporterMap 对象,我们在本地服务暴露的时候,最后将serviceKey 与exporter缓存了exporterMap 这个map中。
这个InjvmInvoker 先放这,我们回到com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy 这个方法继续看
6.com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy
// 判断check属性, 默认是check的
Boolean c = check;
if (c == null && consumer != null) {
c = consumer.isCheck();
}
if (c == null) {
c = true; // default true
}
// 进行check
if (c && !invoker.isAvailable()) {
// make it possible for consumer to retry later if provider is temporarily unavailable
initialized = false;
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to check the status of the service " + interfaceName + ". No provider available for the service " + (group == null ? "" : group + "/") + interfaceName + (version == null ? "" : ":" + version) + " from the url " + invoker.getUrl() + " to the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion());
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Refer dubbo service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " from url " + invoker.getUrl());
}
// create service proxy
return (T) proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker);
这里首先是判断了用户配置的check属性,如果用户没有配置默认是需要check的,接着就是check=true的话进行check,check失败设置初始化=false 然后抛出异常。
接着就是(T) proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker); 这句话,创建service代理对象。
其实这个proxyFactory 我们在服务暴露的时候见过了,我们再来看下
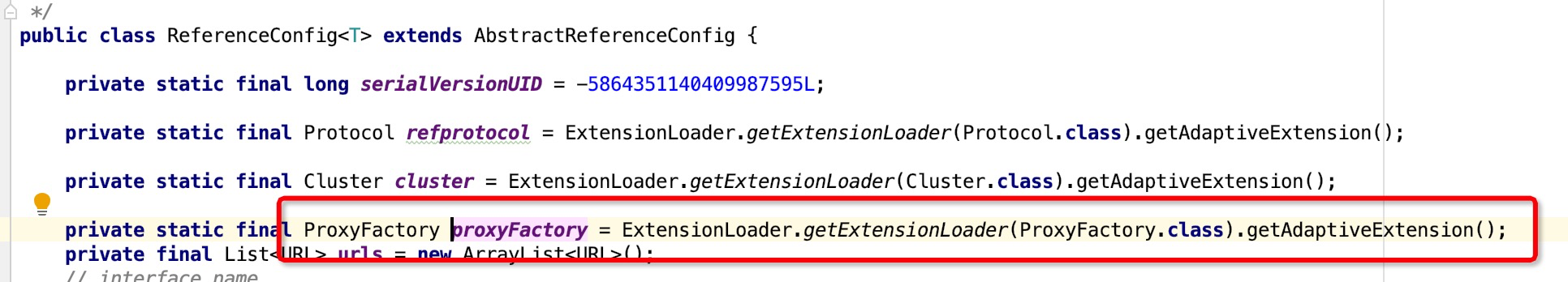
其实根据dubbo spi 扩展点自适应特性,当你指定proxy属性值的时候 用你指定的实现,如果没有话使用默认的实现,这里也就是javassist,JavassistProxyFactory
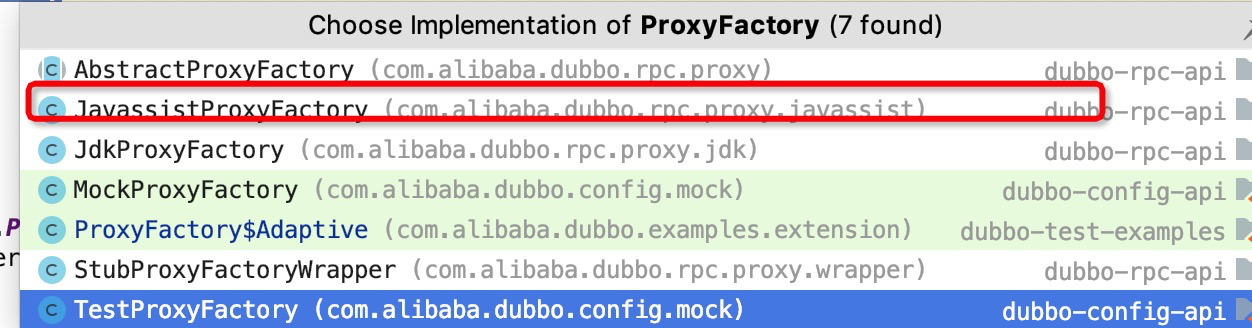
我们看下JavassistProxyFactory 类
7.com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.javassist.JavassistProxyFactory#getProxy
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
这里是我那 Proxy.getProxy 生成的一个代理类。
比如说我这个接口是这个样子的:
public interface IHelloProviderService {
String getName(Integer id);
}
生成的代理类
package com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.ClassGenerator;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.service.EchoService;
import com.xuzhaocai.dubbo.provider.IHelloProviderService;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class proxy0
implements ClassGenerator.DC,
EchoService,
IHelloProviderService {
public static Method[] methods;
private InvocationHandler handler;
@Override
public String getName(Integer n) {
Object[] arrobject = new Object[]{n};
Object object = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[0], arrobject);
return (String)object;
}
public Object $echo(Object object) {
Object[] arrobject = new Object[]{object};
Object object2 = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[1], arrobject);
return object2;
}
public proxy0() {
}
public proxy0(InvocationHandler invocationHandler) {
this.handler = invocationHandler;
}
}
我们可以看到Proxy生成的代理类实现那个接口,然后在实现接口方法里面将参数封装到数据里面,然后调用了invocationHandler的invoke方法。我们看下这个invocationHandler 。
8.com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.InvokerInvocationHandler
/**
* InvokerHandler
*/
public class InvokerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final Invoker<?> invoker;
public InvokerInvocationHandler(Invoker<?> handler) {
this.invoker = handler;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return method.invoke(invoker, args);
}
if ("toString".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.toString();
}
if ("hashCode".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.hashCode();
}
if ("equals".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 1) {
return invoker.equals(args[0]);
}
return invoker.invoke(new RpcInvocation(method, args)).recreate();
}
}
在这里invocationHandler对象里面invoker就是咱们前面InjvmInvoker 对象。我们可以看到这个InvokerInvocationHandler#invoke 方法里面帮我们获取了执行的方法名与方法参数类型,如果是toString,hashCode,equals 方法直接调用InjvmInvoker 的,并将方法与参数封装成一个RpcInvocation ,然后调用了InjvmInvoker 的invoke方法,
我们先来看下new RpcInvocation(method, args);

我们看下这个InjvmInvoker。
9. com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.injvm.InjvmInvoker
这个InjvmInvoker 继承 AbstractInvoker ,然后AbstractInvoker 实现Invoker 接口,实现了Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException;方法,与 Class<T> getInterface();方法。
class InjvmInvoker<T> extends AbstractInvoker<T> {
private final String key;
private final Map<String, Exporter<?>> exporterMap;
InjvmInvoker(Class<T> type, URL url, String key, Map<String, Exporter<?>> exporterMap) {
super(type, url);
this.key = key;
this.exporterMap = exporterMap;
}
@Override
public boolean isAvailable() {
InjvmExporter<?> exporter = (InjvmExporter<?>) exporterMap.get(key);
if (exporter == null) {
return false;
} else {
return super.isAvailable();
}
}
@Override
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Exporter<?> exporter = InjvmProtocol.getExporter(exporterMap, getUrl());
if (exporter == null) {
throw new RpcException("Service [" + key + "] not found.");
}
RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress(NetUtils.LOCALHOST, 0);
return exporter.getInvoker().invoke(invocation);
}
}
我们看到invoke方法没有在InjvmInvoker类中,我们看下它的父类中invoke方法:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invocation inv) throws RpcException {
// if invoker is destroyed due to address refresh from registry, let's allow the current invoke to proceed
if (destroyed.get()) {
logger.warn("Invoker for service " + this + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " is destroyed, "
+ ", dubbo version is " + Version.getVersion() + ", this invoker should not be used any longer");
}
RpcInvocation invocation = (RpcInvocation) inv;
invocation.setInvoker(this);//设置invoker ,将自己设置进去
if (attachment != null && attachment.size() > 0) {
invocation.addAttachmentsIfAbsent(attachment);
}
Map<String, String> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachments();
if (contextAttachments != null && contextAttachments.size() != 0) {
/**
* invocation.addAttachmentsIfAbsent(context){@link RpcInvocation#addAttachmentsIfAbsent(Map)}should not be used here,
* because the {@link RpcContext#setAttachment(String, String)} is passed in the Filter when the call is triggered
* by the built-in retry mechanism of the Dubbo. The attachment to update RpcContext will no longer work, which is
* a mistake in most cases (for example, through Filter to RpcContext output traceId and spanId and other information).
*/
invocation.addAttachments(contextAttachments);
}
if (getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.ASYNC_KEY, false)) {
invocation.setAttachment(Constants.ASYNC_KEY, Boolean.TRUE.toString());
}
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
try {
return doInvoke(invocation);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) { // biz exception
Throwable te = e.getTargetException();
if (te == null) {
return new RpcResult(e);
} else {
if (te instanceof RpcException) {
((RpcException) te).setCode(RpcException.BIZ_EXCEPTION);
}
return new RpcResult(te);
}
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) {
return new RpcResult(e);
} else {
throw e;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
return new RpcResult(e);
}
}
可以看到前面判断了一下销毁没有,然后从Rpc上下文中get到一些kv然后设置进去。我们看后面一句doInvoke(invocation);,这个才是真正的调用,子类实现了这个方法,这里也就是咱们的InjvmInvoker类
@Override
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Exporter<?> exporter = InjvmProtocol.getExporter(exporterMap, getUrl());
if (exporter == null) {
throw new RpcException("Service [" + key + "] not found.");
}
RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress(NetUtils.LOCALHOST, 0);
return exporter.getInvoker().invoke(invocation);
}
首先InjvmProtocol.getExporter(exporterMap, getUrl());这行代码其实是从exporterMap 这个缓存中获取我们这个url中的服务名对应的实现类,我们可以回想下,我们在本地服务暴露的时候,然后以serviceKey为key ,exporter为value缓存到了这个map中,如果获取的这个exporter是null的话抛出异常,如果不是null的话,往RpcContext中设置RemoteAddress 的ip是127.0.0.1 ,port是0。最后调用了exporter.getInvoker().invoke(invocation);,我们可以回顾下当初服务暴露的时候invoker是这样子创建的:
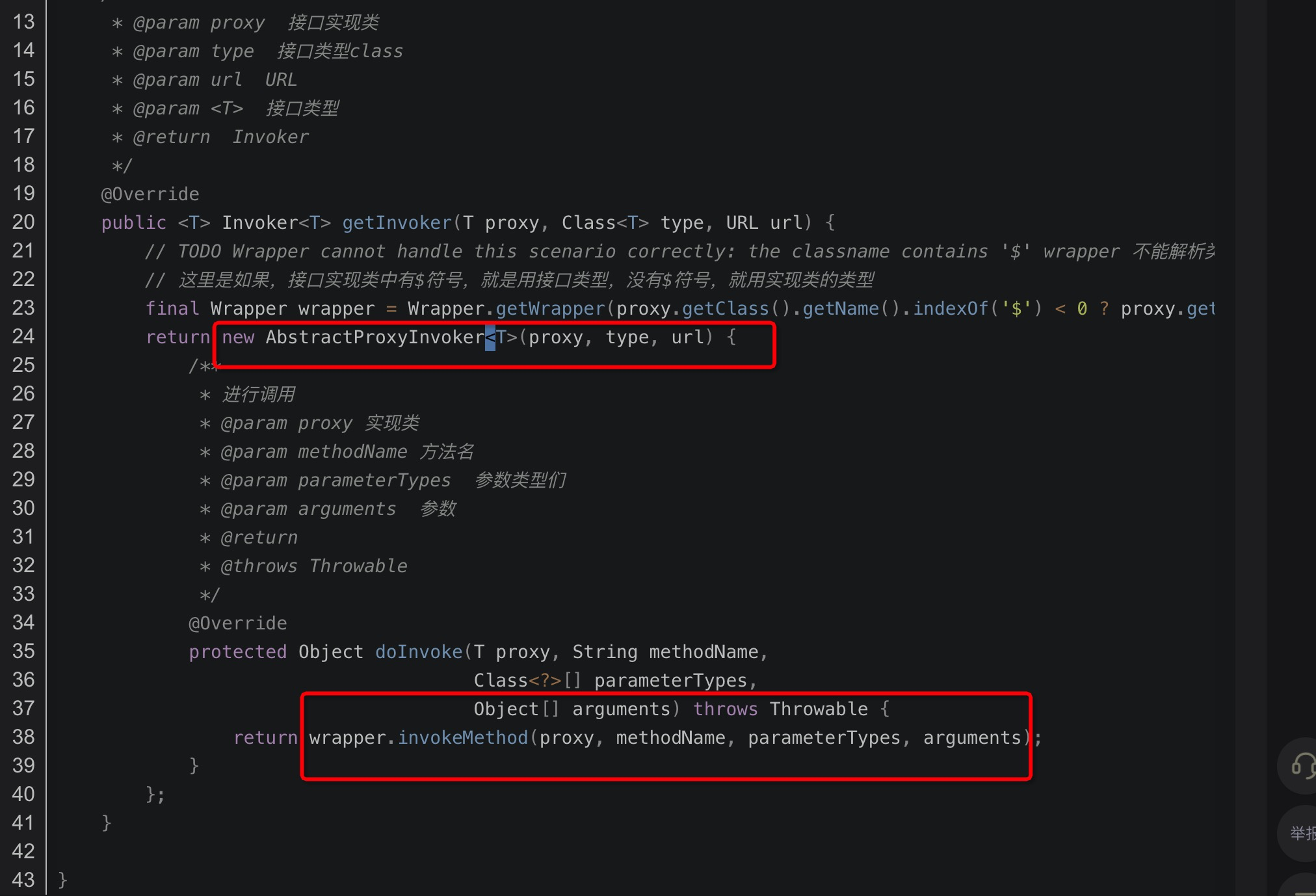
然后最后调用的是wrapper.invokeMethod的方法。我们再来看下这个wrapper的结构是啥样子的:
public class Wrapper$1 {
public static String[] pns;// 字段名
public static Map pts;//<字段名,字段类型>
public static String[] mns;//方法名
public static String[] dmns;//自己方法的名字
public static Class[] mts;//方法参数类型
public String[] getPropertyNames(){ return pns; }
public boolean hasProperty(String n){ return pts.containsKey(n); }
public Class getPropertyType(String n){ return (Class)pts.get(n); }
public String[] getMethodNames(){ return mns; }
public String[] getDeclaredMethodNames(){ return dmns; }
public void setPropertyValue(Object o, String n, Object v){
com.xuzhaocai.dubbo.provider.IHelloProviderService w;
try{
w = (( com.xuzhaocai.dubbo.provider.IHelloProviderService)$1);
}catch(Throwable e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
}
if( $2.equals("字段名")){
w."字段名"= $3;
return ;
}
}
public Object getPropertyValue(Object o, String n){
com.xuzhaocai.dubbo.provider.IHelloProviderService w;
try{
w = (( com.xuzhaocai.dubbo.provider.IHelloProviderService)$1);
}catch(Throwable e){
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
}
if( $2.equals("字段名")){
return ($w) w."字段名";
}
return null;
}
public Object invokeMethod(Object o, String n, Class[] p, Object[] v) throws InvocationTargetException{
com.xuzhaocai.dubbo.provider.IHelloProviderService w;
try{
w = (( com.xuzhaocai.dubbo.provider.IHelloProviderService)$1);
}catch(Throwable e){
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
}
try{
if("方法名".equals($2) && 方法参数个数 == $3.length && $3[1].getName().equals("方法第几个参数的name")){
w.方法名(参数);
}
if("方法名".equals($2) && 方法参数个数 == $3.length && $3[1].getName().equals("方法第几个参数的name")){
w.方法名(参数);
}
} catch(Throwable e) {
throw new java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException(e);
}
throw new NoSuchMethodException("Not found method "+$2+" in class 你传进来那个实现类");
}
}
其实到最后就是调用的服务提供者的方法

本地服务暴露有想了解的可以读下《深度解析dubbo服务本地暴露(injvm)》这篇文章。
最后
以上就是有魅力水壶最近收集整理的关于深度解析dubbo服务本地引用(injvm)的全部内容,更多相关深度解析dubbo服务本地引用(injvm)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。






![dubbo优雅停机原理分析[dubbo2.5.10]引入Apache dubbo starter官方优雅停机解释源码分析总结参考资料](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg5.png)

发表评论 取消回复